Wind turbine blade having twisted spar web
a technology of wind turbine blades and spar webs, applied in wind turbines, reaction engines, motors, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing torsional rigidity, increasing torsional flexibility, and decoupling tower stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
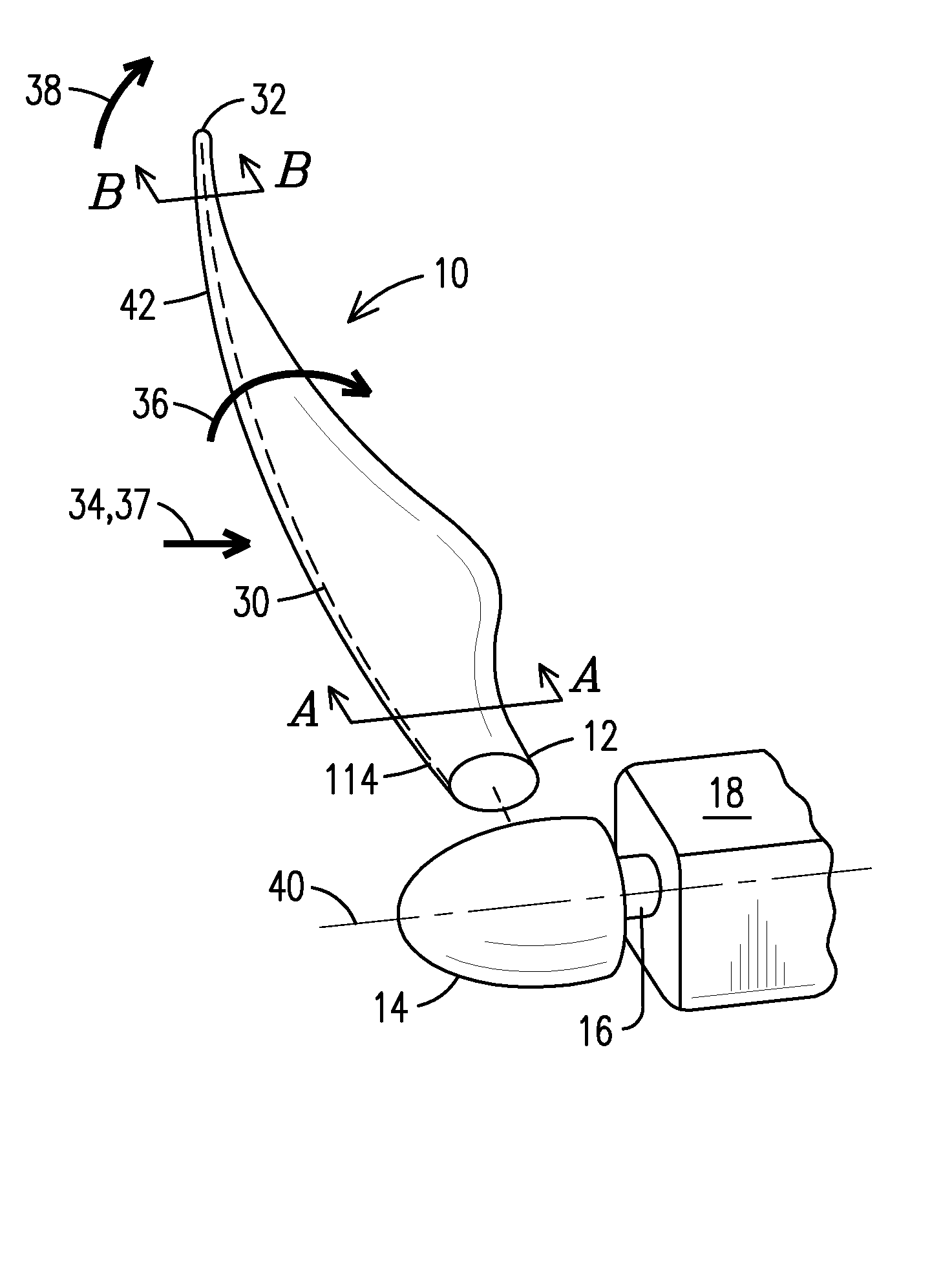
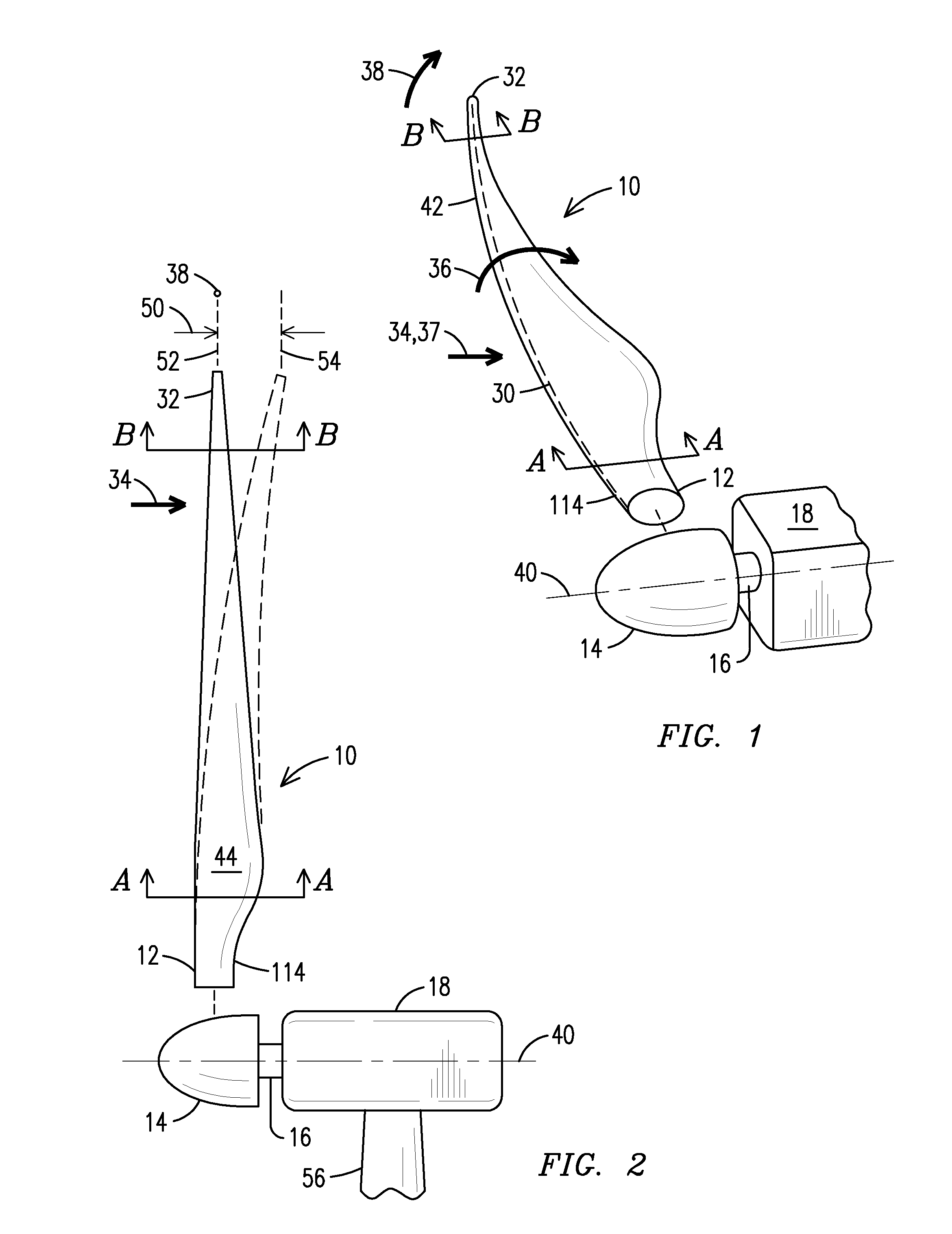
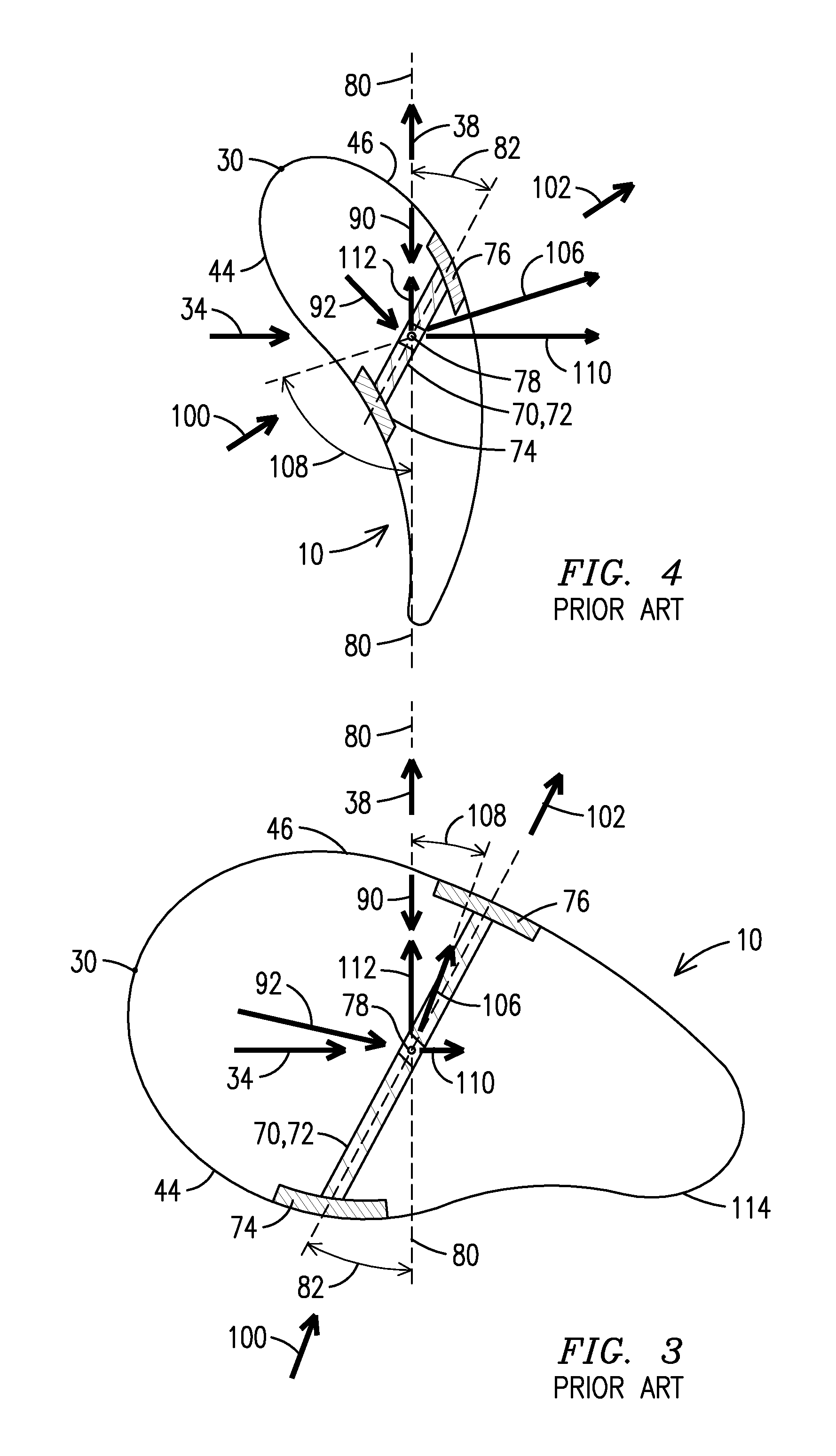
[0020]The present inventor has recognized that blade design has evolved from designing blades of sufficient strength to designing blades of stiffness sufficient to prevent the blade from colliding with the tower support. The present inventor has also recognized that local forces change from a base of the blade to a tip of the blade. In particular, at the base of the blade rotational forces (within a plane of rotation) have “accumulated” from the tip to the blade to the base, while tower deflection forces (toward the tower) are negligible. A skin of the blade is very robust at the blade and can withstand the deflection forces itself, but may need the assistance of a structural spar to handle the rotational forces. In contrast, at the tip of the blade the rotational forces are negligible, while deflection forces have “accumulated” from the base to the tip, resulting in greater tower deflection. Since the blade is thin and oriented close to parallel to the plane of rotation, it can han...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com