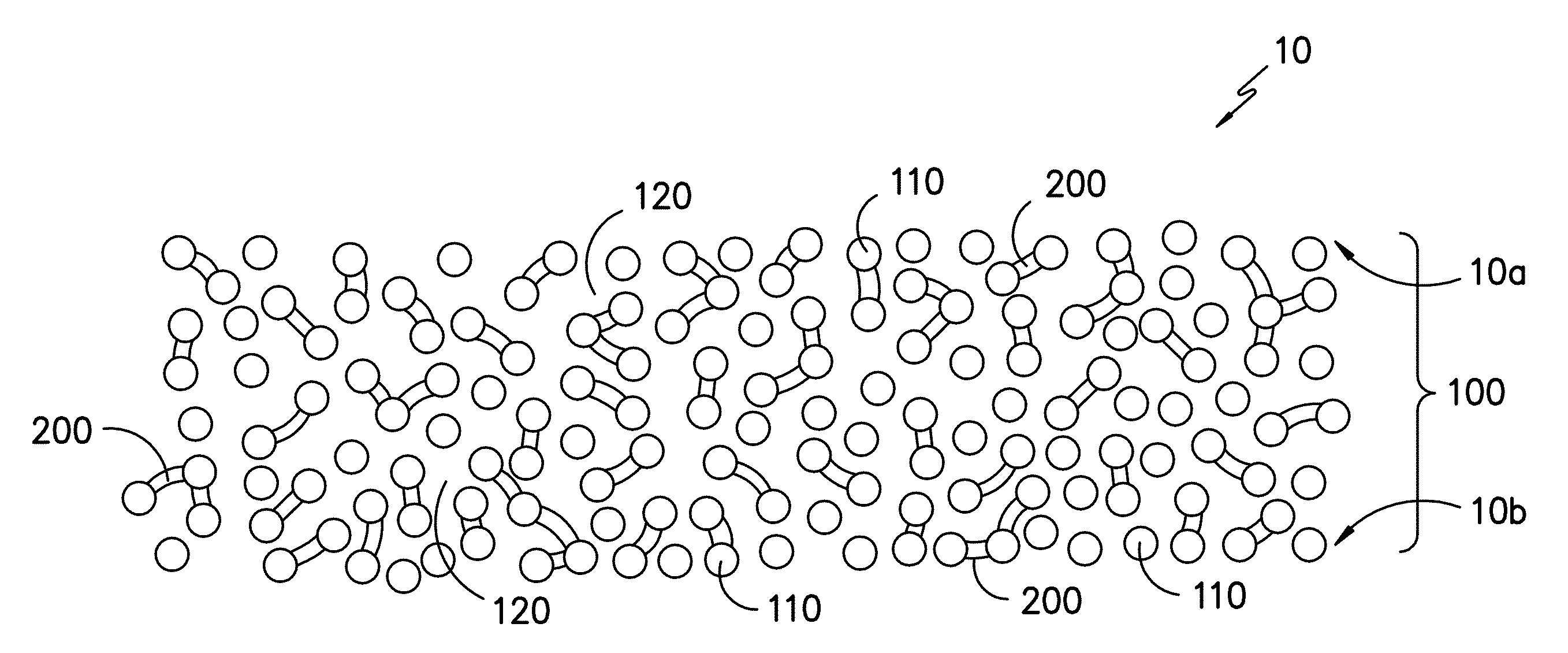
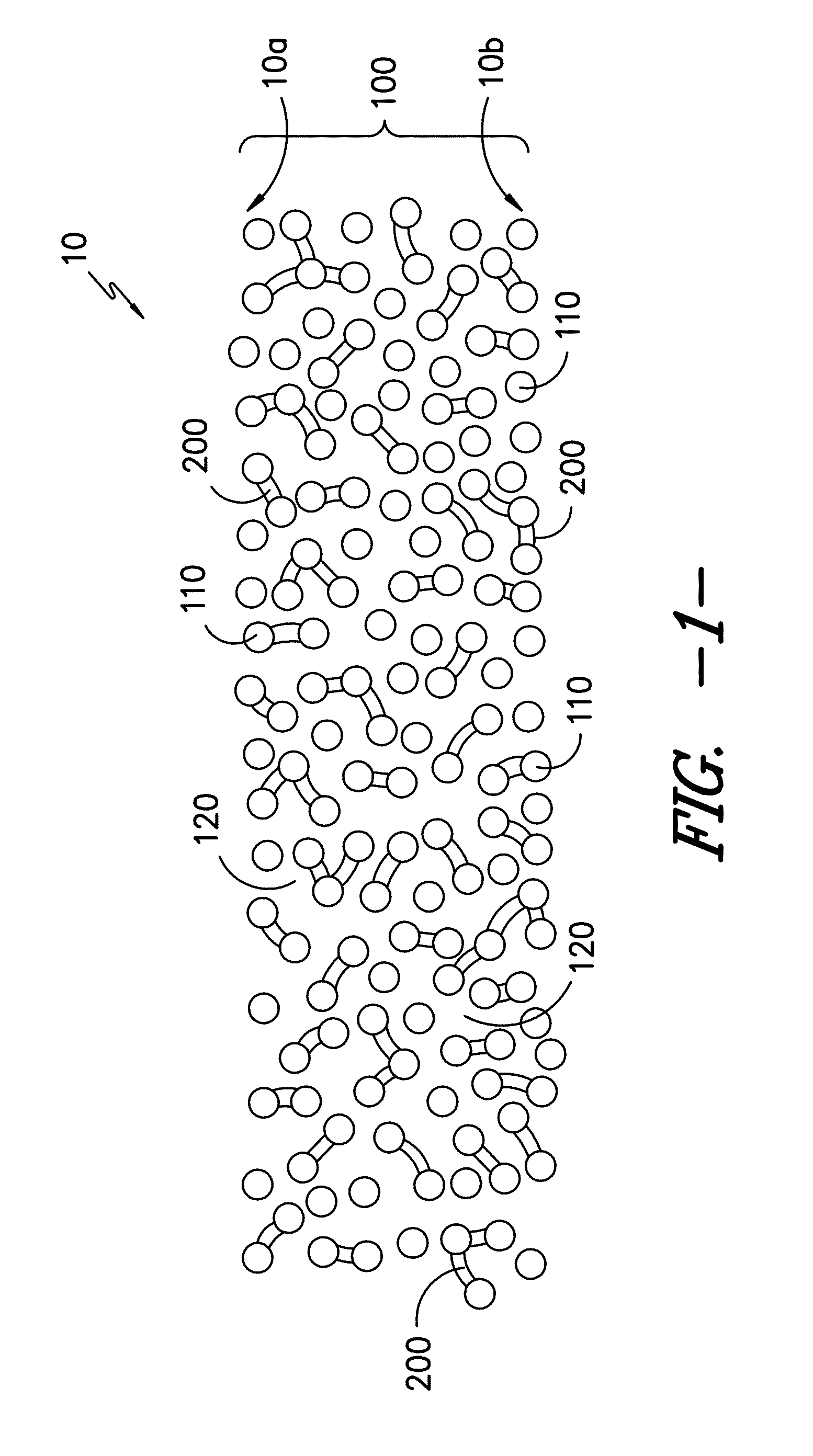
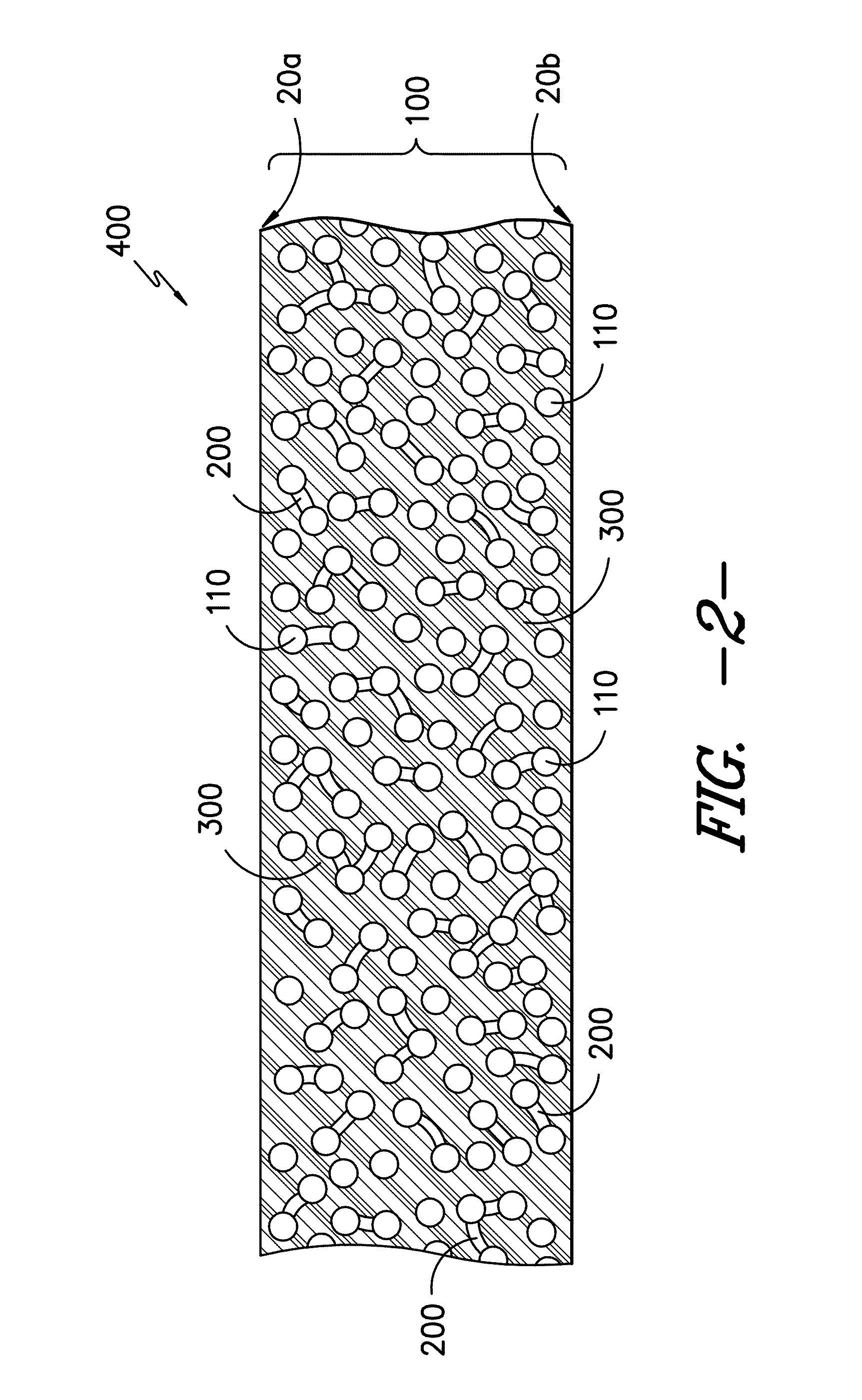
Infusible unidirectional fabric
a technology of unidirectional fabrics and fabrics, applied in the direction of mechanical equipment, machines/engines, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the maximum achievable fiber volume fraction of a composite made with such reinforcements, not offering any improvement in mechanical properties, and typically imparting performance penalties on the final composite system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0108]An unsaturated polyester control sample was made using the sample layup procedure using the 090 fabric and the ±45 fabric. The stacked textiles were infused in a standard vacuum infusion apparatus at a vacuum of less than 50 mbar with unsaturated polyester resin (Aropol Q67700 available from Ashland) and 1.5 parts per hundred resin (phr) methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP). The resin flow direction was along the 0° direction of the 090 fabric. The panel was cured at room temperature for more than 8 hours and further post cured at 80° C. for more than 4 hours. Fatigue testing of the unmodified glass reinforced unsaturated polyester composite at R=0.1 with a load of 1450 N / mm of specimen gage section width measured a lifetime of approximately 1×104 cycles.
[0109]Example 2 to Example 7 showed how the film forming preventing agents affect the infusibility of the fiber fabric. The fiberglass fabrics used in Examples 2-6, and 8 were in small widths so will be referred to herein as fi...
example 2
[0110]A fiberglass tape was made in the following manner. First, a 9600 Tex fiberglass tow from PPG (HYBON® 2026) was spread into a 20 mm wide tape by a fiber tow spreading device. Next, four of the 20 mm wide tapes were combined and aligned in the same direction to form a 40 mm wide tape with twice the original tape thickness. A SBR latex (GENCAL® 7555 from OMNOVA) was mixed with water at a SBR latex to deionized water ratio of 1:4. The fiber tape was then dipped in the coating mixture and dried in an oven at 150° C. for 30 minutes. Next, the fiber tape was washed using deionized water and dried in oven at 150° C. for 15 minutes.
example 3
[0111]A 40 mm wide, fiberglass tape was made using the same fiberglass materials and process as Example 2. A SBR latex (GENCAL® 7555 from OMNOVA) was mixed with water and glycerin at a SBR latex to deionized water to glycerin ratio of 1:2:2. The fiber tape was dipped in the coating mixture and dried in an oven at 150° C. for 30 minutes. Next, the fiber tape was washed by deionized water and dried in oven at 150° C. for 15 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com