Power consumption control method and information processing device
a power consumption control and information processing technology, applied in the direction of liquid/fluent solid measurement, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing power consumption, increasing size, increasing cost, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing system power consumption with certainty and low power capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
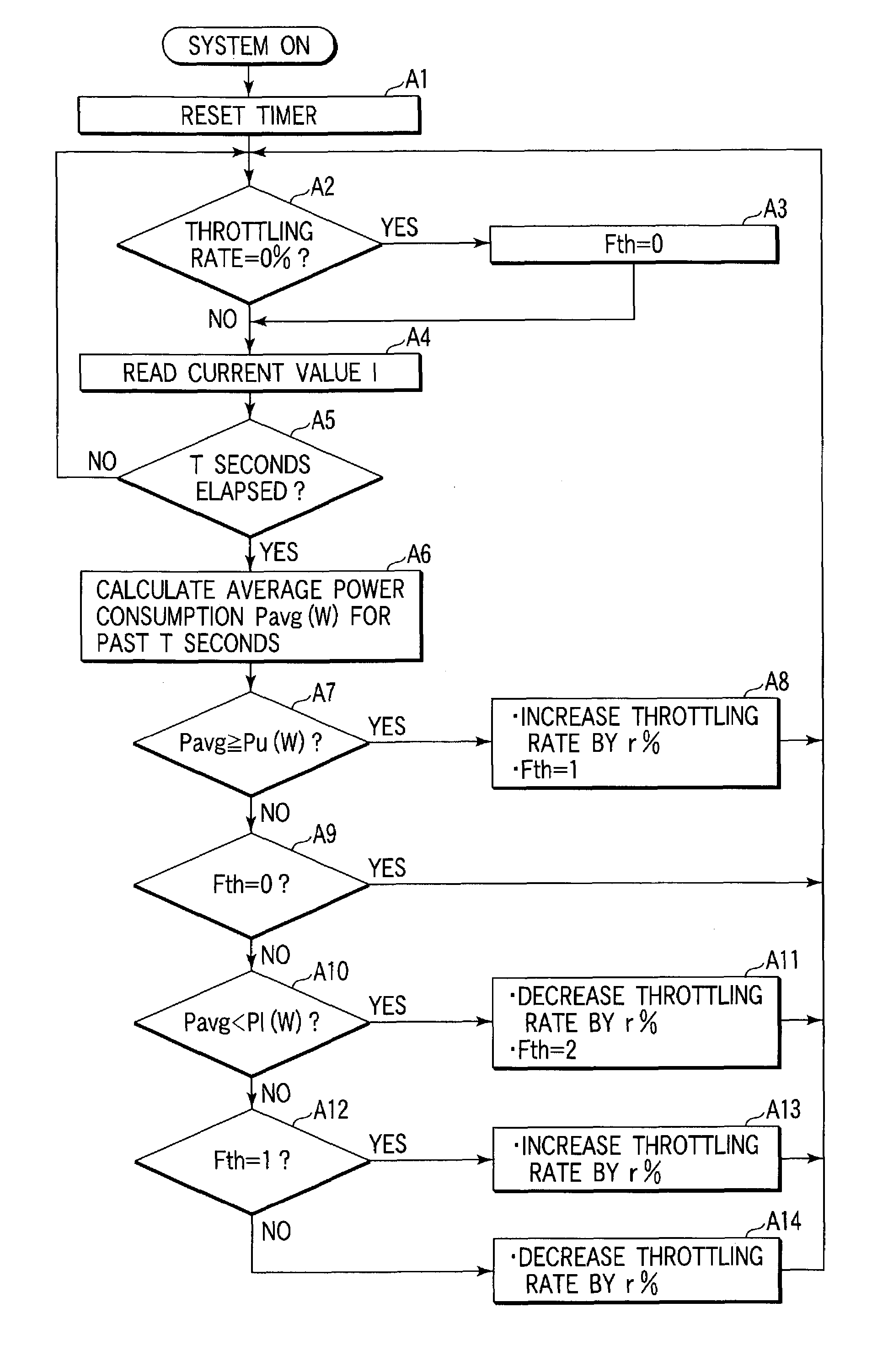
first embodiment
[0020][First Embodiment]
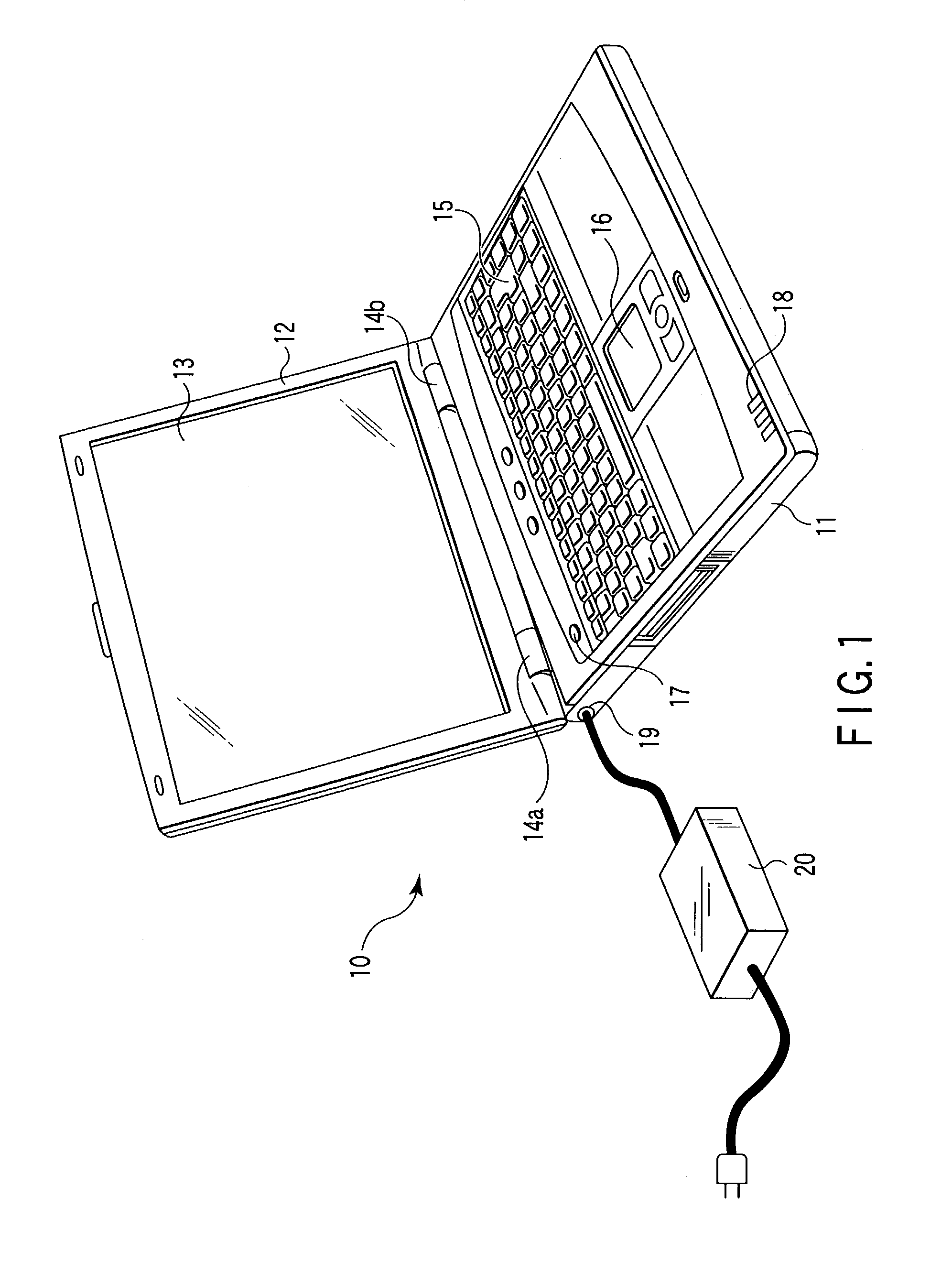
[0021]FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a notebook personal computer. In FIG. 1, the personal computer 10 comprises a case body 11 and a lid 12. The lid 12 houses an LCD (liquid crystal display) panel 13 as an example of a display device. The lid 12 is held so that the lid 12 can be flipped over with hinges 14a and 14b at the rear edge of the case body 11.
[0022]The case body 11 is provided on top with a keyboard (KB) 15, a touch pad 16, a power switch 17, a status display LED 18, etc. Also, the case body is provided with a jack 19 on its left side, into which a plug connected to an AC adapter 20 is inserted. The AC adapter 20 converts an externally applied AC (alternating current) voltage into a DC (direct current) voltage for application to the computer. Further, circuit boards, a battery pack and so on are housed in the case body 11.
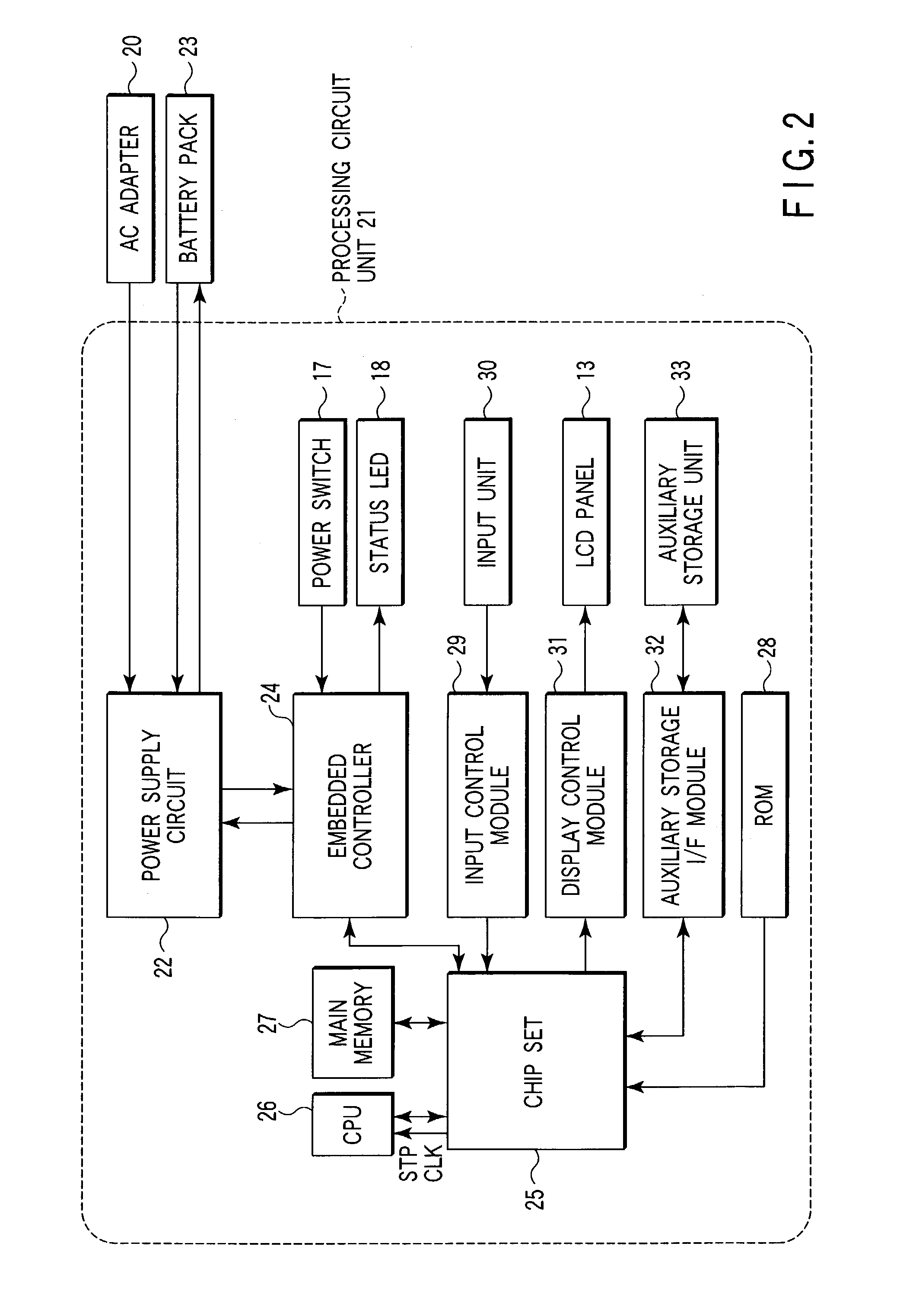
[0023]FIG. 2 is a block diagram of the personal computer 10.
[0024]In FIG. 2, a processing circuit unit 21 is provided with a pow...
second embodiment
[0053][Second Embodiment]
[0054]A second embodiment of the present invention will be described next with reference to FIG. 5, which illustrates, in block diagram form, a personal computer according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0055]In the first embodiment, the embedded controller 24 is used for throttling control of the CPU 26. In the second embodiment, unlike the first embodiment, a current detecting circuit 50 is placed to detect a system-consumed current in the power supply circuit 22 and the on-off control of throttling of the CPU 26 is effected by that current detecting circuit 50 according to the system current. The configuration of FIG. 5 is the same as that of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 2 except for the arrangement of the current sensor 50. In FIG. 5, therefore, components corresponding to those in FIG. 2 are denoted by like reference numerals and detailed descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0056]The current detecting circuit 50 is constructed, as ...
third embodiment
[0061][Third Embodiment]
[0062]A third embodiment of the present invention will be described next. The third embodiment is directed to a configuration such that, when the notebook personal computer shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 is battery-powered, the user is allowed to set a battery operating time. In this case, the user can specify the battery operating time set mode through the input device 30.
[0063]FIG. 7 is a flowchart for the process when the user sets a battery operating time. When the user specifies the battery operating time set mode through the input device 30 (step B1), the CPU 26 checks a residual power of the battery pack 23 through the embedded controller 24 and then calculates a maximum battery operating time under conditions of throttling control (step B2).
[0064]The CPU 26 sets or reads out from a database two or more candidates for the battery operating time within the range of the maximum battery operating time and displays them on the display screen so that the user can m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com