Wireless sensor network for measurement of electrical energy consumption
a technology of electrical energy consumption and wireless sensors, applied in the integration of power network operation systems, transmission, sustainable buildings, etc., can solve the problems of low precision, low cost, and inability to meet the needs of users, and achieve the effect of precise measurement of energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
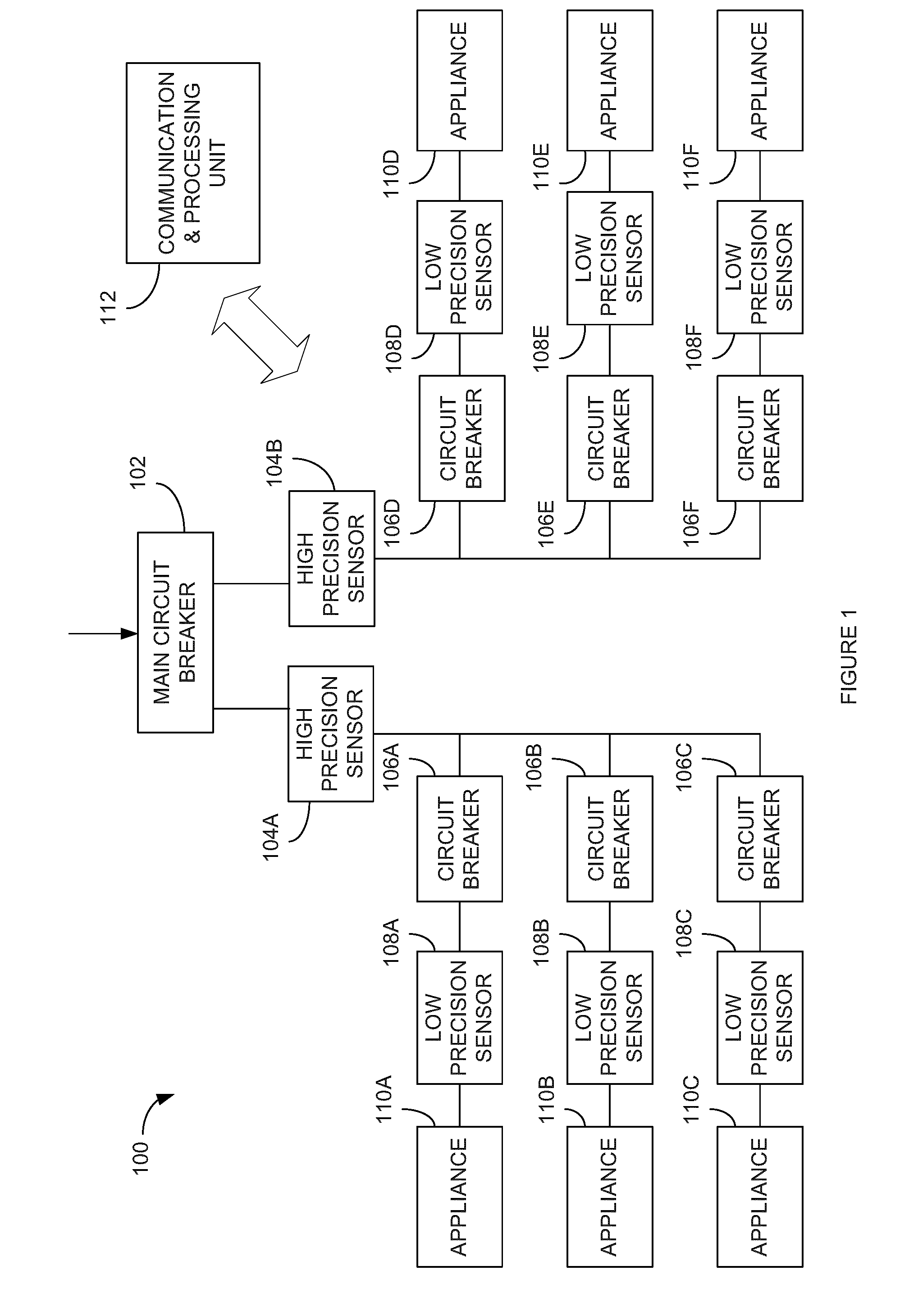
[0035]In a first embodiment, the auto-calibration algorithm comprises attributing the measure of the current sum to each circuit proportionally to the measure of each low precision sensor 108. For example, using:
İT: the precise measurement of the total current;
Î1, Î2, Î3: the low precision measurements of circuit breakers 1, 2 and 3;
[0036]The improved precision measurement of the current of each sensor is:
İ1=İT*Î1(Î1+Î2+Î3)
İ2=İT*Î2(Î1+Î2+Î3)
İ3=İT*Î3(Î1+Î2+Î3)
[0037]Using this technique, each individual low precision current measurement În can be calibrated to a more precise value.
second embodiment
[0038]In a second embodiment, the auto-calibration algorithm comprises summing waveforms provided by each sensor 108 for a given time window. Optimization techniques such as the Newton-Raphson technique, the bisection technique or the polynomial approximation technique may then be used to minimize the error, i.e. the difference between the computed sum and the precise measurement provided by sensors 104a, 104b, by adjusting a multiplicative gain for each signal provided by sensors 108. For example, using:
iT(t): the precise measurement of the total current;
Î1(t), Î2(t), Î3(t): the low precision measurements of circuit breakers 1, 2 and 3;
[0039]The following expression is computed:
e=İT(t)−(G1*Î1(t)+G2*Î2(t)+G3*Î3(t))
[0040]The parameter “e” may be minimized by adjusting G1, G2 and G3 using various optimization techniques. After convergence of the optimization algorithm, the precise measurement of each circuit is obtained by multiplying the measured current În(t) by its respective gain ...
third embodiment
[0041]In a third embodiment, mathematical correlation operations may be used to isolate each signal component from the precise sum. The correlation is calculated between each current signal from sensors 108 and the precise sum of currents provided by sensors 104a, 104b. Using this technique, the precise sum of current waveforms can be broken down into constituent signals corresponding to the current waveforms provided by low precision sensors 108. These constituent signals are attributed to each circuit based on the likelihood of the waveform. The error may thus be corrected, by the communication and processing unit 112 or a further processing unit (not shown), in order to increase precision of the measurements to be used for analysis.
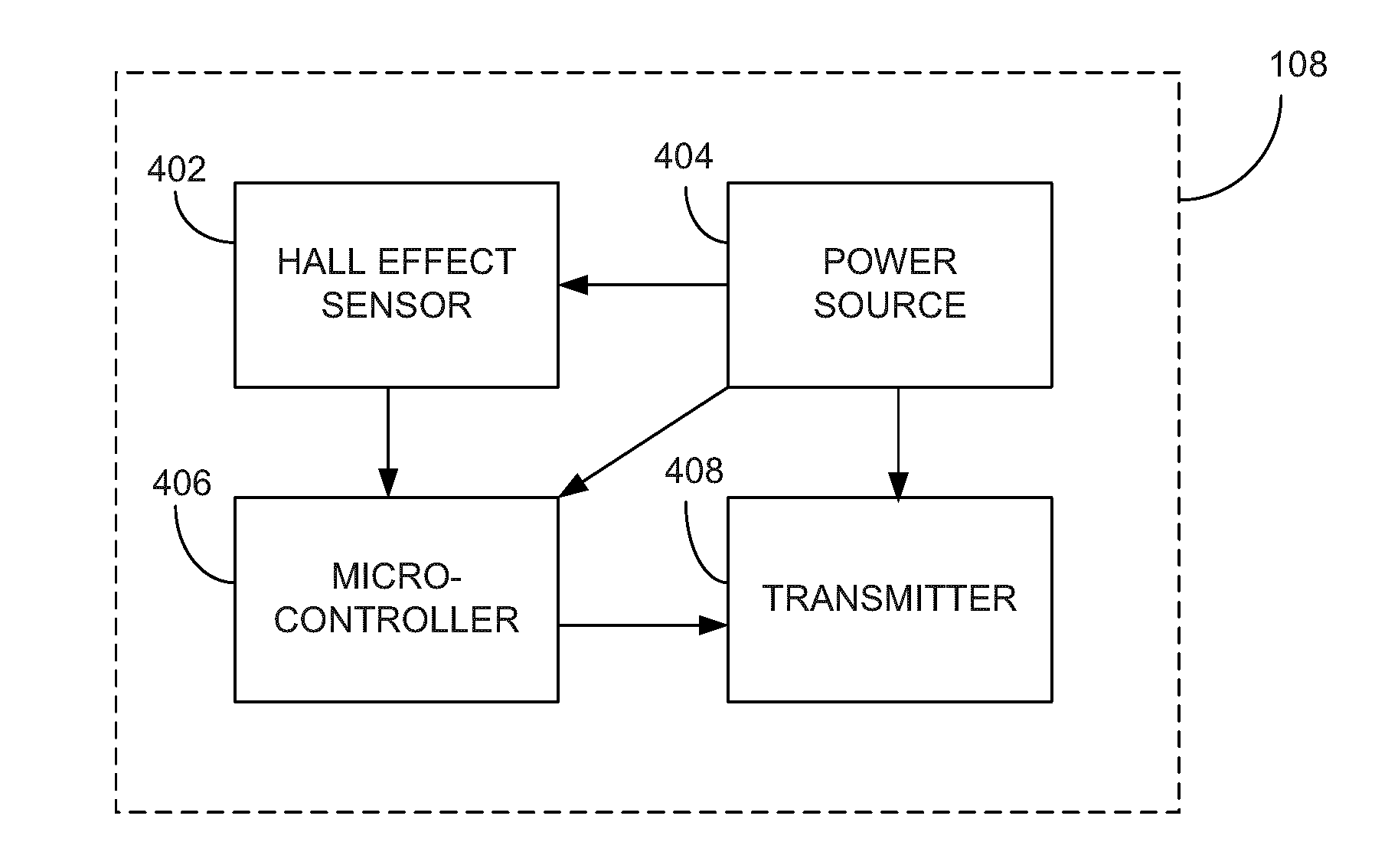
[0042]Other auto-calibration techniques known to those skilled in the art may be used in order to mitigate the effects of the sensitivity of the Hall effect sensors in the application as described.
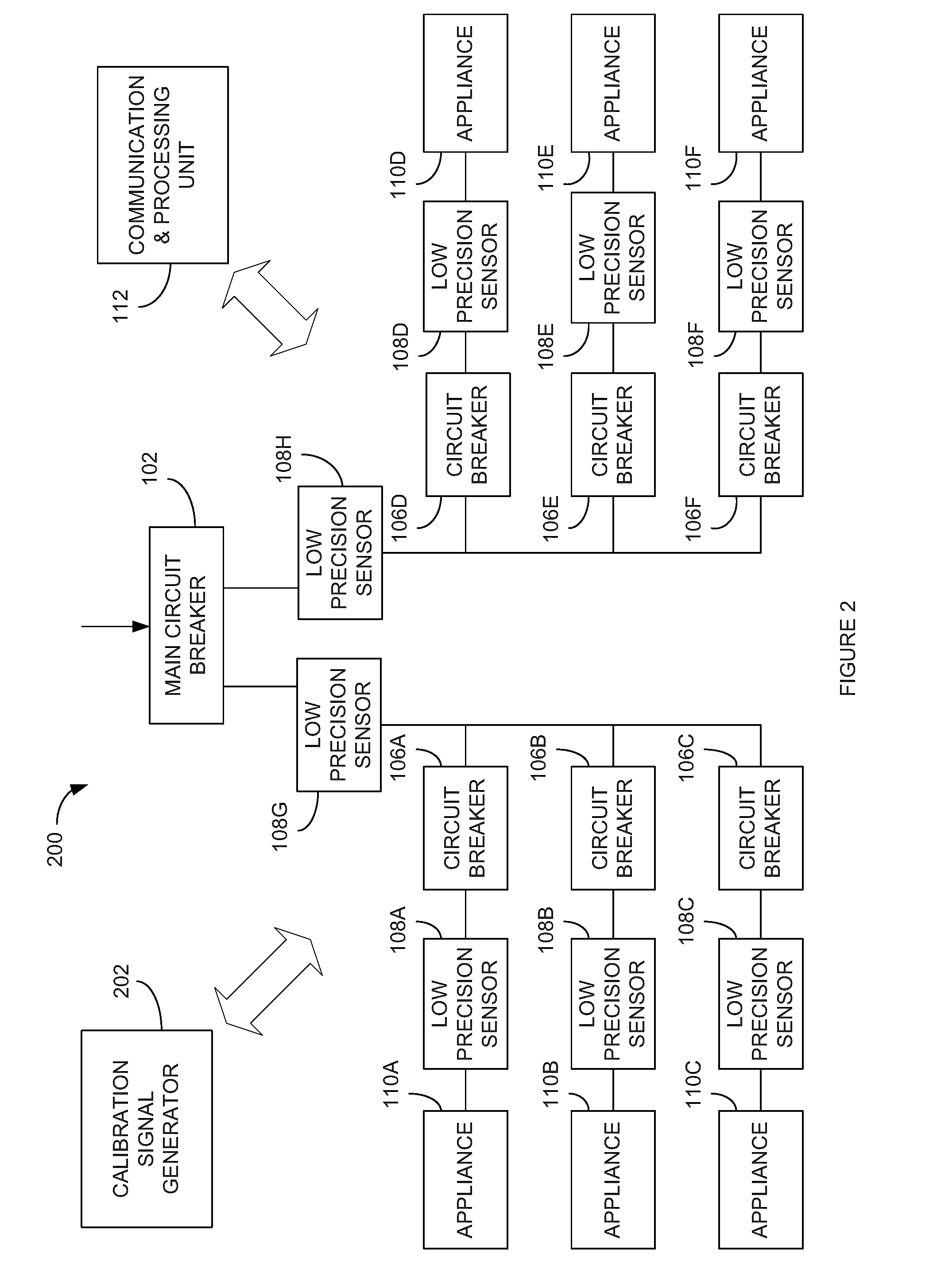
[0043]Referring to FIG. 2, there is illustrated an alte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com