Analytical method for controlled and measured internal fluid after surgery
a technology of internal fluid and analytic method, which is applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of high pressure, possible loss of vacuum, large volume, etc., and achieve the effects of preventing the loss of vacuum, facilitating handling, and maintaining sterility and a seal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
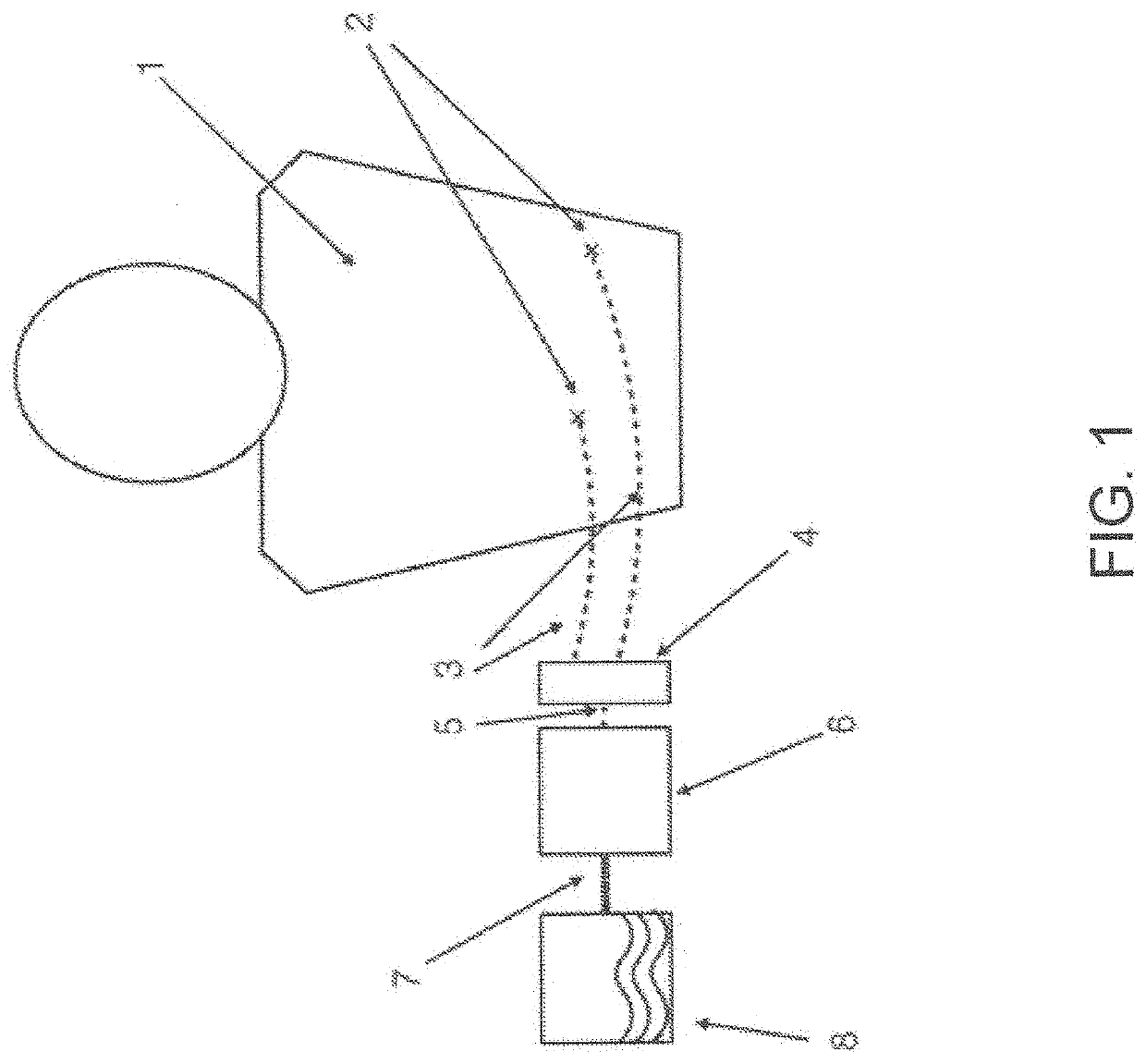
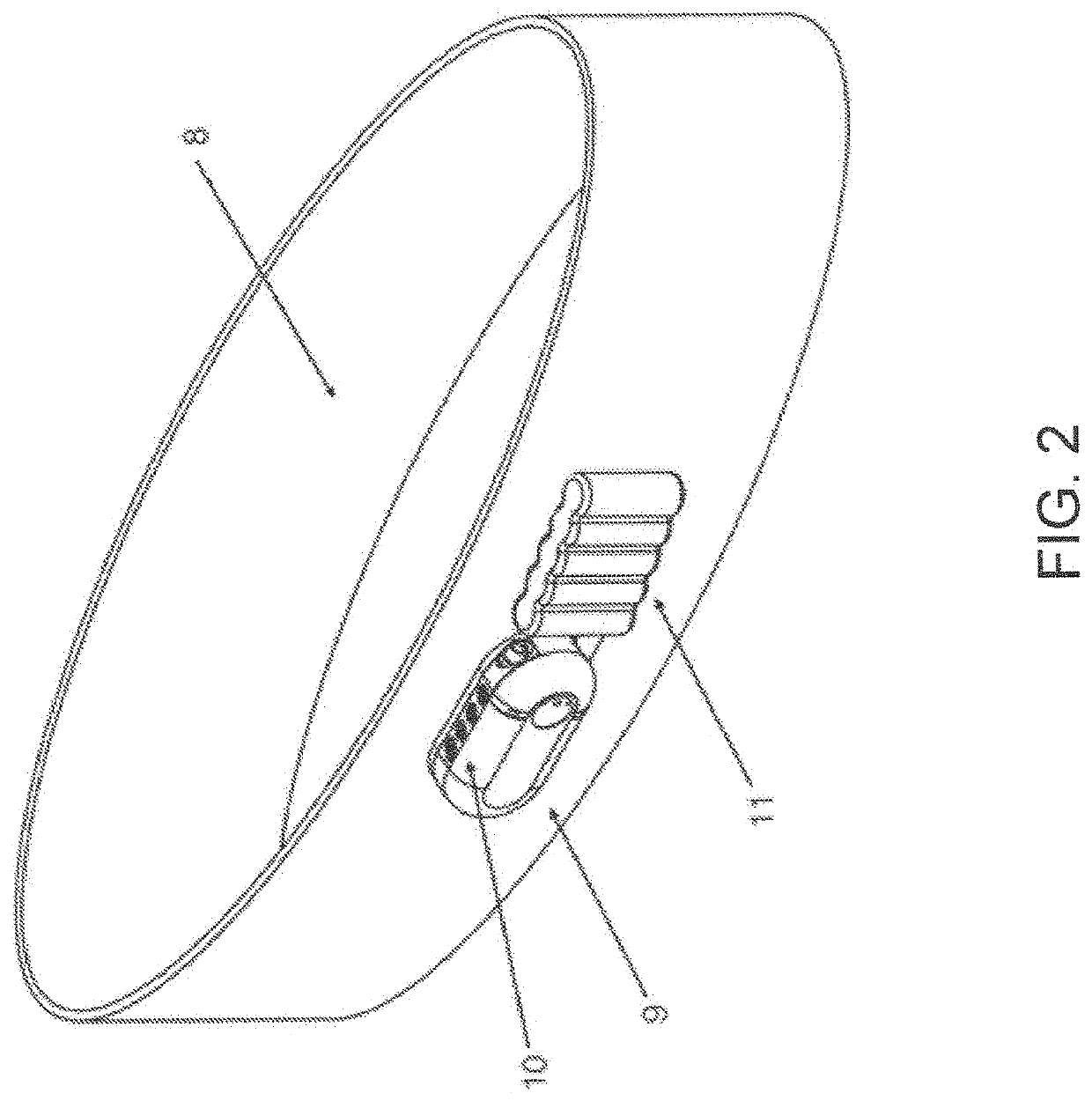
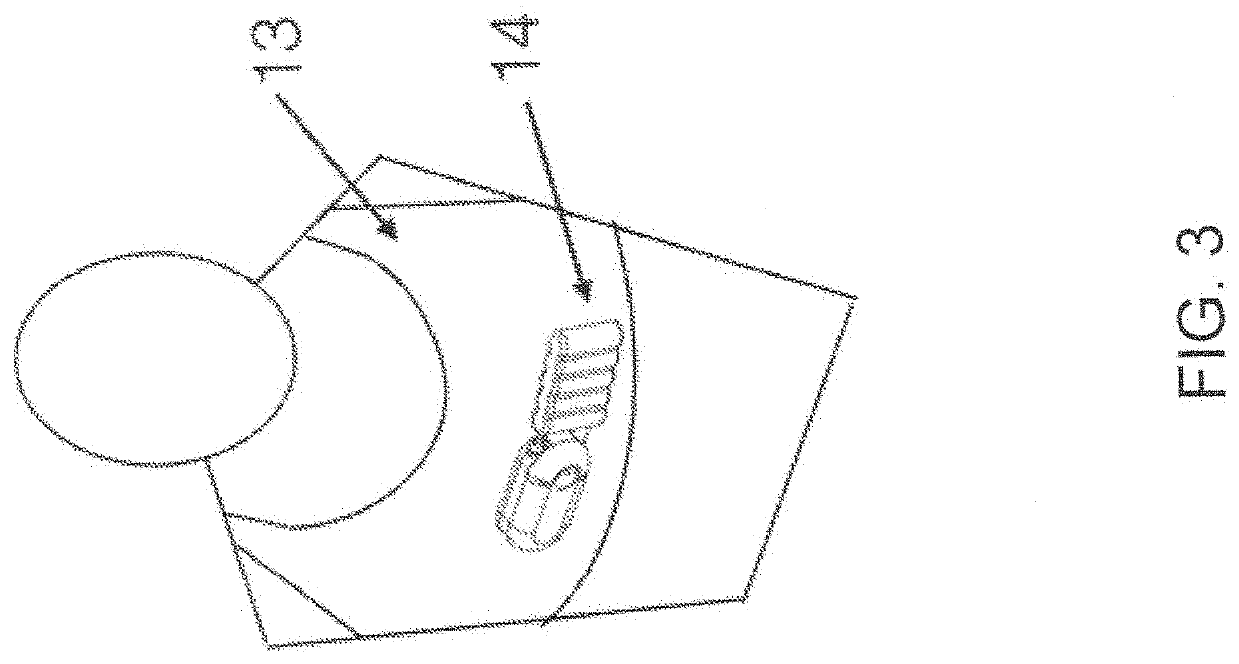
[0060]In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention comprises a system and apparatus for the collection of serous or serosanguinous fluid from the percutaneous site after surgery. There are large amounts of fluid that collect in patients who undergo large void-forming surgeries. This results in large volumes to be collected, measured, and emptied. In order to effectively remove the fluid in a continuous manner, air must be removed from the collection reservoir. Otherwise, either the reservoir is filled quickly with air / liquid mixture and emptying must take place to remove fluid often, or the reservoir overfills leading to high pressure levels and possibly backflow.
[0061]In several embodiments, the present invention makes use of a powered source of negative pressure which helps overcome clogging observed in prior art devices, and one or more reservoirs which allow excess air to be removed. The invention comprises disposable reservoirs with one-way valves that are easy to ha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com