Alignment device
a technology of aligning device and guide, which is applied in the direction of photomechanical equipment, instruments, printing, etc., can solve the problems of limited guide accuracy, limited final positioning accuracy, and limited final positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Hereinafter, desirable embodiments of the present invention will be explained referring to figures.
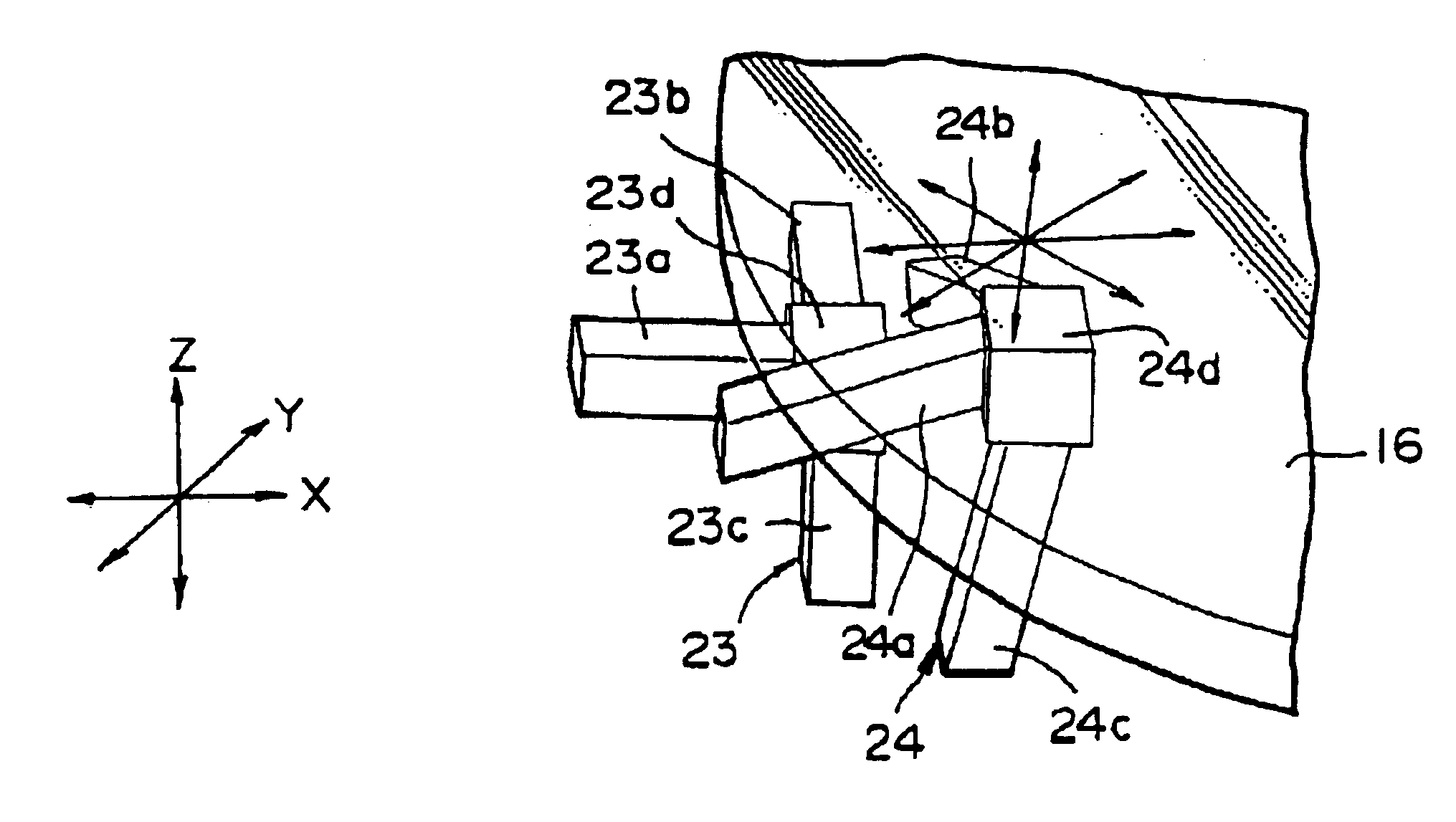
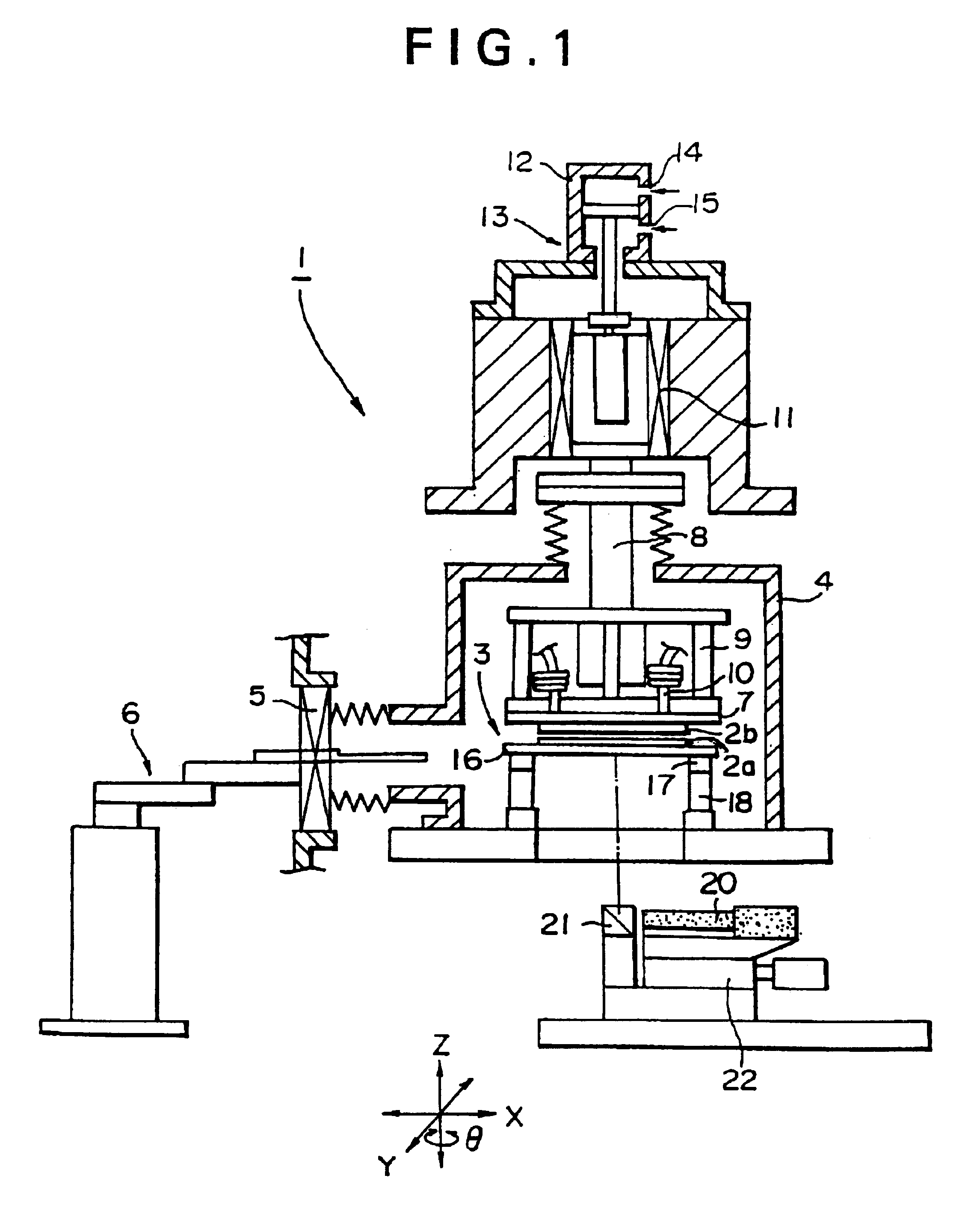
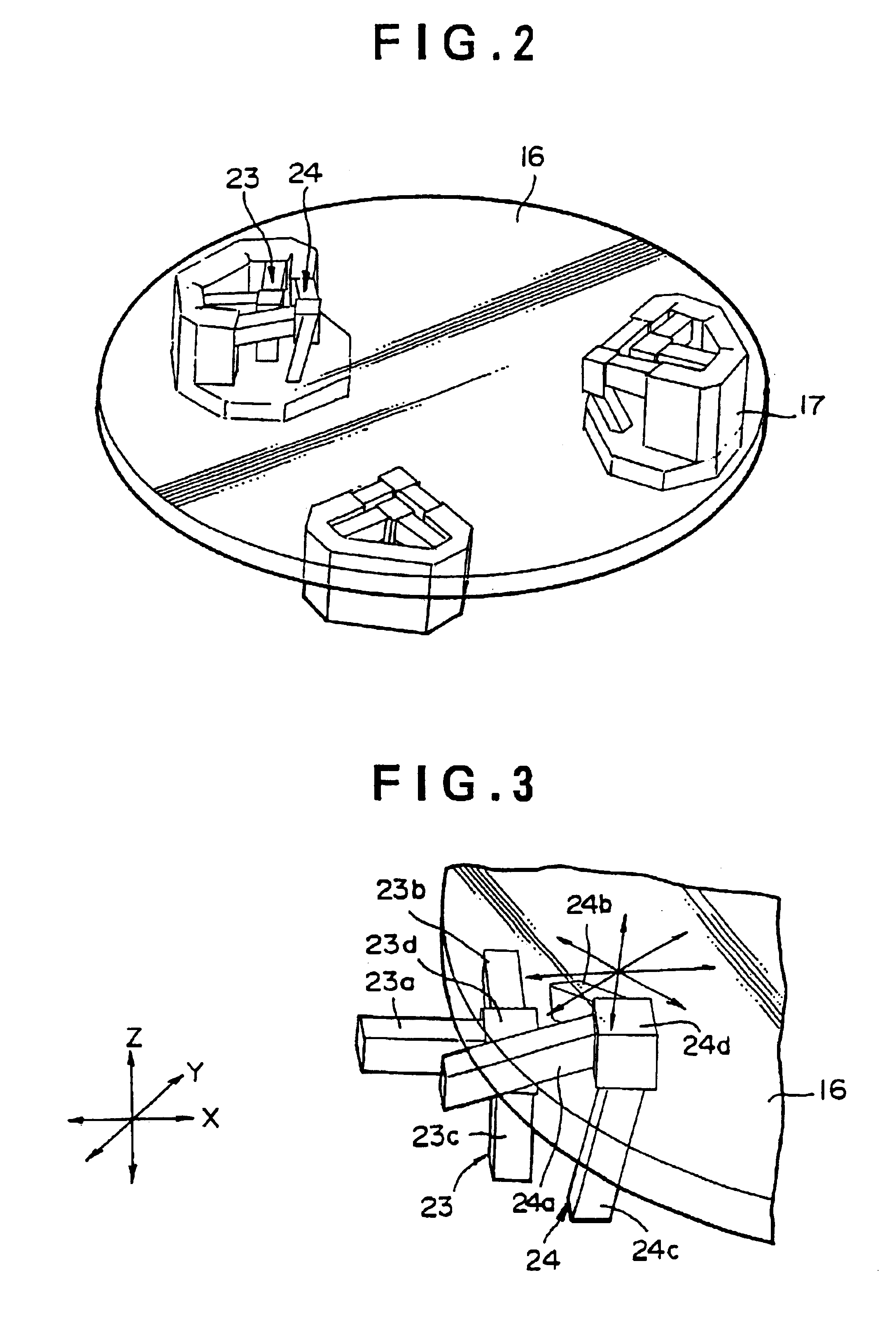
FIG. 1 shows a mounting apparatus for bonding wafers to each other which is incorporated with an alignment device according to an embodiment of the present invention. Mounting apparatus 1 bonds a wafer 2a and a wafer 2b prepared as object to be bonded to each other, and in this embodiment, an alignment device 3 according to the present invention is incorporated for positioning the wafer 2a provided as an object to be positioned.
Although the bonding of wafer 2a and wafer 2b is carried out in a bonding chamber 4 in this embodiment, the chamber 4 may be provided as needed. In this embodiment, a gate 5 capable of being opened / closed is provided to bonding chamber 4, and at a condition where the gate 5 is opened, wafers 2a and 2b as objects to be bonded to each other are introduced into the bonding chamber 4 by a robot 6 provided as a conveying means.
In the bonding part for bonding the obje...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| piezoelectric | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com