Methods and compositions for increasing susceptibility to radiation treatment by inhibiting suppression of numerical chromosomal instability of cancer cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Ionizing Radiation Leads to Numerical Chromosomal Instability In Vitro
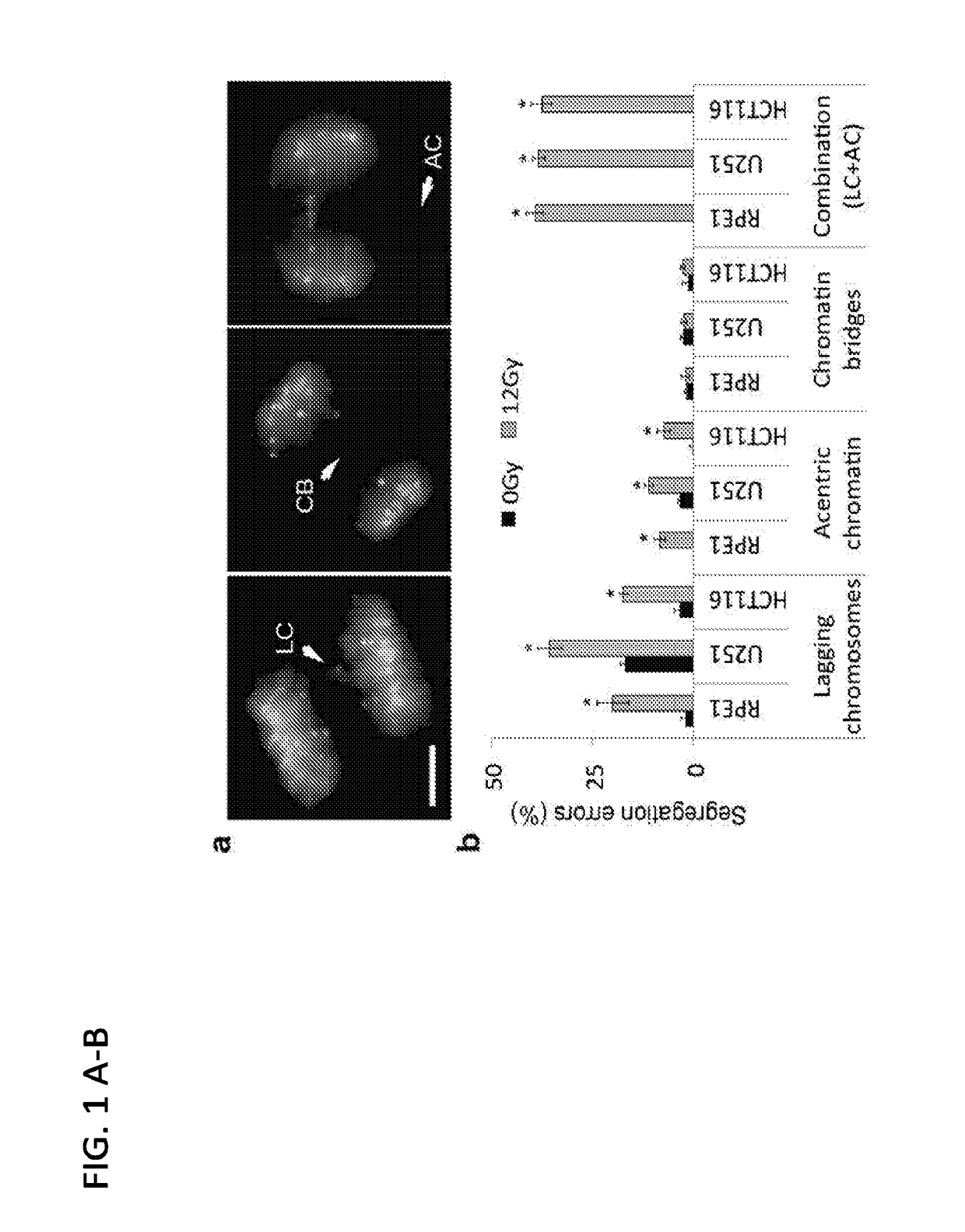
[0118]High-resolution fluorescence microscopy was used to examine various types of errors during anaphase in three human cell lines derived from normal human retinal epithelium (RPE1), colorectal cancer (HCT116) or glioma (U251). These cells were either near-diploid and chromosomally stable (RPE and HCT116) or aneuploid and chromosomally unstable (U251). RPE1 and HCT116 had an intact p53-signalling pathway (Thompson et al. Cell Biol. 2010; 188:369-381, whereas U251 contain defective p53 signalling (Gomez-Godinez et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:e202-e202. (2010). Briefly, cells were exposed to various doses of IR and evaluated 25 minutes later for signs of chromosome segregation during anaphase. 25 minutes provided sufficient time for many of the cells that were in mitosis during DNA damage induction to enter anaphase, but not sufficient time for cells that were in G2 to proceed through to anaphase. High-resolution fl...
example 2
Frequency and Type of Chromosome Segregation Error is Dependent on the Time Interval Between Radiation and Chromosome Segregation Analysis
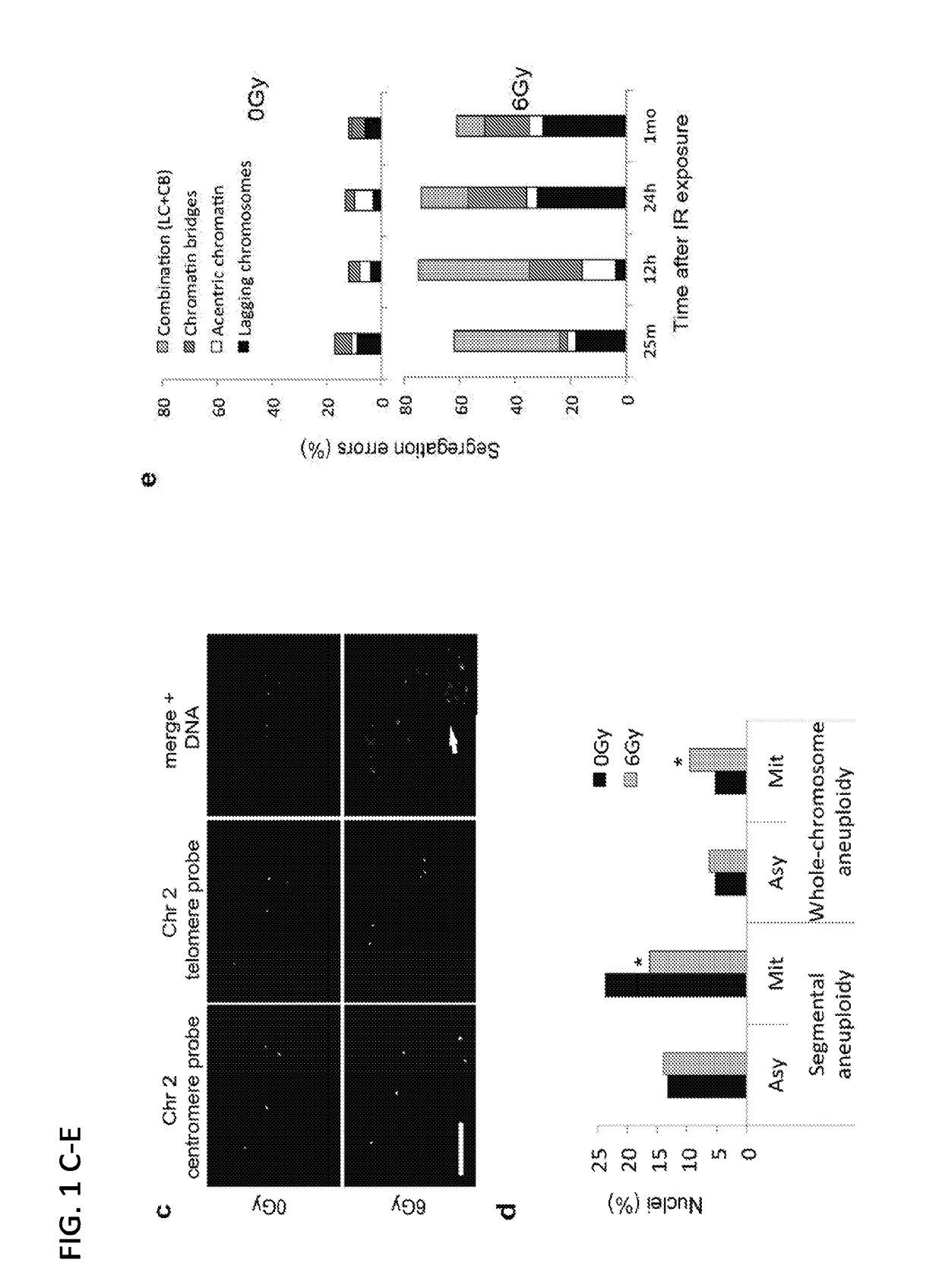
[0120]The inventors sought out to evaluate whether the frequency and types of chromosome segregation errors are dependent on the time interval between IR exposure and the analysis of anaphase chromosome segregation. HCCT116 cells devoid of tumor suppressor, p53, were used in this experiment, to allow for the proliferation of aneuploidy cells should they emerge (Thompson and Compton, J Cell Biol. 188(3):369-81, 2010). HCT116 p53− / − cells were exposed to 0 or 6 Gy of IR and chromosome segregation errors were evaluated at 25 minutes, 12 h, 25 h, and 1 month following the IR exposure. As shown in FIG. 1e, anaphase spindles examined 25 minutes after irradiation exhibited similar chromosome missegregation profiles compared with p53-competent HCT116 cells 25 minutes after IR exposure. However, 12 h after irradiation there was a significant increase in ch...
example 3
IR Induces w-CIN In Vivo
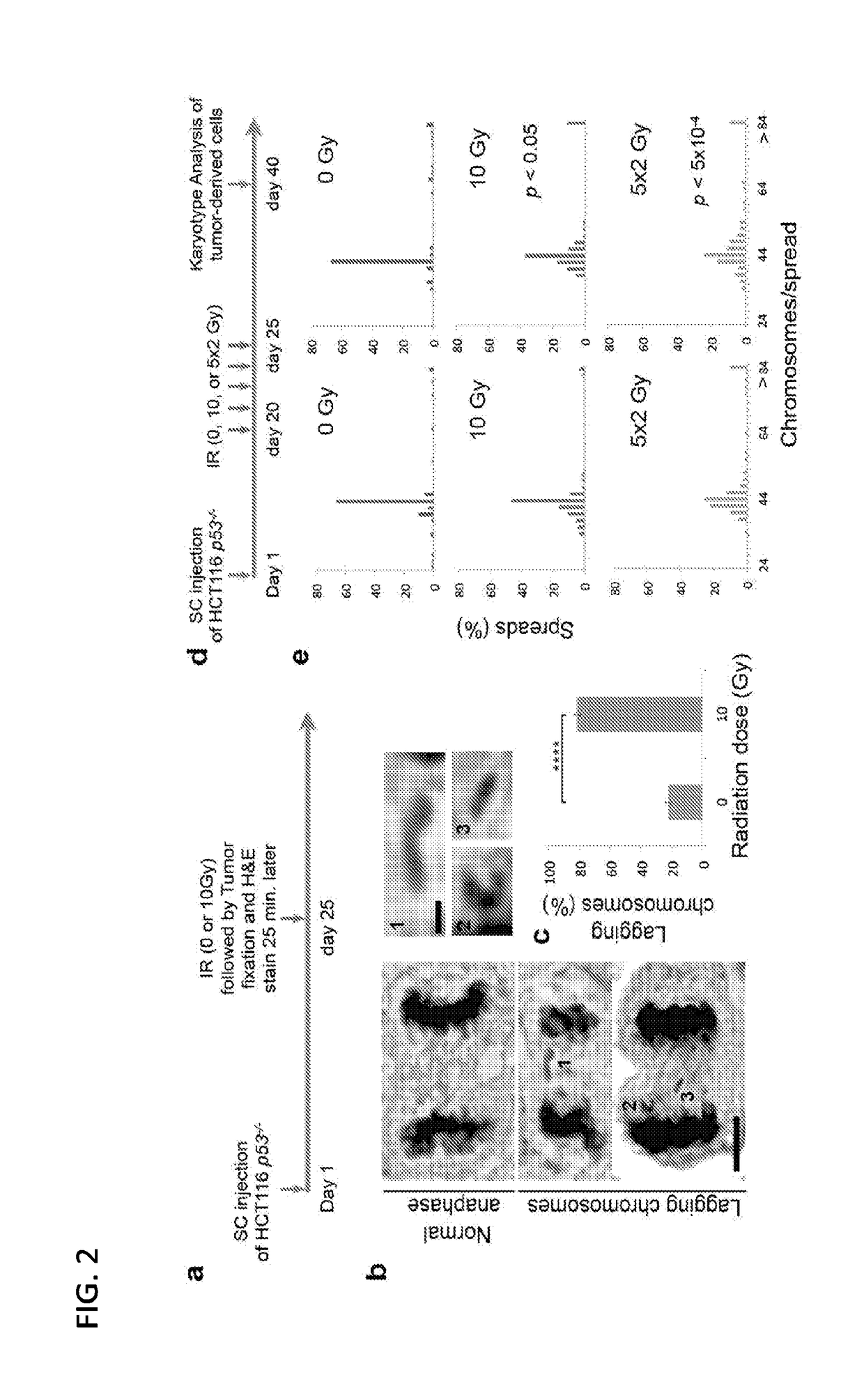
[0121]To determine whether IR can directly perturb the process of chromosome segregation in vivo, the inventors used tumour-forming HCT116 p53− / − cells that normally exhibit low rates of chromosomes missegregation and are thus considered chromosomally stable and near-diploid (Thompson and Compton, J Cell Biol. 188(3):369-81, 2010). HCT116 p53− / − cells were subcutaneously injected into nude mice and after 25 days transplanted tumours were exposed to 0 or 10 Gy of IR. Following formalin-fixation of tumours 25 min later, tumour sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and the effects of radiation on mitotic cells were evaluated (FIG. 2a, b). FIG. 2b shows an example of normal anaphase and anaphase cells containing lagging chromosomes in HCT116 p53− / − xenografts after IR exposure. As demonstrated in FIG. 2c, tumours exposed to 10 Gy of IR exhibited significantly higher rates of chromosome segregation errors during anaphase compared with control, non-irrad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com