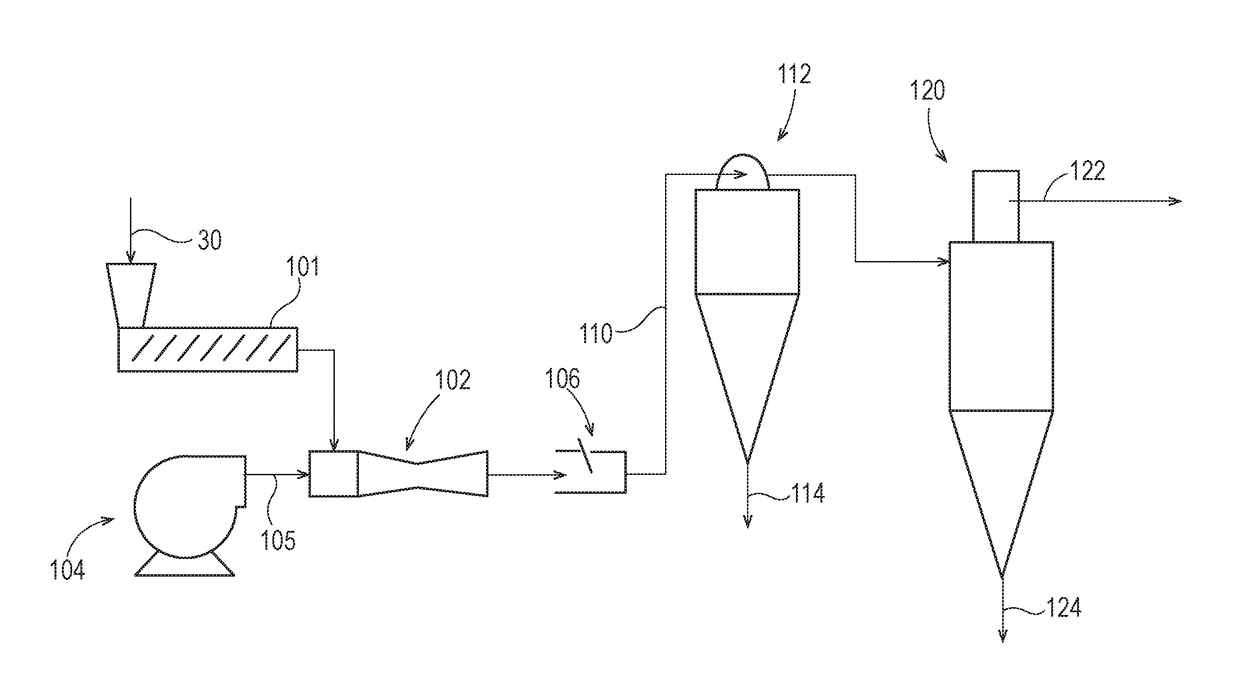
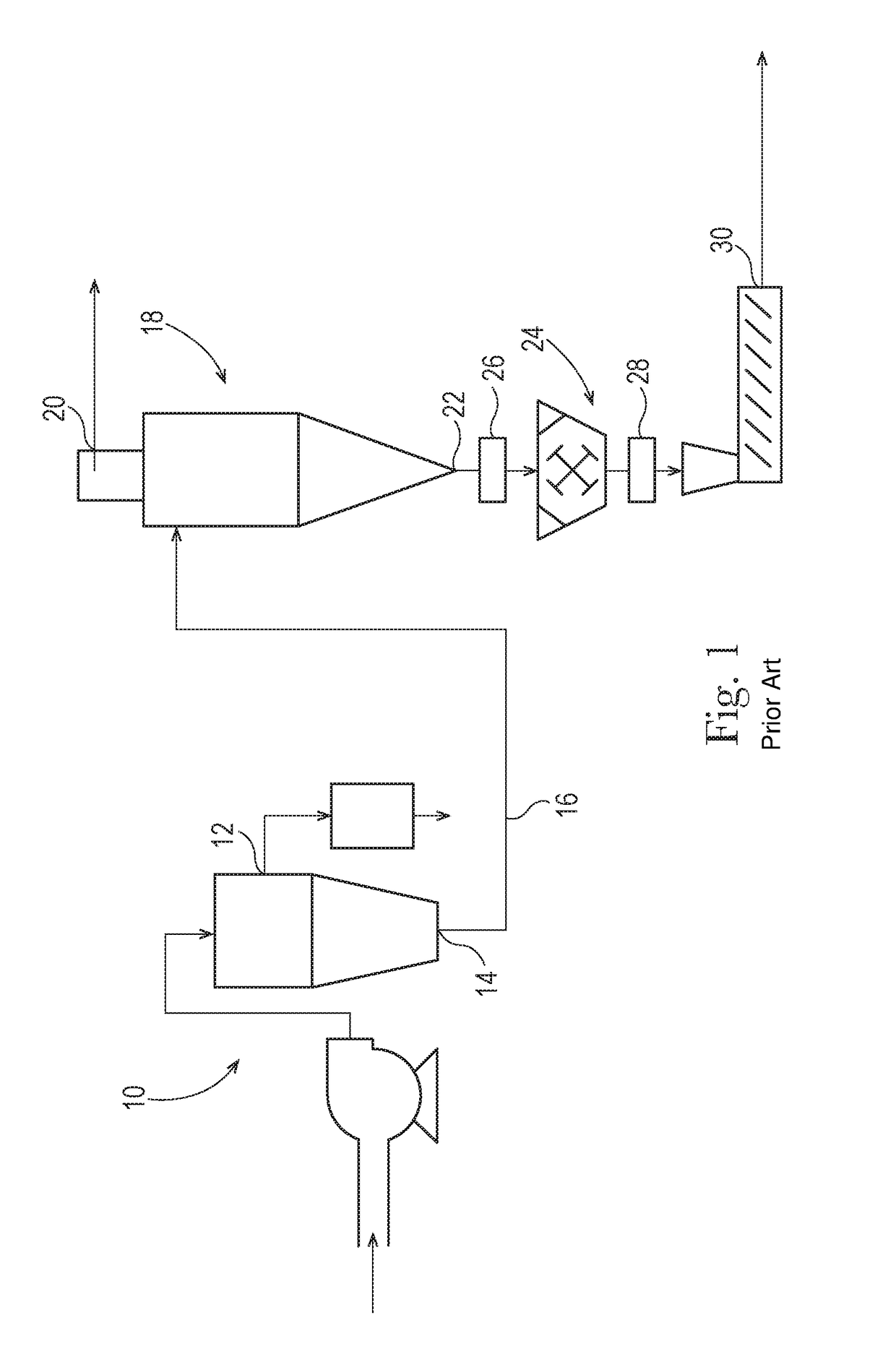
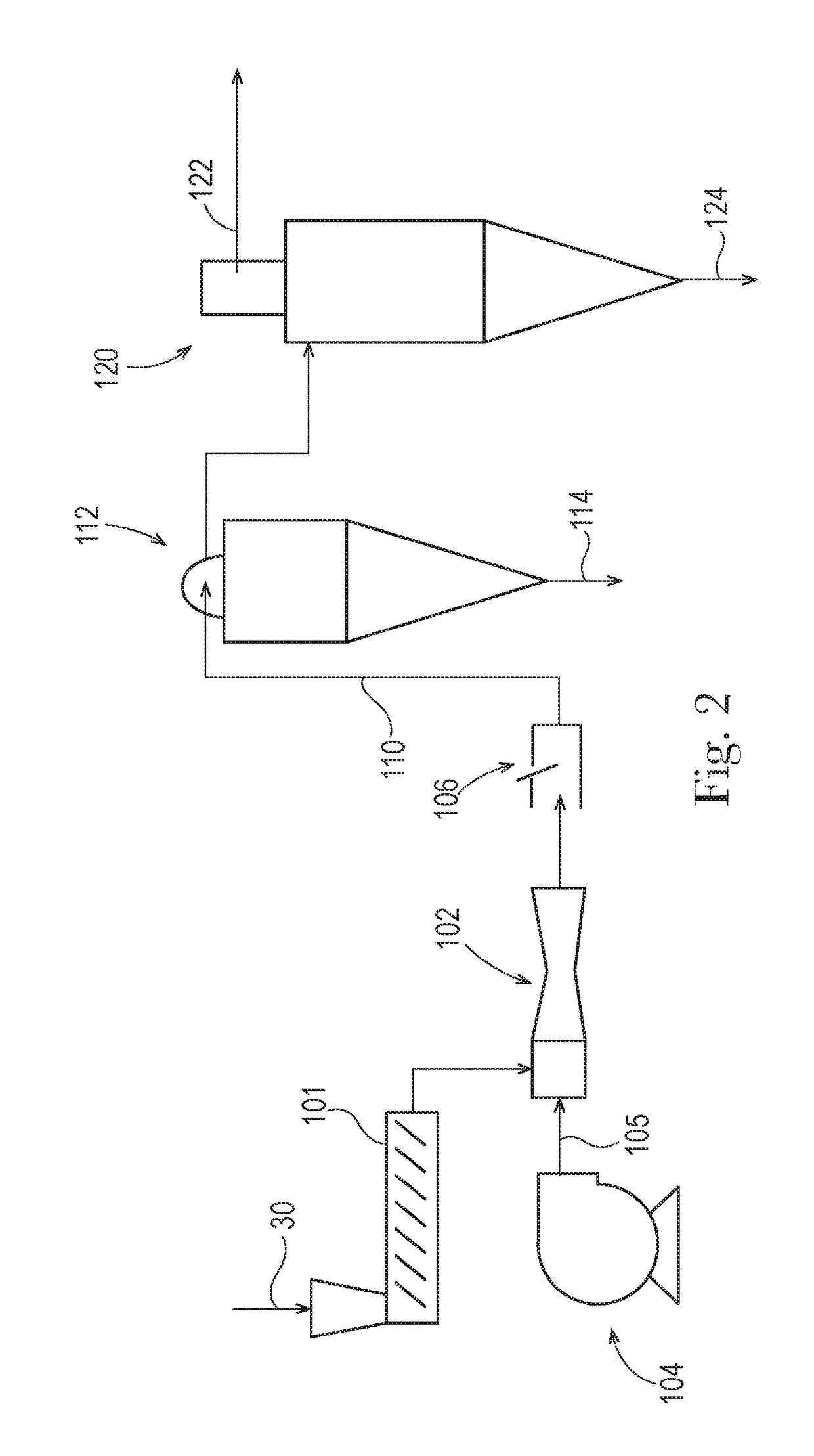
Flushable Fibrous Structures
a technology of fibrous structure and flue, which is applied in the field of flue, can solve the problems that fibrous structures that float or take a significant amount of time to sink may not experience a sufficient level of force, and affect the ultimate flushability of structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0009]The following text sets forth a broad description of numerous different embodiments of the present invention. The description is to be construed as exemplary only and does not describe every possible embodiment since describing every possible embodiment would be impractical, if not impossible. And it will be understood that any feature, characteristic, component, composition, ingredient, product, step or methodology described herein can be deleted, combined with or substituted for, in whole or part, any other feature, characteristic, component, composition, ingredient, product, step or methodology described herein. Numerous alternative embodiments could be implemented, using either current technology or technology developed after the filing date of this patent, which would still fall within the scope of the claims. All publications and patents cited herein are incorporated herein by reference.
[0010]It should also be understood that, unless a term is expressly defined in this s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com