Railway condition monitoring device, railway vehicle bogie, railway vehicle, railway brake control device
a technology for condition monitoring and railway vehicles, which is applied in the direction of railway signalling, railway signalling and safety, and vehicle signalling, etc. it can solve the problems of surplus maintenance man-hours and replacement materials, affecting the operation of railway vehicles, and disadvantageous in terms of cost, so as to improve versatility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
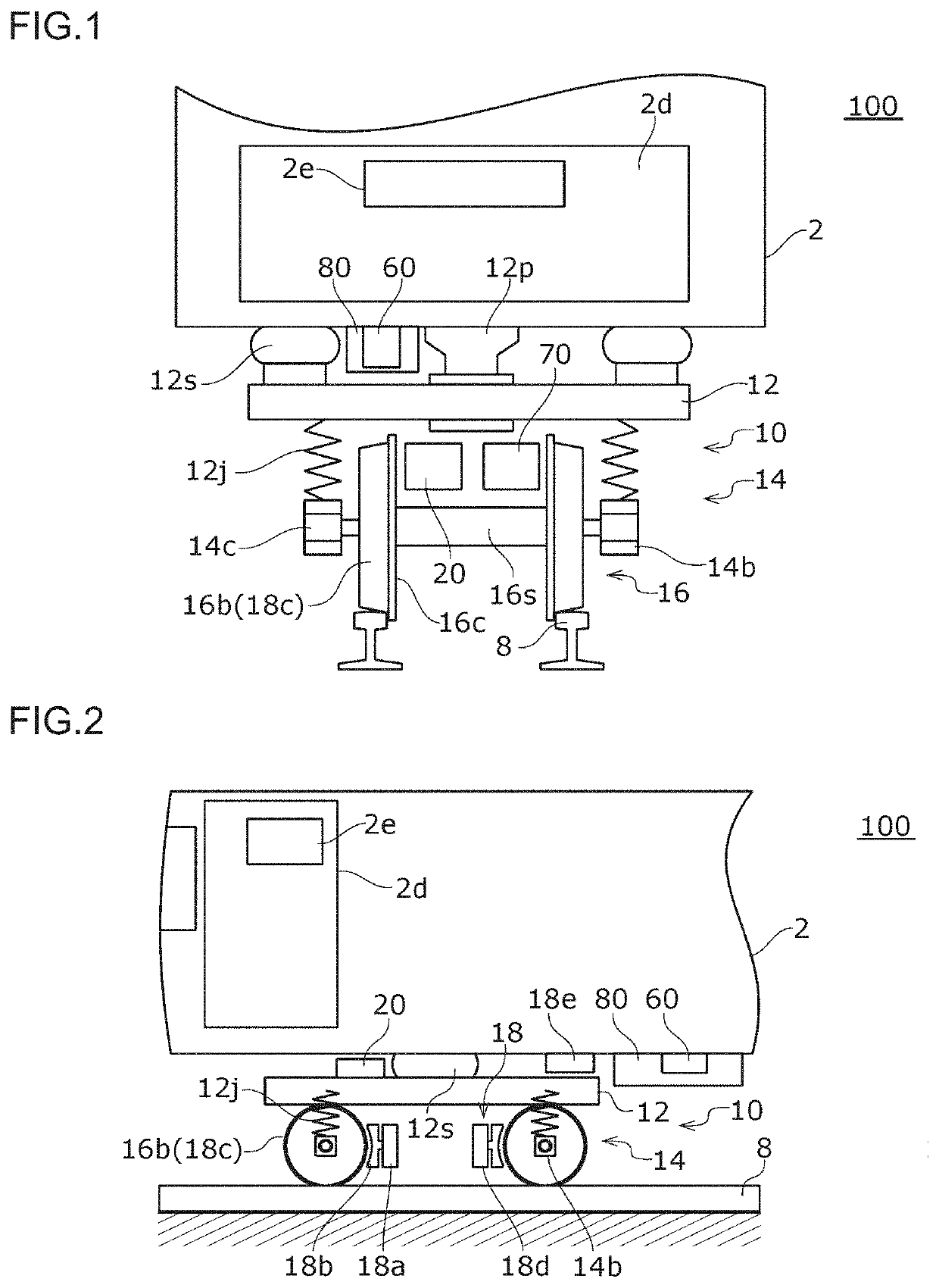
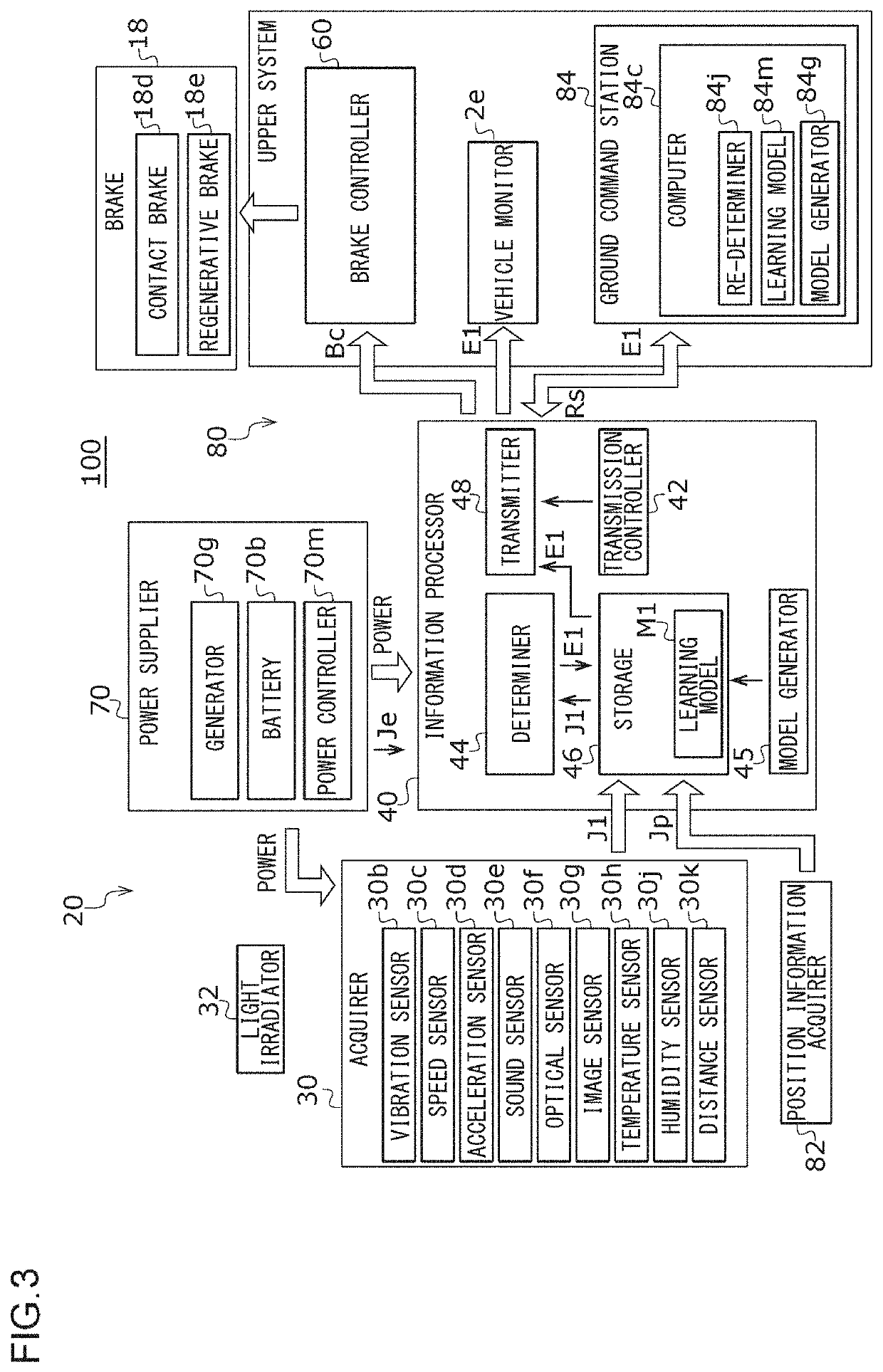
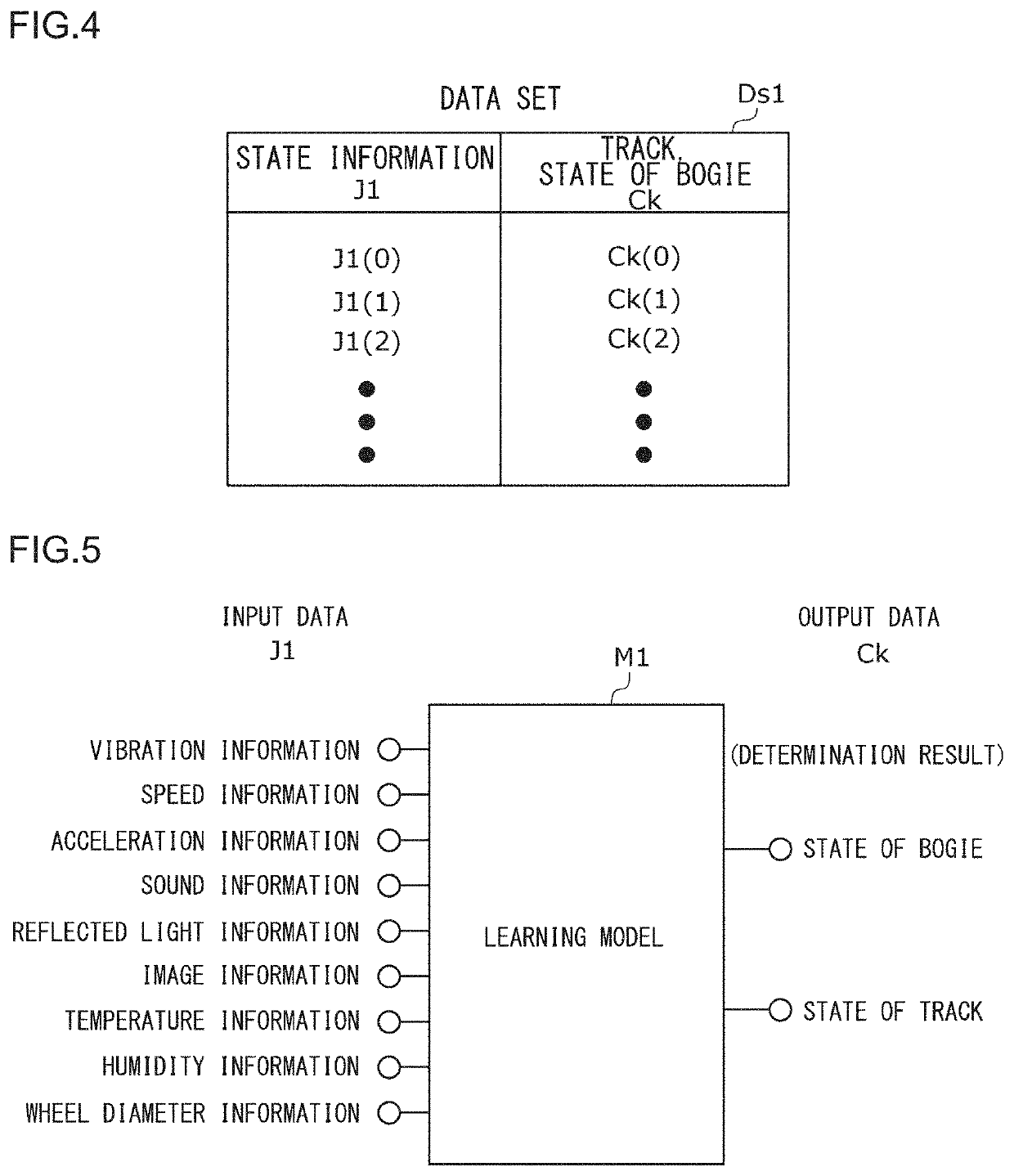
[0047]A railway condition monitoring device 20 (hereinafter, simply referred to as “condition monitoring device 20”) and a railway brake control device 80 (hereinafter, simply referred to as “brake control device 80”) according to a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 5. FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a front view illustrating a railway vehicle 100. FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram illustrating the railway vehicle 100 as viewed from the side. FIG. 3 is a block diagram schematically illustrating a condition monitoring device 20 and a brake control device 80 according to the present embodiment. The condition monitoring device 20 and the brake control device 80 according to the present embodiment are mounted on the railway vehicle 100. In particular, the condition monitoring device 20 is mounted on the bogie 10 of the railway vehicle 100.
[0048]Each functional block illustrated in each drawing of the present disclosure including FIG. 3...
second embodiment
[0103]A railway condition monitoring device 20 and a railway brake control device 80 according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1, 2, and 6 to 8. The condition monitoring device 20 and the brake control device 80 according to the present embodiment are mounted on the railway vehicle 100. FIG. 6 is a block diagram schematically illustrating a condition monitoring device 20 and a brake control device 80 according to the present embodiment.
[0104]As illustrated in FIG. 6, the condition monitoring device 20 includes an acquirer 30, an information processor 40, a power supplier 70, and a position information acquirer 82. In addition, the brake control device 80 includes the acquirer 30, the information processor 40, and a brake controller 60. The information processor 40 includes a determiner 44, a storage 46, a transmitter 48, and a transmission controller 42. The acquirer 30 includes a vibration sensor 30b and a speed sensor 30c. ...
third embodiment
[0139]A railway condition monitoring device 20 and a railway brake control device 80 according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1, 2, and 9 to 12. The condition monitoring device 20 and the brake control device 80 according to the present embodiment are mounted on the railway vehicle 100. FIG. 9 is a block diagram schematically illustrating a condition monitoring device 20 and a brake control device 80 according to the present embodiment.
[0140]Brake squeal may occur when the contact brake 18d is operated. The brake squeal is an abnormal noise in which vibration from a friction surface caused by a touch of a brake shoe 18b to a braking member 18c during braking is amplified and generated by the brake shoe 18b or the braking member 18c, and is called braking noise. The brake squeal occurs due to the wear or the like of the friction surface of the brake shoe 18b and the braking member 18c. If the brake squeal occurs, the brake sho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com