Asynchronous machine with optimized distribution of electrical losses between stator and rotor
a technology of asynchronous machines and rotors, applied in the direction of windings, dynamo-electric components, transportation and packaging, etc., to achieve the effects of high torque density, improved suitability for use, and higher continuous torqu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
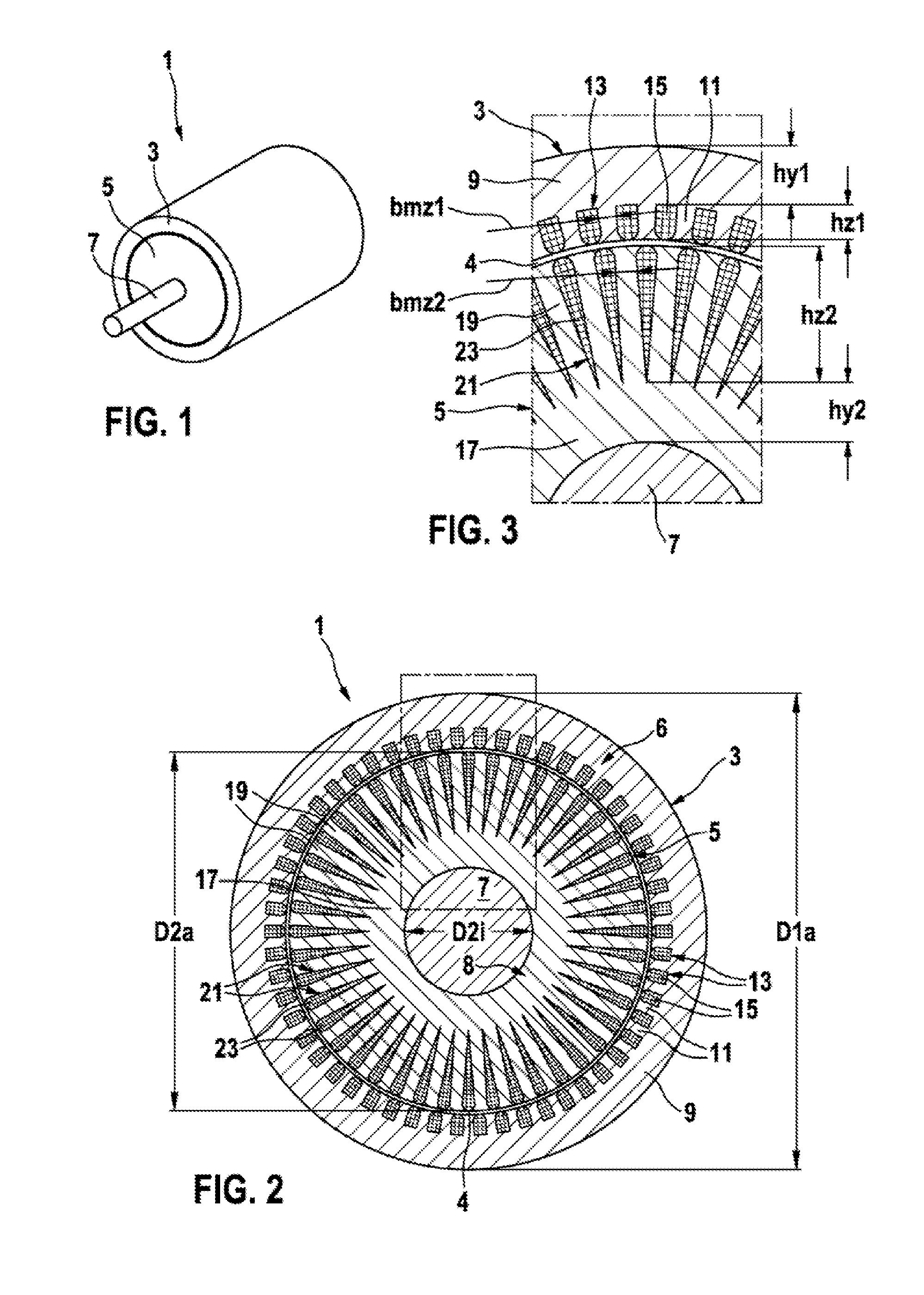
[0032]FIG. 1 illustrates an asynchronous machine 1 in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. The asynchronous machine 1 comprises a stator 3, a rotor 5 and a shaft 7. The stator 3 surrounds the rotor 5 in an annular manner. The rotor 5 is consequently received within the stator 3 in such a manner as to be able to rotate about the shaft 7. The stator 3 and rotor 5 comprise a cylindrical form.
[0033]FIGS. 2 and 3 illustrate an electrical machine 1 in the cross section and also an enlarged section of such a cross section. A small gap 4 is embodied between the stator 3 and the rotor 5. Both the stator 3 and also the rotor 5 comprise a plurality of lamellae 6, 8 that are arranged in the axial direction one after the other.
[0034]The stator 3 comprises a stator yoke 9 that lies on the exterior. The stator yoke 9 is annular or rather cylindrical in shape. A dimension of the stator yoke 9 is described in the radial direction as stator yoke height hy1. Stator teeth 11 project ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com