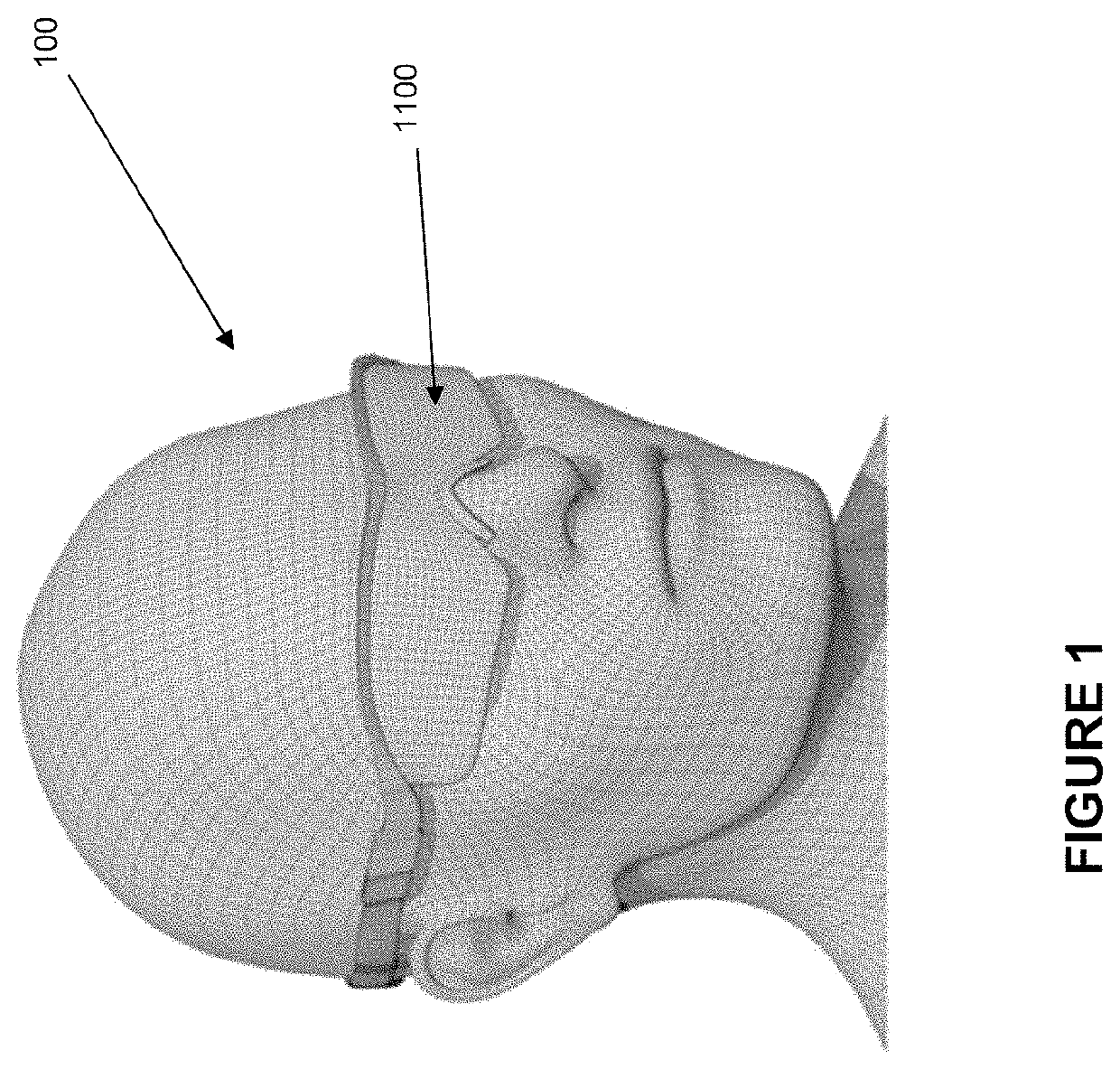
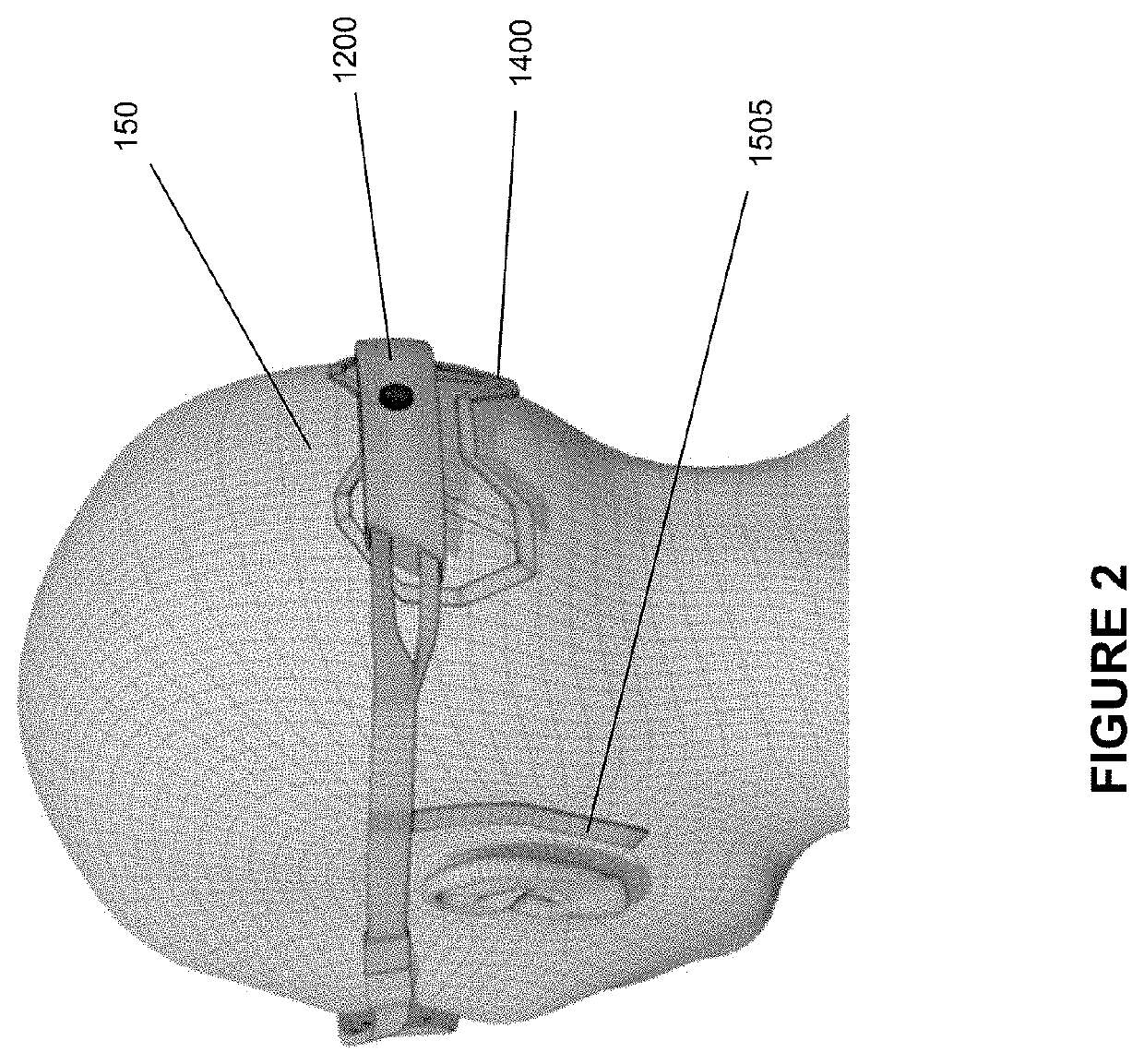
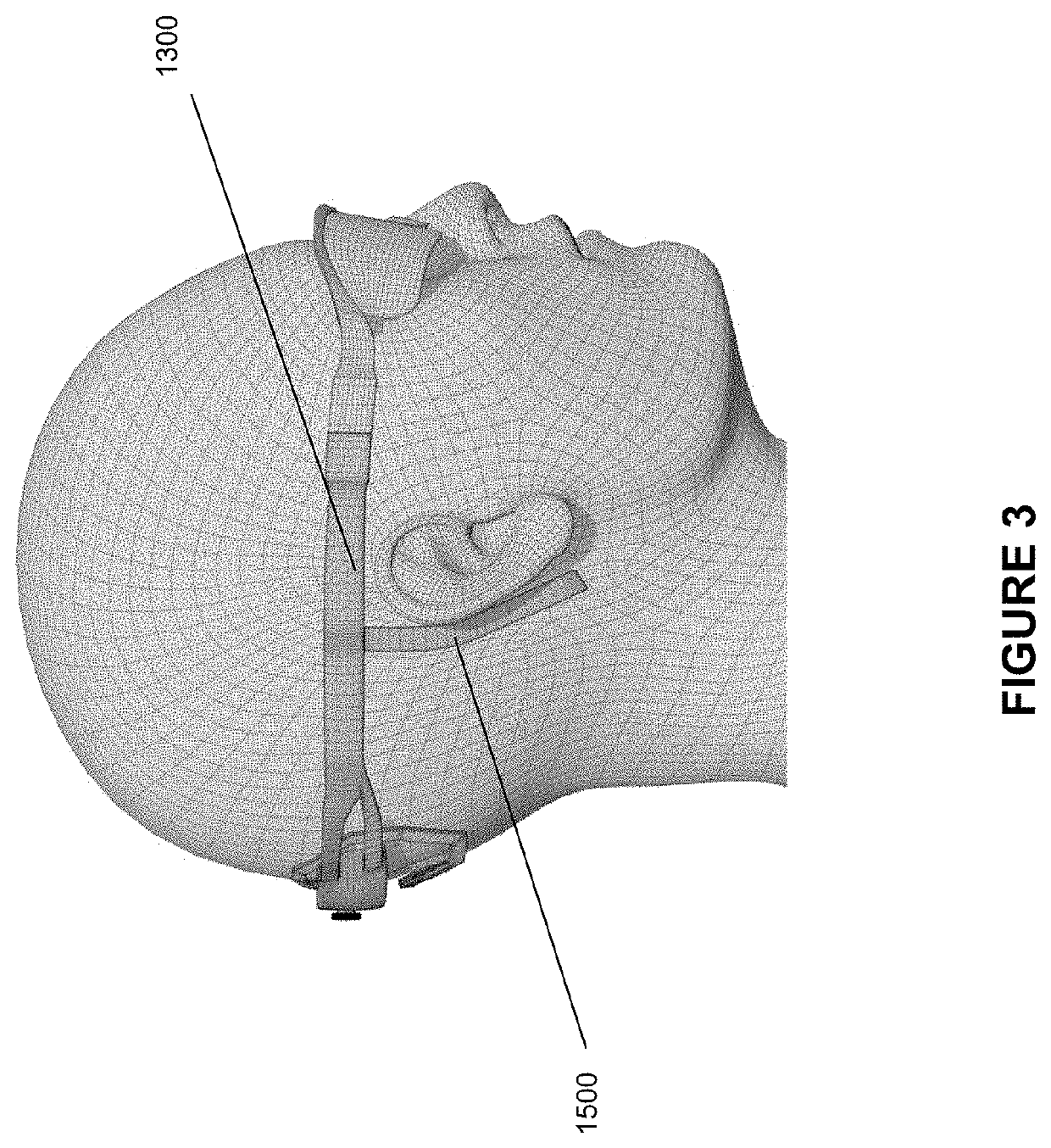
Head mountable device
a mountable device and head technology, applied in the field of head mountable devices, can solve the problems of difficult detection of mild traumatic brain injury using mri scans or ct scans, unreliable methods of diagnosis, and high labor intensity of workers, and achieve the effects of improving labor intensity, improving labor intensity, and improving labor intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0165]The aim of this study was to evaluate the utility of a portable electrophysiology platform to record measurable SSVEPs from healthy individuals.
[0166]Participants
[0167]All participants were screened for a history of epilepsy, seizures and existing or previous brain injuries and conditions. Any positive findings excluded the participant from the study.
[0168]Equipment
[0169]Two main components of the system were identified: the visual stimulus generation component, and the EEG recorder. A computer was used to capture the data from the EEG recorder, and perform signal analysis on the data. The visual stimulus was delivered in two separate setups: a portable smartphone setup, and another utilising a traditional LCD computer monitor. For the portable setup, a Sony Xperia Z1 Compact smartphone (Sony Corporation, Minato, Tokyo, Japan) housed in a Google Cardboard (Google Inc., Googleplex, Mountain View, Calif., U.S.A.) was used. A Dell U2415 LCD monitor (Dell Technologies, One Dell Wa...
experiment i
[0205]4 healthy adults (3 males, 1 female, Mage=21.5, SDage=1.708) participated in Experiment I. All 4 subjects had 20 / 20 vision, and successfully completed all sections of Experiment I.
[0206]Delivery Platform
[0207]The mean Ratio Response of the LCD monitor was 6.415±0.627. Use of the portable platform yielded similar response ratios to the LCD monitor, with a mean Ratio Response of 6.199±0.501.
TABLE 4Response for Different Delivery PlafformsTraditionalSubjectLCDPortable17.3276.91225.9115.75236.2745.99546.1476.138Mean6.4156.199SD0.62650.5012
Stimulus Image
[0208]Both the pattern reversal and flash reversal images had similar responses, with a mean Ratio Response of 6.142±0.353 and 6.199±0.443 respectively.
TABLE 5Response Ratios for Different Stimulus ImagesSubjectFlash Rev.Pattern Rev.16.7216.63425.6255.80736.0156.12045.8656.006Mean6.0576.142SD0.47120.3527
[0209]Stimulus Frequency
[0210]Table 6 summarises the results of differing stimulus frequencies. A stimulus frequency of 15 Hz yield...
experiment ii
[0213]Experiment II evaluated 20 healthy adults (13 males, 7 females, Mage=36.47, SDage=18.54). All 20 participants had 20 / 20 vision, and successfully completed Experiment II.
[0214]The SSVEP parameters used for Experiment II were determined from Experiment I. Using the portable stimulus system, a flash-reversal image flickering at 15 Hz recorded for 30 seconds was used. With these parameters, the mean Ratio Response was 5.551±1.164.
[0215]A D'Agostino & Pearson normality test was performed and had a P-value of 0.9019, meaning the data were consistent with a Gaussian distribution.
[0216]Discussion
[0217]In this study we have been able to show that an EEG can reliably detect a 15 Hz SSVEP in normal subjects from a stimulus generated on a portable smartphone system with the same reliability as a standard LCD monitor.
[0218]The proposed system serves as a proof of concept for a dedicated portable diagnostic system. The results demonstrate that a reliable and consistent response can be expec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com