Flexural vibration piece and oscillator using the same
a technology of flexural vibration and oscillator, which is applied in the direction of device details, device material selection, piezoelectric/electrostrictive device details, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to realize a desired performance, difficult to form grooves or holes along with miniaturization, and difficult to achieve vibration energy loss. , to achieve the effect of stable oscillation characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
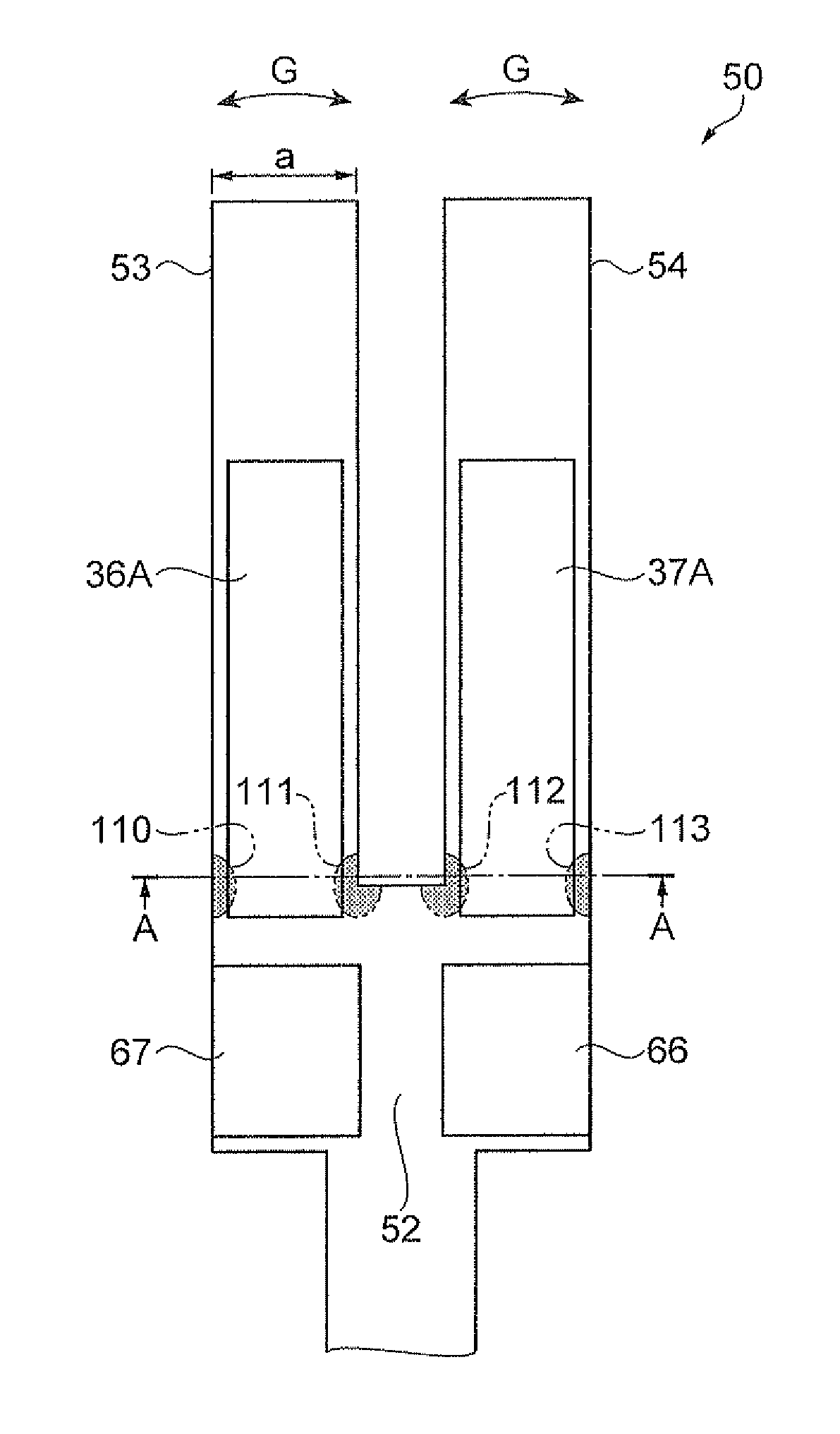
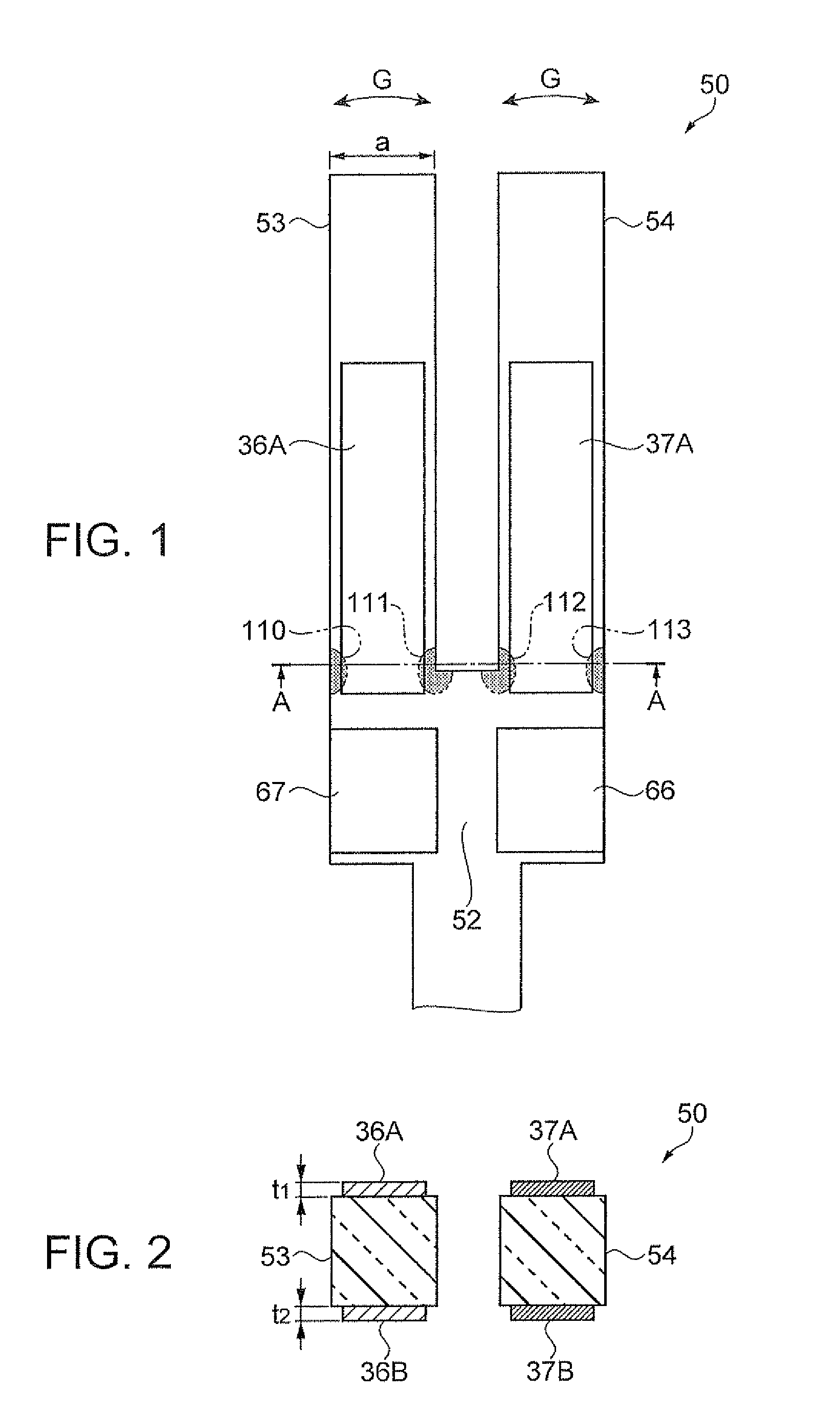
[0047]FIGS. 1 and 2 schematically explain a tuning fork-type quartz vibration piece as a flexural vibration piece of a first embodiment. FIG. 1 is a plan view of one main surface side. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along line A-A in FIG. 1.
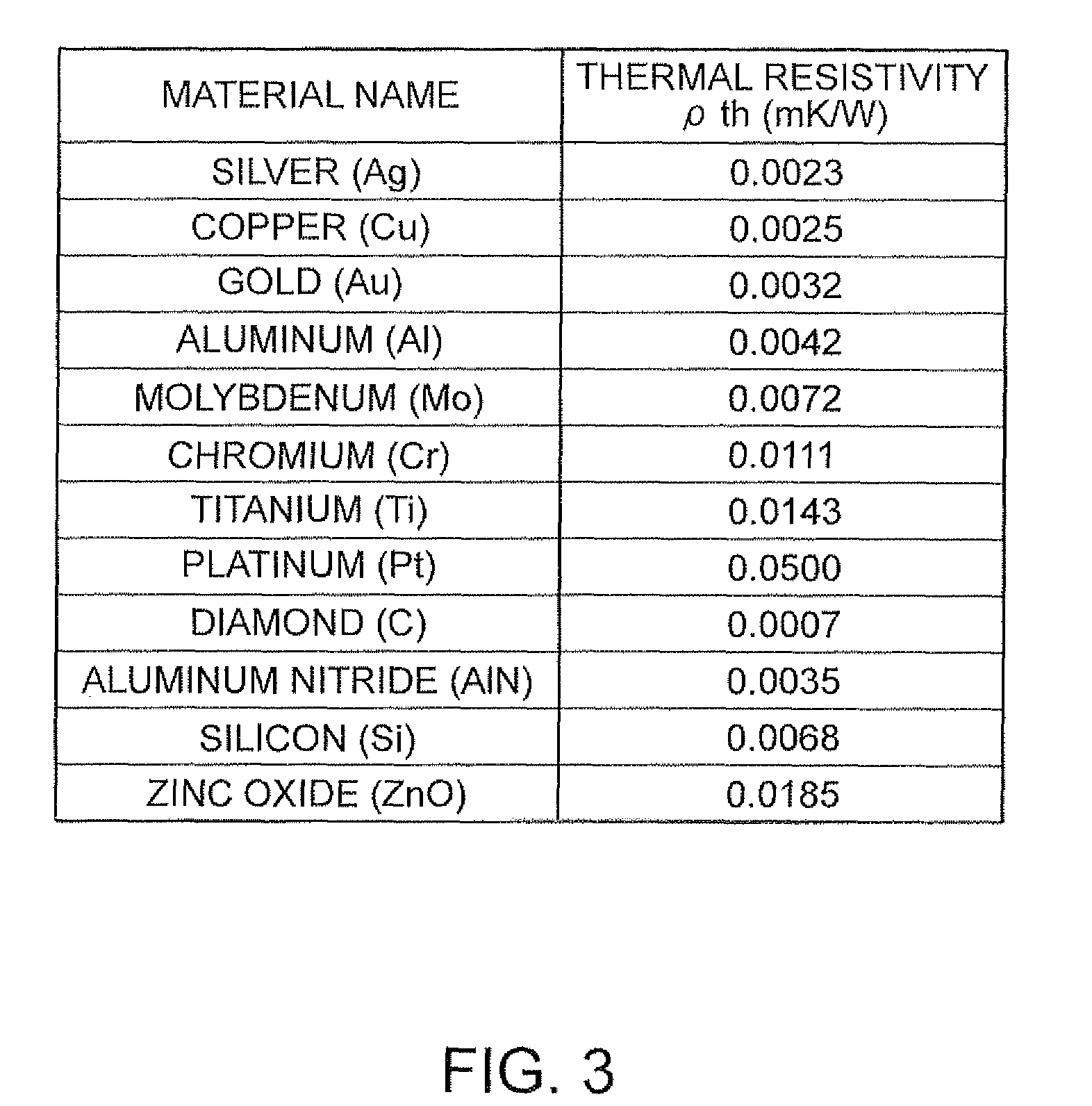
[0048]In FIG. 1, a tuning fork-type quartz vibration piece 50 of the embodiment is formed to have a so-called tuning fork-type external shape with a base 52 that is formed by processing a flexural vibrator material and a pair of vibration arms 53 and 54 bifurcated from one end side (an upper end side in the drawing) of the base 52 and extending in parallel to each other. As the flexural vibrator material, a material cut out from a single crystal of quartz is used in the embodiment in the same manner as in a related-art tuning fork-type quartz vibration piece. For example, the material is formed from a so-called Z-cut quartz thin plate with the Y-axis of crystal axis of quartz being directed to a longitudinal direction of the vibration arm...
second embodiment
[0076]In the first embodiment, parts of the excitation electrodes 36A, 36B, 37A, and 37B of the tuning fork-type quartz vibration piece 50 are used as the heat conduction paths. This is not restrictive, and a heat conduction path may be disposed separately from the excitation electrode on the flexural vibrator.
[0077]FIGS. 4A and 4B schematically explain a tuning fork-type quartz vibration piece in which heat conduction paths are disposed separately from excitation electrodes on the flexural vibrator. FIG. 4A is a plan view of one main surface side, and FIG. 4B is a cross-sectional view taken along line B-B in FIG. 4A. In FIGS. 4A and 4B of a second embodiment, the same constituent as in the first embodiment is denoted by the same reference numeral, and the description thereof is omitted.
[0078]In FIG. 4A, a tuning fork-type quartz vibration piece 150 of the second embodiment has a tuning fork-type external shape with the base 52 formed of a flexural vibrator material and the pair of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com