Storage device and storage unit
a storage device and storage unit technology, applied in semiconductor devices, digital storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to retain the intermediate resistance value for a long time, the resistance variation (random telegraph noise) is likely to occur in every reading, and the oxygen defect formed in writing tends to be repeatedly generated and disappeared, so as to improve the thermal and chemical stability of the conductive path, and reduce the effect of conductive path deteriorati
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment (
1. First Embodiment (An example in which a resistance change layer includes boron (B) and oxygen (O))
1-1. Storage Device
1-2. Storage Unit
[0030]2. Modification Example 1 (An example in which a resistance change layer has a laminate configuration)
second embodiment (
3. Second Embodiment (An example in which an ion source layer and a resistance change layer each include a transition metal element)
4. Modification Example 2 (An example in which a resistance change layer has a laminate configuration)
5. Examples
first embodiment
1 FIRST EMBODIMENT
(1-1. Storage Device)
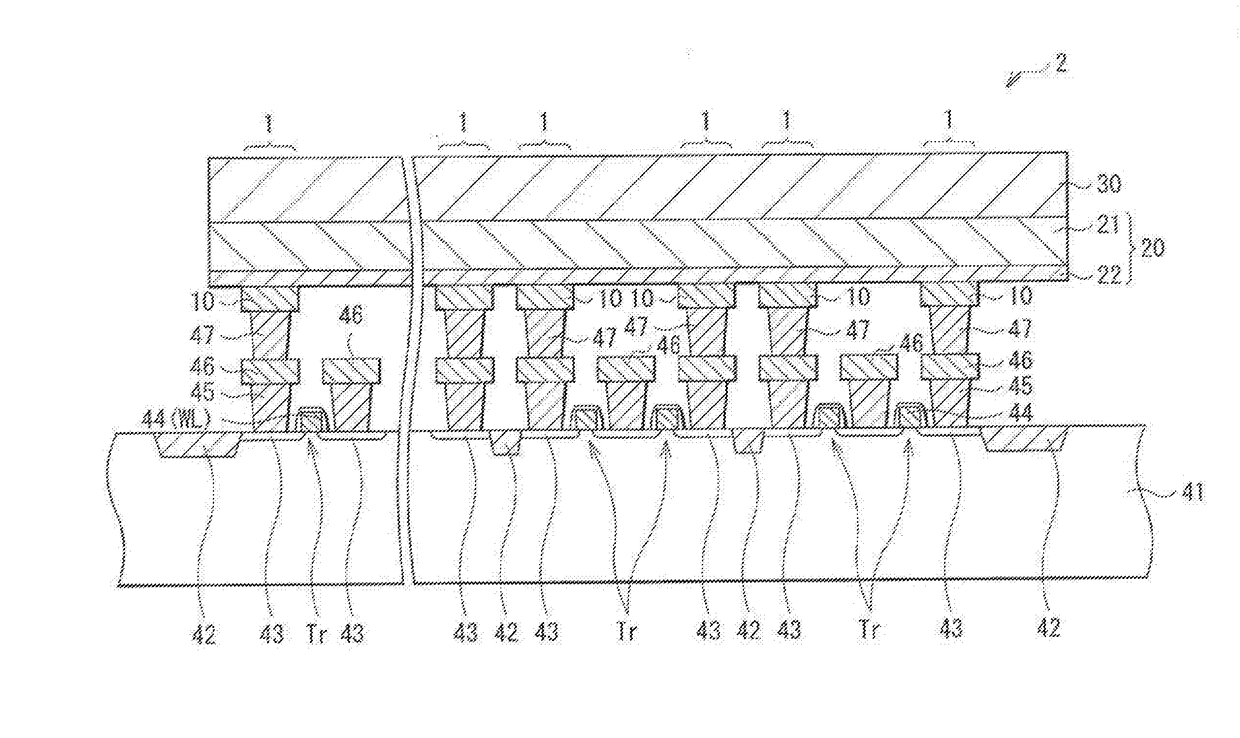
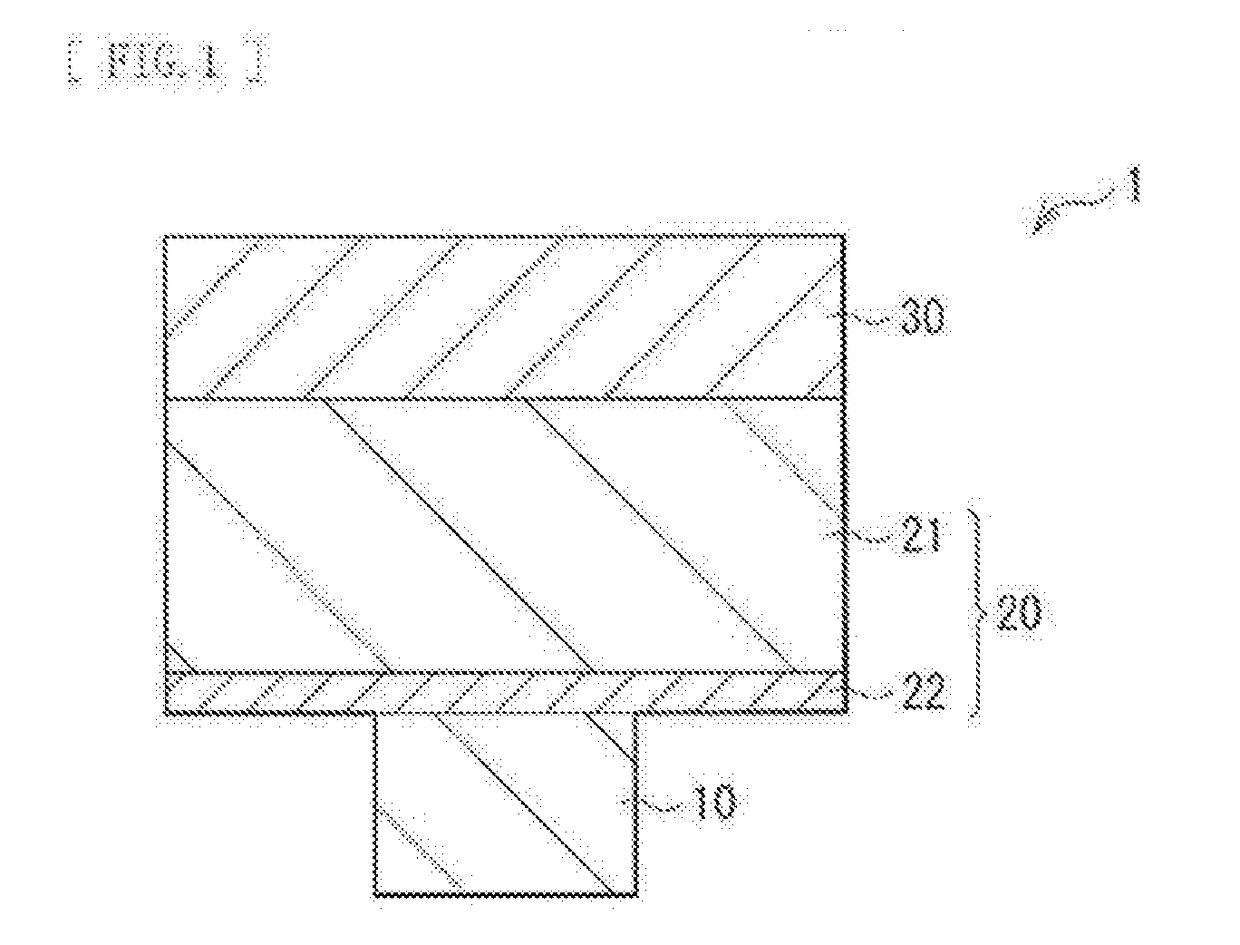
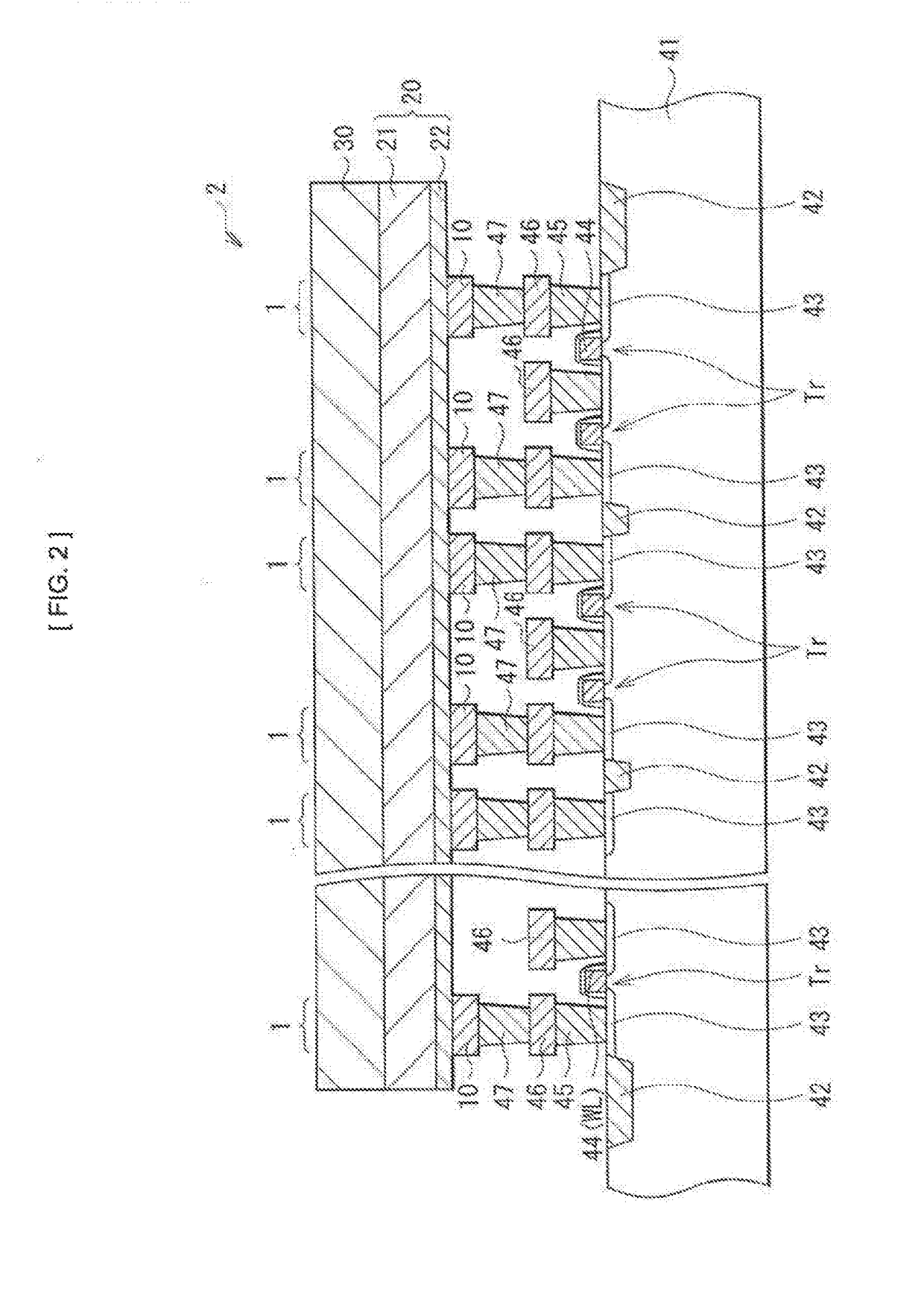
[0031]FIG. 1 illustrates a sectional configuration of a storage device 1 according to a first embodiment of the present disclosure. This storage device 1 includes a lower electrode 10 (a first electrode), a storage layer 20 including an ion source layer 21, and an upper electrode 30 (a second electrode) in this order.
[0032]For example, as will be described later (FIG. 2), the lower electrode 10 is provided on a substrate 41 that may be made of silicon and in which a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) circuit may be formed, and may serve as a connection section with the CMOS circuit. This lower electrode 10 may be made of a wiring material for use in a semiconductor process, for example, tungsten (W), tungsten nitride (WN), copper (Cu), aluminum (Al), molybdenum (Mo), tantalum (Ta), silicide, or the like. In a case where the lower electrode 10 is made of a material, such as Cu, that may cause ion conduction by an electrical field, a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com