Self-aligned trench contact and local interconnect with replacement gate process
a technology of trench contacts and replacement gate structures, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of difficult bidirectional local interconnection patterning, easy failure of misalignment, and most replacement gate processes that are not self-aligned, etc., to reduce the number of resistive interfaces, improve manufacturing yield, and reduce the potential for misalignment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
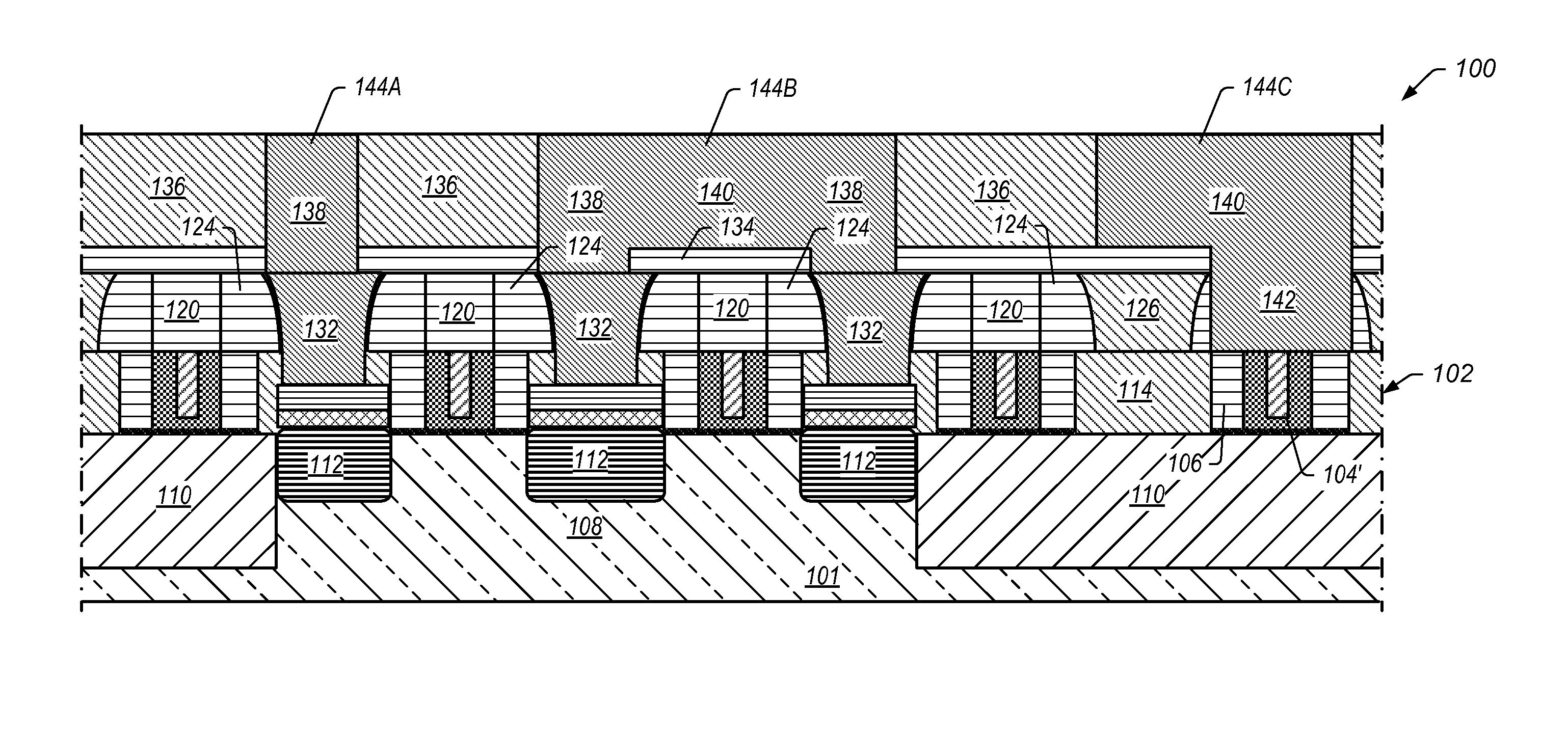
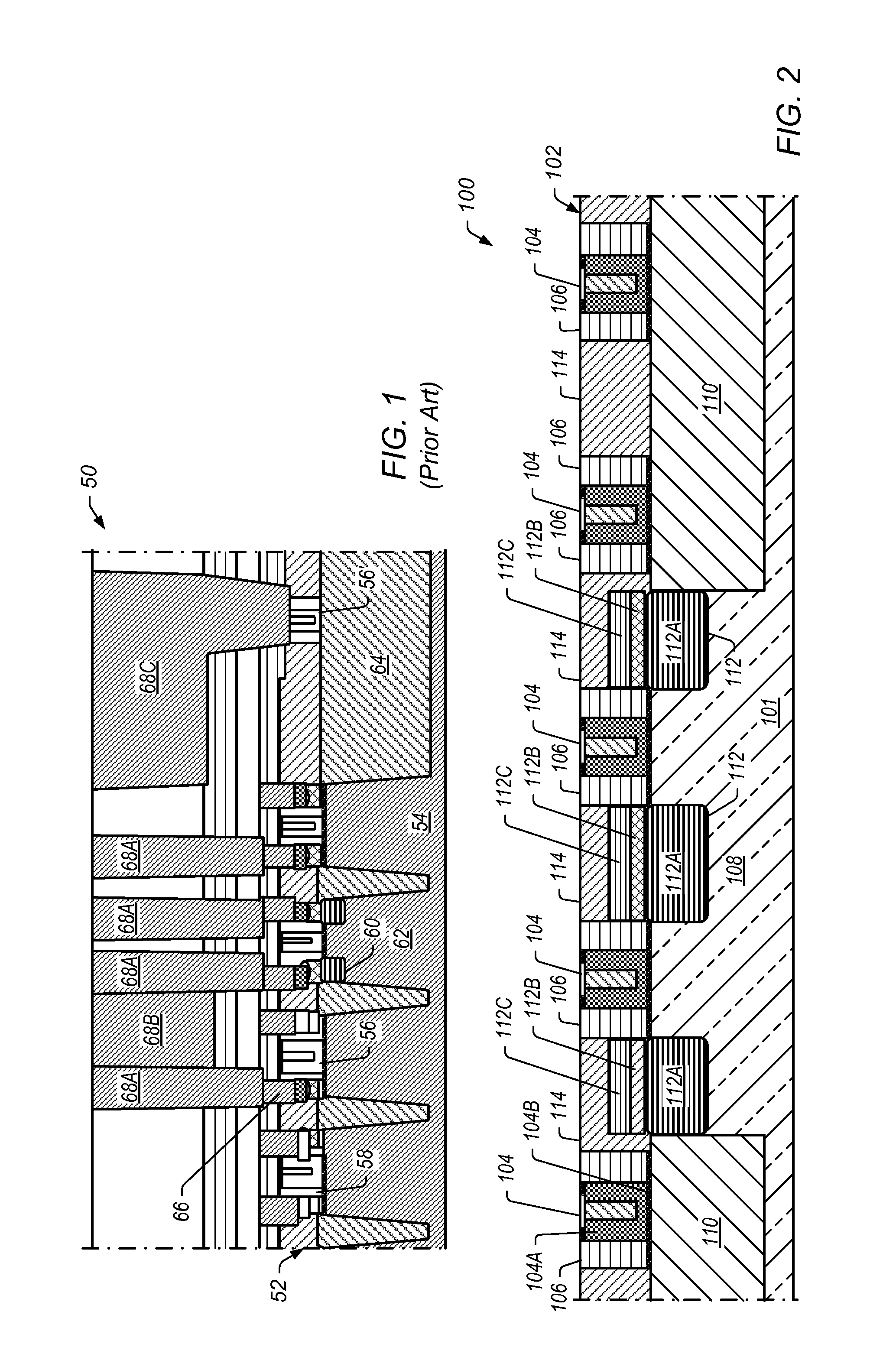
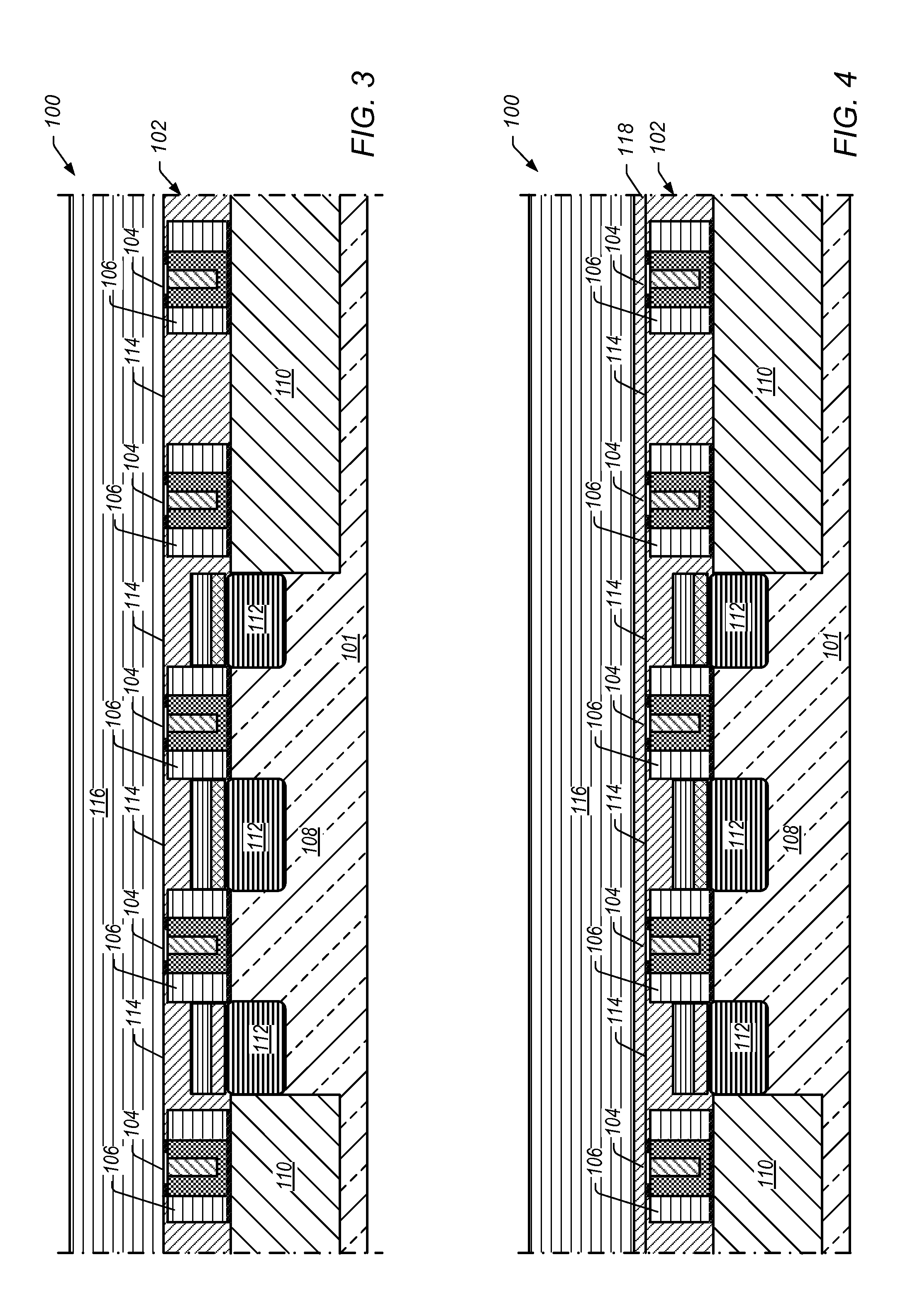
[0013]In certain embodiments, a semiconductor device fabrication process includes providing a transistor with one or more replacement metal gates on a semiconductor substrate. The transistor includes gate spacers of a first insulating material around each gate and a first insulating layer of a second insulating material between the gates and gate spacers. At least some of the second insulating material overlies sources and drains of the gates.
[0014]One or more insulating mandrels are formed and aligned over the gates. The insulating mandrels include the first insulating material. Each insulating mandrel has approximately the same width as its underlying gate with each mandrel being at least as wide as its underlying gate. Mandrel spacers are formed around each insulating mandrel. The mandrel spacers include the first insulating material. Each mandrel spacer has a profile that slopes from being wider at the bottom to narrower at the top.
[0015]A second insulating layer of the second i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com