Use of high acyl gellan in whipping cream
a high-acyl gellan, whipping cream technology, applied in the field of whipping cream, can solve the problems of poor whipping effect, poor overrun, and inability to pour cream out of containers, so as to achieve good whipping effect, good whipping effect, and acceptable storage stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0168]3 vegetable whipping creams i.e. sample 5, 6 and 7 were produced according to the following process:[0169]1.Heat water to 70° C. in mixer tank[0170]2. Add Na-caseinate, sucrose and sorbitol to the water[0171]3. Melt fat at 70° C.[0172]4. Add GRINDSTED® WP 950 (or alternative compositions of emulsifiers, hydrocolloids and salts) to the melted oil[0173]5. Add oil blend to the water phase[0174]6. Premix on Silverson—3700 rpm for 1 minute[0175]7. De-aerate for approximately 30 minutes in the bucket
UHT Treatment:
[0176]8. Preheat to 90° C.[0177]9. Indirect heating 142° C. for 3 seconds[0178]10. Downstream homogenization at 150 / 30 bar, 75° C.[0179]11. Cool to 8° C. (register the filling temp)[0180]12. Filling and store cold (5° C.)
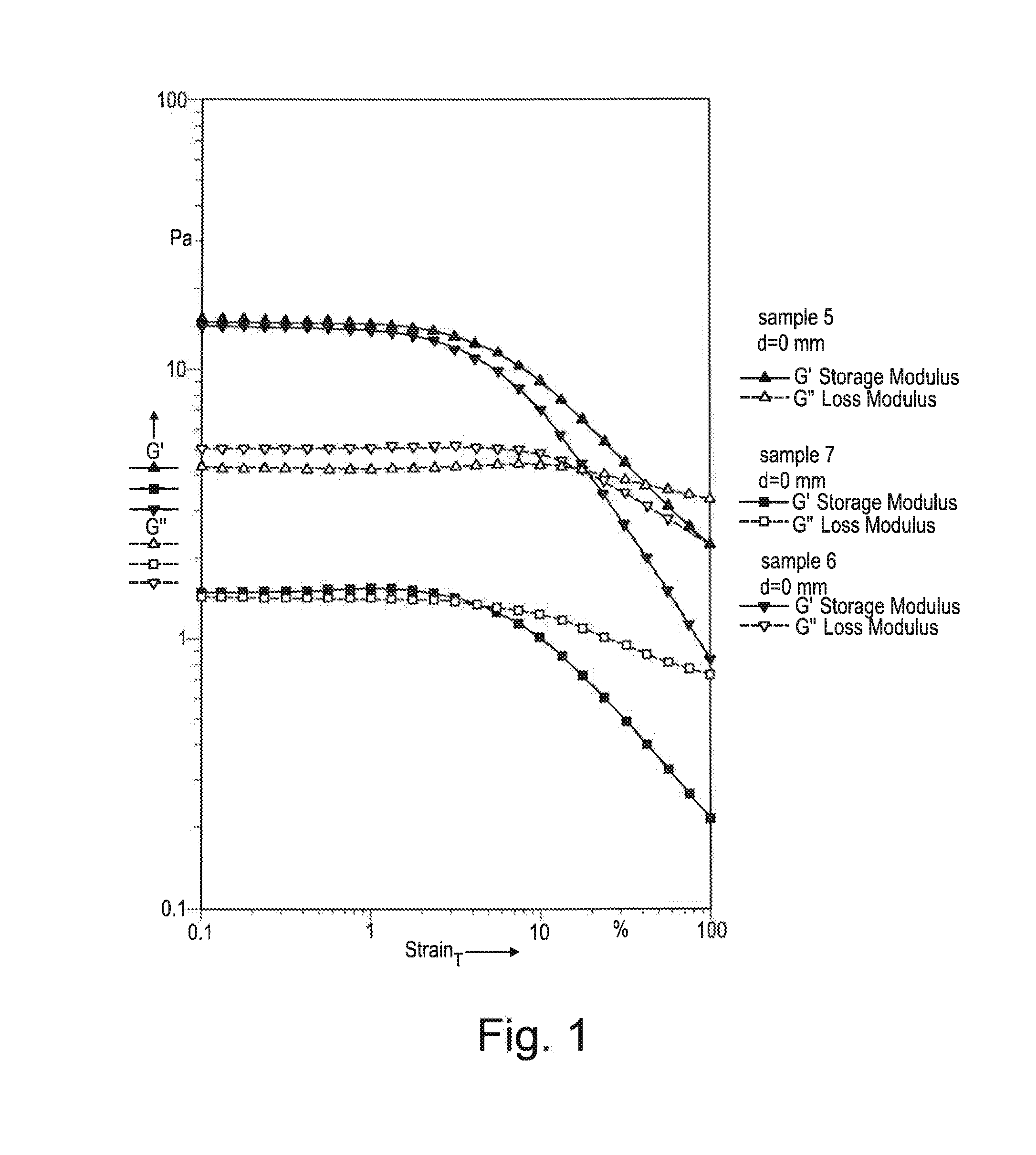
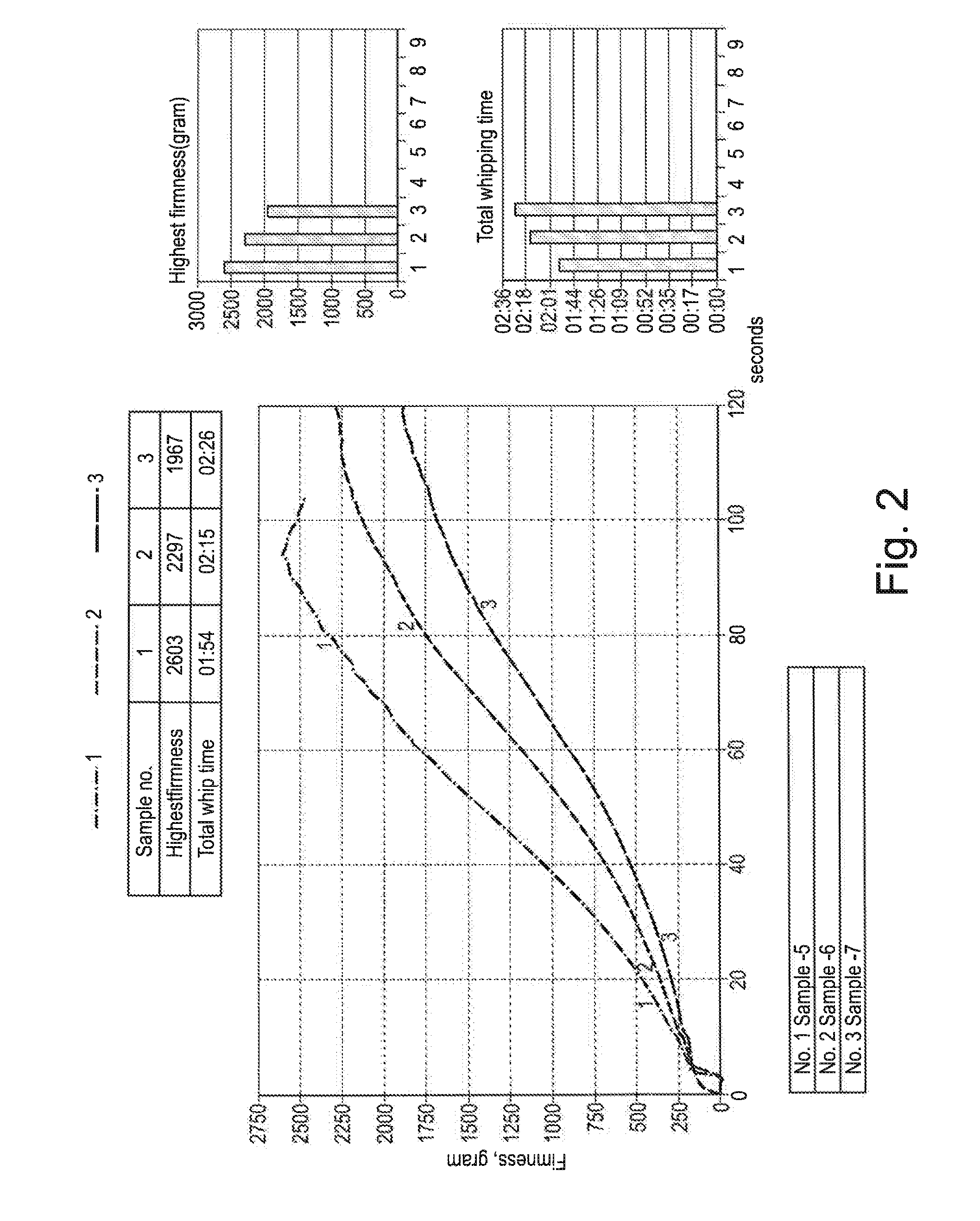
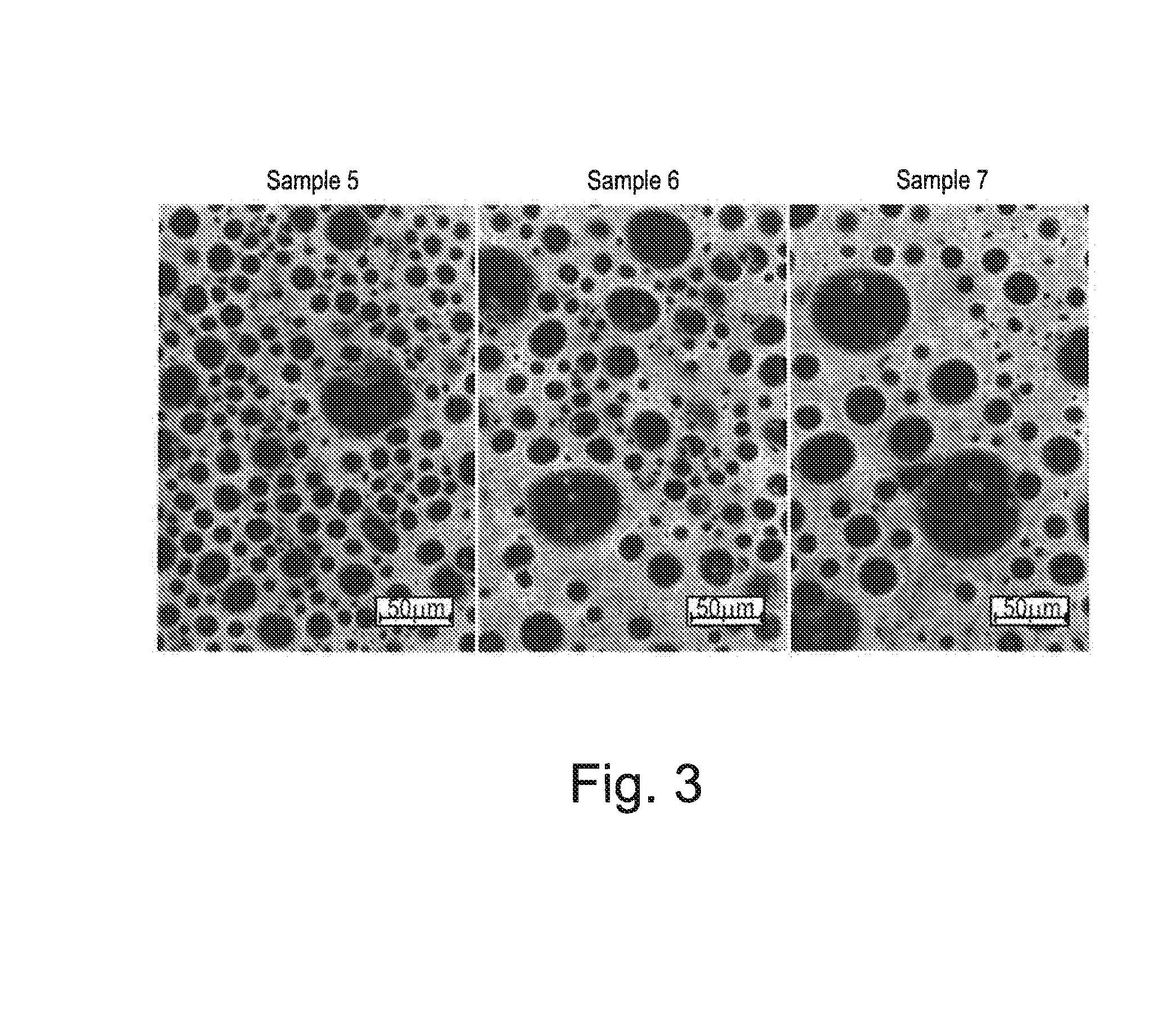
[0181]The recipes for sample 5, 6 and 7 are shown in table 1. Sample 5 contained 0.05% HA gellan from CPKelco (Kelcogel HMB-P), sample 6 contained 0.05% LA gellan from CPKelco (Kelcogel F) and sample 7 was a reference without gellan addition. The fat, Akoto...
example 2
[0192]2 vegetable whipping cream samples were produced, sample 81 and 84, using the same process as in example 1. The recipes are shown in table 3. Sample 81 is a reference cream without gellan, and sample 84 contains 0.05% HA gellan (Kelcogel HMB-P). Samples were whipped after minimum 3 days storage at 5° C. and evaluated for their tolerance towards addition of acid fruit syrups, using the following procedure:
[0193]200 g Yoghurt-Erdbeer Sahne Fond (Vortella Lebensmittelwerk, Pr. Oldendorf, Germany) was mixed in 400 ml cold water and hydrated. 400 g cream at 5° C. was whipped at speed 3 in a Hobart mixer until max firmness (practical experience based on splashing sound from foam and foam appearance). Hydrated fond was added to the bowl and the foam was mixed in the Hobart for 20 seconds at speed 2. The resulting whipped cream was transferred to a plate, and the surface of the cream was scrabed off to evaluate degree of graininess. Pictures of the foams were taken and shown in FIG. 4...
example 3
[0194]Whipping cream samples were produced with decreasing amount of sodium caseinate to obtain increased fat agglomeration and fat coalescence in the vegetable cream, in this way both increasing the whipping properties (faster whipping time and increased foam firmness), but also increasing the risk of thickening of the cream in the bottle due to the fat agglomeration. A similar series of whipping cream samples with decreasing amount of sodium caseinate was added 0.035% HA gellan. The HA gellan product used was Gellan NM 205, consisting of 78% HA gellan and 22% dextrose. Gellan NM205 is produced by DuPont. The recipes are shown in table 4 (Samples 1-6). GRINDSTED® WP 950 Emulsifier & Stabiliser System is produced by DuPont. The flavours, S-Vanilla 507441 T and D -Cream 050001 U30377 are produced by Firmenich.
[0195]Vegetable cream processing is described in example 1. The samples were heat shock treated (Heat shock treatment: 5 days with a temperature cycle each day of approx 16 hour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com