Methods for discovering, partitioning, organizing, and administering communication devices in a transformer area network
a transformer area network and communication device technology, applied in the field of methods, can solve problems such as limiting the amount of data transmitted
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
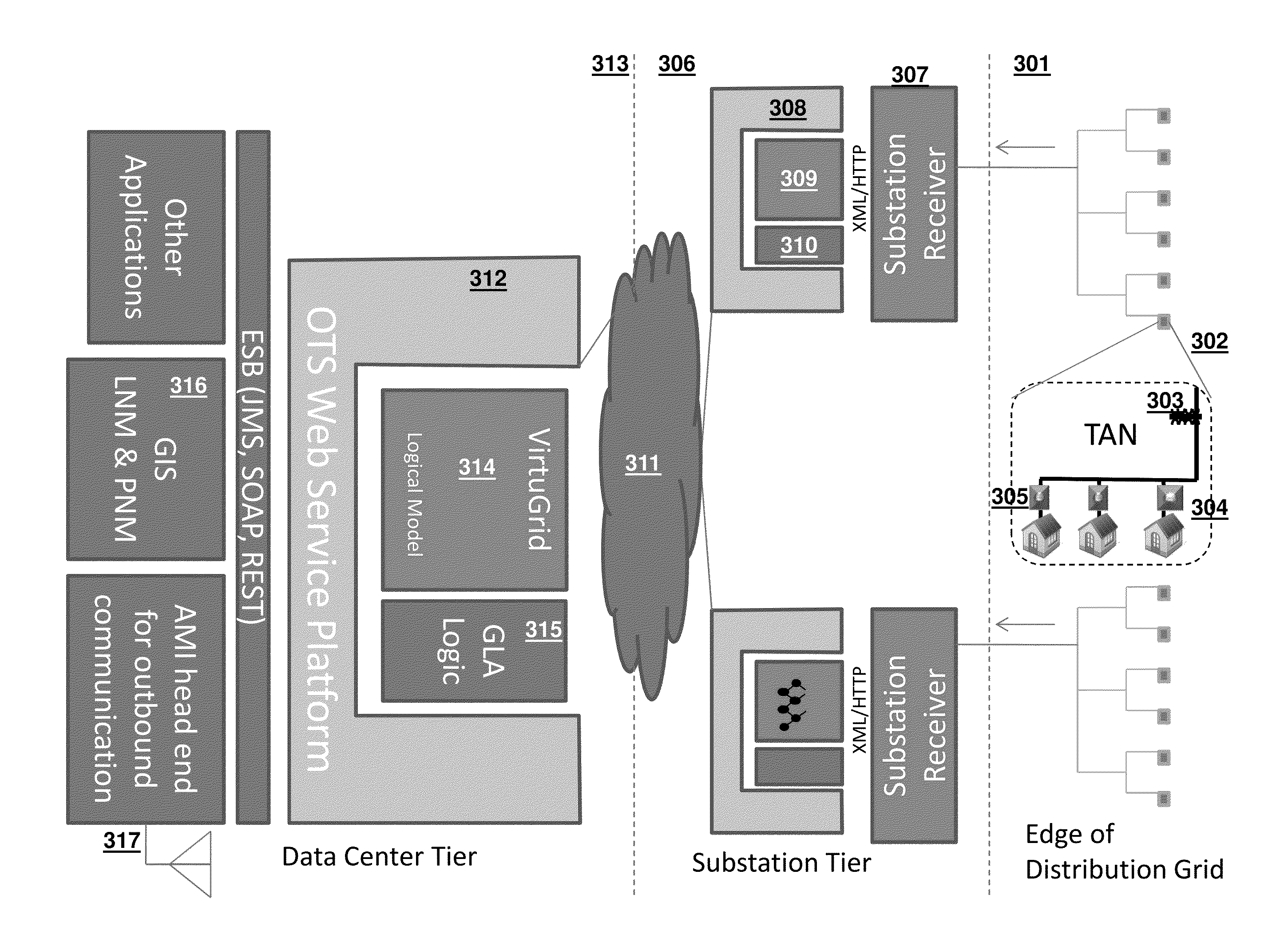
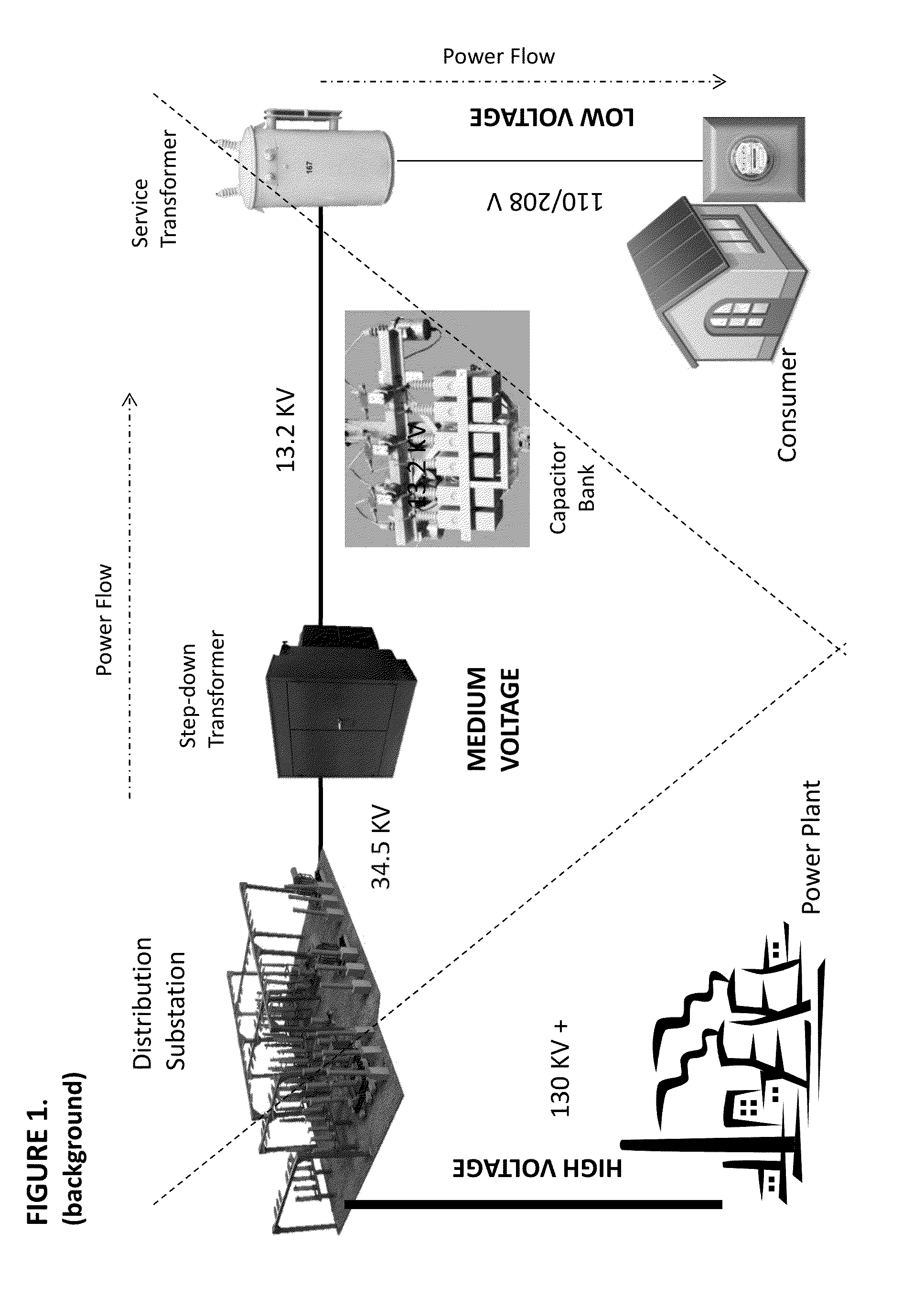
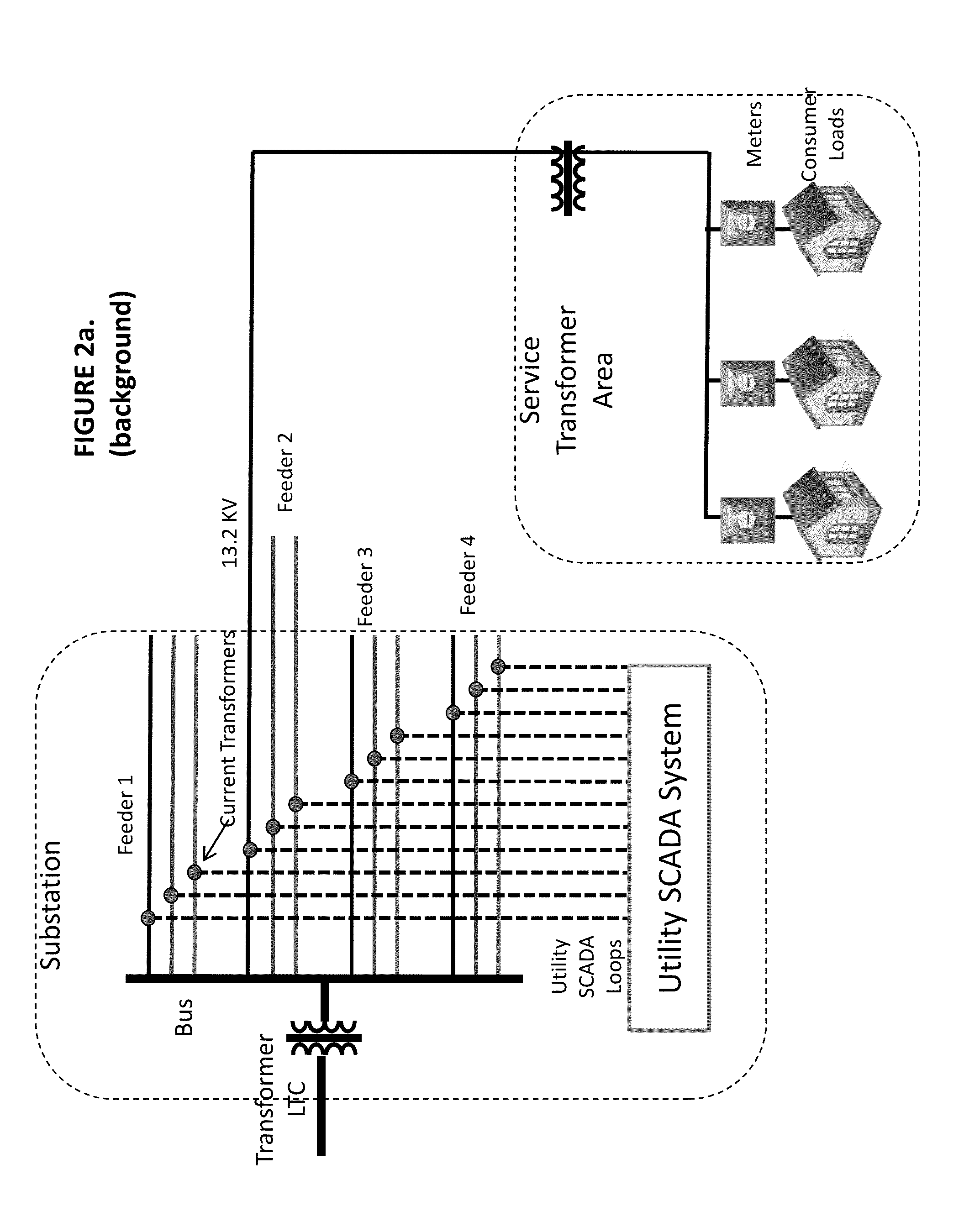
[0073]The present invention comprises a system and methods for constructing and operating an on-grid data collection network in such a way as to integrate the network with other adjacent networks and devices present at the edge, substations, and features of an electrical distribution network, wherein the other networks and devices may include Smart Meters and the AMI and a conventional network such as the Internet. The system and methods further integrate the data collected by the on-grid data collection network at a data center and may publish the collected data to other applications. The system and methods may also employ the capabilities of the integrated networks to infer otherwise unknown static and transient attributes of the electrical distribution grid and report them via the integrated networks for the purpose of improving the physical and logical network models of the Smart Grid. This leads to the ability of the models to support Smart Grid applications such as conservatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com