Apparatus and method for dynamic spectral filtration
a dynamic spectral filter and apparatus technology, applied in the field of diagnostic imaging, can solve the problems of limited energy separation between samples, little opportunity to change the filtering between samples, and typical systems that do not include the ability to discriminate the spectral energy content of x-rays, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing energy separation and increasing energy separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
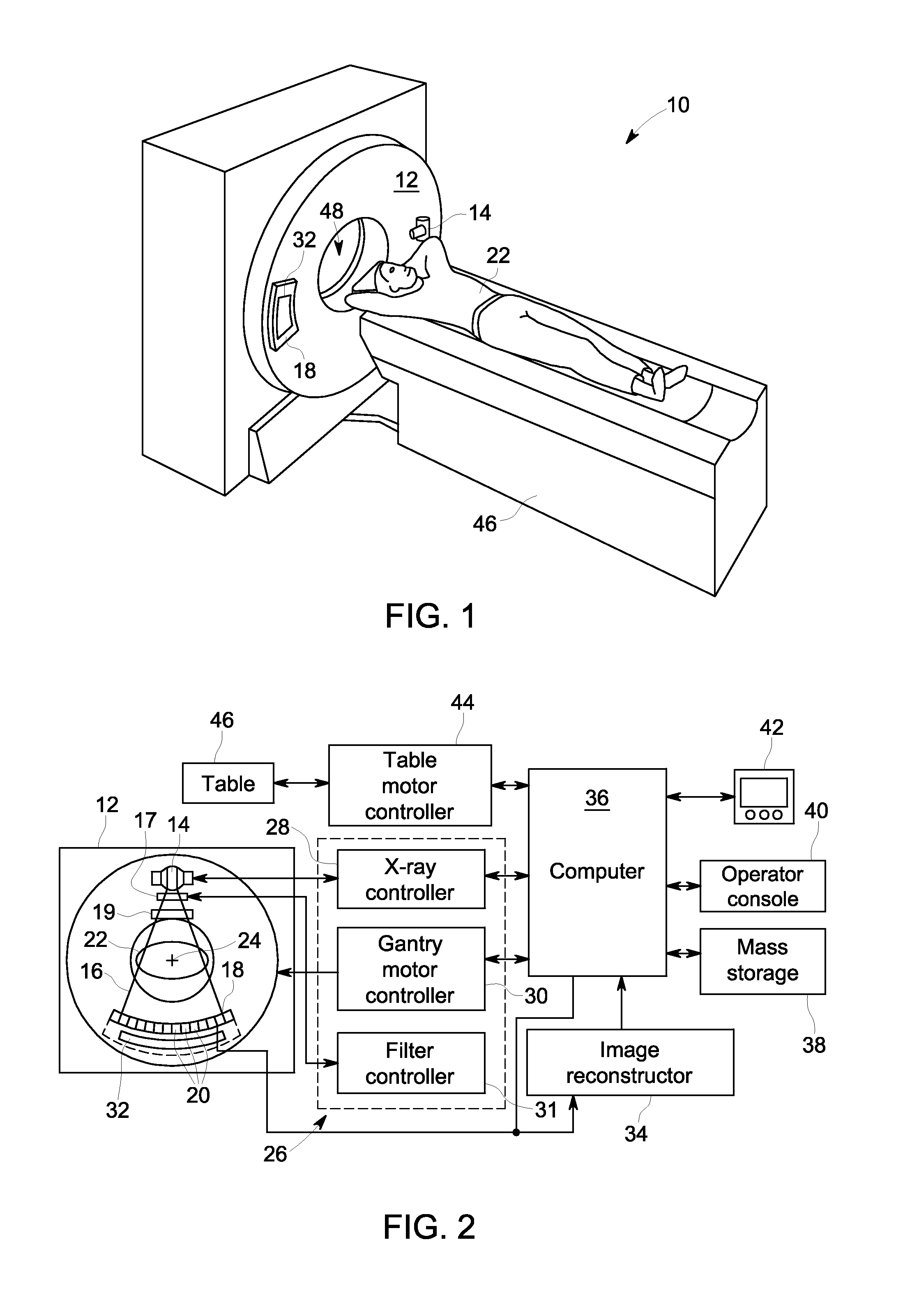
[0026]The operating environment of the present invention is described with respect to a sixty-four-slice computed tomography (CT) system. However, it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the invention is equally applicable for use with other multi-slice configurations. Moreover, the invention will be described with respect to the detection and conversion of x-rays. However, one skilled in the art will further appreciate that the invention is equally applicable for the detection and conversion of other high frequency electromagnetic energy. The invention will be described with respect to a “third generation” CT scanner, but is equally applicable with other CT systems.
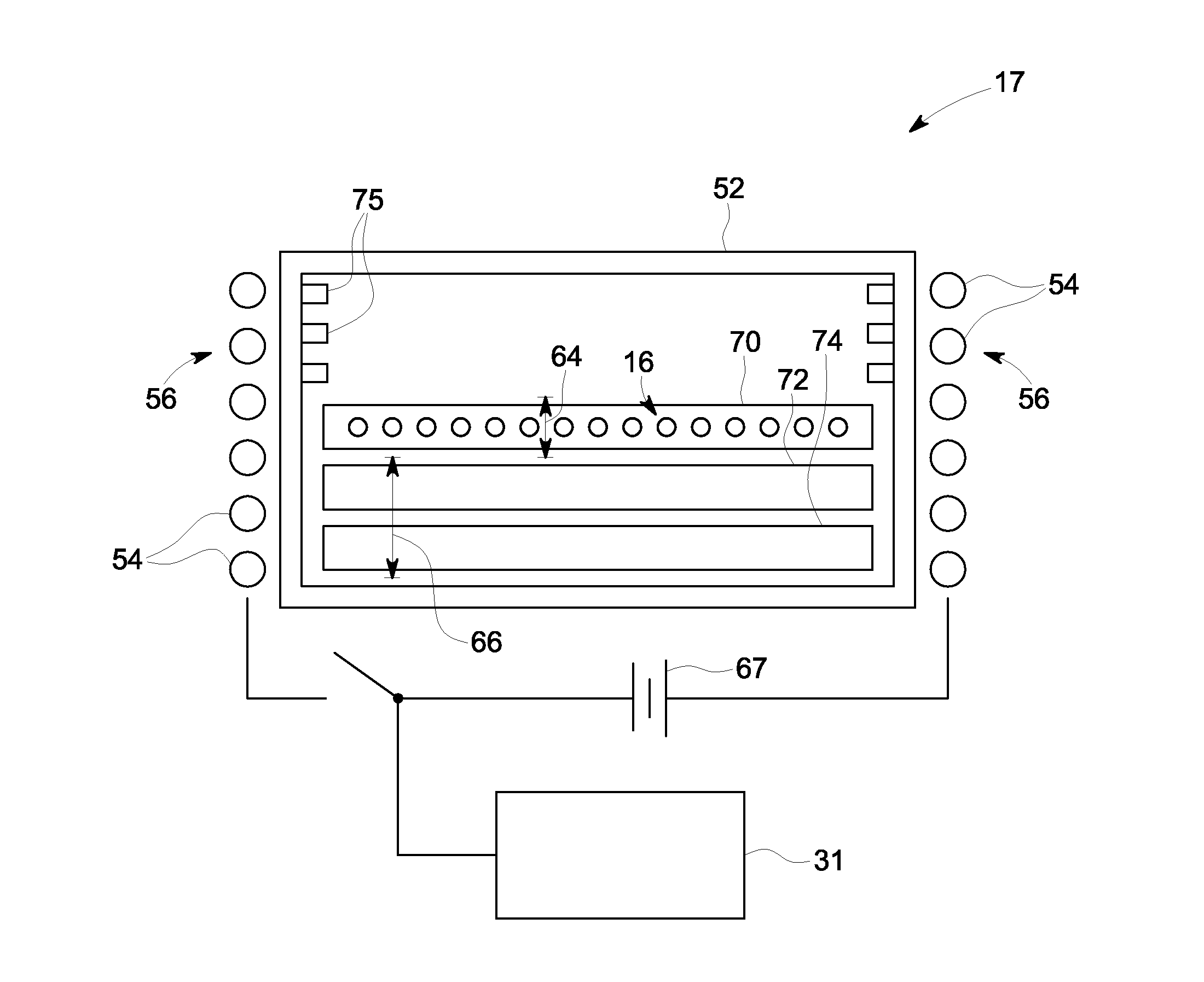
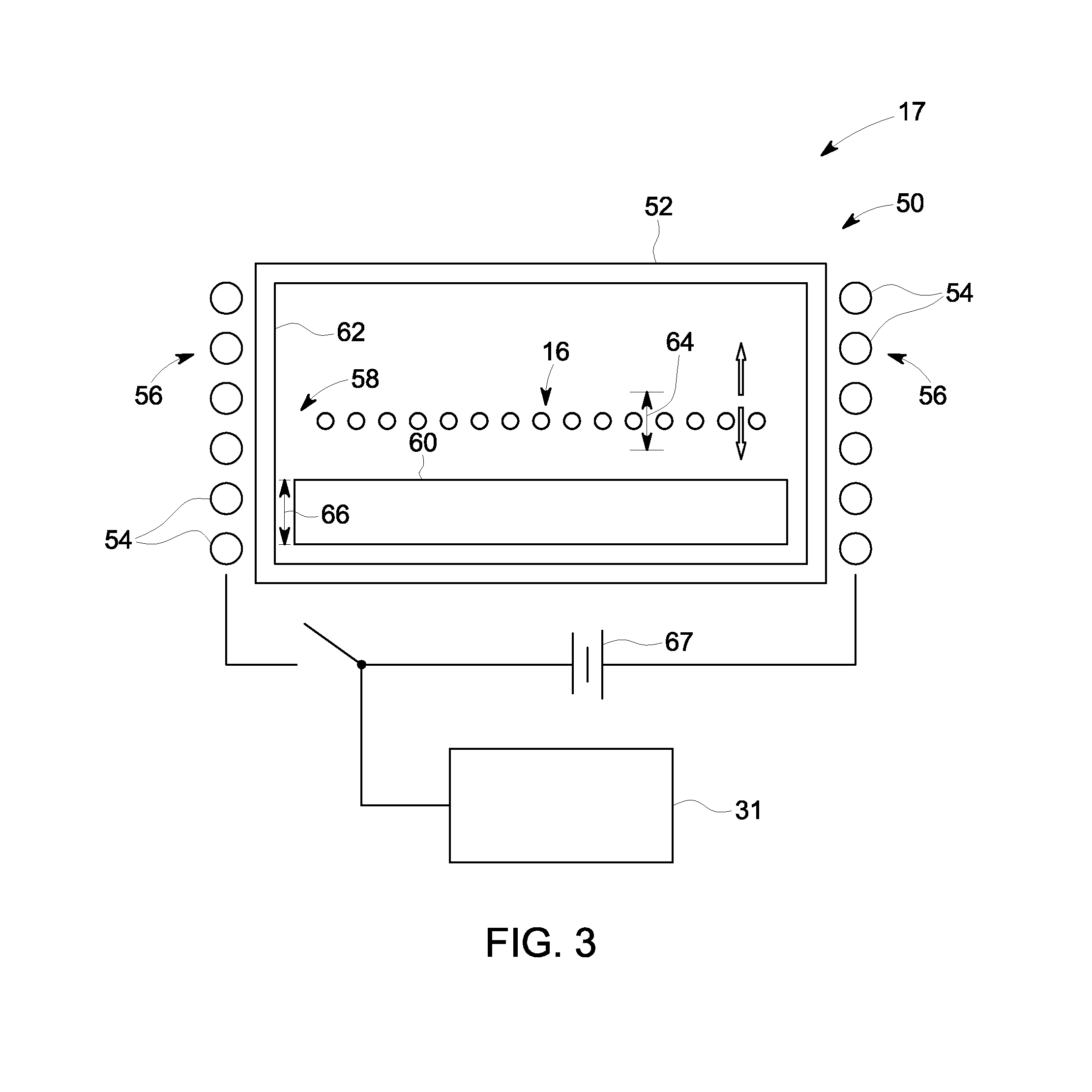
[0027]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, a computed tomography (CT) imaging system 10 is shown as including a gantry 12 representative of a “third generation” CT scanner. Gantry 12 has an x-ray source 14 that projects a beam of x-rays 16 through a dynamically controlled multi-position spectral filter 17 and towa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| fan angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fan angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com