Nucleic acid construct comprising nucleic acid derived from genome of hepatitis C virus of genotype 1B, hepatitis C virus genome-replicating cells transfected with the same, and method for producing infectious hepatitis C virus particles
a technology of hepatitis c virus and nucleic acid, which is applied in the field of nucleic acid constructs, can solve the problems of inability to compare the replication mechanism or replication efficiency of hcv between different genotypes, the difficulty of revealing the relationship between the hcv genotype and the replication mechanism or replication efficiency of hcv, and the limited type of hcv particles that can be artificially prepared as hcv vaccine raw materials,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
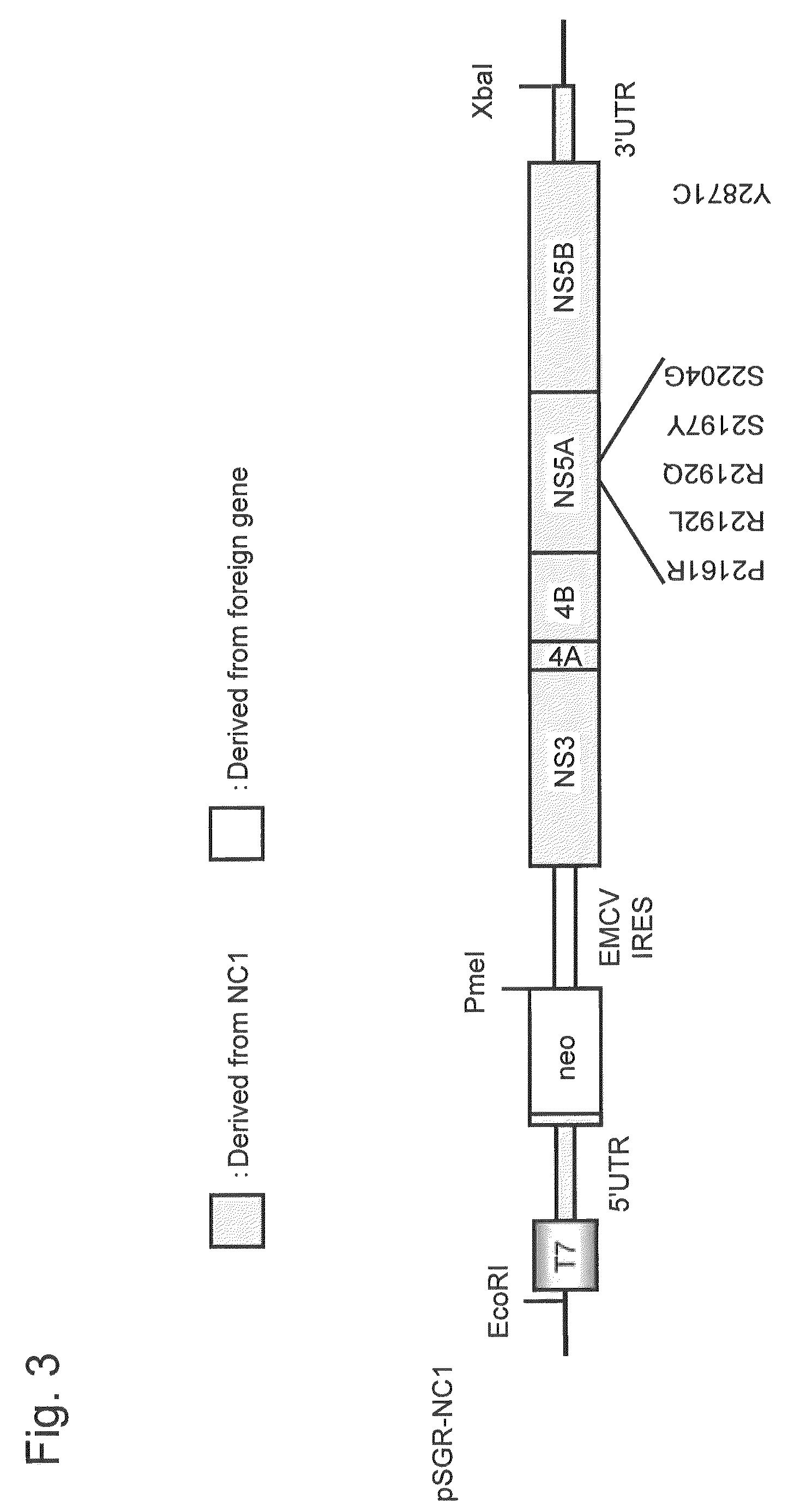
Construction of HCV Subgenomic Replicon RNA Expression Vector of Wild-type NC1 Strain
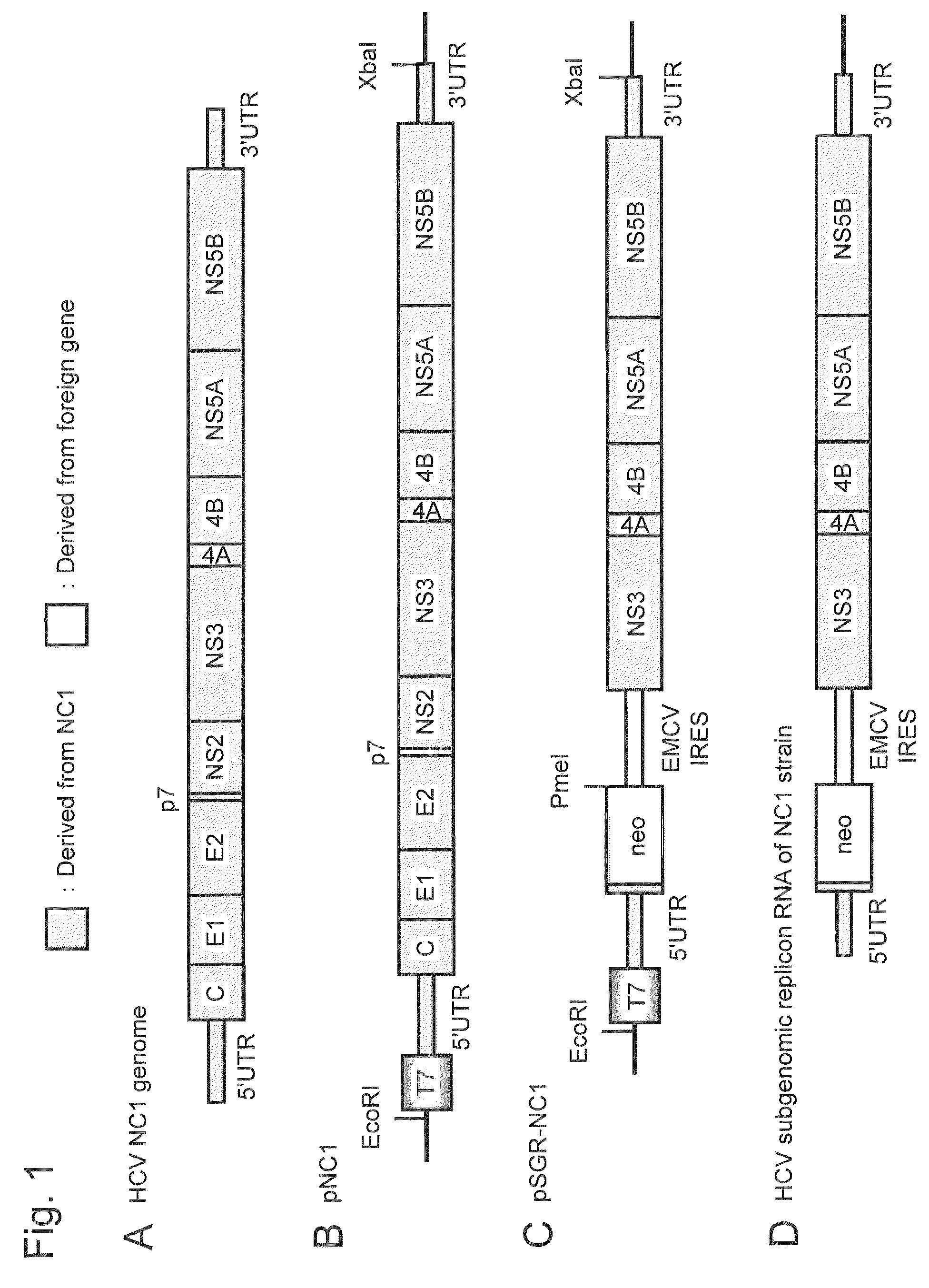
[0216]An HCV subgenomic replicon RNA expression vector, plasmid pSGR-NC1, was constructed using the non-structural region of a cloned DNA (full-length genomic clone DNA) corresponding to the full-length genomic RNA of the NC1 strain, which is a novel HCV of genotype 1b separated from an acute severe hepatitis C patient.
[0217]Specifically, RNA was extracted from patient's serum and purified with Isogen-LS (Nippon Gene Co., Ltd.), and cDNA was synthesized using a random hexamer primer. PCR primers were designed based on the conserved sequence (Con1 strain: GenBank Accession No. AJ238799) of a known HCV genome of genotype 1b. Five fragments of cDNA were amplified using the designed PCR primers and the synthesized cDNA as a template. The amplification product of the sequence at the 5′ end, which is difficult to obtain, was obtained by a 5′ RACE method. Each fragment was cloned into a cloning vector for ...
example 2
Production of HCV Subgenomic Replicon RNA of Wild-type NC1 Strain
[0224]The expression vector pSGR-NC1 constructed in Example 1 was cleaved with restriction enzyme XbaI. Subsequently. 20 U of Mung Bean Nuclease was added to 10 to 20 μg of the XbaI cleaved fragment (the total amount of the reaction solution: 50 μL), followed by incubation at 30° C. for 30 minutes. Mung Bean Nuclease is an enzyme that catalyzes a reaction of smoothing through selective decomposition of the single-stranded portion of a double-stranded DNA. In general, RNA transcription by an RNA polymerase directly using the XbaI cleaved fragment as a template DNA synthesizes a replicon RNA having extra four nucleotides CUAG, a part of the Xbal recognition sequence, on the 3′ end. In this Example, accordingly, the XbaI cleaved fragment was treated with Mung Bean Nuclease to remove the four nucleotides CTAG from the XbaI cleaved fragment.
[0225]Subsequently, proteins in the Mung Bean Nuclease treated solution containing t...
example 3
Establishment of HCV Subgenomic Replicon-replicatiug Cell Clone of the NC1 Strain
[0227]Total cellular RNA extracted from Huh7 cells by a common method was mixed with 1 μg of the HCV subgenomic replicon RNA of the wild-type NC1 strain produced in Example 2 and the total RNA amount was adjusted to 10 μg. Subsequently, the RNA mixture was transfected into Huh7 cells by electroporation. The electroporated Huh7 cells were seeded in a culture dish and were cultured for 16 to 24 hours, and G418 (neomycin) was then added to the culture dish. The culture was continued while replacing the culture solution twice a week.
[0228]After the culture for 21 days after the seeding, viable cells were stained with crystal violet. As a result colony formation of the cells transfected with the HCV subgenomic replicon RNA of the NC1 strain was confirmed. The colony formation indicates that the HCV subgenomic replicon RNA was replicated in the cells (FIG. 2).
[0229]The colonies of viable cells were further cl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nucleic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| full-length genome nucleotide sequences | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com