Chimeric antigen receptor and methods of use thereof
a technology of chimeric antigen and receptor, applied in the field can solve the problem that the car is not pharmacologically controlled, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of chimeric antigen receptors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of CAR
[0309]Materials and Methods
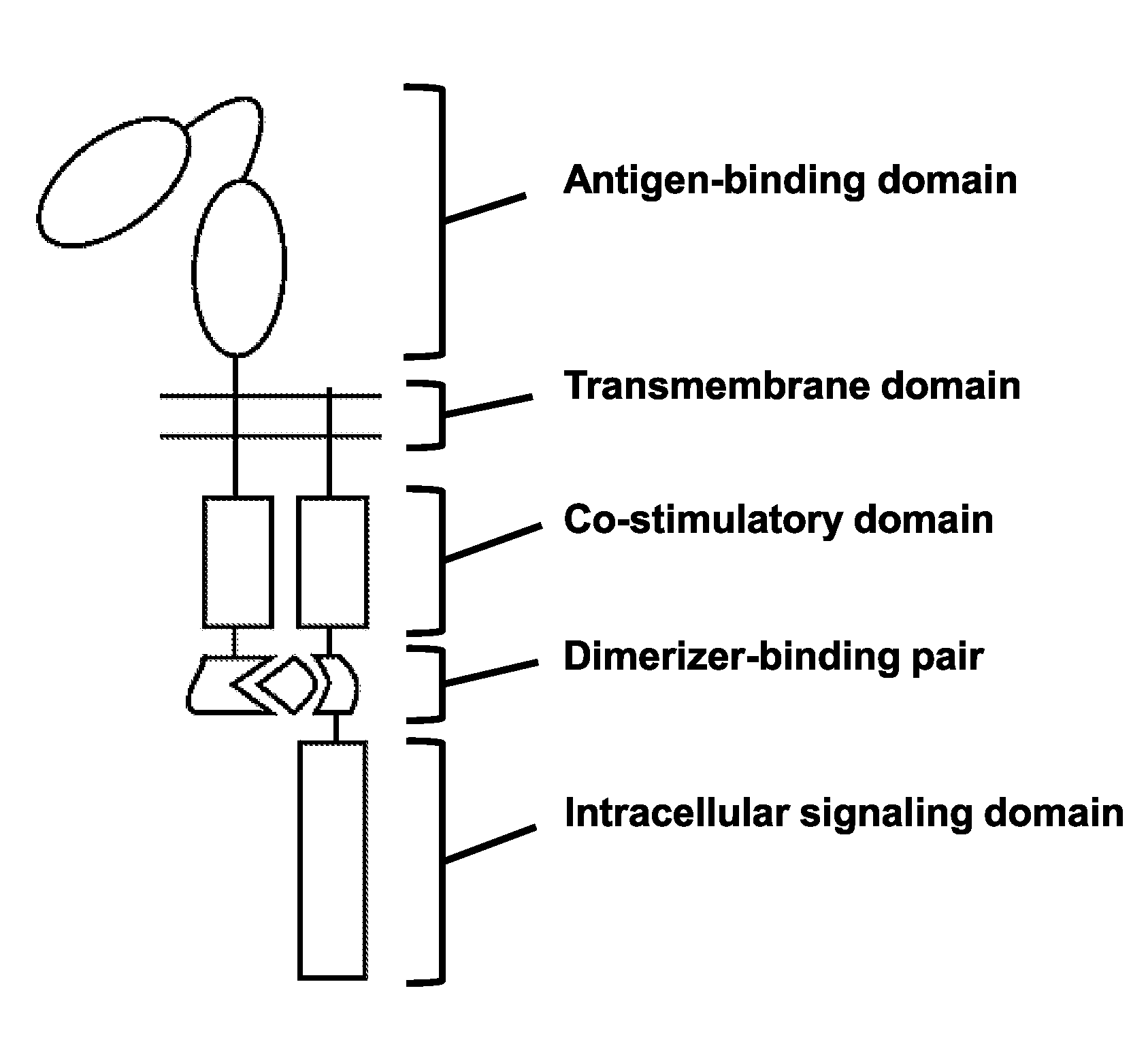
[0310]The anti-human CD19 scFv was selected as the antigen recognition domain in CARs throughout the design optimization process. FIGS. 18A and 18B summarize the molecular structure of each CAR consisting of two numerically identified polypeptides. All membrane-anchored polypeptides are di-sulfide bonded homo-dimers. The membrane-anchored polypeptides are depicted as monomers for graphical simplicity.
[0311]Generation of CAR Constructs
[0312]Sequence encoding the anti-human CD19 scFv was cloned from a construct. The human 4-1BB co-stimulation and CD3 zeta ITAM signaling chains were cloned from cDNAs supplied by Open Biosystems. FKBP- and FRB-encoding sequences were cloned from plasmids supplied by Addgene.
[0313]Standard molecular cloning techniques (polymerase chain reaction (PCR), restriction digestion, ligation, etc.) were applied to generate lentiviral expression plasmids.
[0314]Effector and Target Cell Culturing Conditions
[0315]Human prim...
example 2
CARs Targeting Mesothelin
[0331]Materials and Methods
[0332]A number of chimeric antigen receptor constructs were made and tested. The constructs shown here encode three different anti-human mesothelin scFv as the antigen recognition domains. FIGS. 19A, 19B, and 19C summarize the molecular structure of each anti-human mesothelin CAR, with each CAR comprising two polypeptides. The intercellular portion of each anti-human mesothelin CAR comprises two 4-1BB co-stimulatory domains, an FKBP and FRB dimerizer-binding pair, and an ITAM intracellular signaling domain. The three different antigen recognition domains shown here are anti-mesothelin HN1 scFv, SS1 scFv, and m912 scFv. All membrane-anchored polypeptides are di-sulfide bonded homo-dimers.
[0333]Generation of CAR Constructs
[0334]Sequences encoding the anti-mesothelin were cloned from constructs or synthesized via gene assembly by PCR. The human 4-1BB co-stimulation and CD3 zeta ITAM signaling chains were cloned from cDNAs supplied by ...
example 3
Gibberellic Acid as a Dimerizer of On-Switch CARs
[0346]Materials and Methods
[0347]FIG. 20A summarizes the molecular structure of the subject gibberellic acid dimerizer CAR. The antigen binding portion comprises the anti-human CD19 scFv. The intracellular portion comprises two 4-1BB co-stimulatory domains, a GID1 and GAI dimerizer-binding pair, and an ITAM intracellular signaling domain. All membrane-anchored polypeptides are di-sulfide bonded homo-dimers.
[0348]Generation of CAR Constructs
[0349]Sequences encoding the gibberellic acid dimerizer CAR were cloned from constructs. The anti-CD 19 scFv was cloned from a plasmid. The human 4-1BB co-stimulation and CD3 zeta ITAM signaling chains were cloned from cDNAs supplied by Open Biosystems. GID1- and GAI-encoding sequences were cloned from Addgene plasmids. Standard molecular cloning techniques (polymerase chain reaction (PCR), restriction digestion, ligation, etc.) were applied to generate lentiviral expression plasmids.
[0350]Effector ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com