Stabilized thermal energy output system
a technology of thermal energy output and stable temperature, which is applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, electric heating, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the tolerance of graphite medium to temperatures well below that of the graphite medium itself, and affecting the operation of the maximum operating temperature of the graphite medium,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
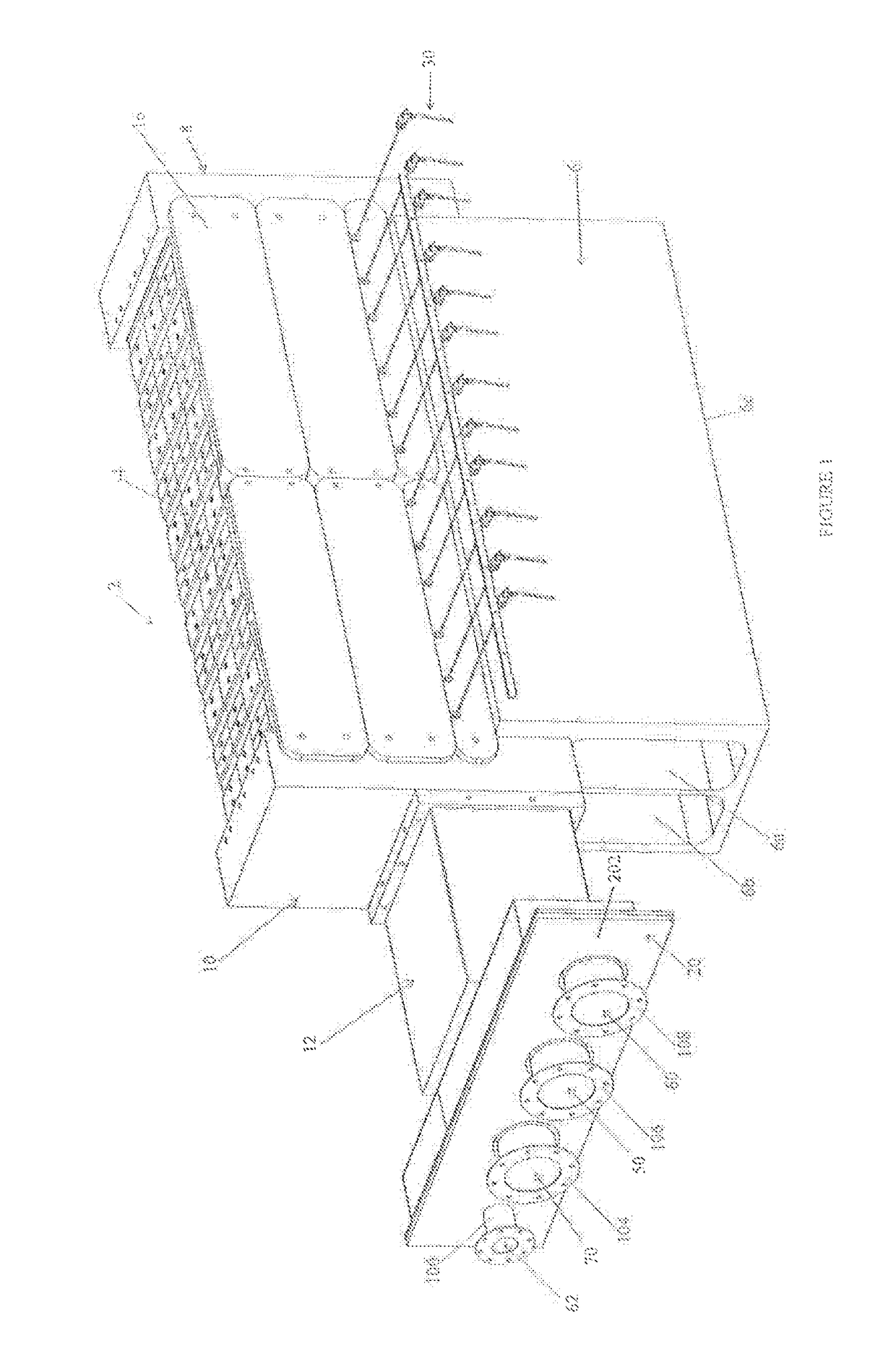
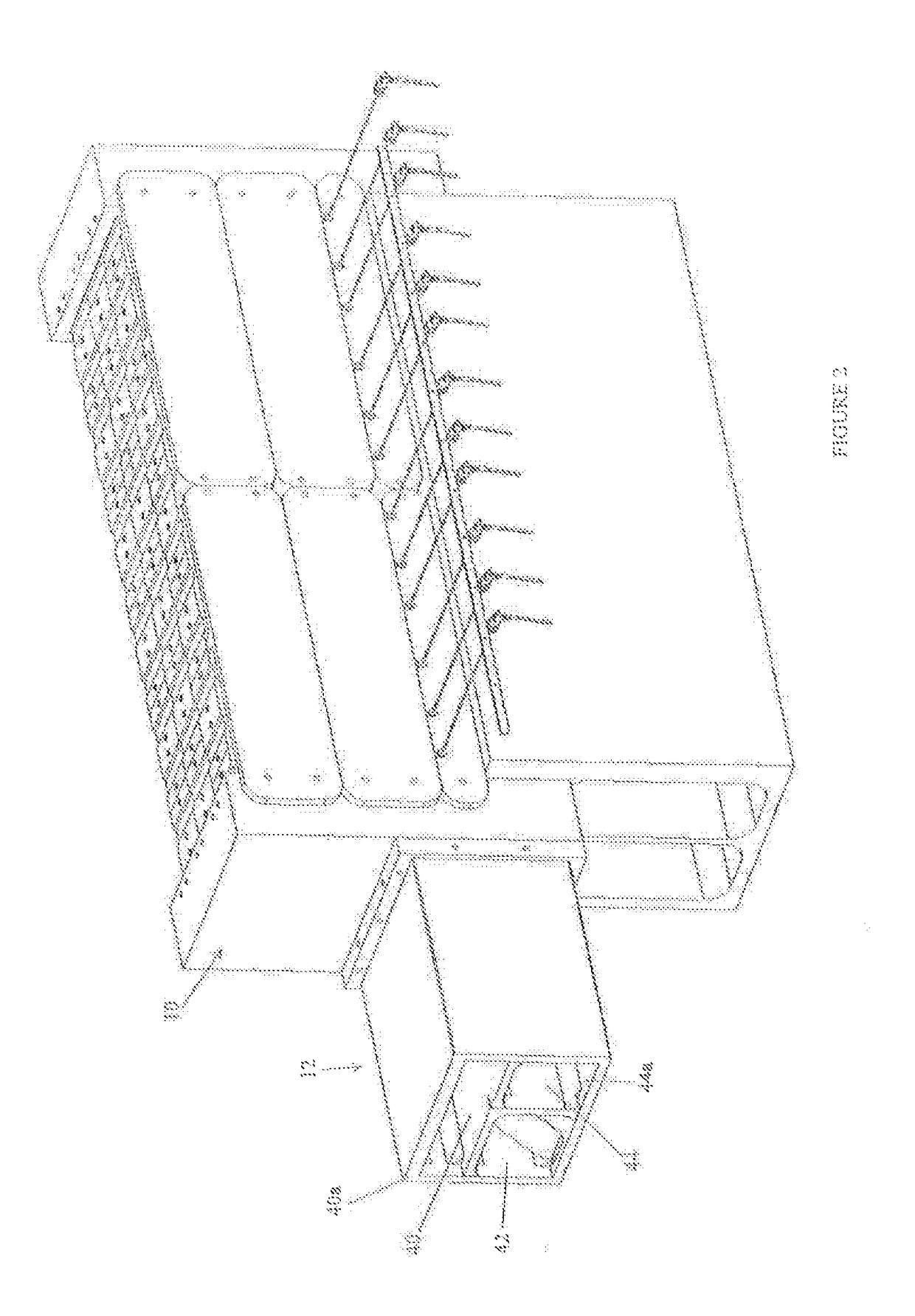
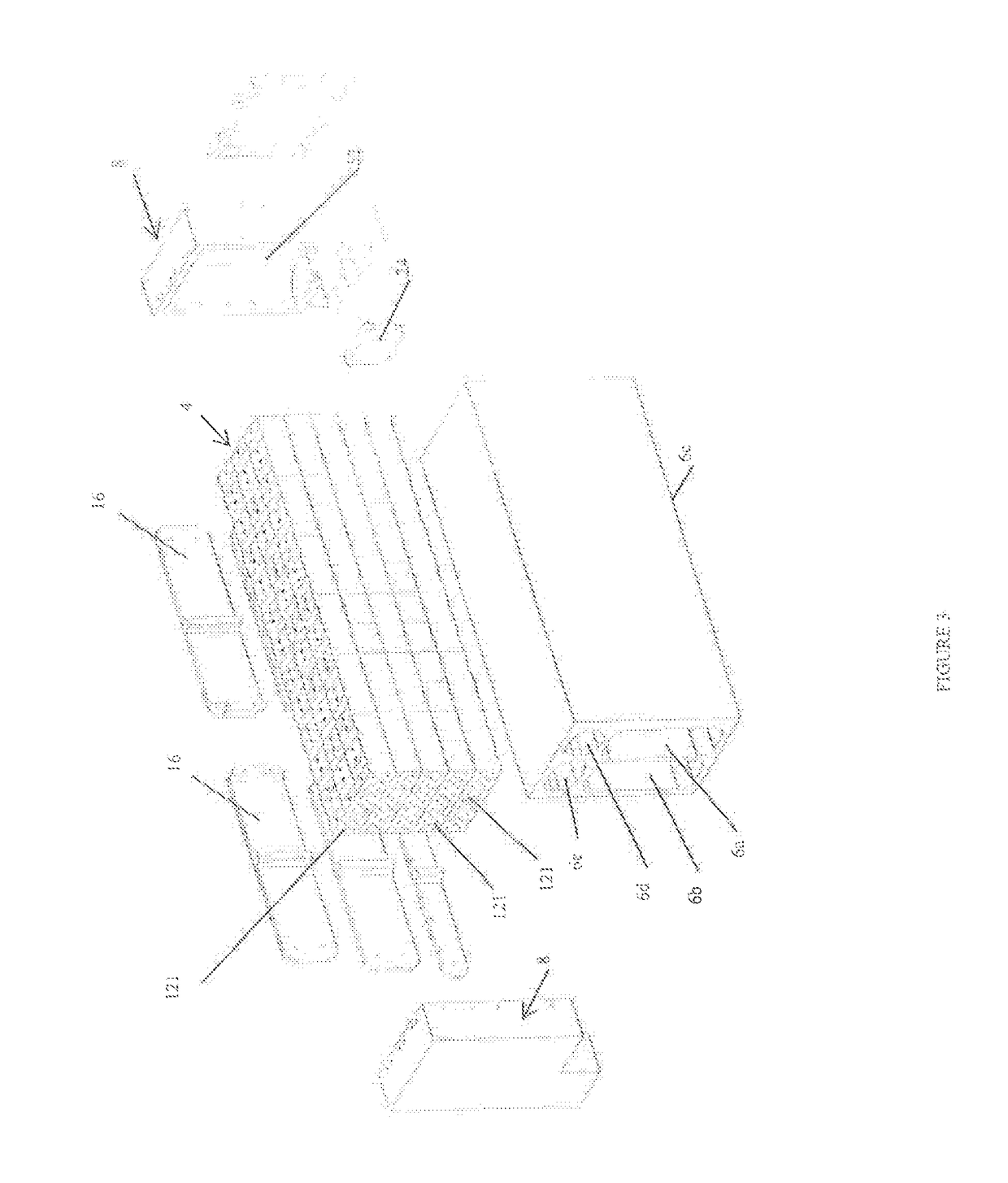
[0035]FIG. 1 generally shows the high temperature thermal energy storage and transfer arrangement 2 where enveloping insulation and an associated containment vessel have not been shown. In one embodiment, the containment vessel is a bulk shipping container sized for shipping by truck. The working components of the storage and transfer arrangement are clearly illustrated. The graphite storage segment 4 rest on top of a support block 6 that is made of a high temperature ceramic material. The ceramic material is chosen to provide minimal thermal expansion and contraction at cycling high temperatures and to provide insulating properties with respect to conductive heat transfer through the support block which could receive an insulating coating as a further thermal barrier between the support block and the graphite body.
[0036]The preferred embodiment will be described with respect to a high temperature graphite storage segment 4, however, the invention involves support of such a high tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com