Torque sensor unit
a technology of torque sensor and torque sensor, which is applied in the direction of instruments, force/torque/work measurement apparatus, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems affecting the detection accuracy of absolute rotation angle, and achieve the effect of accurate determination, excellent positioning ability, and high mounting accuracy of magnets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
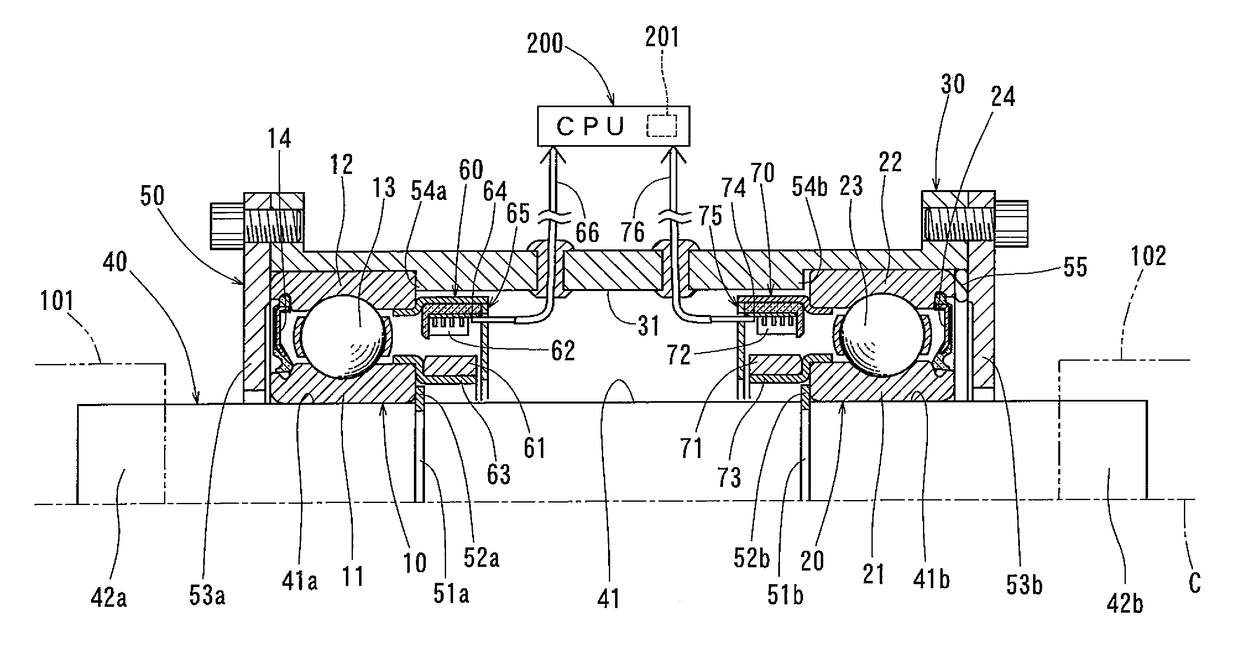
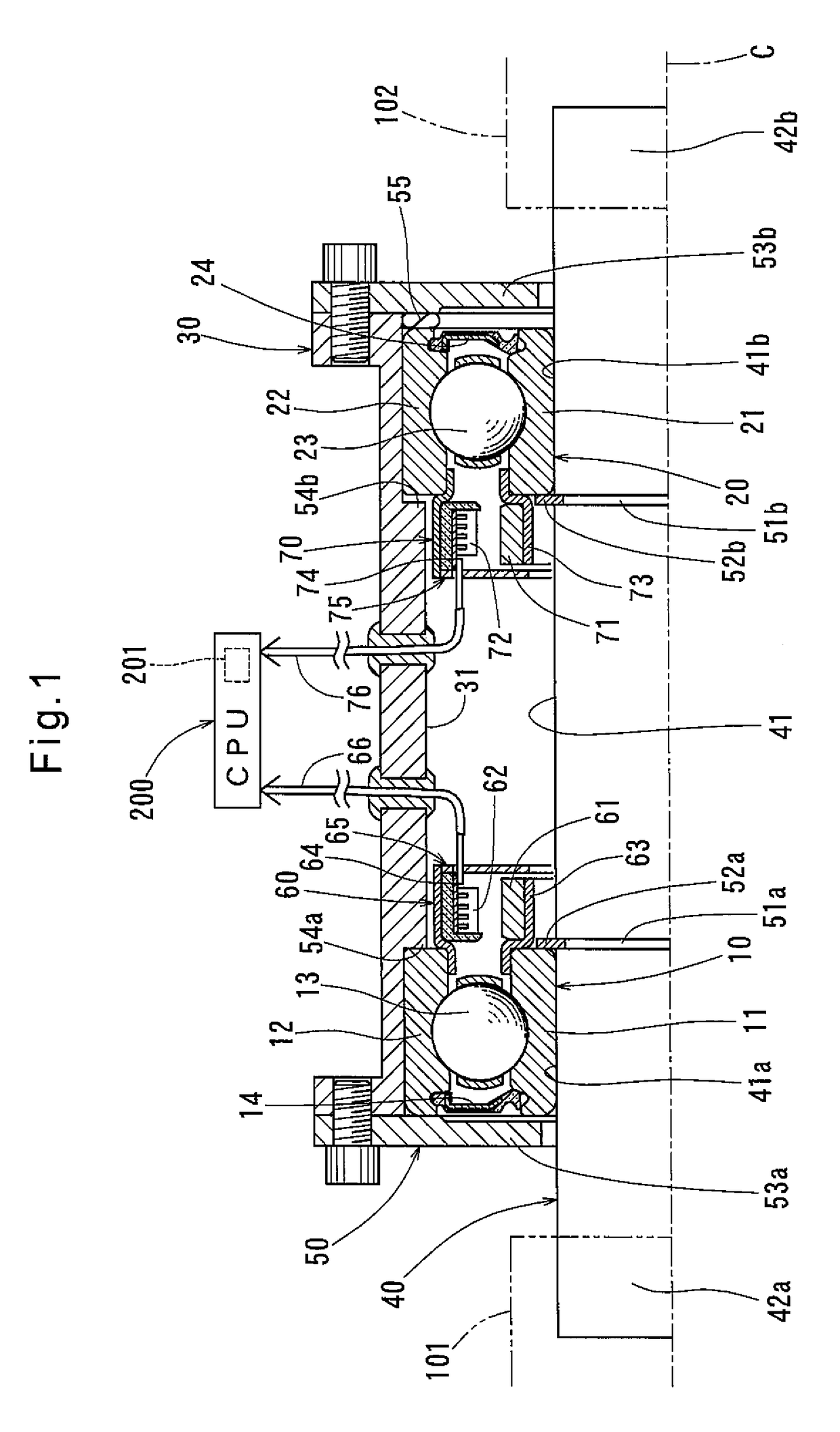
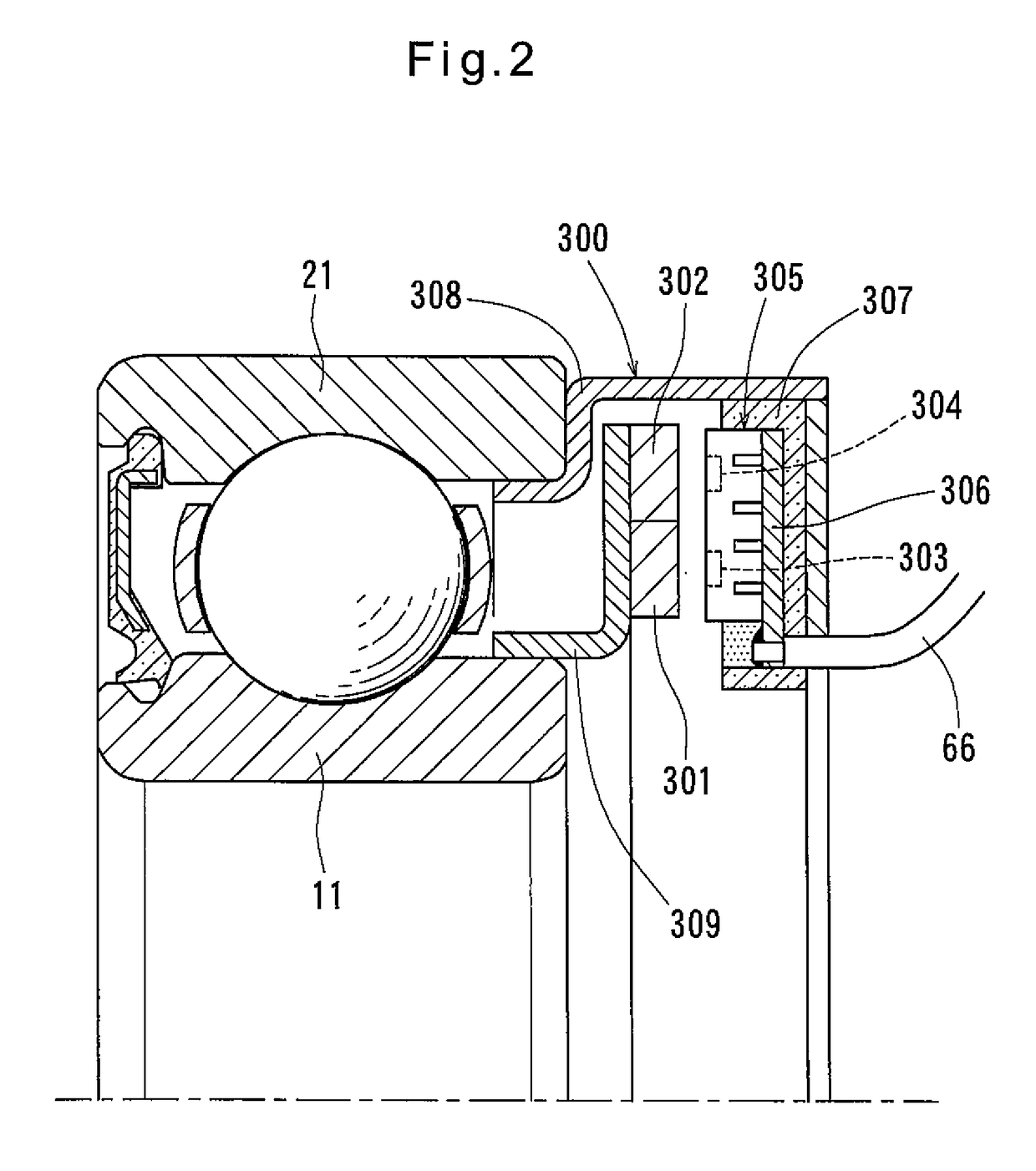
[0025]Now a torque sensor unit as a first specific example is described with reference to FIG. 1. As shown, this torque sensor unit includes a first rolling bearing 10, a second rolling bearing 20, a housing 30, a shaft member 40, a bearing restricting means 50, a first magnetic angle sensor 60, and a second magnetic angle sensor 70. The magnetic angle sensor 60 is fixed to the rolling bearing 10, while the magnetic angle sensor 70 is fixed to the rolling bearing 20.
[0026]The first rolling bearing 10 includes a first inner race 11, a first outer race 12, and a plurality of rolling elements 13 disposed between the inner race 11 and the outer race 12. The second rolling bearing 20 includes a second inner race 21, a second outer race 22, and a plurality of rolling elements 23 disposed between the inner race 21 and the outer race 22. The rolling bearings 10 and 20 themselves have the ability of position the inner and outer races 11 and 12, and the inner and outer races 21 and 22, respec...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absolute rotation angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com