Method for discarding corrupted data packets in a reliable transport fabric
a reliable transport fabric and data packet technology, applied in data switching networks, instruments, frequency-division multiplexes, etc., can solve the problems of repeated rejection, high time consumption, and traditional bus systems that typically do not allow users to add/remove components to/from the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
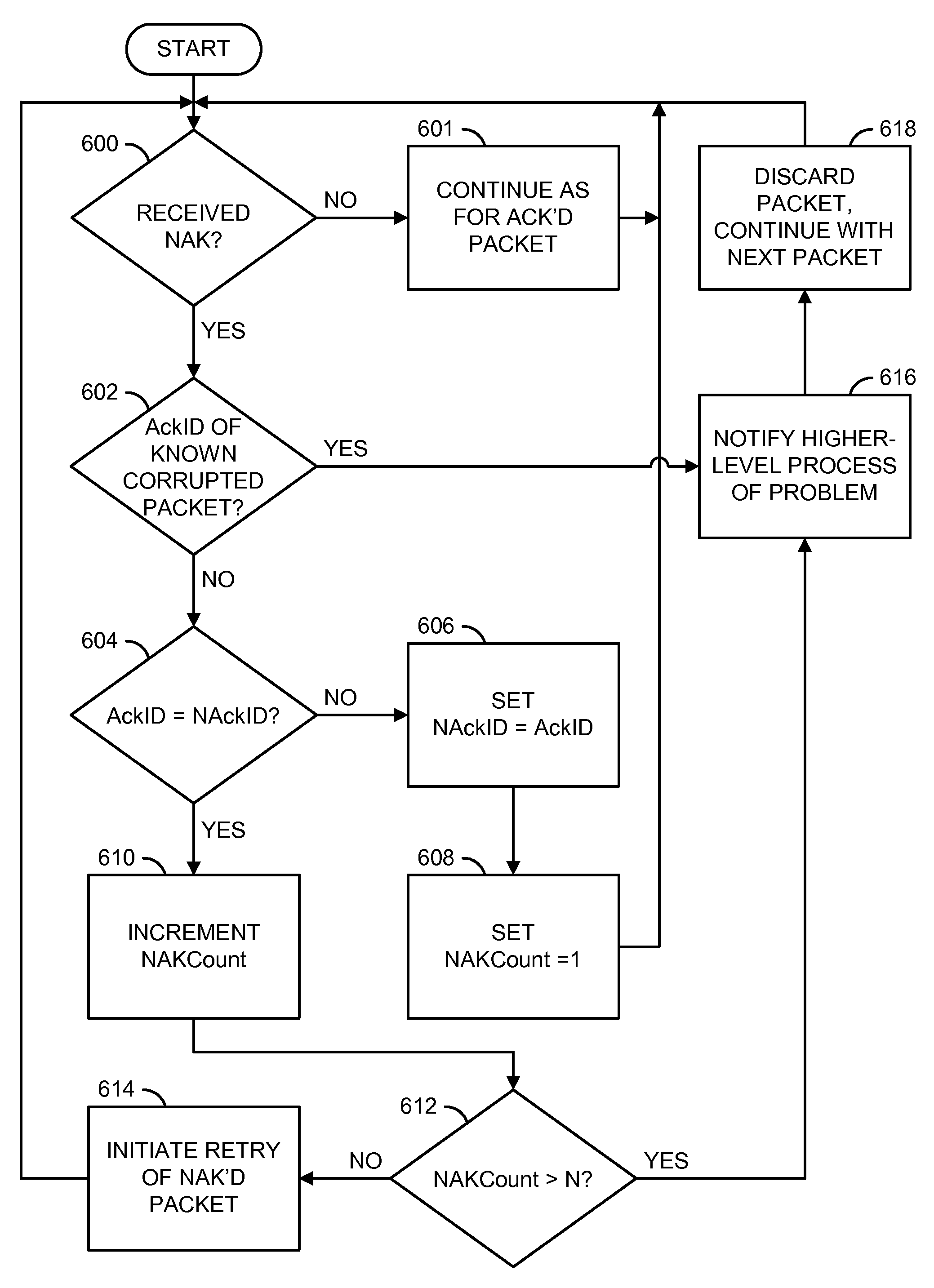
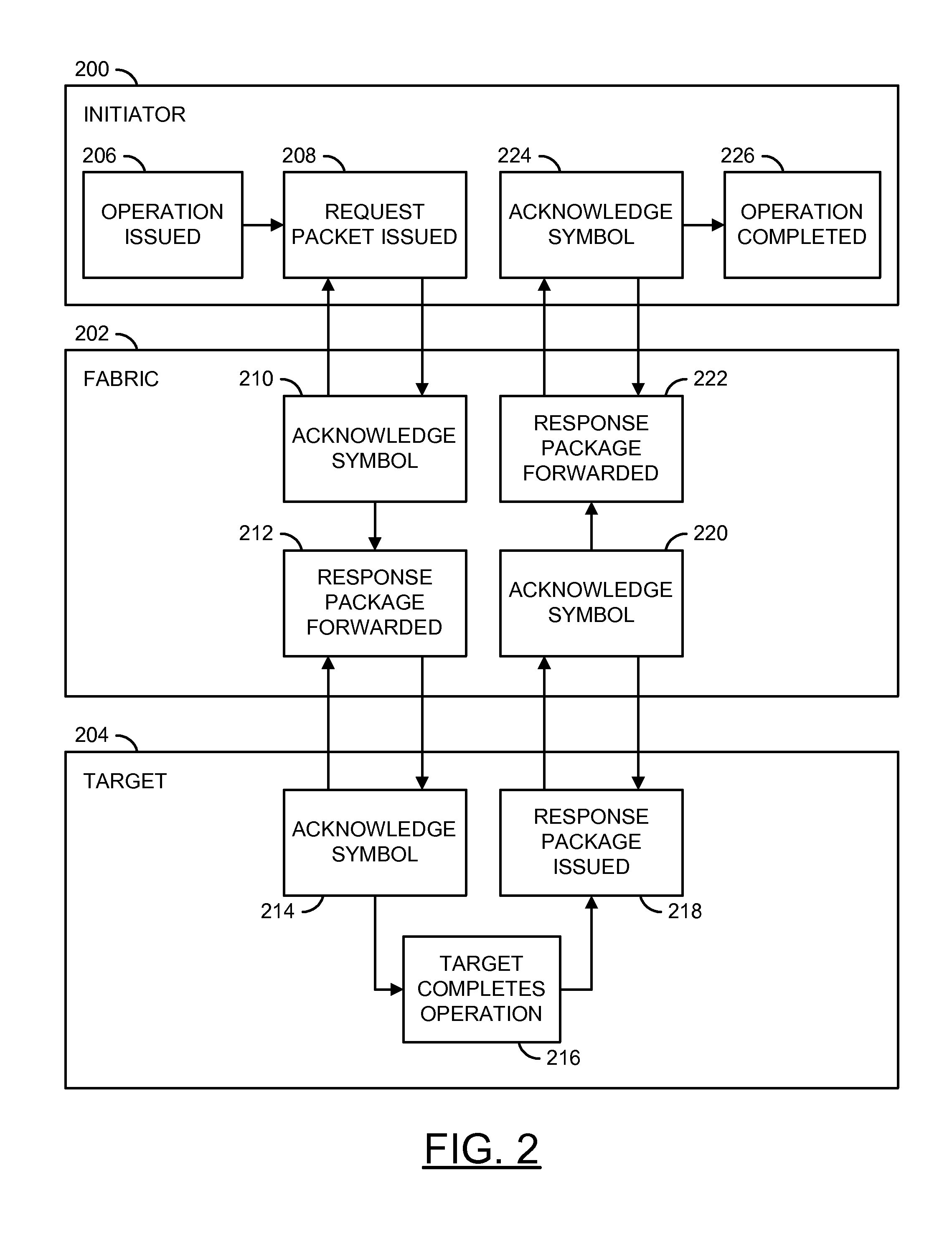
[0018]The following is intended to provide a detailed description of an example of the invention and should not be taken to be limiting of the invention itself. Rather, any number of variations may fall within the scope of the invention, which is defined in the claims following the description.
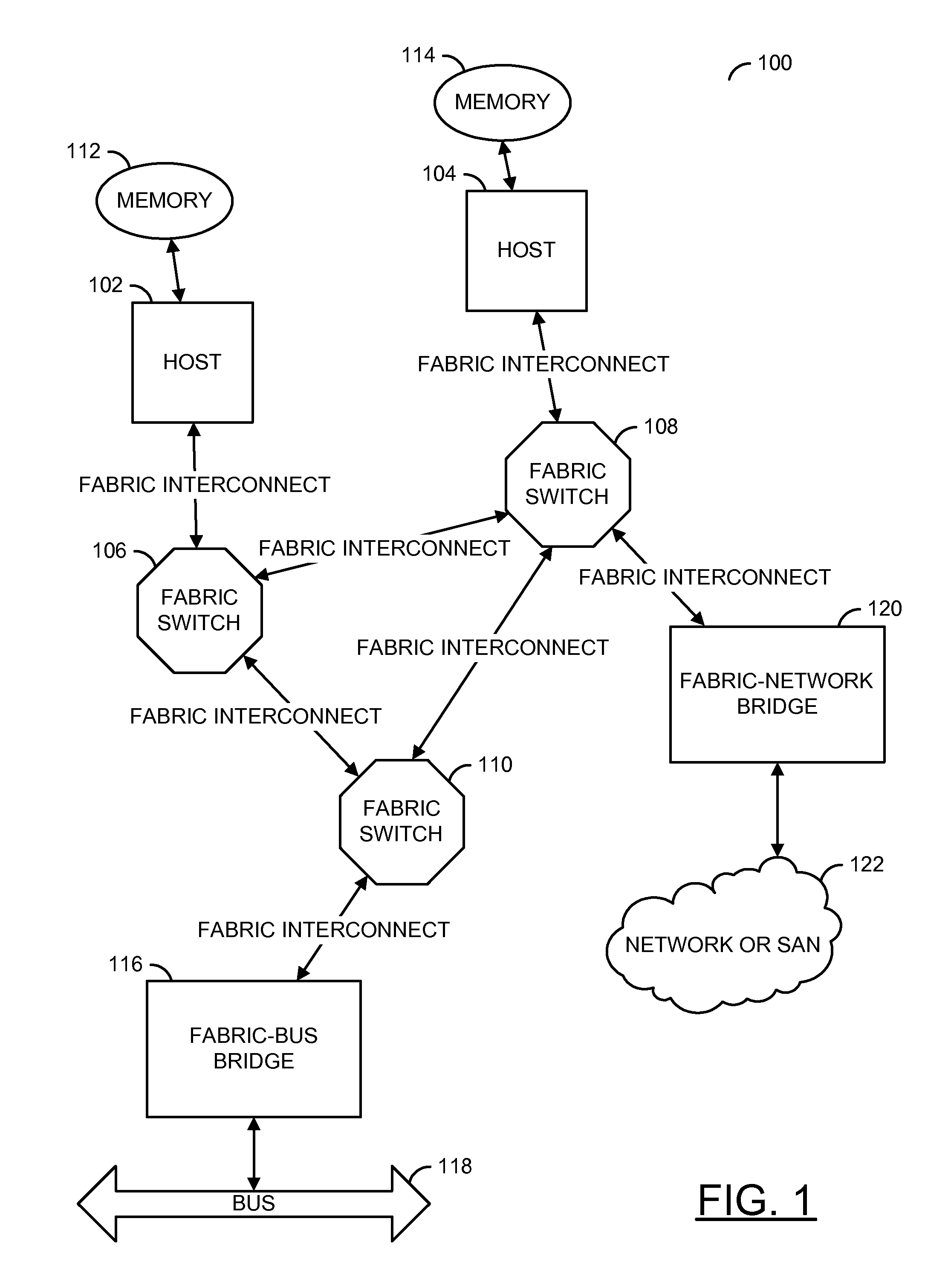
[0019]FIG. 1 is a diagram of a system 100 employing a fabric-based interconnect in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention. In this preferred embodiment, the RAPIDIO™ interconnect standard is utilized. System 100 comprises a plurality of system components, referred to as “hosts”102 and 104. Hosts 102 and 104 represent any of a virtually limitless number of possible system components, such as processors, peripheral devices or device controllers, communication interfaces, and the like, which may be interfaced together through the use of a fabric-based interconnect. The fabric-based interconnect itself is supported by a plurality of fabric switches 106, 108, and 110, which...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com