Systems and methods for passivation of servo motors
a technology of servo motors and passivation, applied in the direction of electric controllers, instruments, ignition automatic control, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient operation of motors, inconvenient movement, and inability to passivate servo motors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
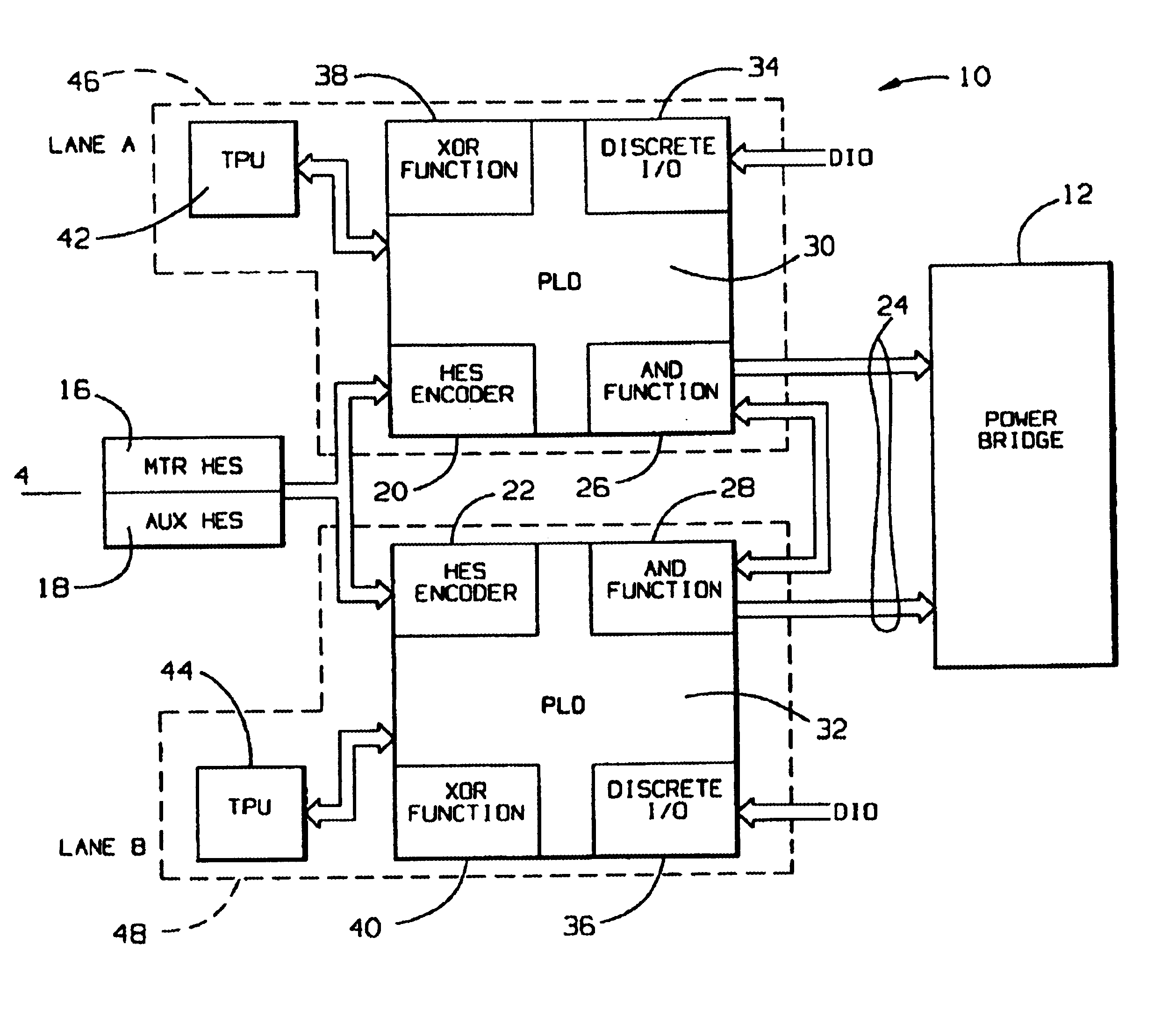
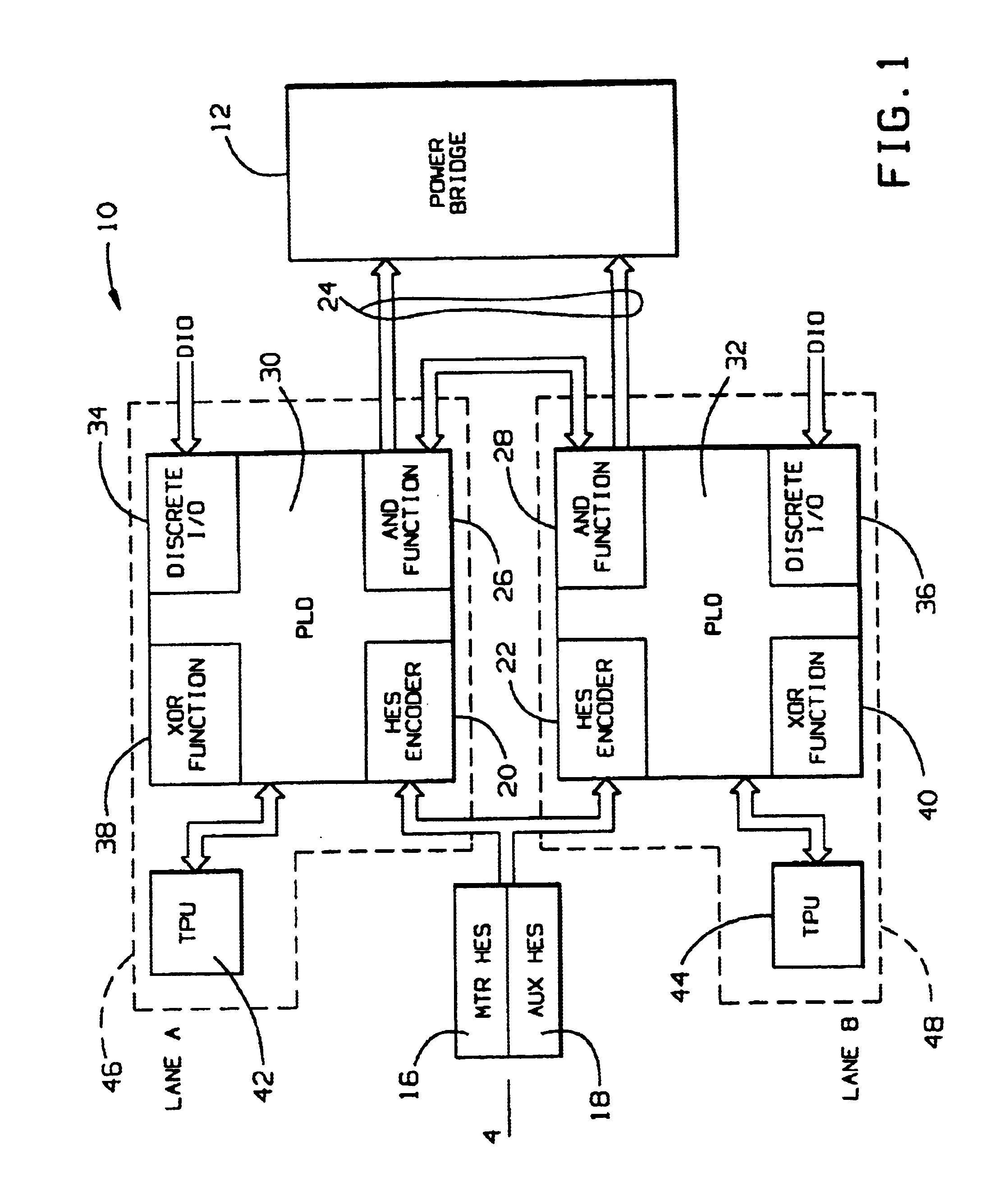
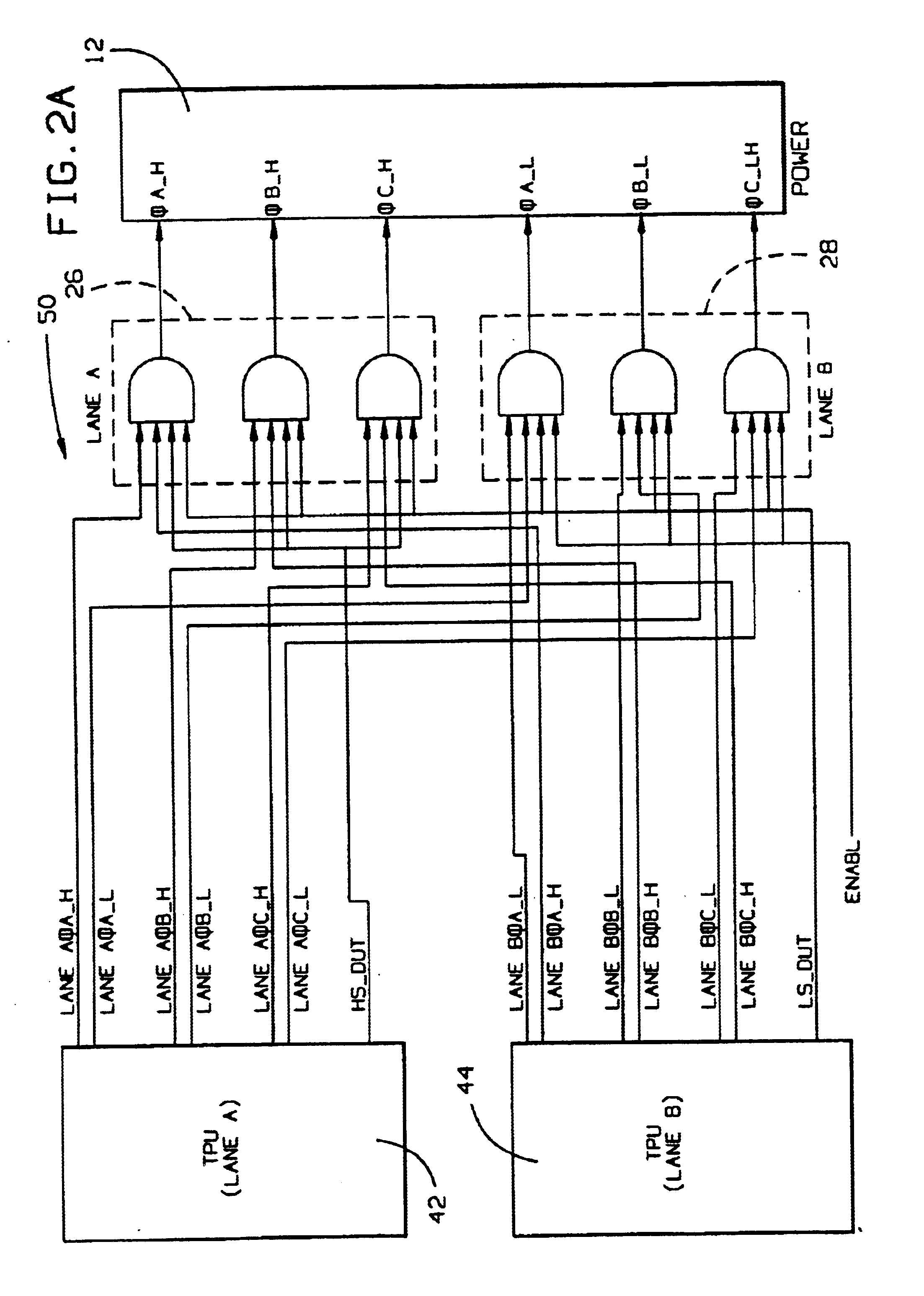
[0017]With reference to the drawings and particularly FIG. 1, which illustrates an embodiment for controlling brushless motors, the system generally indicated at 10 is provided for controlling a power bridge 12, employing the described systems and methods for passivation of servo motors. A sensor assembly 14 includes a motor Hall Effect Sensor (HES) 16 and an auxiliary HES 18 for generating signals indicative of the position of the motor rotor, which are provided to HES encoders 20 and 22 of respective Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs) 30 and 32 discussed below to provide position counter information from the sensor assembly 14 for the implementation of independent decision-making channel control paths to a PWM interface 24, which provides commutation signals to the power bridge 12. As further discussed below, the PWM interface 24 derives signals from logical AND functions 26 and 28 implemented with PLDs 30 and 32. The PLDs 30 and 32 also provide input / output functions with discrete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com