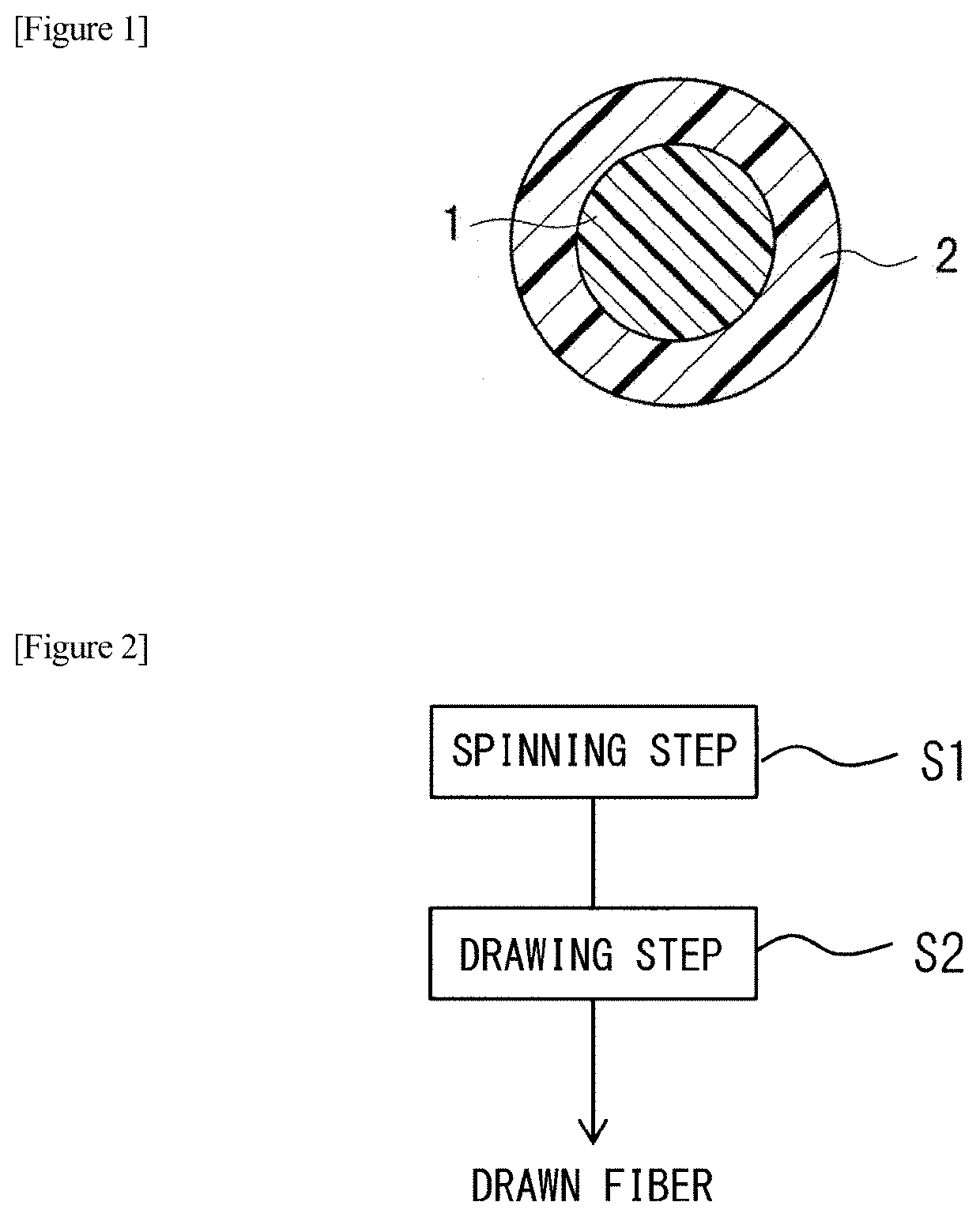
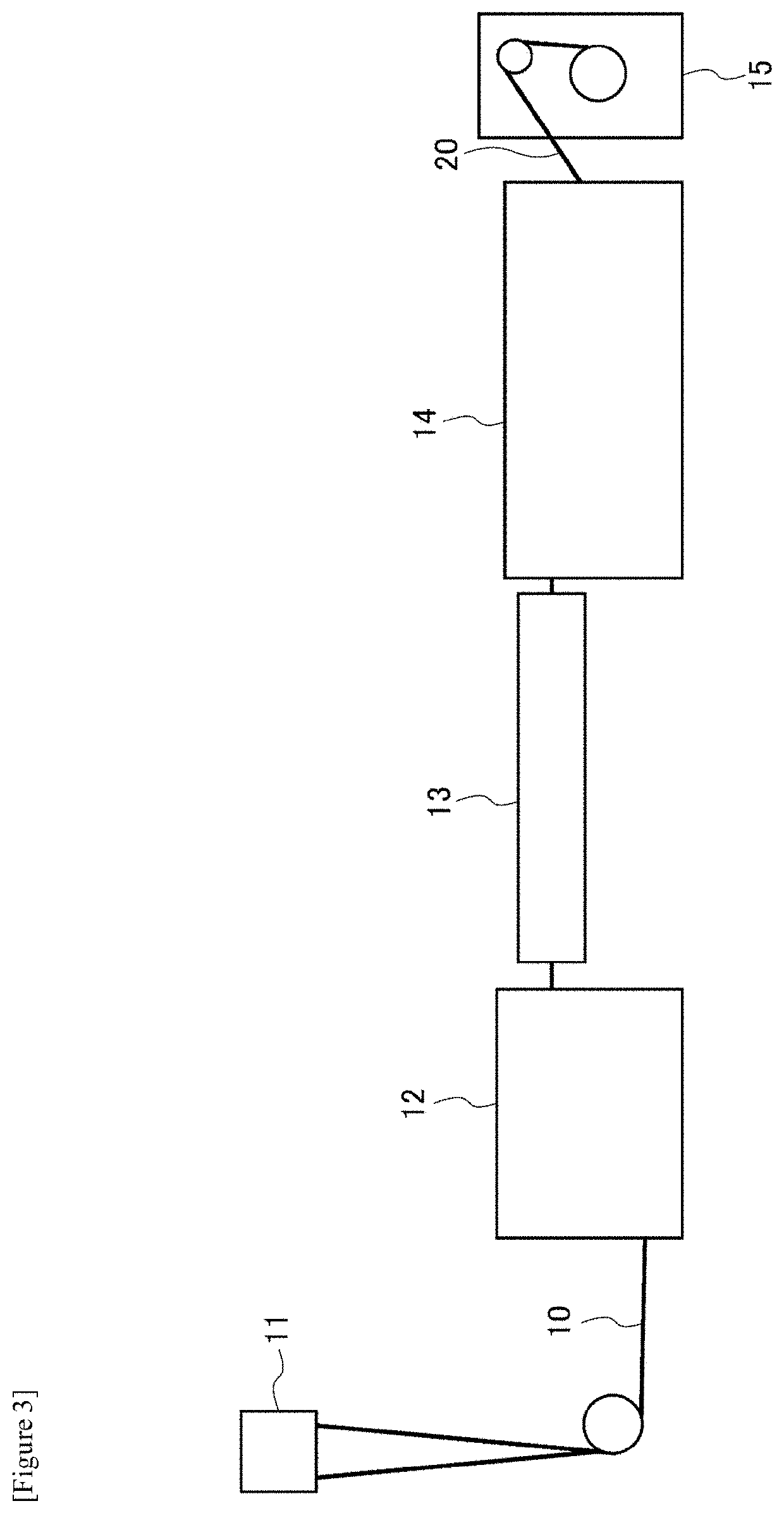
Drawn composite fiber, non-woven fabric, and method of producing drawn composite fiber
a composite fiber and non-woven fabric technology, applied in the direction of fibre treatment, filament/thread forming, melt spinning methods, etc., can solve the problems of deterioration of the appearance of processed non-woven fabrics, deterioration of the processability of non-woven fabrics, and breakage of single yarns, so as to increase the thermal shrinkage and enhance the single yarn strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
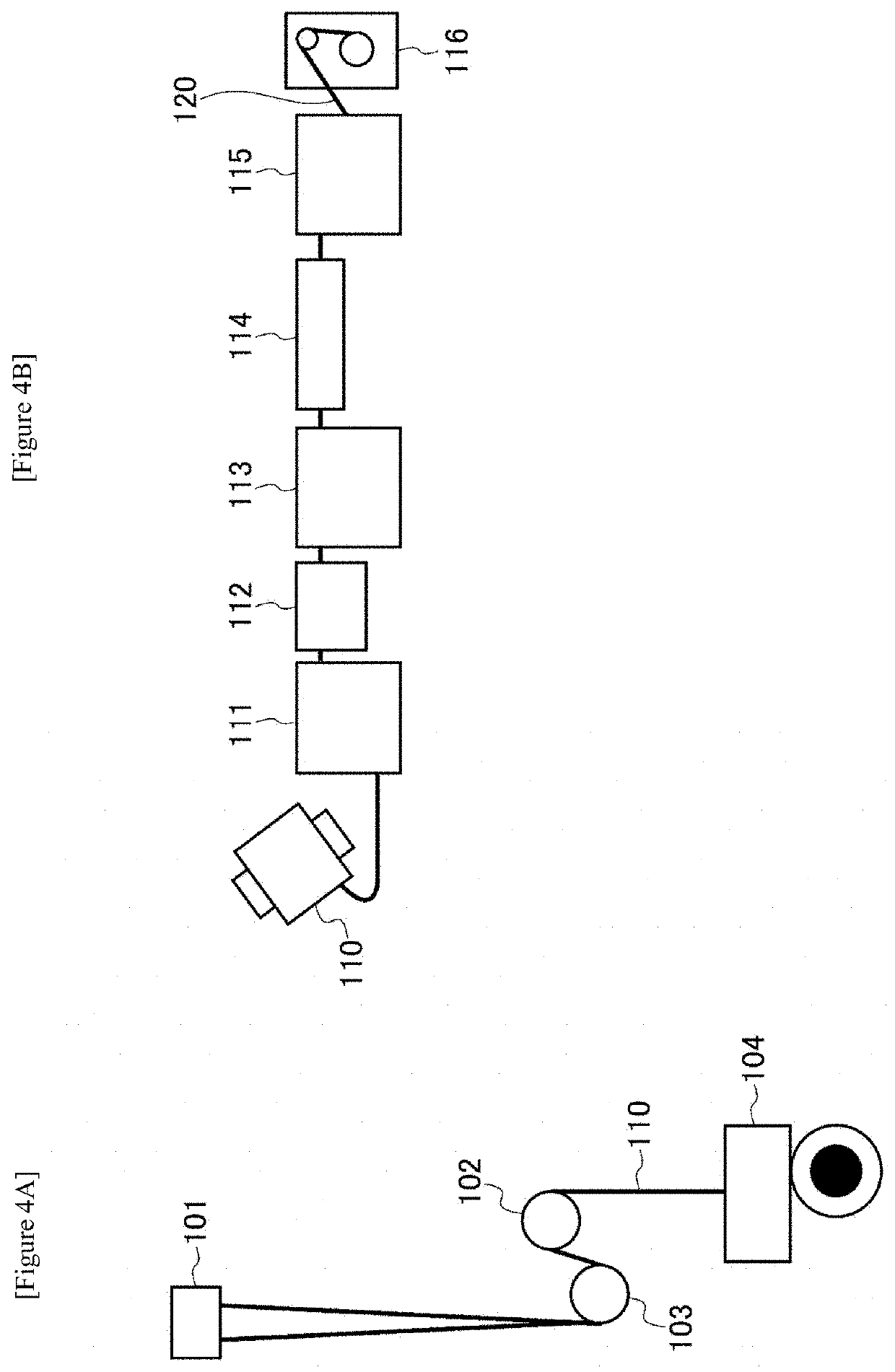
[0078]The spinning step and the drawing step were consecutively performed using the apparatus illustrated in FIG. 3, to produce a drawn composite fiber having a sheath-core structure.
[0079](1) Spinning Step
[0080]An undrawn fiber with a sheath-core structure having a fineness of 1.88 dtex was produced by melt-spinning using a core material A and a sheath material a. In such a case, a sheath-core-type composite spinneret was used, and a sheath-core ratio (sheath material / core material) was set at 35 / 65. As spinning conditions, extruder cylinder temperature was set at 255° C., spinneret temperature was set at 270° C., and a spinning speed was set at 180 m / min.
[0081](2) Drawing Step
[0082]The drawing step was performed subsequently to the spinning step. Specifically, the undrawn fiber 10 obtained in the spinning step was introduced into the introduction roller 12 at a speed of 180 m / min, the speed of the drawn fiber delivery roller 14 was increased, and the undrawn fiber 10 was drawn in ...
example 2
[0084]An undrawn fiber having a fineness of 1.72 dtex was melt-spun by a method and under conditions similar to those in Example 1 except that a core material B was used instead of the core material A, and a sheath-core ratio (sheath material / core material) was set at 25 / 75, and the undrawn fiber was drawn by a method and under conditions similar to those in Example 1.
[0085]As a result, the speed of a drawn fiber delivery roller 14 and a draw magnification, at which yarn breakage did not occur in a spinning step and a drawing step, and it was possible to perform industrially stable drawing, were 841 m / min and 4.67 times, respectively. Moreover, the fineness of a drawn composite fiber of Example 2 produced under such conditions was 0.4 dtex.
example 3
[0086]An undrawn fiber having a fineness of 1.60 dtex was melt-spun by a method and under conditions similar to those in Example 1 except that a sheath-core ratio (sheath material / core material) was set at 50 / 50, and the undrawn fiber was drawn by a method and under conditions similar to those in Example 1.
[0087]As a result, the speed of a drawn fiber delivery roller 14 and a draw magnification, at which yarn breakage did not occur in a spinning step and a drawing step, and it was possible to perform industrially stable drawing, were 781 m / min and 4.34 times, respectively. Moreover, the fineness of a drawn composite fiber of Example 3 produced under such conditions was 0.4 dtex.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melt flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com