Methods for Controlling Formation Fines Migration
a technology of fines and formations, applied in the direction of fluid removal, chemistry apparatus and processes, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the fluid production capability of certain portions of a subterranean, affecting the quality of formations,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
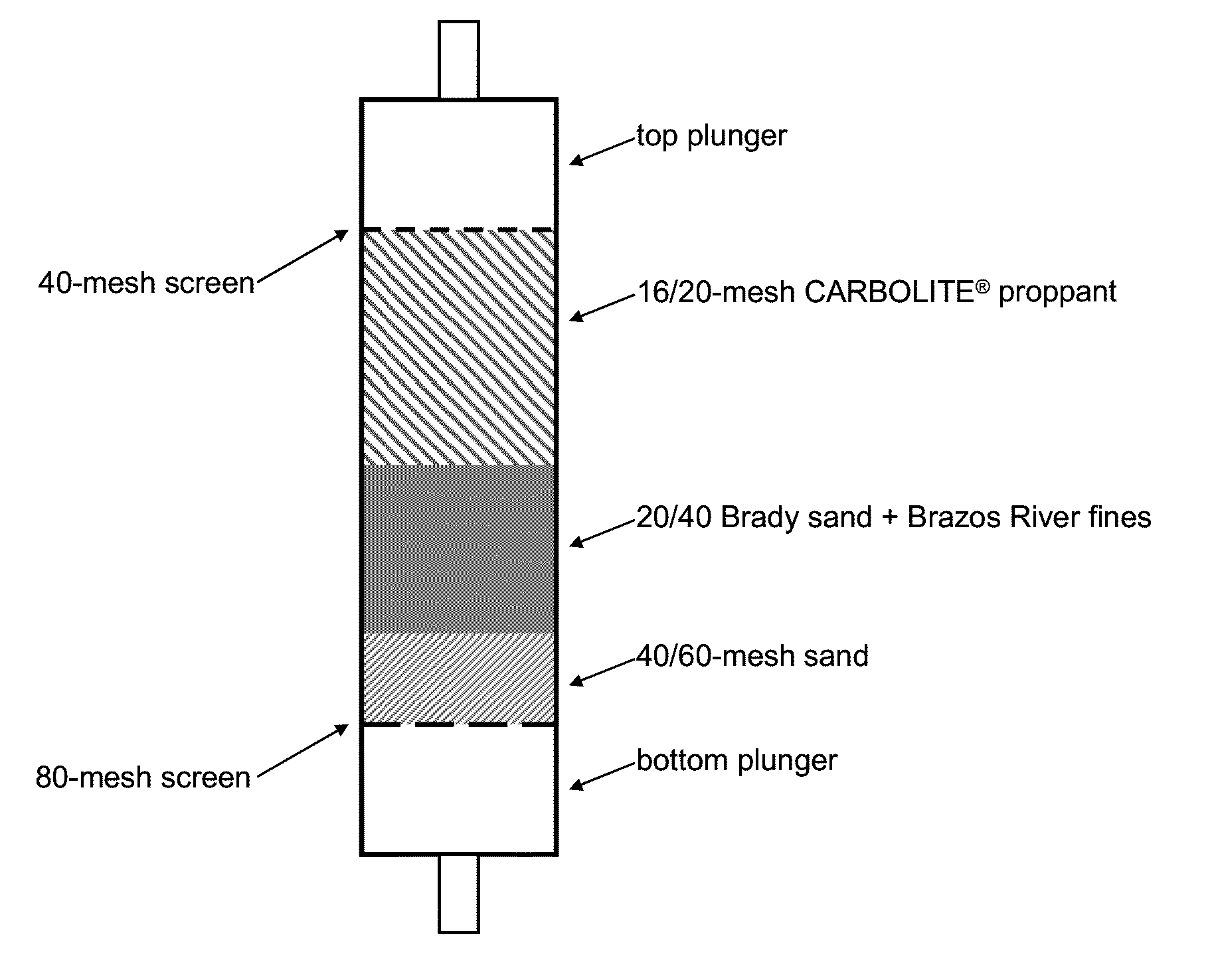
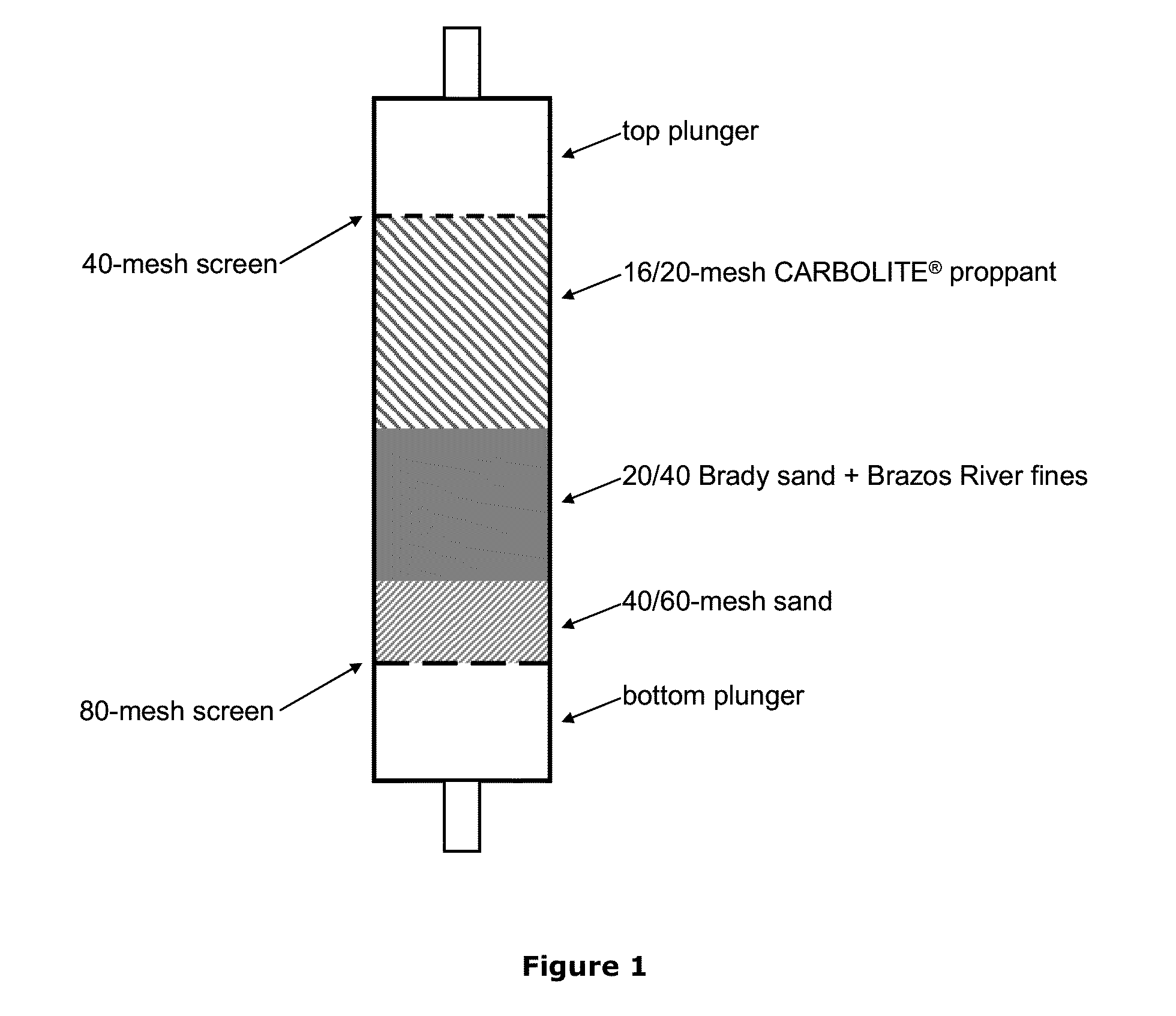
[0062]As illustrated in FIG. 1, a cell was assembled with the following in order from bottom to top: a bottom plunger, an 80-mesh screen, a 40 / 60-mesh sand, 60 g of 20 / 40 Brady sand+20 g of Brazos River fines, 16 / 20 mesh lightweight ceramic proppant (CarboLite® available from Carbo Ceramics), a 40-mesh screen, and a top plunger. In the following tests, samples were generally injected into the cell via the top plunger, allowed to consolidate, then flushed from the reverse direction (i.e., from the bottom plunger) such that the effluent was collected and analyzed for the concentration of solids so as to indicate the efficacy of consolidation. Further, in the following test, the cell was maintained at 200° F. with heat tape wrapped around the exterior of the cell.
[0063]In Test 1, 100 mL of 3% CLA-WEB® solution (a water-soluble cationic oligomer, available from Halliburton Energy Services, Inc.) was passed through to the cell via the top plunger at 8 mL per minute, followed by 100 mL of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com