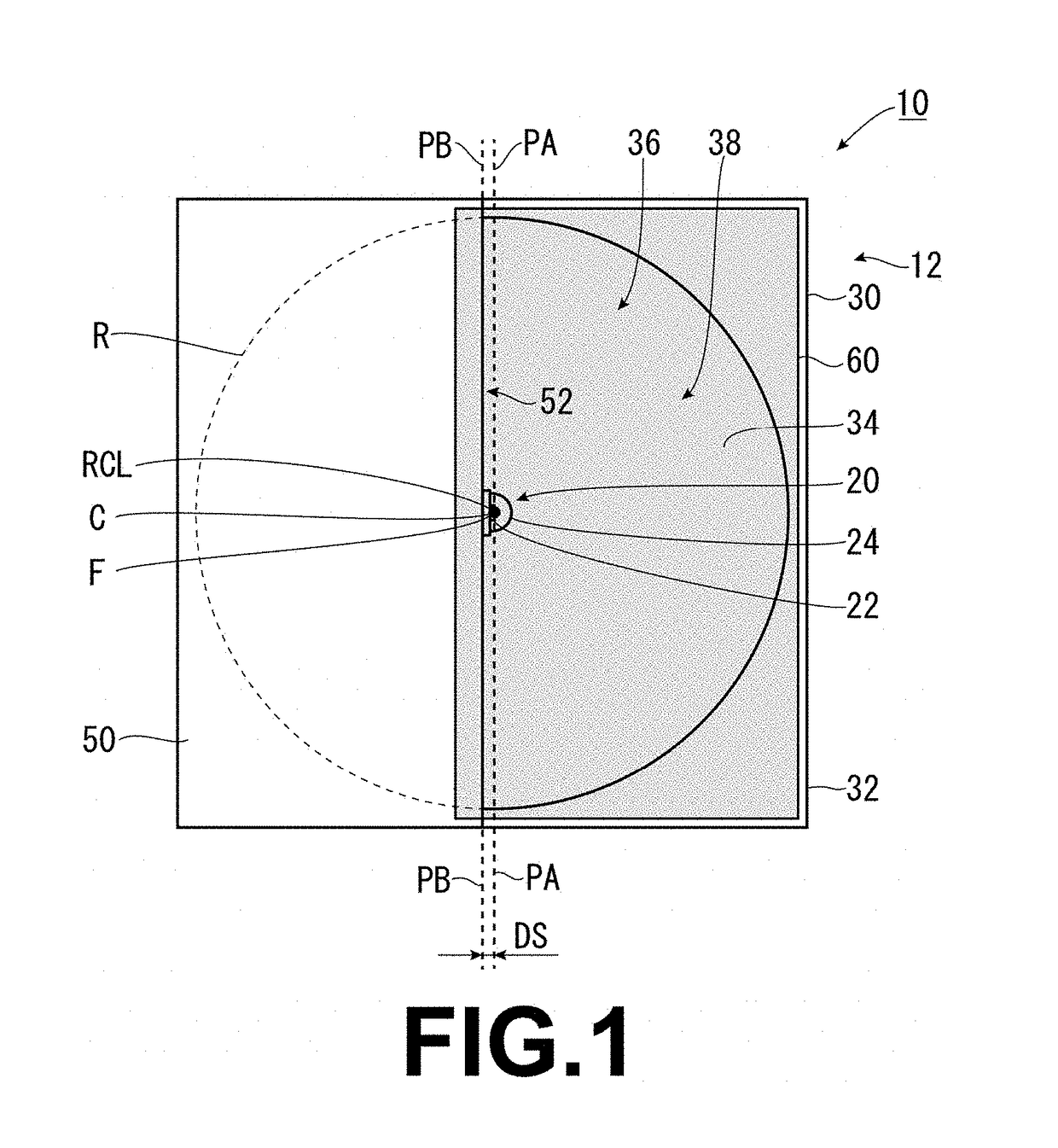
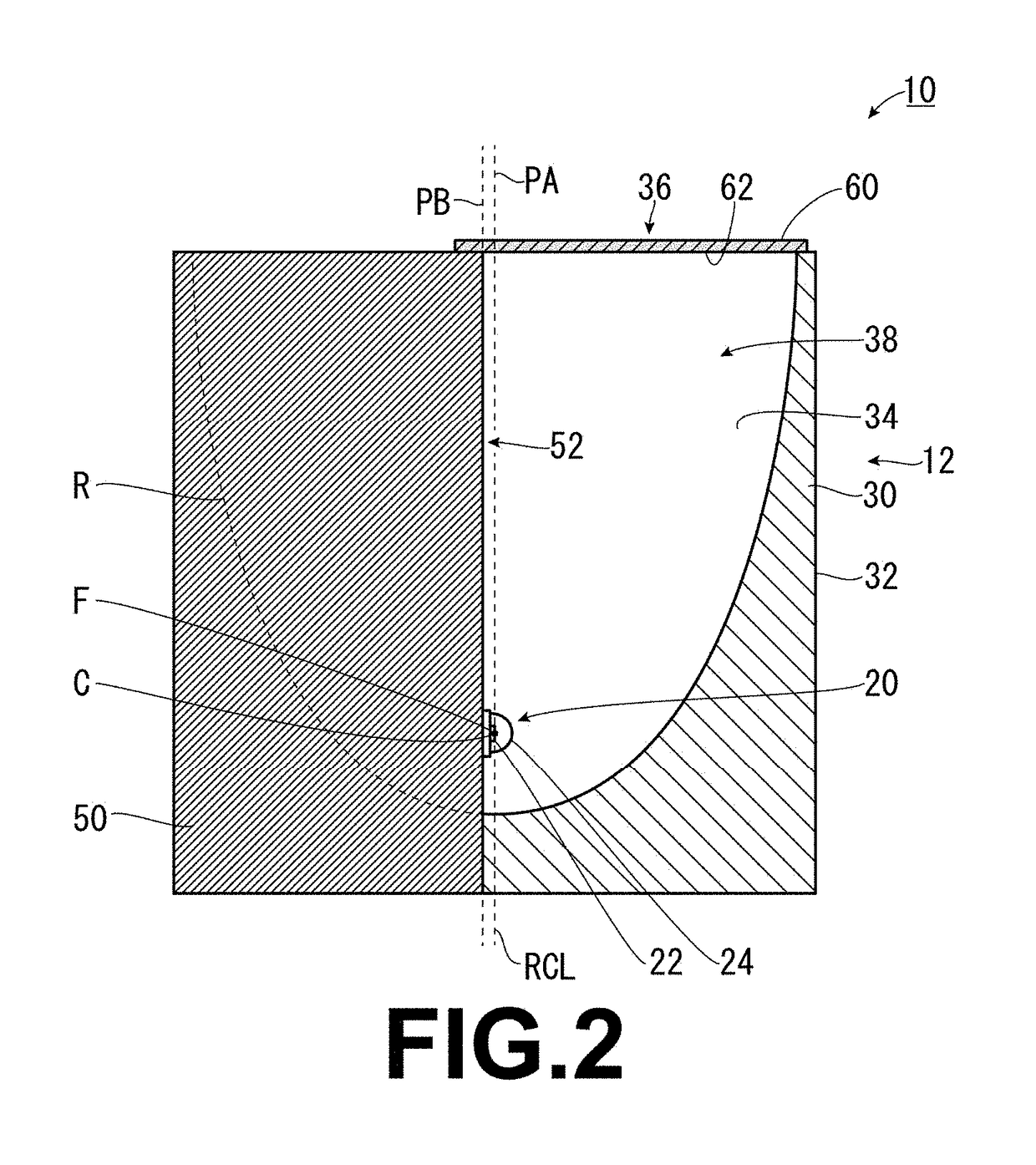
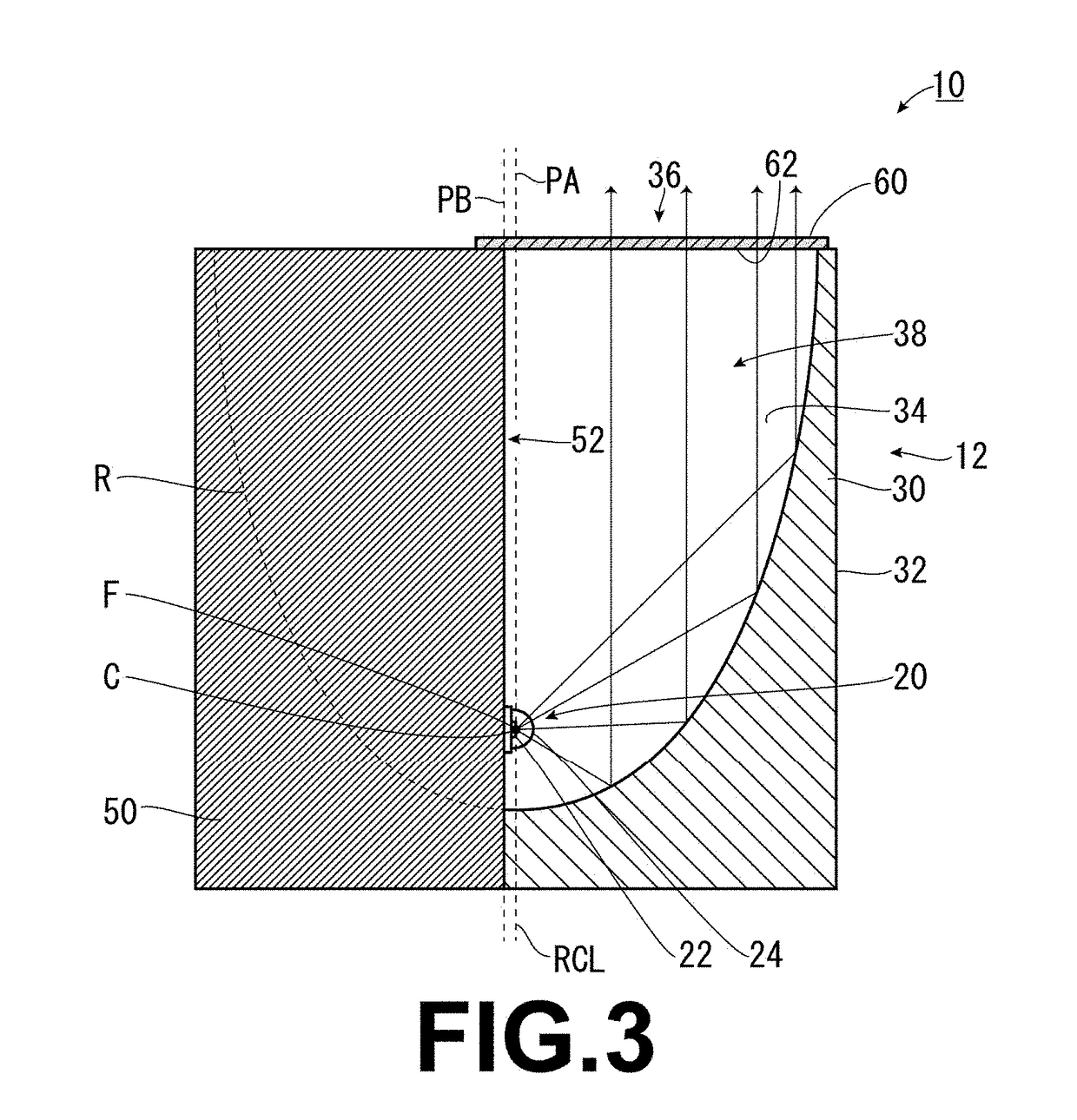
LED lamp
a technology of light-emitting diodes and led lamps, which is applied in the direction of refractors, light-emitting semiconductor devices for light sources, etc., can solve the problems of inability to completely cut off light rays with undesired wavelengths, band-pass filters tend to be inability to exert light blocking (cutoff) functions, and often emerg
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
modification 1
[0068](Modification 1)
[0069]As shown in FIG. 4, at least one of light shielding members 70, 72 and 74 may be added, as a constituent element, to the light emitting diode lamp 10 according to the aforementioned practical example. The light shielding members 70, 72 and 74 are provided for preventing the light emitting diode 20 from being directly seen when the light emitting diode lamp 10 is seen at an angle parallel to the rotational axis RCL of the paraboloid of revolution (i.e., from the front side of the light emitting diode lamp 10). It should be noted that the material, of which the light shielding members 70, 72 and 74 are made, is not limited to a specific material as long as the light shielding members 70, 72 and 74 can block light rays emitted from the light emitting diode 20. For example, metal, opaque resin, ceramic material or so forth can be assumed as the material of the light shielding members 70, 72 and 74.
[0070]The lengths of the light shielding members 70, 72 and 74...
modification 2
[0072](Modification 2)
[0073]Moreover, the heat sink 50 and a light shielding member 78 may be integrated unlike the configuration shown in FIG. 4 that the light shielding members 70, 72 and 74 provided separately from the heat sink 50 are mounted in place. As shown in FIG. 5, at least part of the heat sink 50, located above the light emitting diode 20, is protruded toward the reflective surface 34 so as to form a step 76, as the light shielding member 78, on the light emitting diode mounted lateral face 52 of the heat sink 50 as seen in a cross-sectional view along the up-and-down direction. Accordingly, it is possible to achieve advantageous effects similar to those achieved by forming the light shielding members 70, 72 and 74 provided separately from the heat sink 50 as shown in FIG. 4. Additionally, the light absorbing material may be disposed on the surface of the step 76 in opposition to the light emitting diode 20 in order to avoid a situation that light rays, when striking th...
modification 3
[0074](Modification 3)
[0075]Furthermore, FIG. 6 shows another example of integrating the heat sink 50 and the light shielding member 78. The light emitting diode mounted lateral face 52 of the heat sink 50 may be formed to slant as seen in a cross-sectional view along the up-and-down direction. This will be specifically explained. The light emitting diode mounted lateral face 52 is shaped to slant with respect to the rotational axis RCL as seen in the cross-sectional view along the up-and-down direction such that the position of the emission center C of the light emitting diode 20 is matched with that of the focal point F of the paraboloid of revolution defining the reflective surface 34, while the opening 36-side end (the upward end) of the light emitting diode mounted lateral face 52 is at least located in a position corresponding to the emission center C of the light emitting diode 20. Accordingly, part of the light emitting diode mounted lateral face 52, located above the light ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com