Agitation apparatus and agitation method
a technology of agitation apparatus and agitation method, which is applied in the direction of rotary stirring mixers, manufacturing tools, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient mixing, insufficient mixing, and generation of hammers, so as to reduce the adhesion of a substance, and reduce the risk of insufficient mixing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
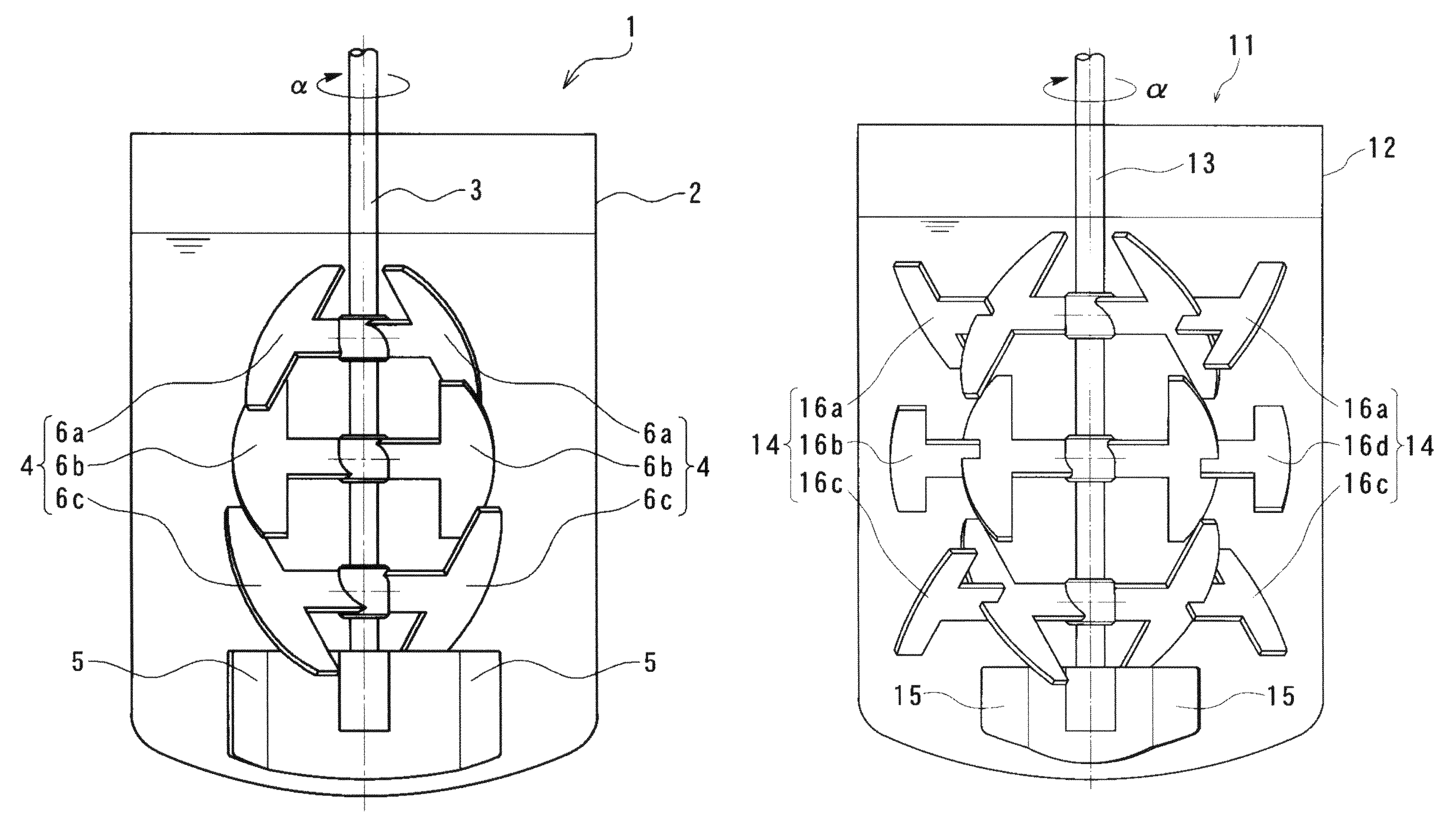
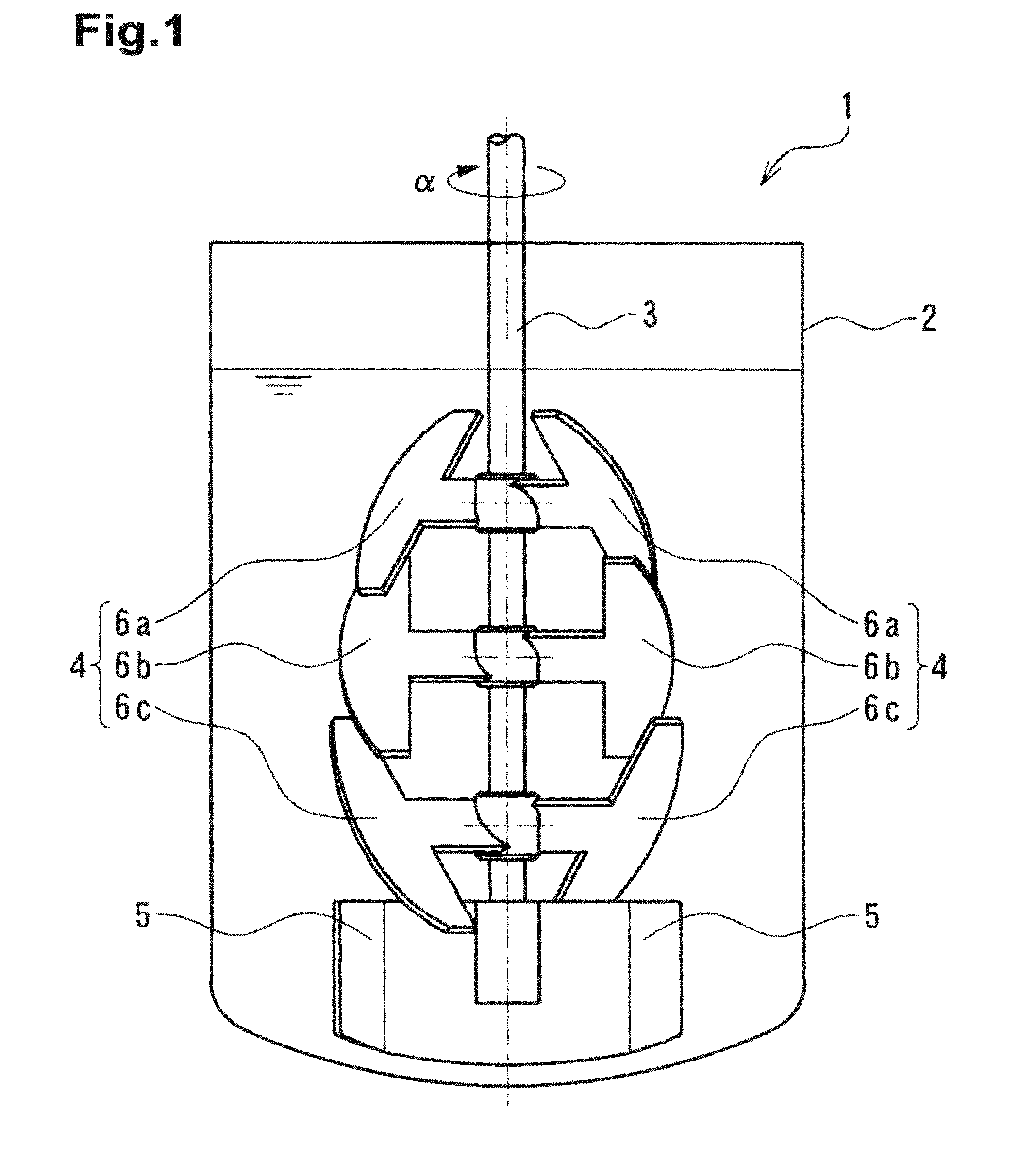
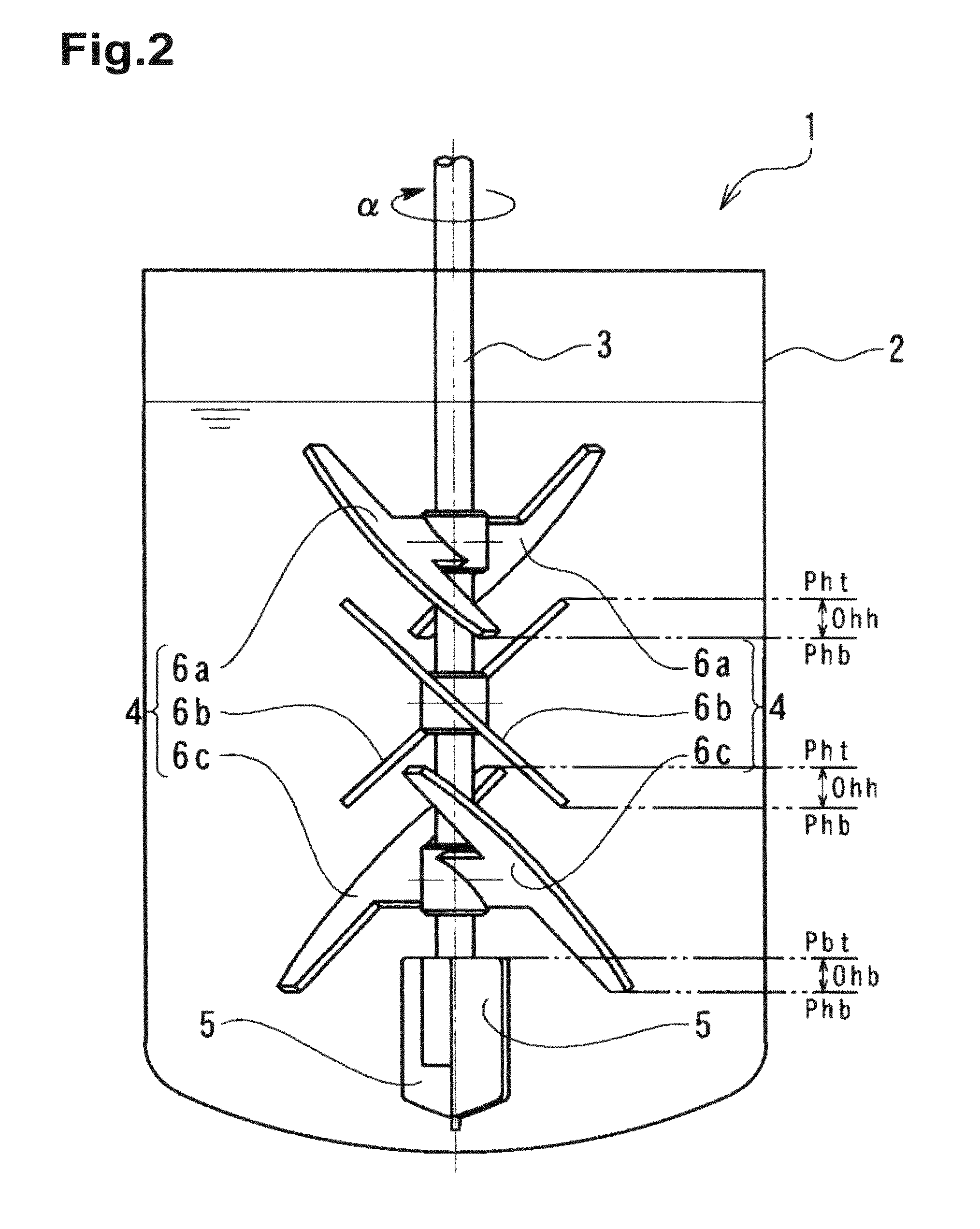
[0198]A solution of starch syrup at 5 Pa·s colored with iodine was decolorized with a solution of sodium thiosulfate prepared with the viscosity equal to that of the starch syrup solution and using starch syrup. The time (a mixing completion time) until the color of the iodine completely disappeared was measured. Specifically, 2 L of the aforementioned colored starch syrup solution was poured into a flask with the inner diameter φ130 mm. The agitation apparatus 1 of the present embodiment, as illustrated in FIGS. 1 to 3, was set and the number of rotation was adjusted so that the agitation power was 1.5 kW / m3. Specifically, the number of rotation was 150 rpm. The starch syrup solution of sodium thiosulfate, by the amount corresponding to 1.1 equivalent of the iodine used for coloration, was poured into the starch syrup solution that was agitated. The time was then measured until the color of the iodine completely disappeared. As a result, the mixing completion time was 4.5 minutes.
example 2
[0200]A solution of starch syrup at 5 Pa·s colored with iodine was decolorized by a solution of sodium thiosulfate prepared at the viscosity equal to that of the starch syrup solution and using starch syrup. The time (the mixing completion time) until the color of the iodine completely disappeared was measured. Specifically, 2 L of the aforementioned colored starch syrup solution was poured into a flask with the inner diameter φ130 mm. The agitation apparatus 1 used in Example 1 was set and the number of rotation was adjusted so that the agitation power was 1.5 kW / m3. Specifically, the number of rotation was 150 rpm. The starch syrup solution of sodium thiosulfate, by the amount corresponding to 1.1 equivalents of the iodine used for coloration, was poured into the starch syrup solution that was agitated. The time was then measured until the color of the iodine completely disappeared. As a result, the mixing completion time was 33 minutes.
example 3
[0201]Using the agitation apparatus 11 of the present embodiment illustrated in FIGS. 4 to 6, the decoloration test was conducted using a solution of starch syrup under the same conditions as those of Example 2. The test was carried out with the number of rotation set to 90 rpm so that the agitation power was 1.5 kW / m3. As a result, the mixing completion time was 6.5 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| rotation angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elevation angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com