Patents
Literature
1703results about "Physics instruments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
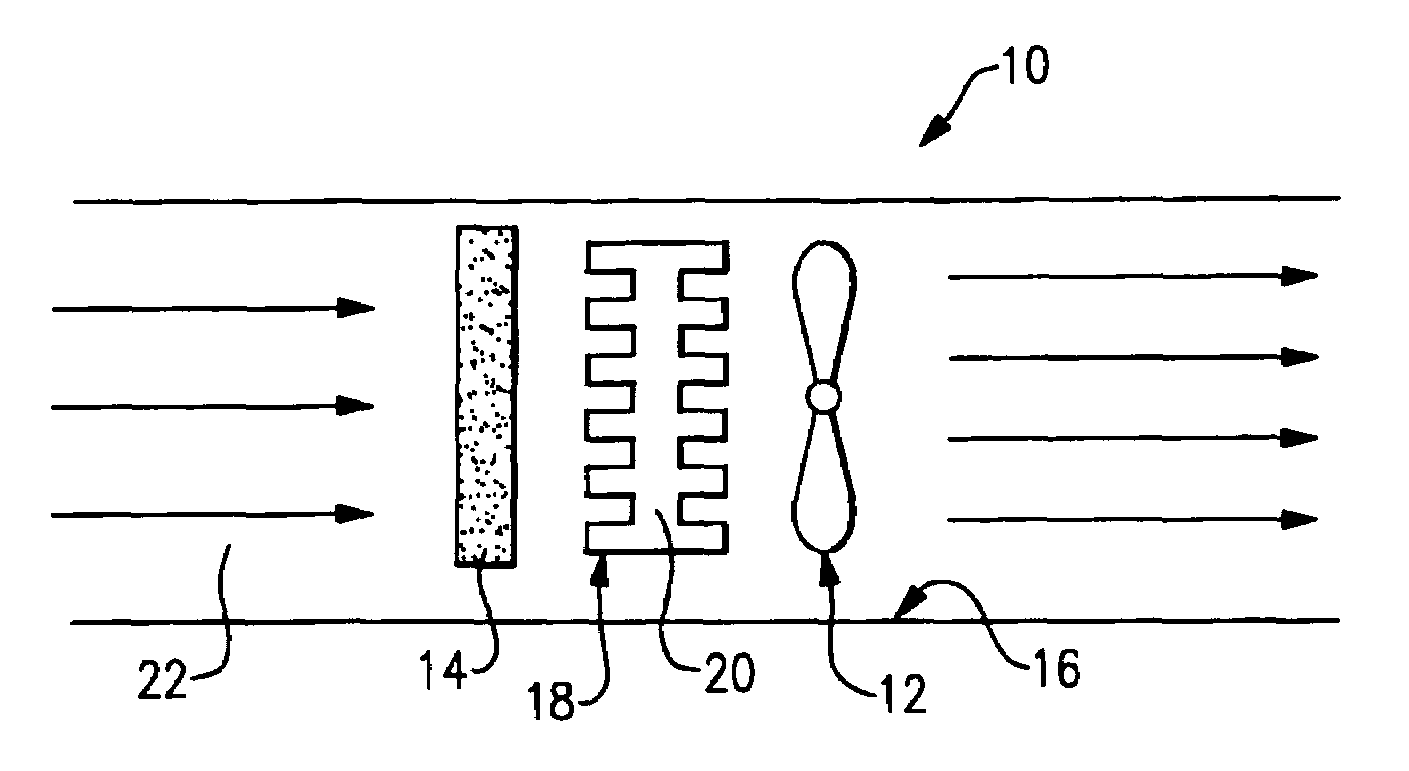
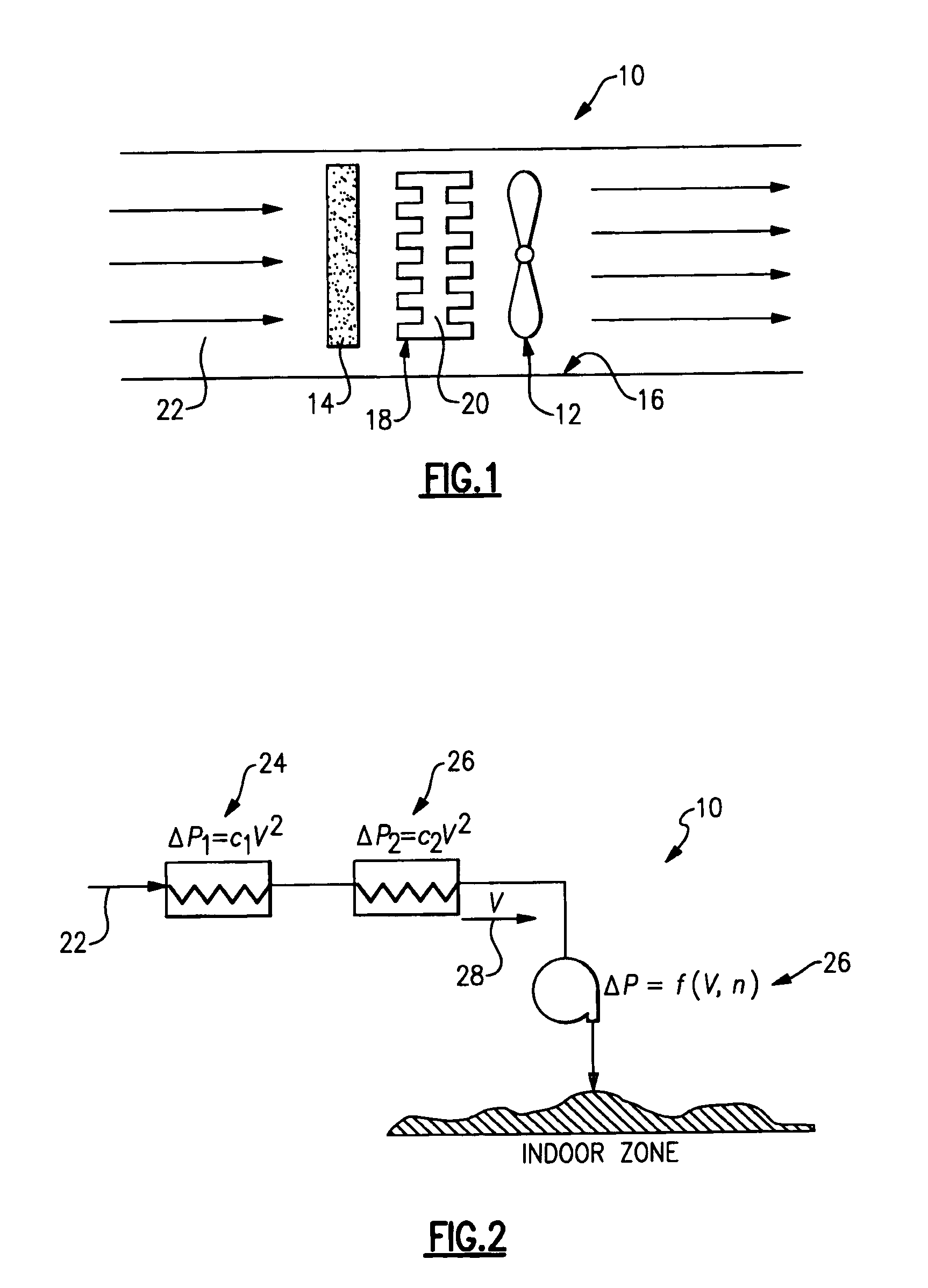
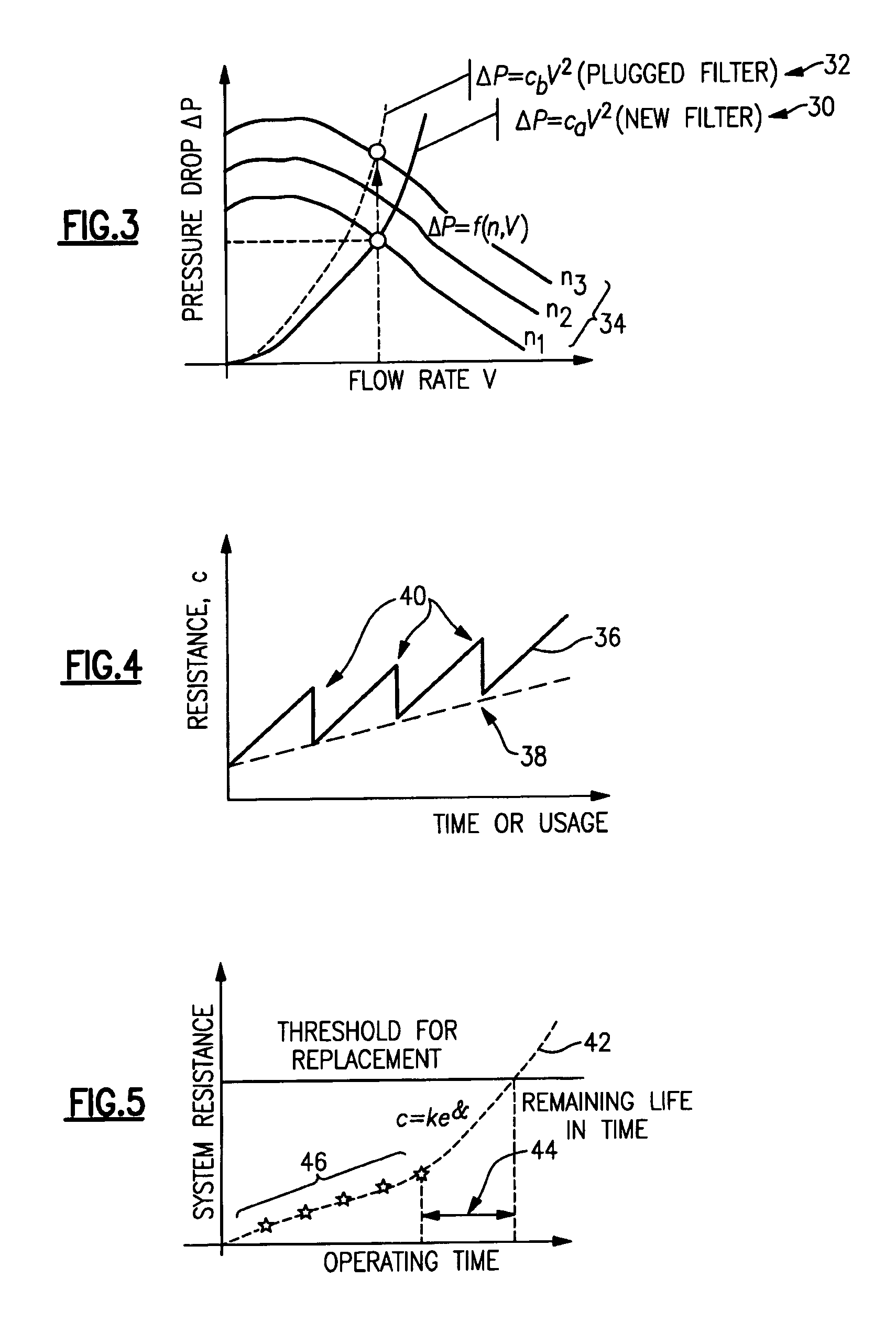
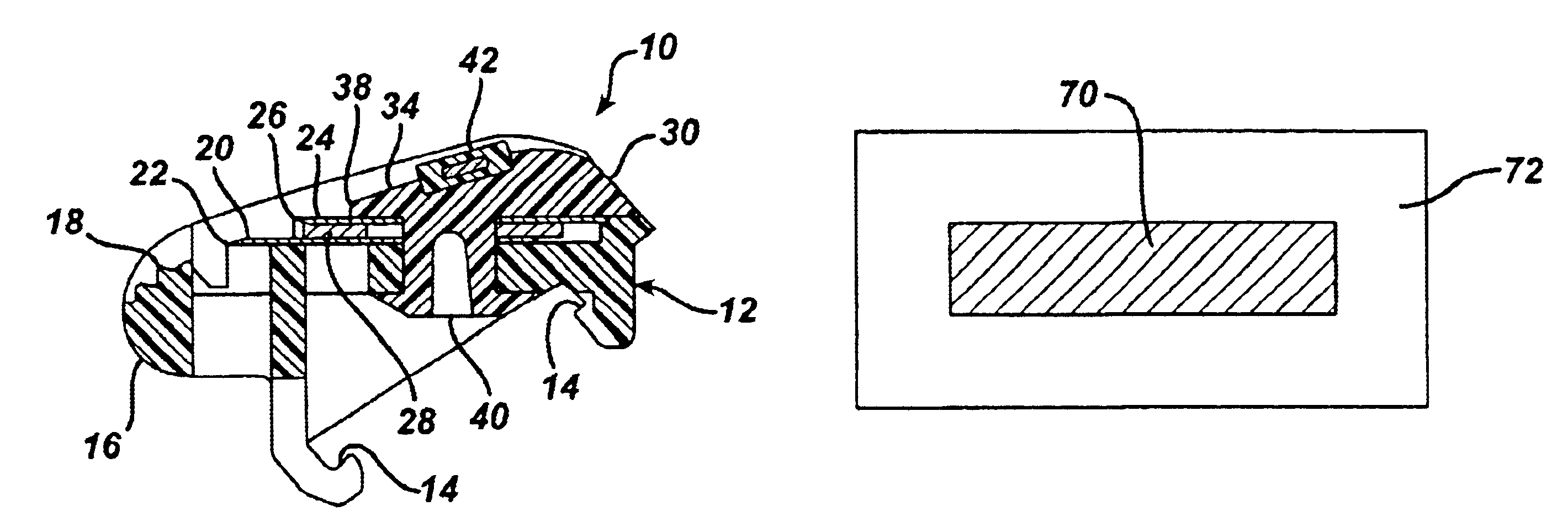
Technique for detecting and predicting air filter condition
InactiveUS7261762B2Combination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentElectrical resistance and conductanceAir filter
Owner:CARRIER CORP
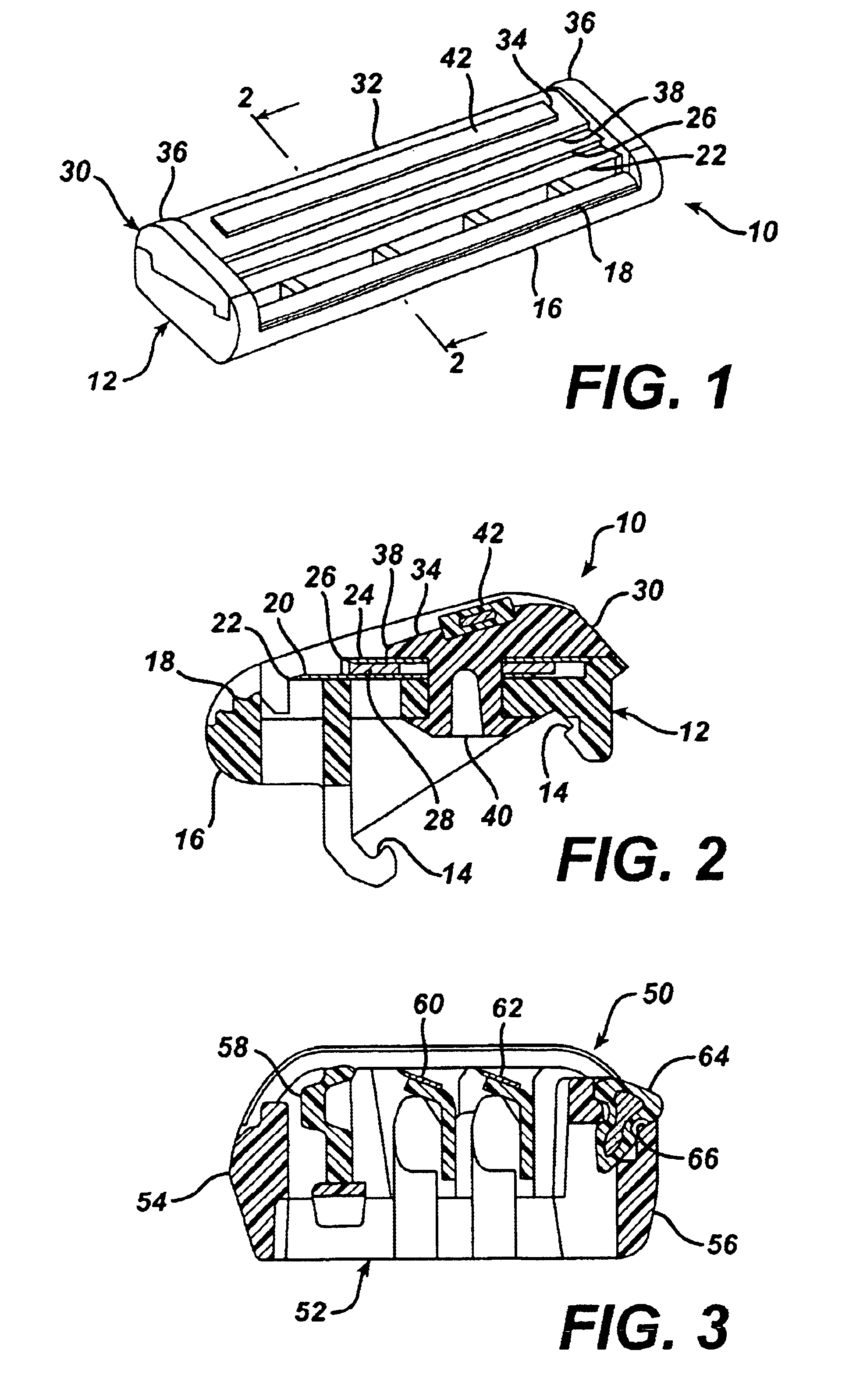
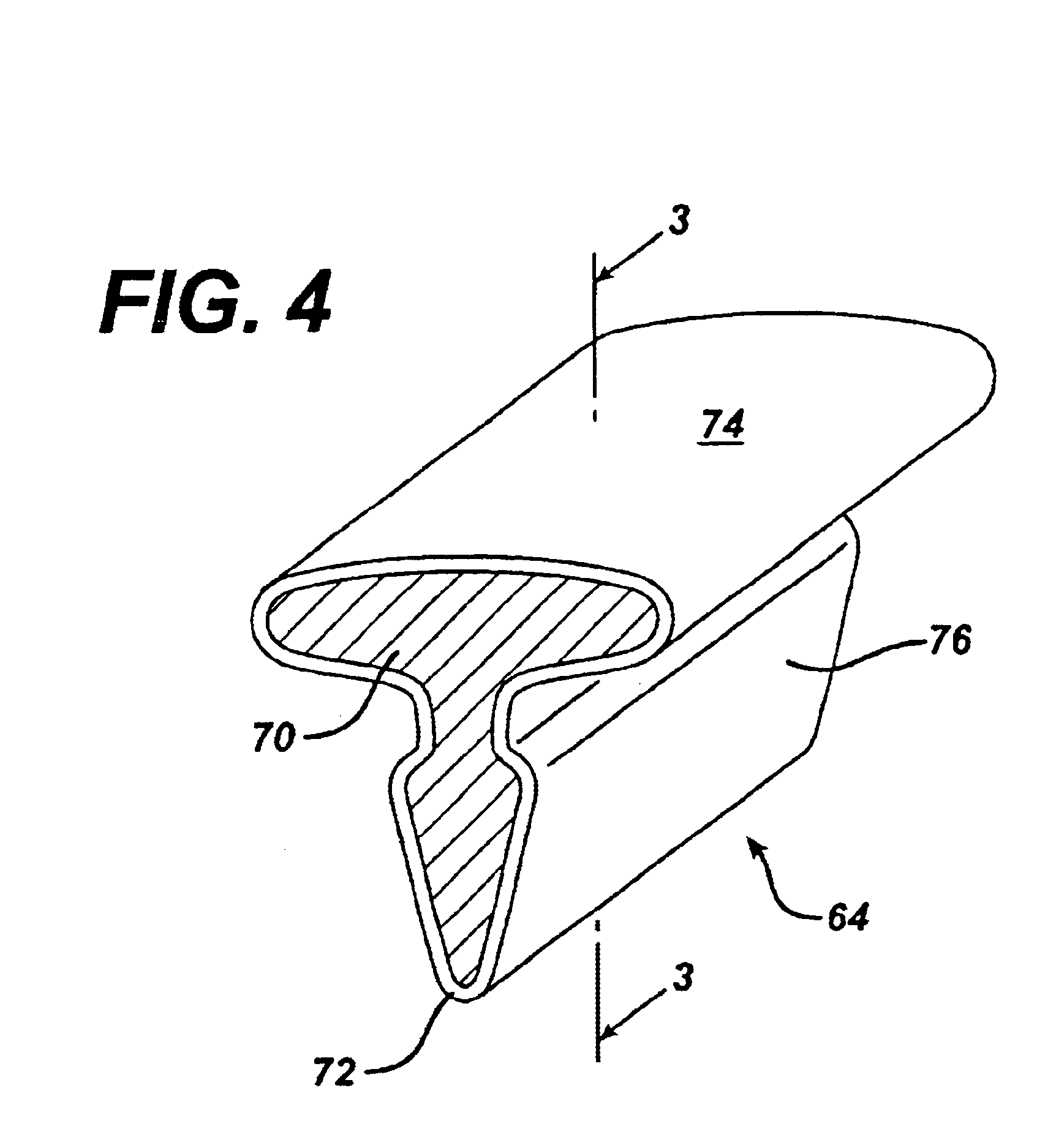
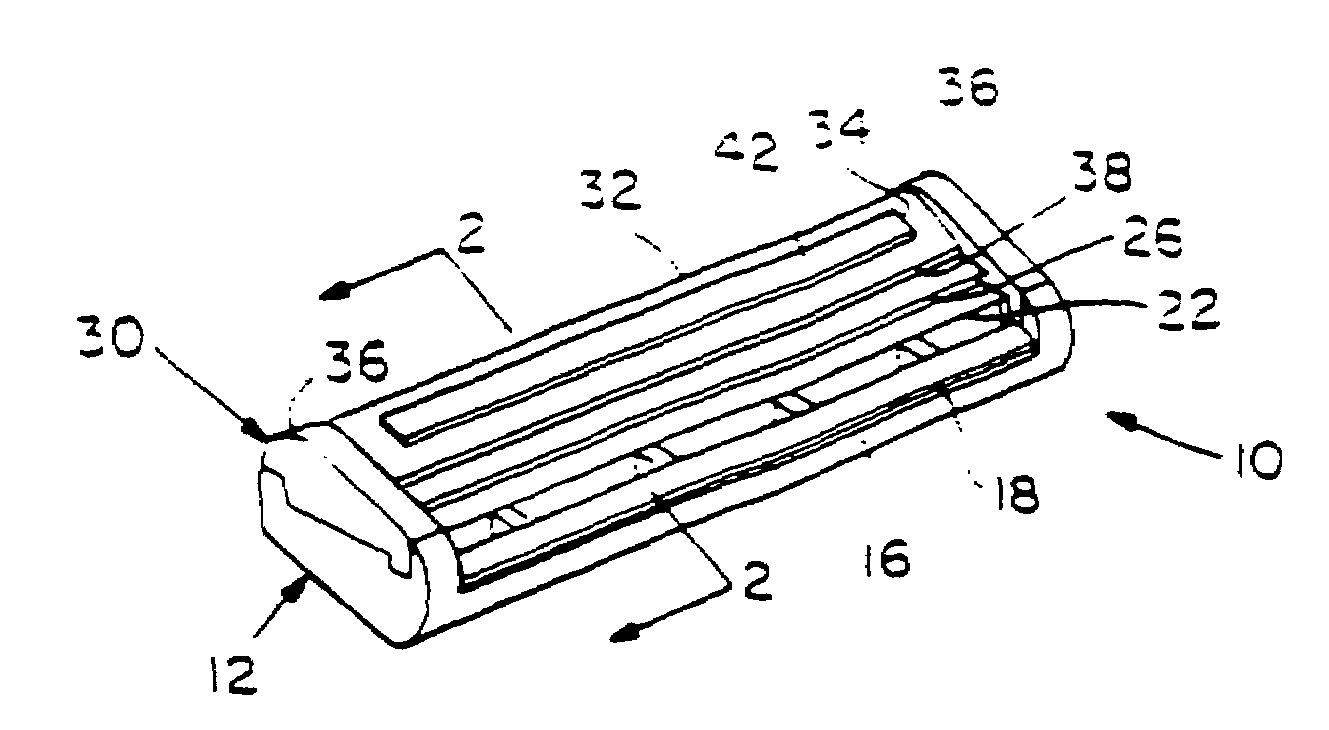
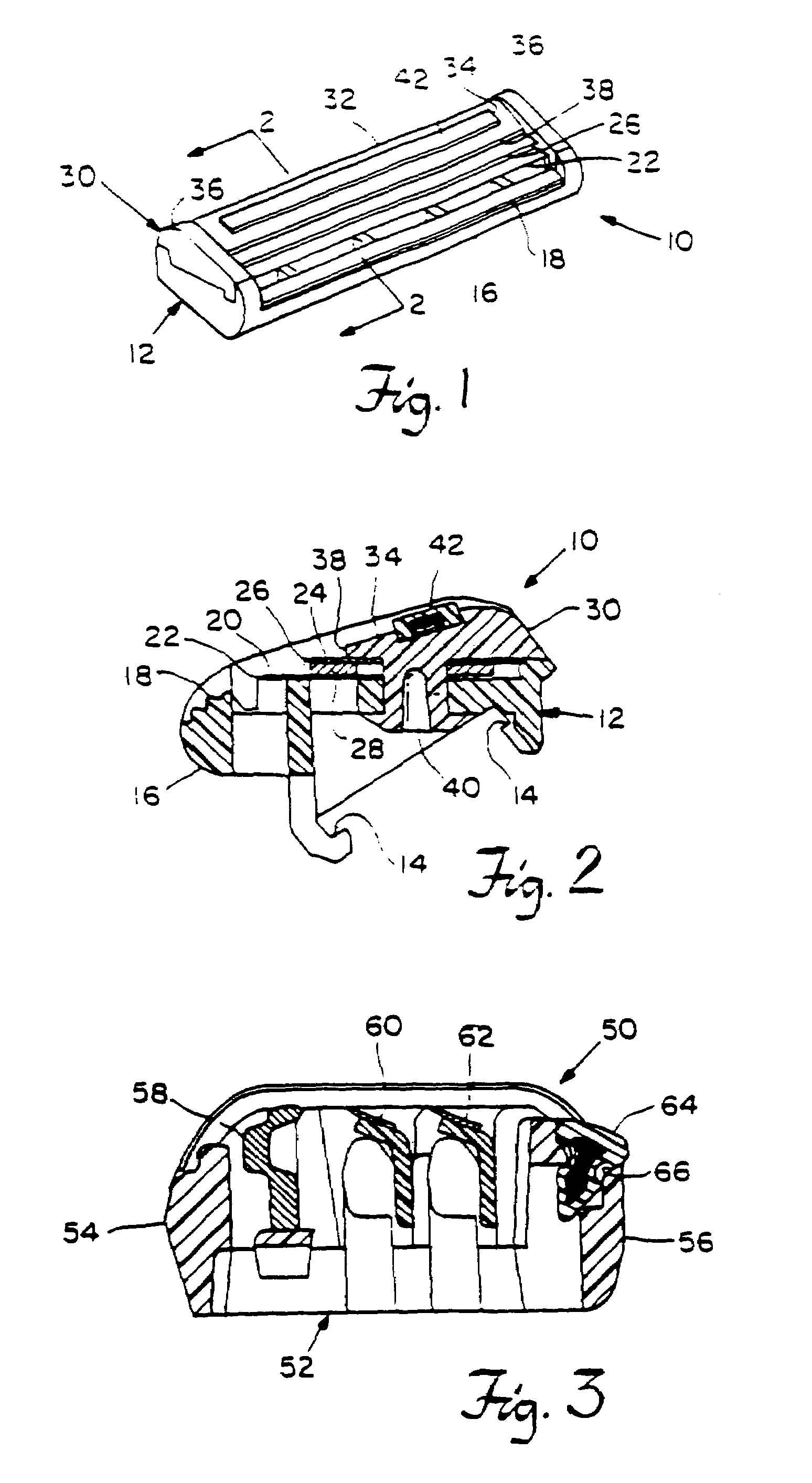
Shaving system
InactiveUS6944952B1High mechanical strengthImproved shaving aid release characteristicMeasurement devicesPhysics instrumentsWater insolubleRigid core
A shaving unit that comprises at least one blade and a skin engaging member that has a surface for engaging the user's skin adjacent the blade edge. The shaving unit may be of a disposable cartridge type adapted for coupling to and uncoupling from a razor handle or may be integral with a handle so that the complete razor is discarded as a unit when the blade or blades become dulled. The blade edge (or edges) cooperate with skin engaging surfaces to define a shaving geometry. The skin engaging member is comprised on an elongated sheath (or skin engaging layer) made of a mixture of water insoluble matrix and an effective amount of shaving aid and a rigid core (or non-skin engaging layer) extending axially through out said sheath. The axial position of the core need not be through the central axis.
Owner:THE GILLETTE CO
Shaving system
InactiveUS7069658B2High mechanical strengthImproved shaving aid release characteristicMeasurement devicesPhysics instrumentsWater insolubleRigid core
A shaving unit that comprises at least one blade and a skin engaging member that has a surface for engaging the user's skin adjacent the blade edge is described herein. The shaving unit may be of a disposable cartridge type adapted for coupling to and uncoupling from a razor handle or may be integral with a handle so that the complete razor is discarded as a unit when the blade or blades become dulled. The blade edge (or edges) cooperate with skin engaging surfaces to define a shaving geometry. The skin engaging member is comprised of an elongated sheath (or skin engaging layer) made of a mixture of water insoluble matrix and an effective amount of shaving aid and a rigid core (or non-skin engaging layer) extending axially throughout said sheath. The axial position of the core need not be through the central axis.
Owner:THE GILLETTE CO
Technique for detecting and predicting air filter condition
InactiveUS20050247194A1Life predictionCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentOperational systemAir filter
Owner:CARRIER CORP
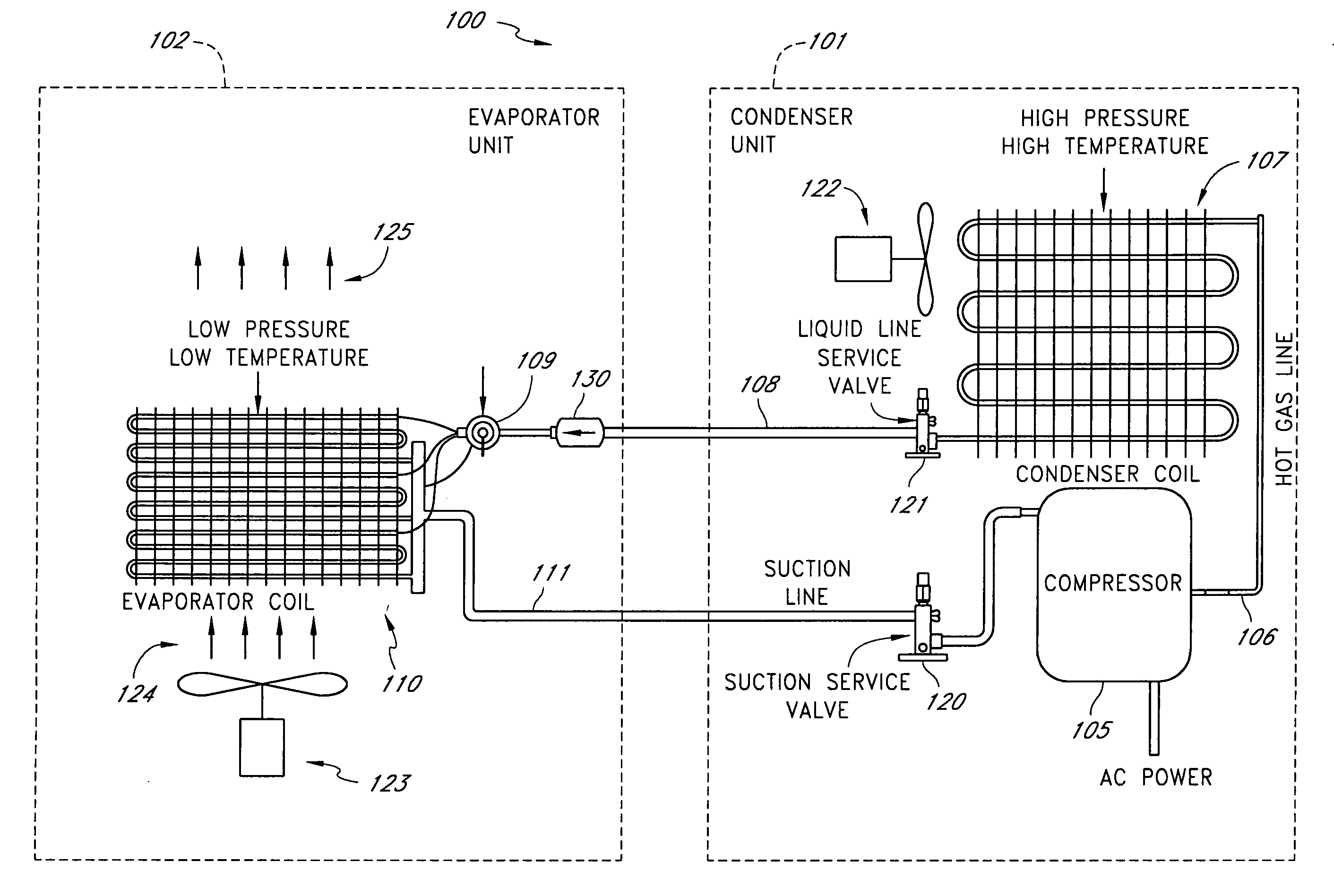
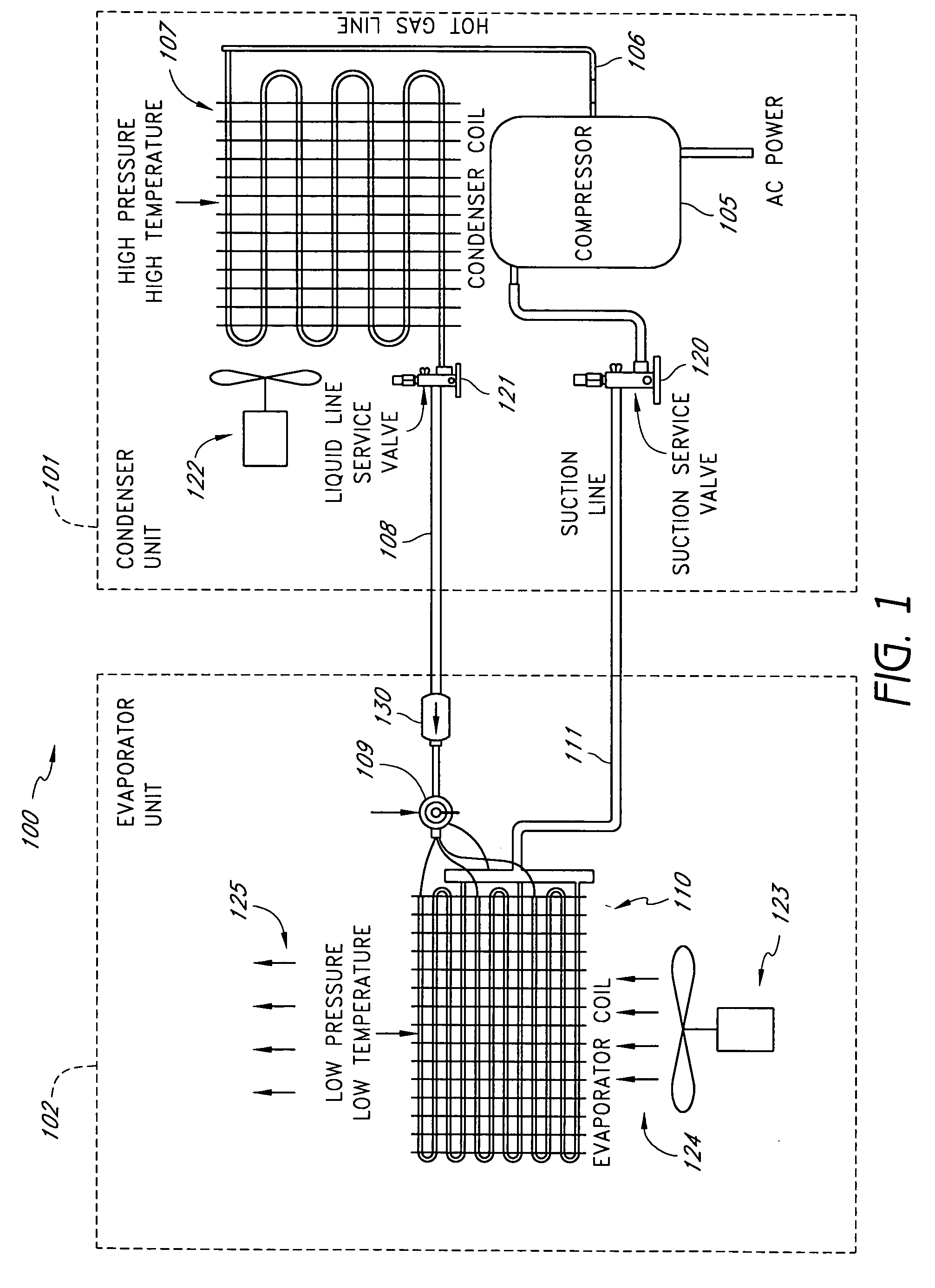
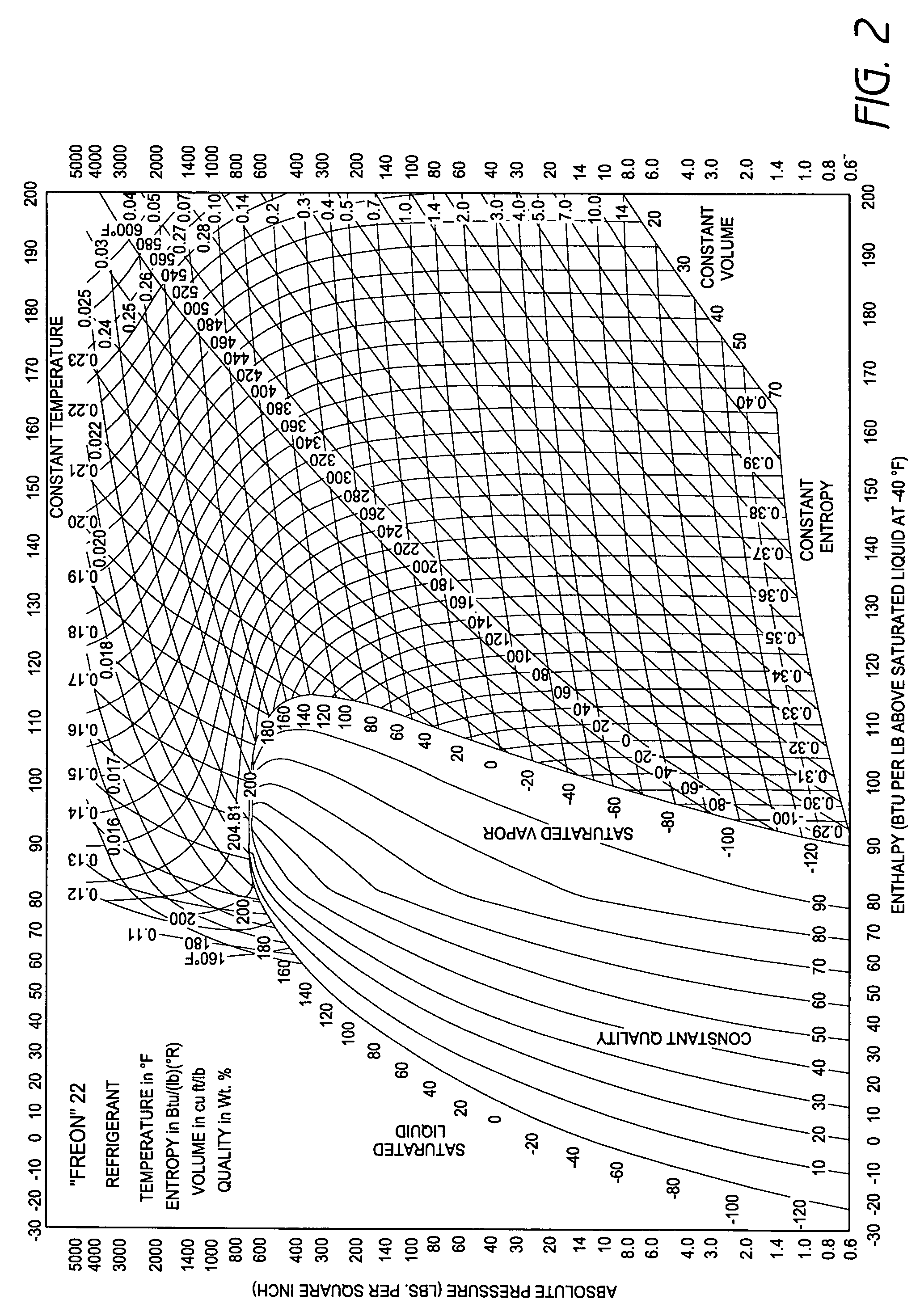
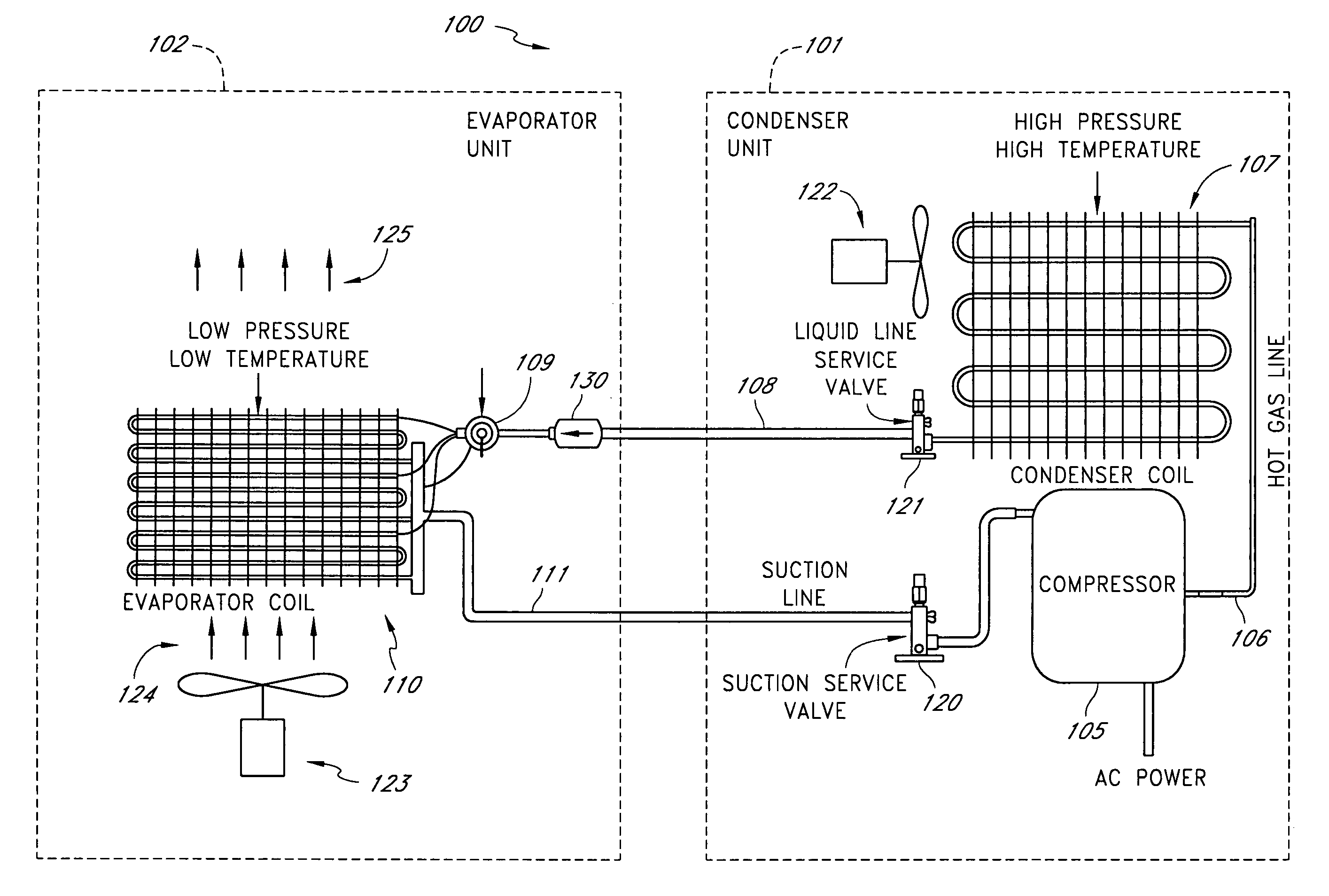
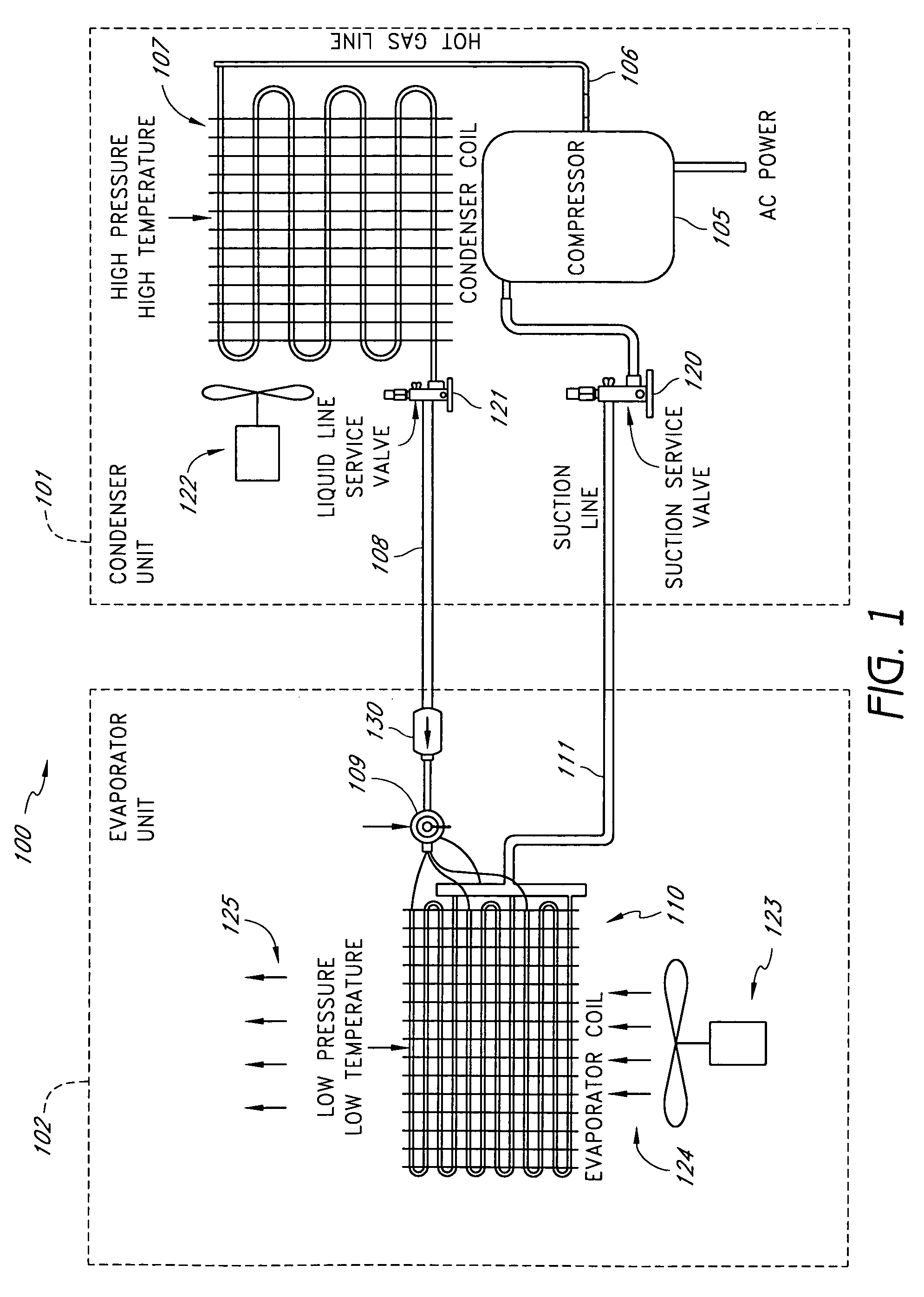
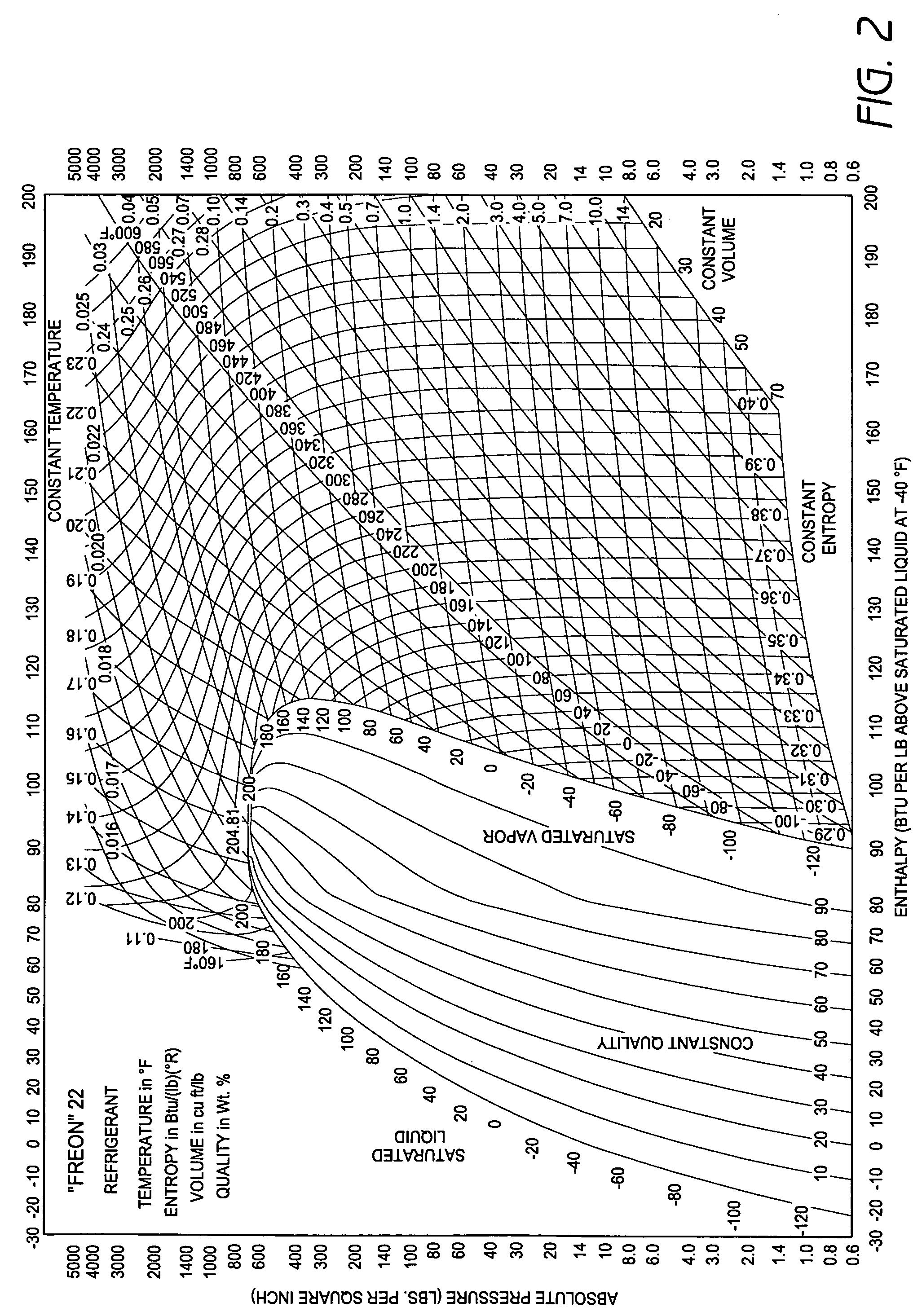
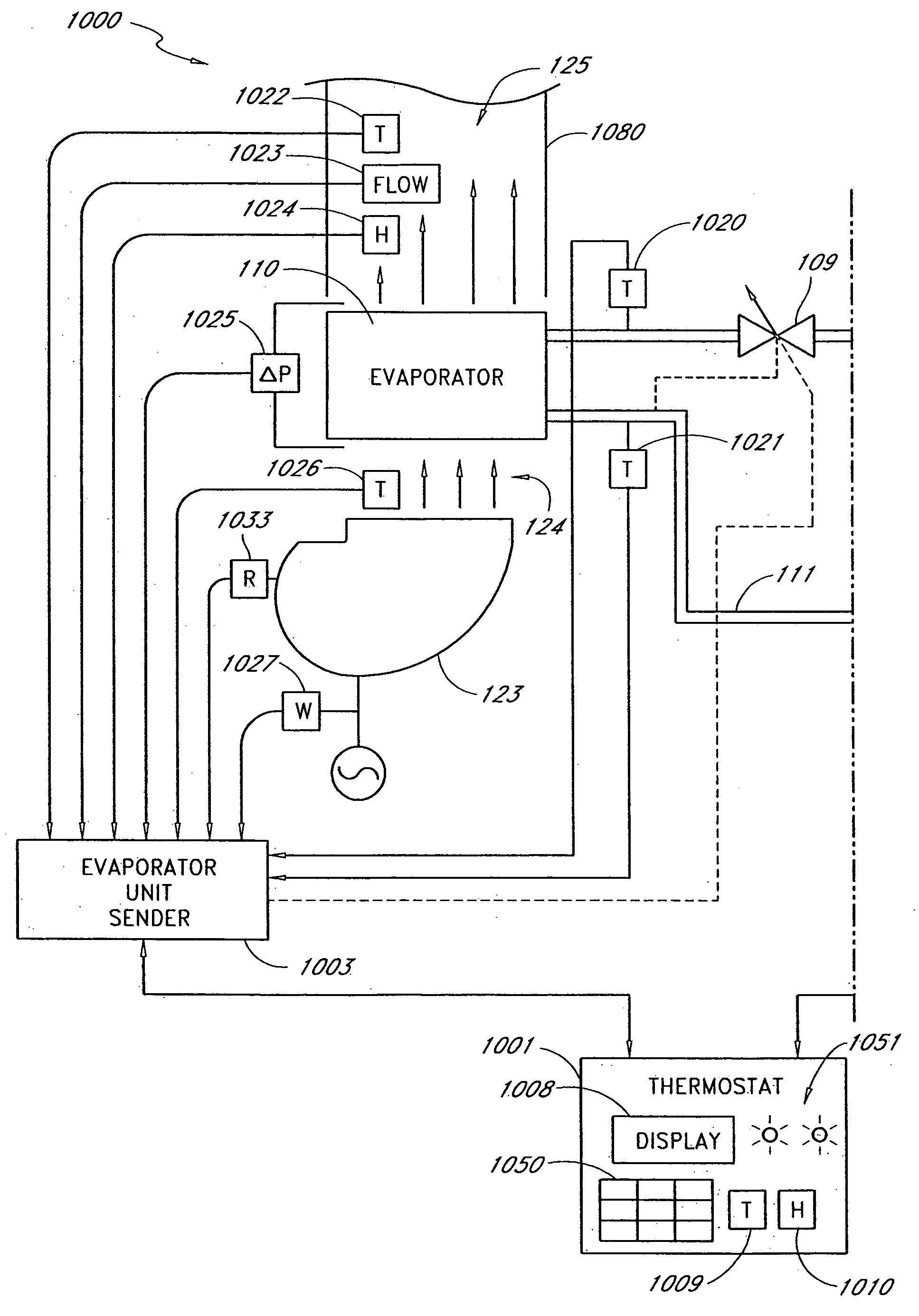
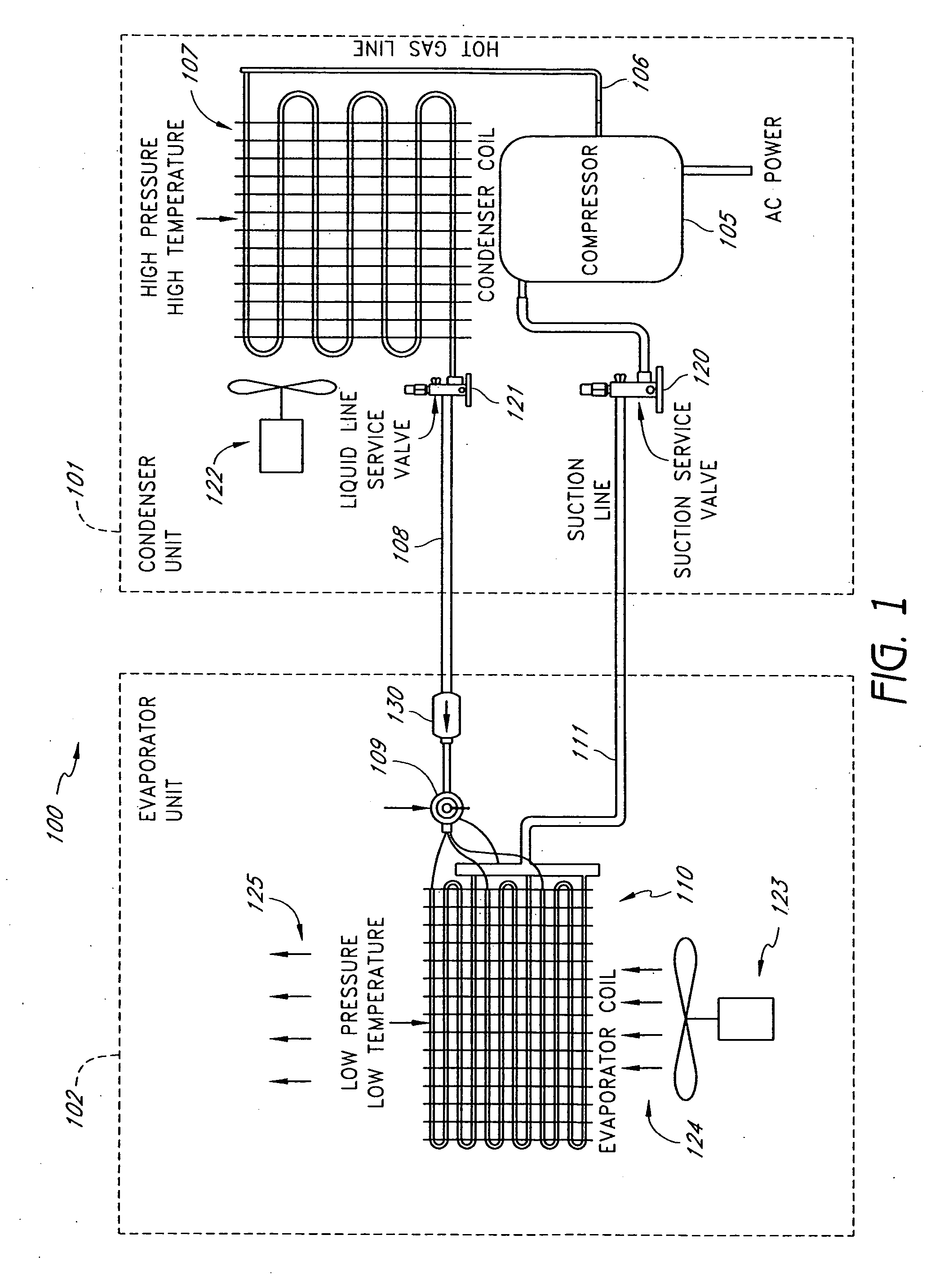
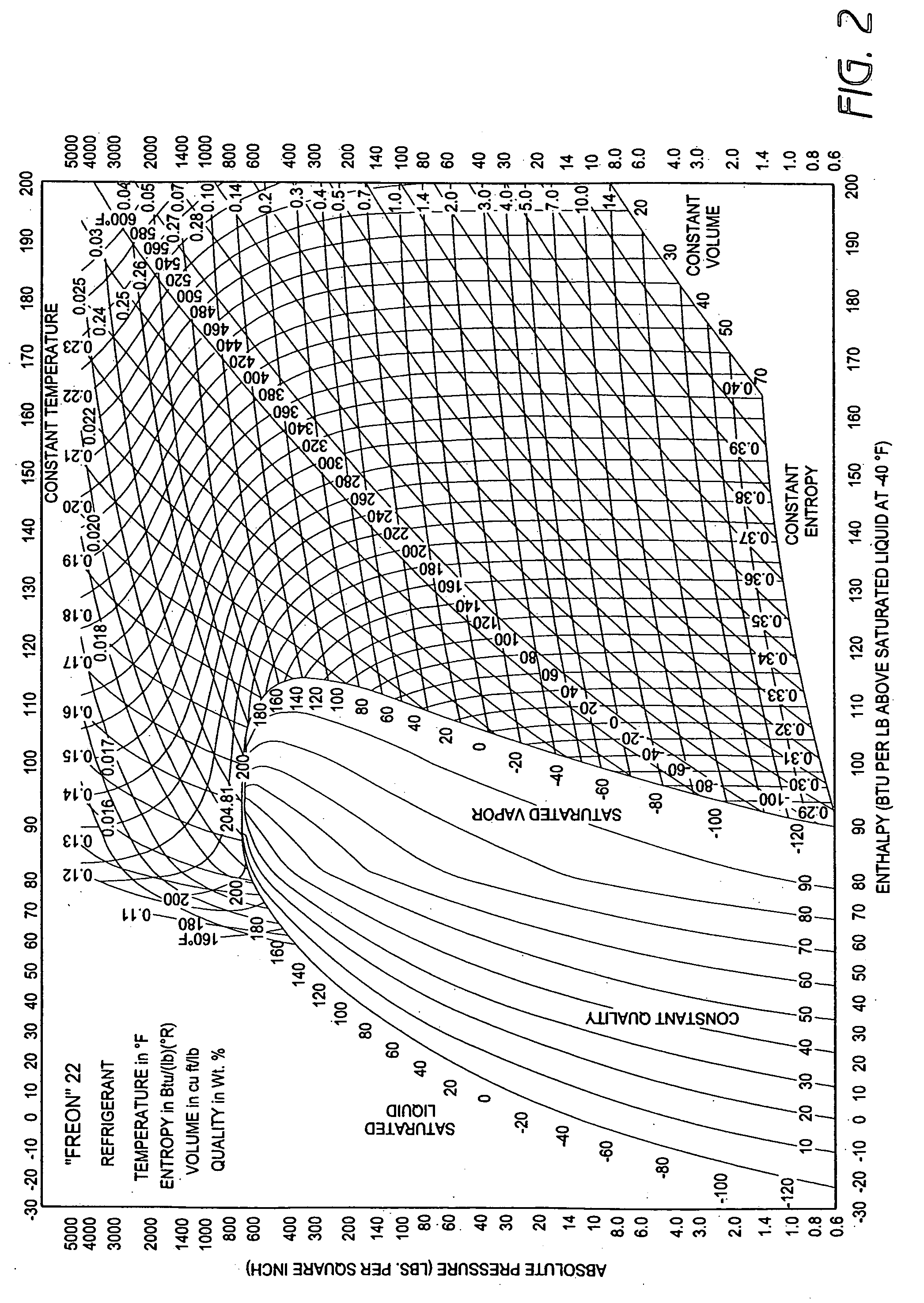
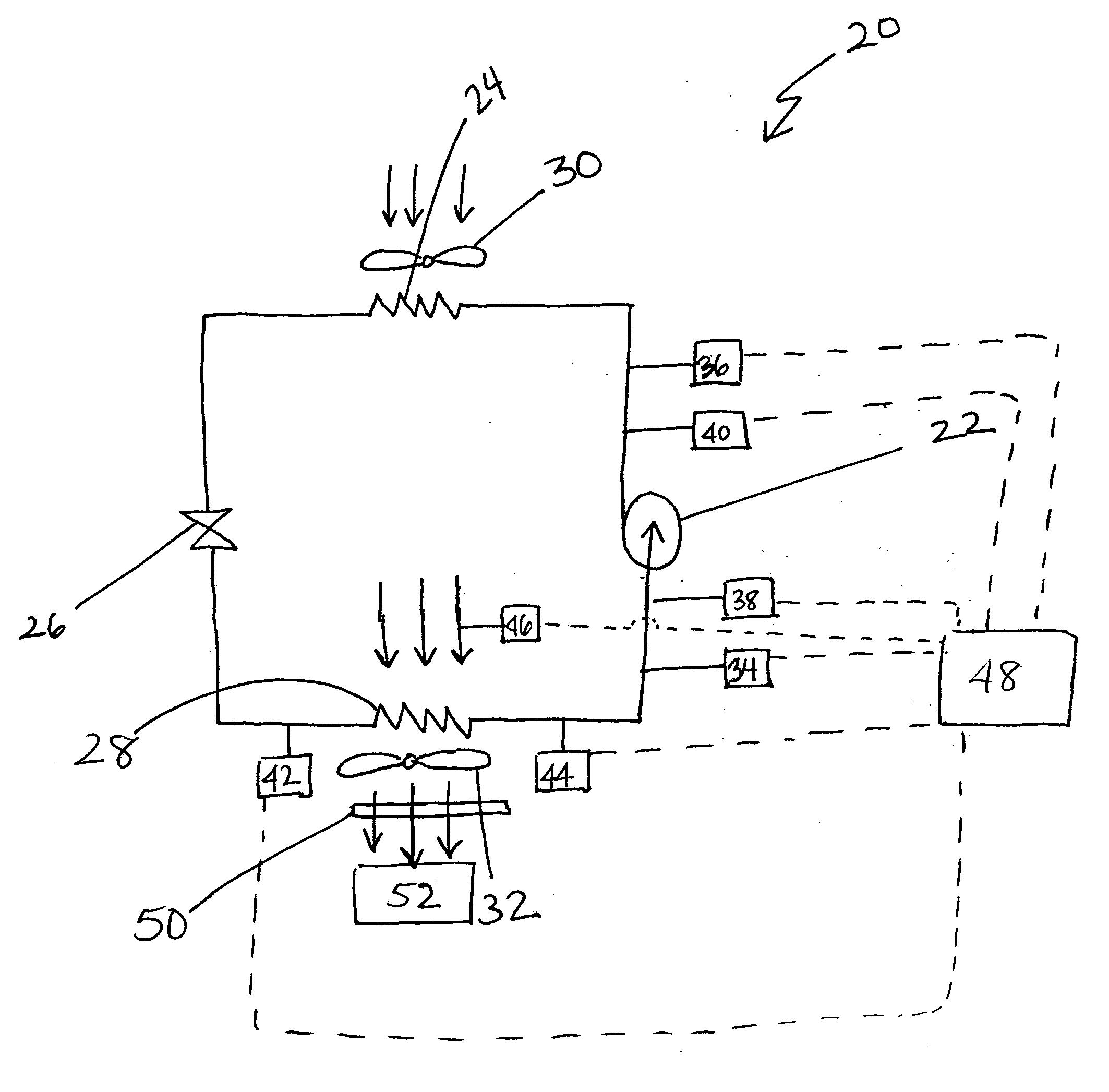
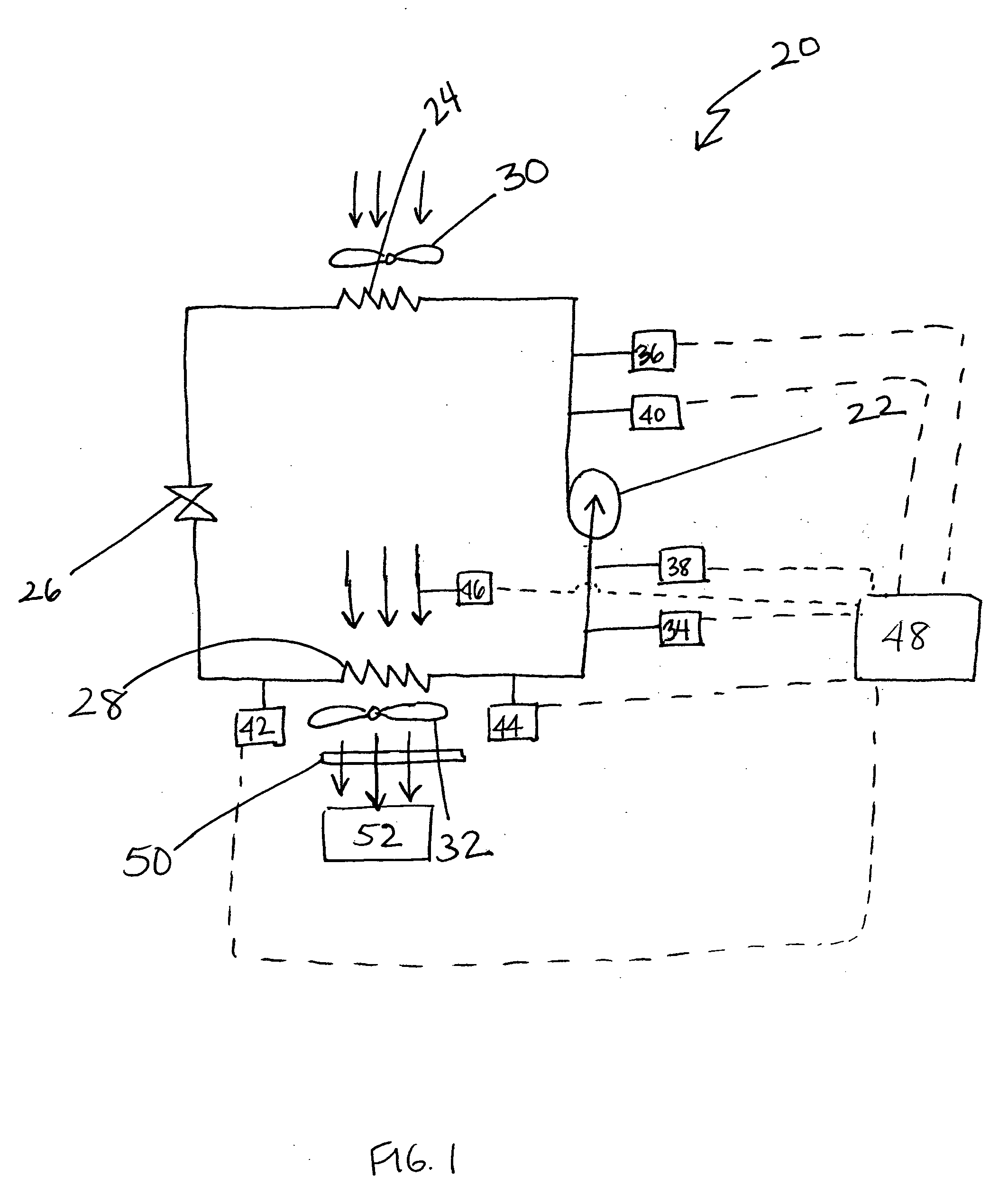
Method and apparatus for monitoring refrigerant-cycle systems
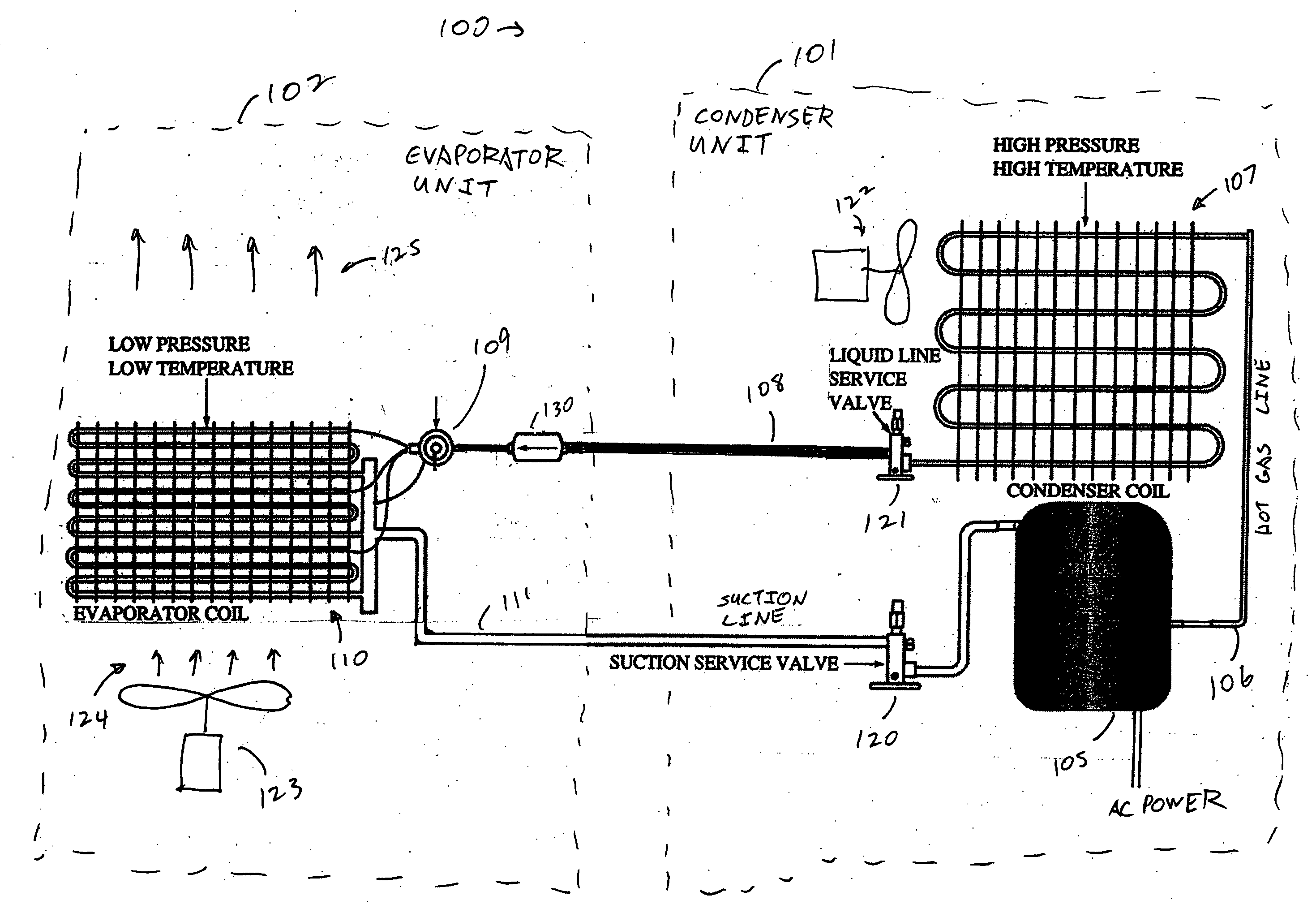
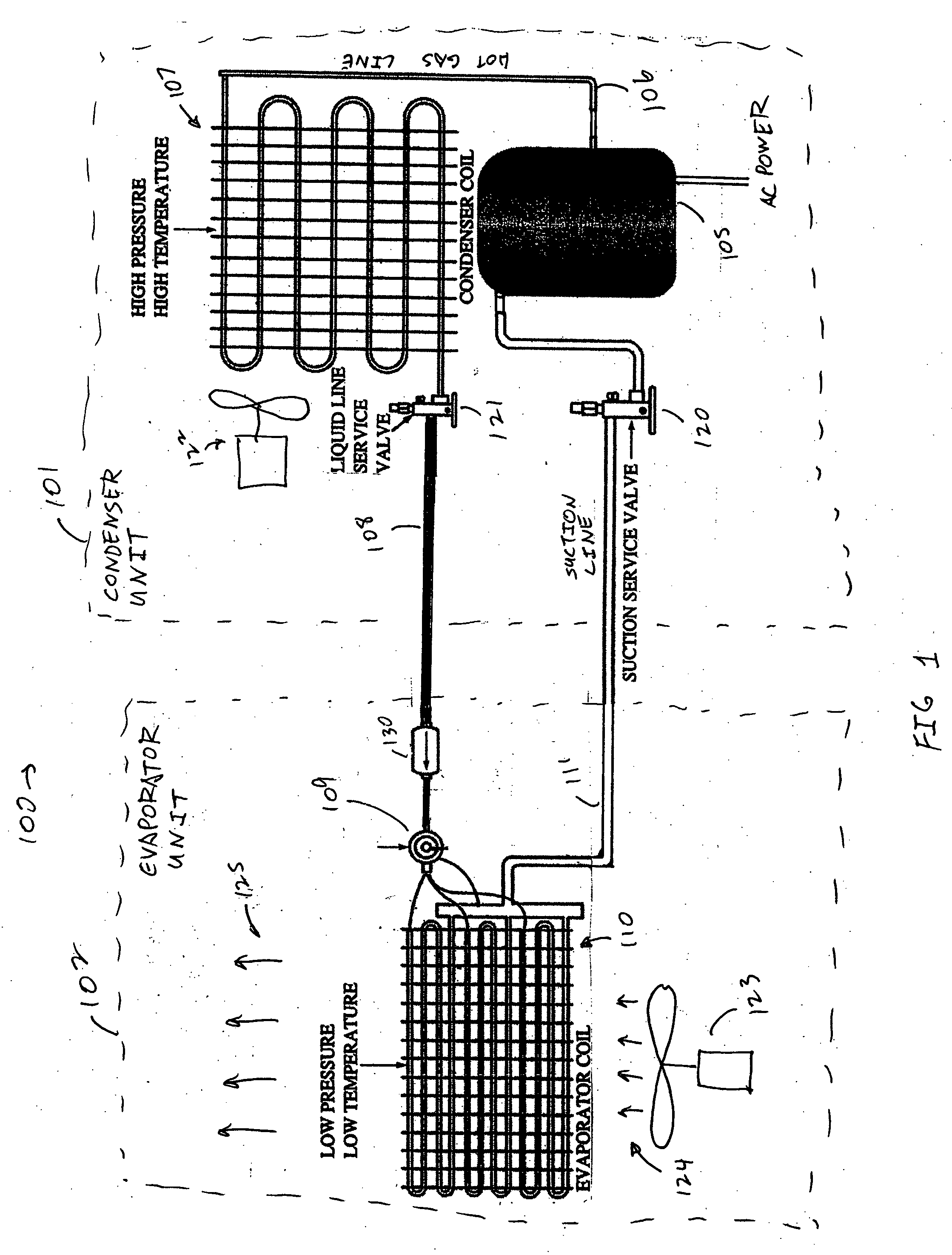
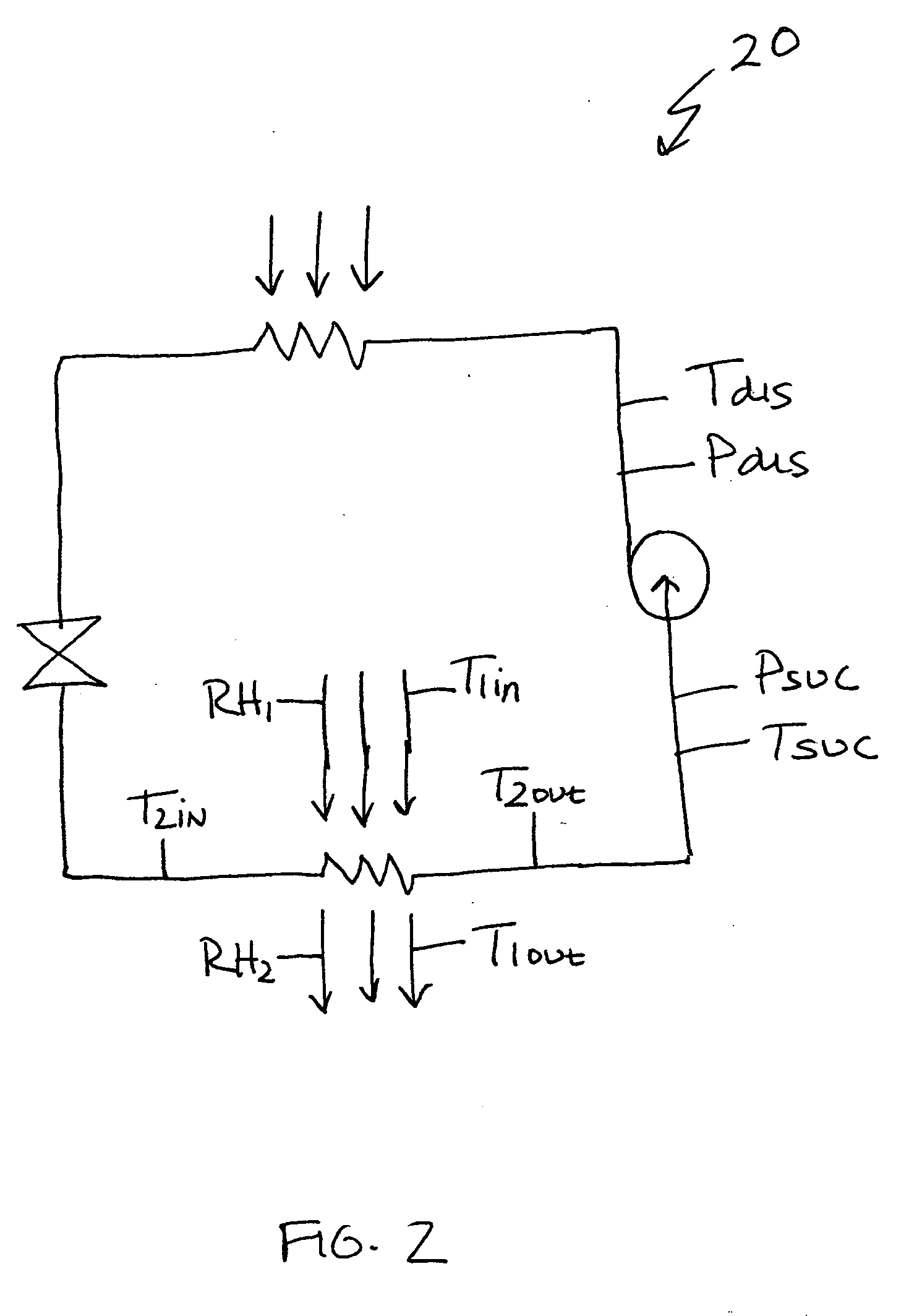
ActiveUS20060032245A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
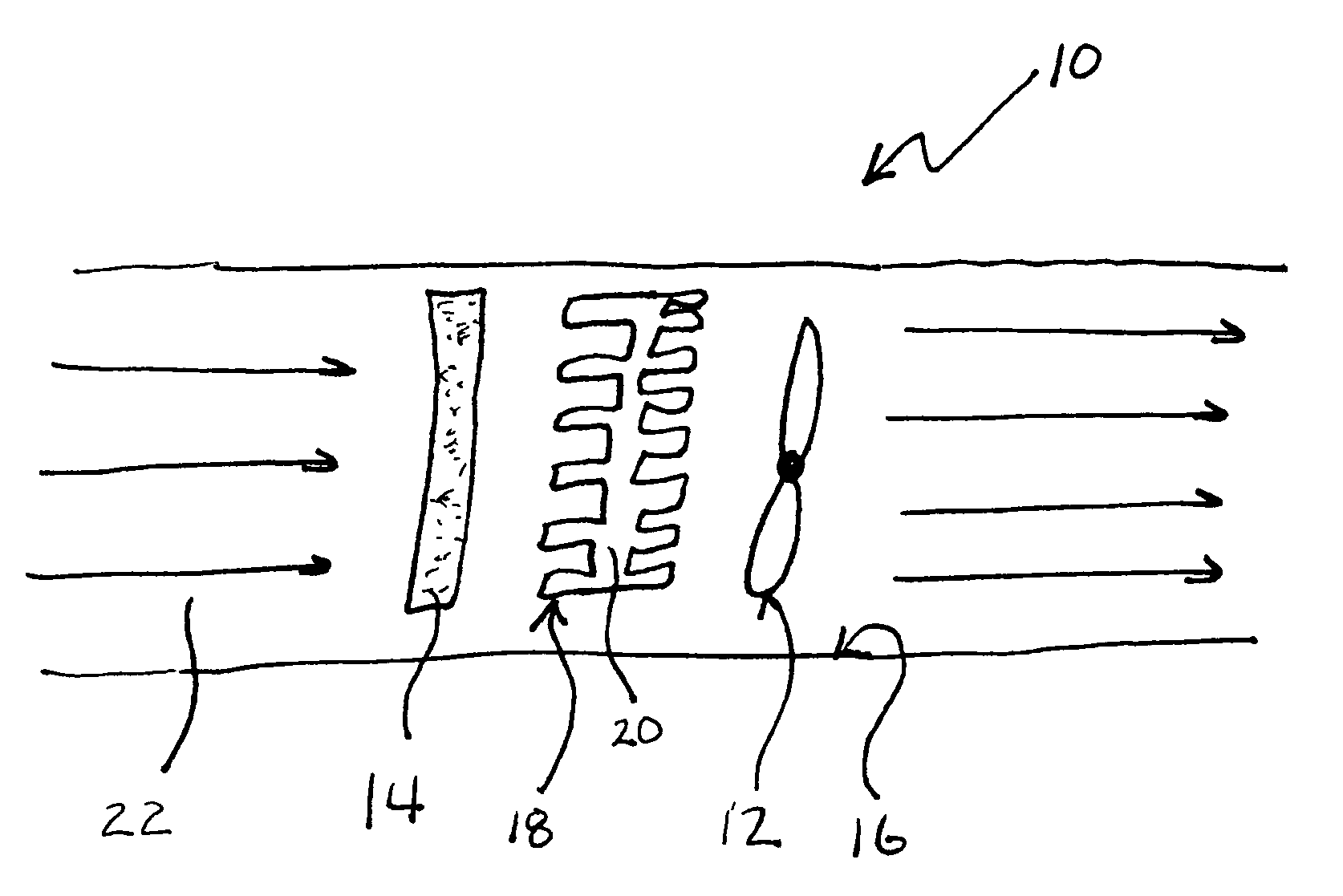
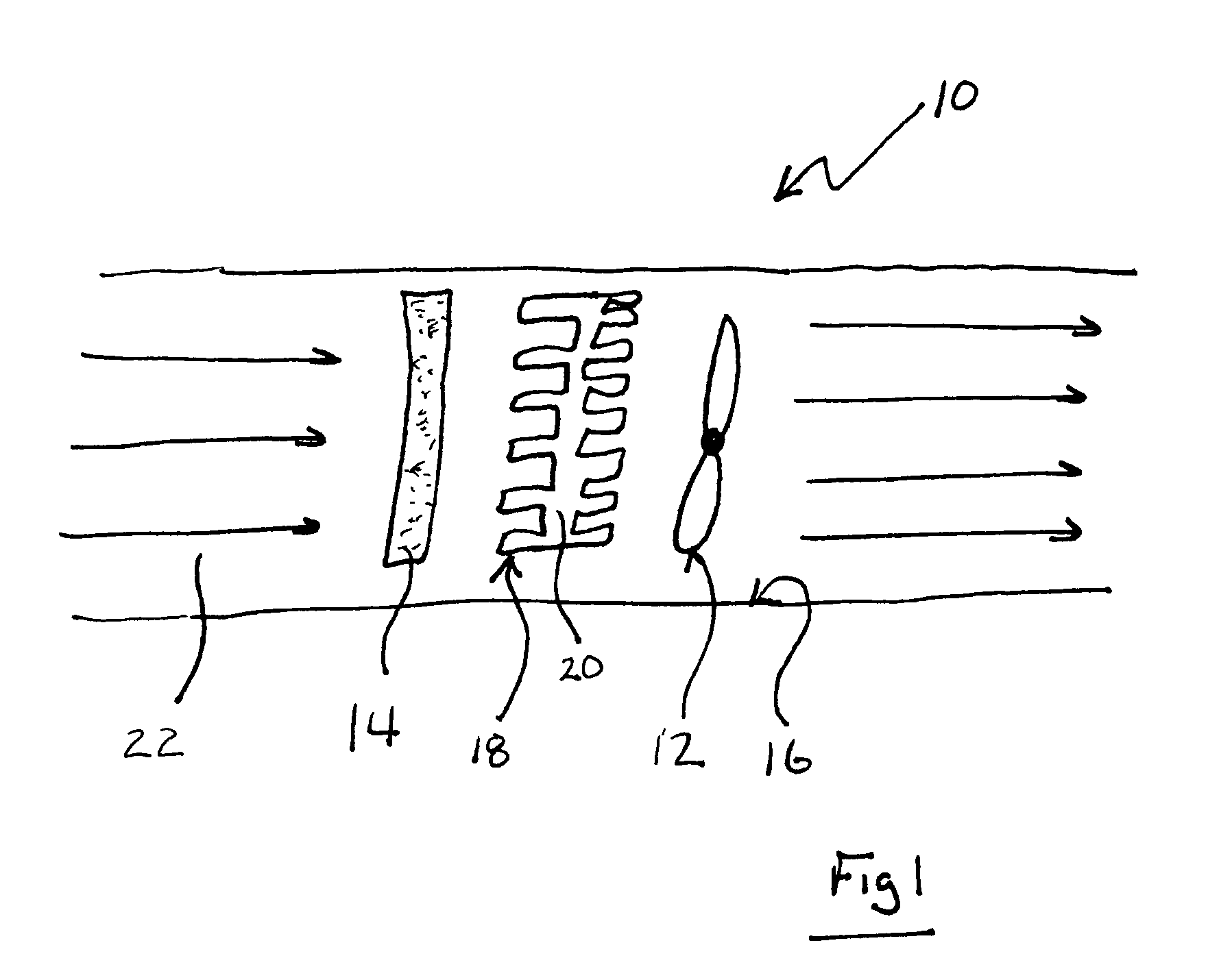
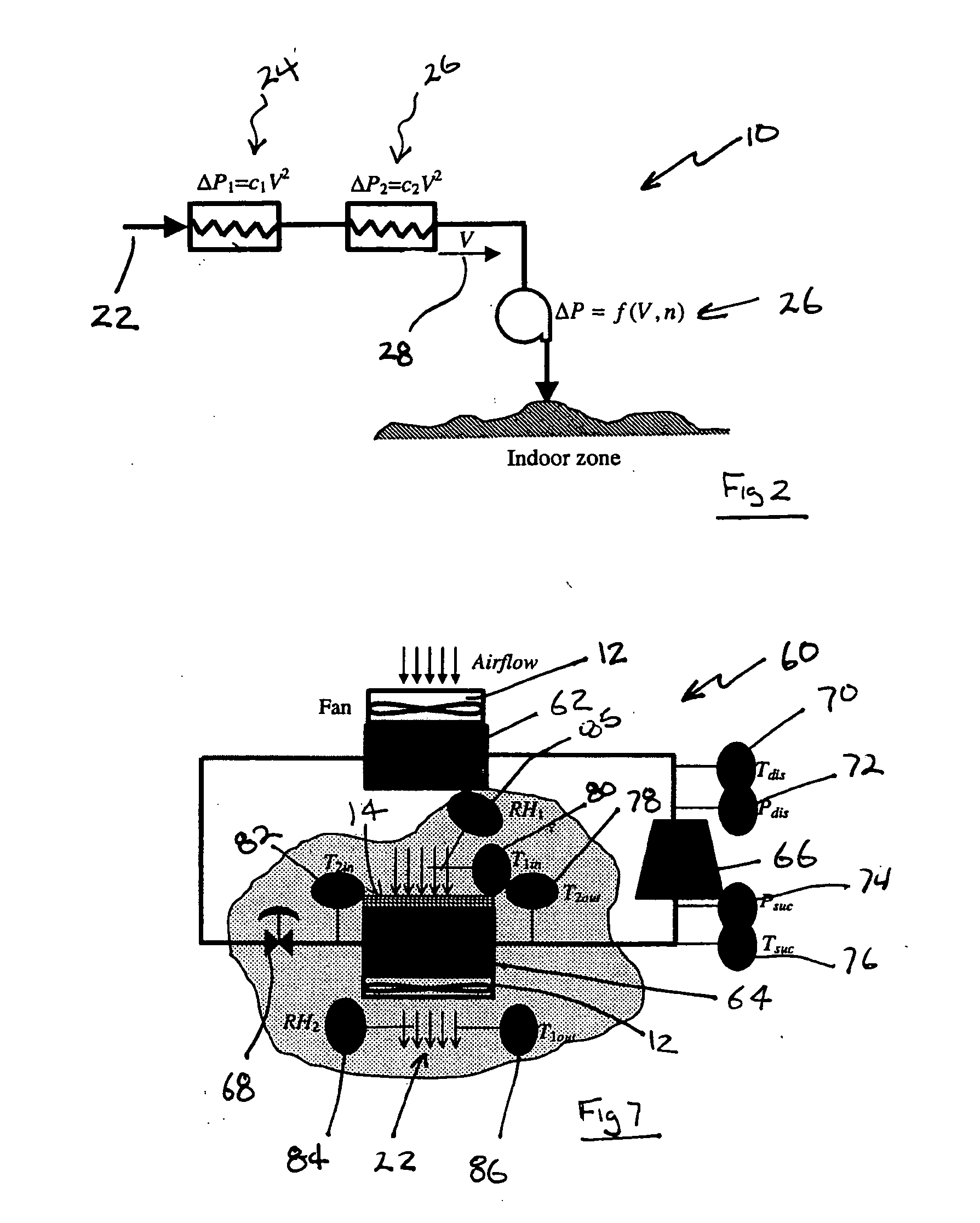
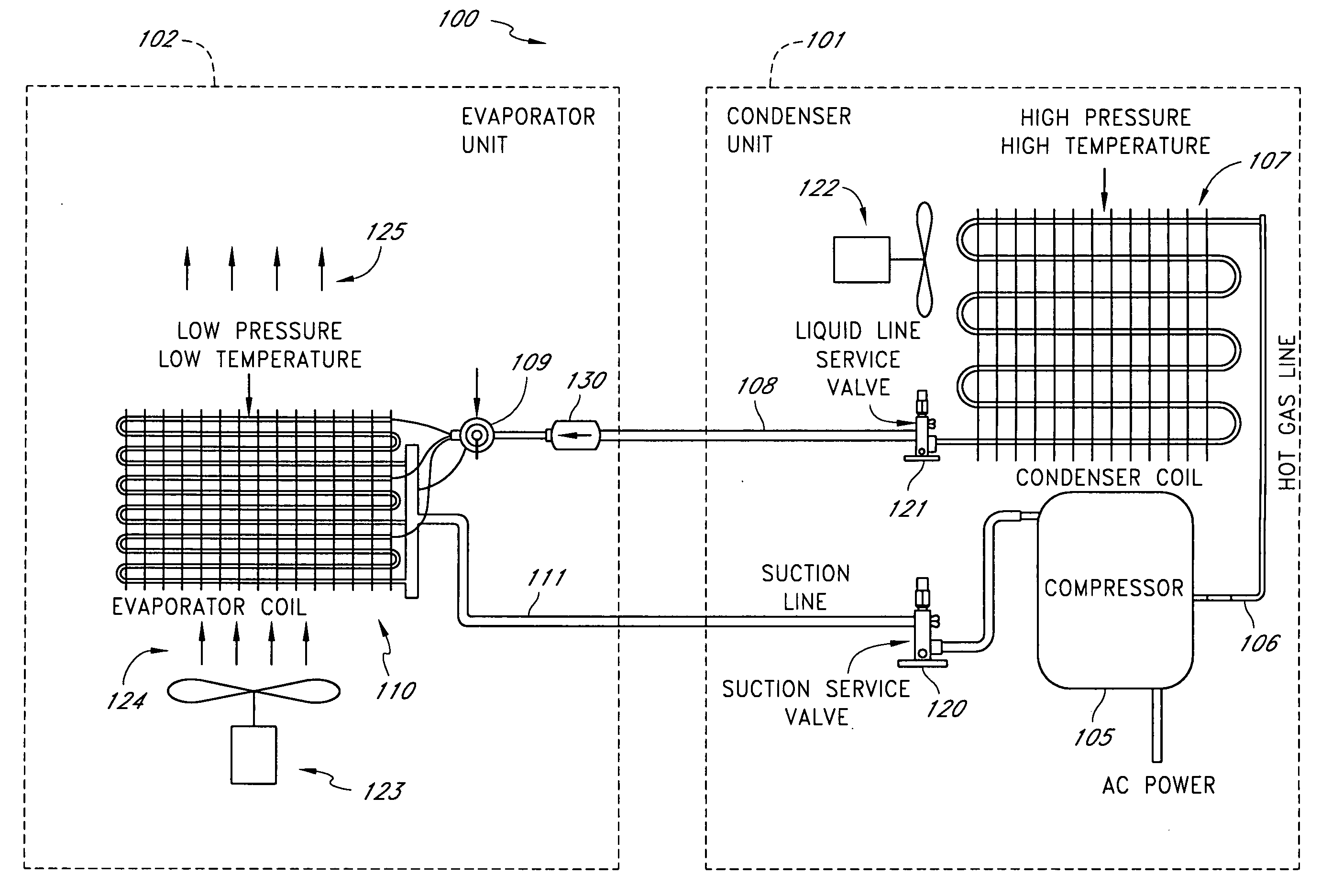
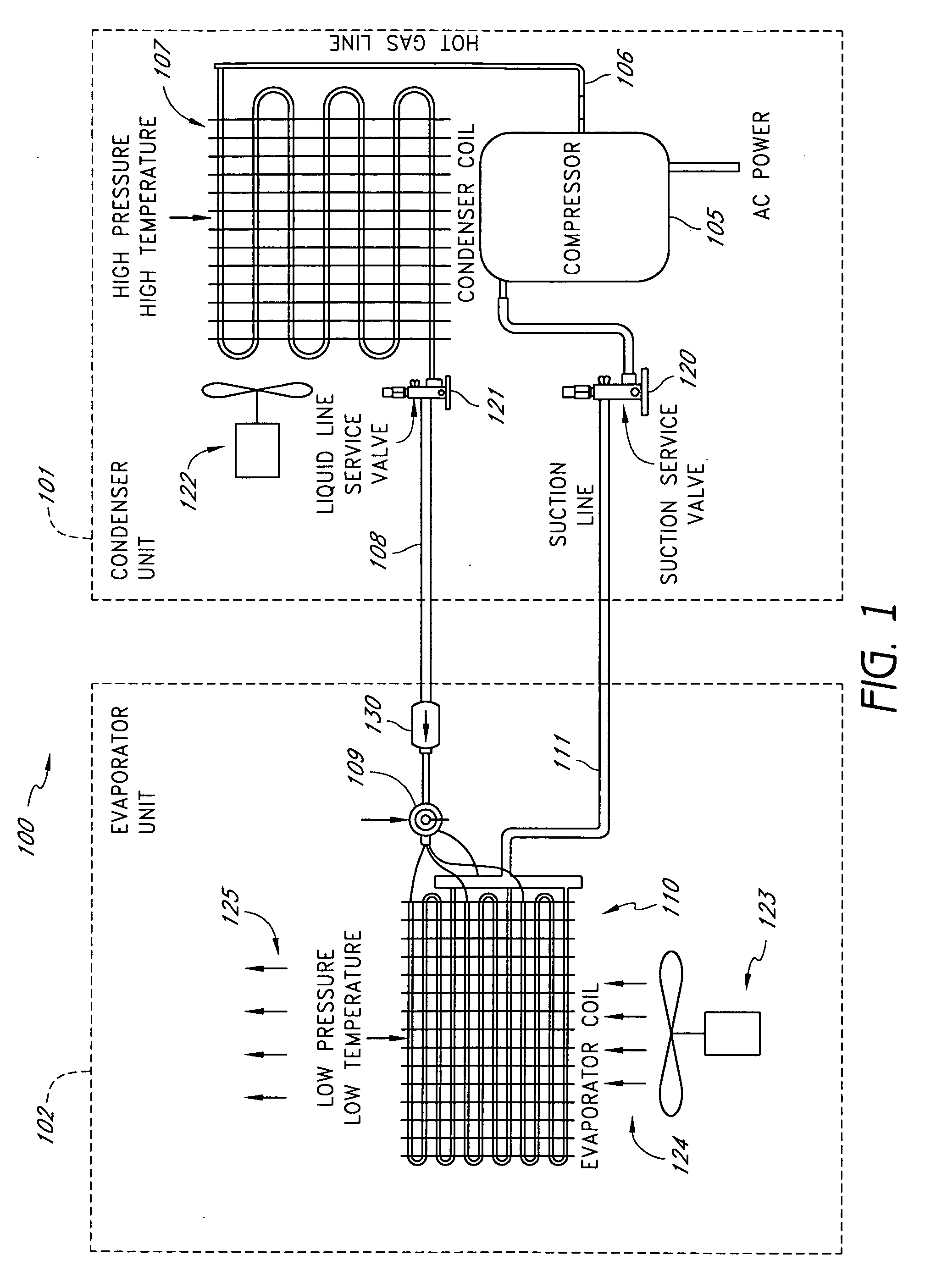
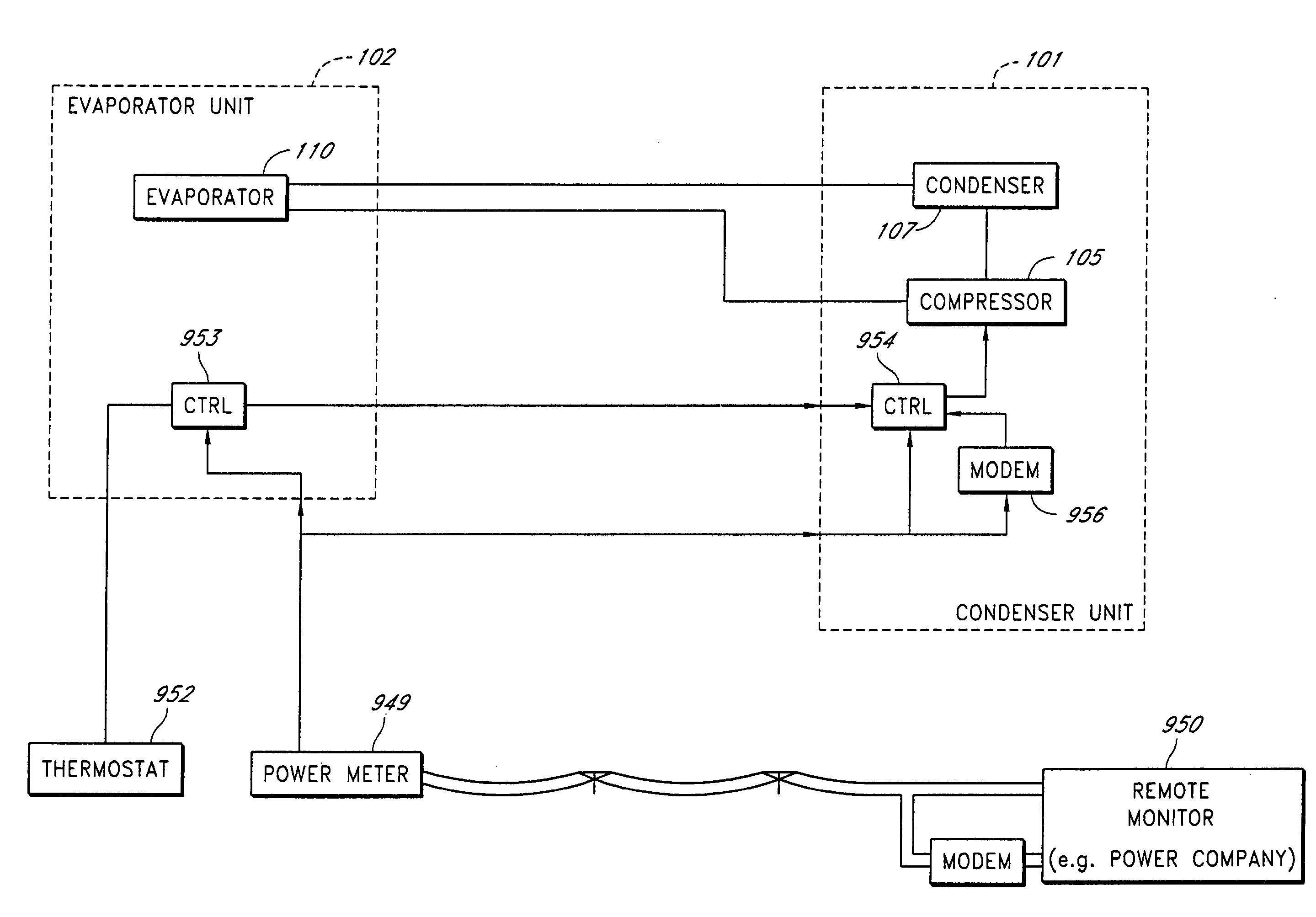
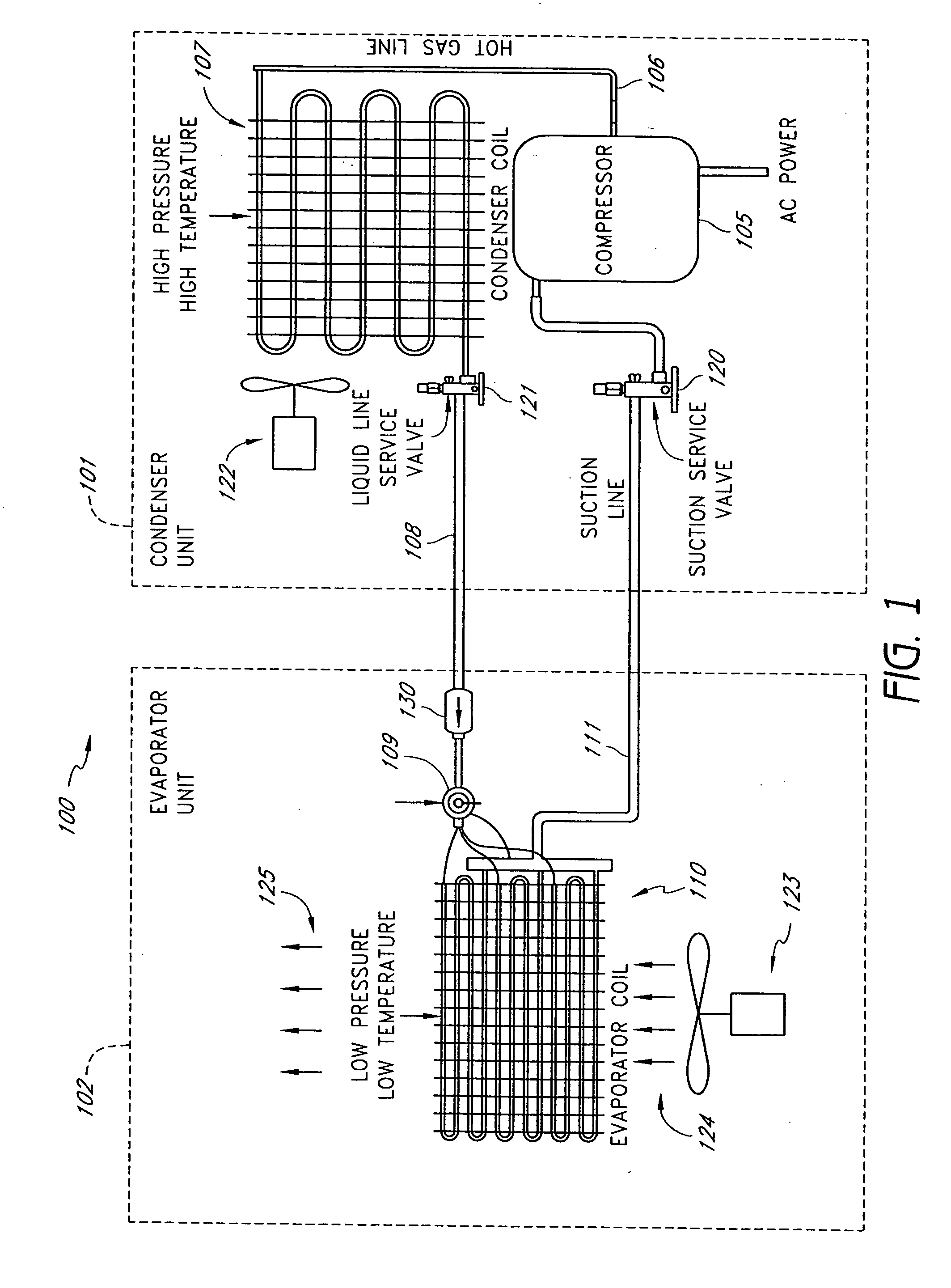
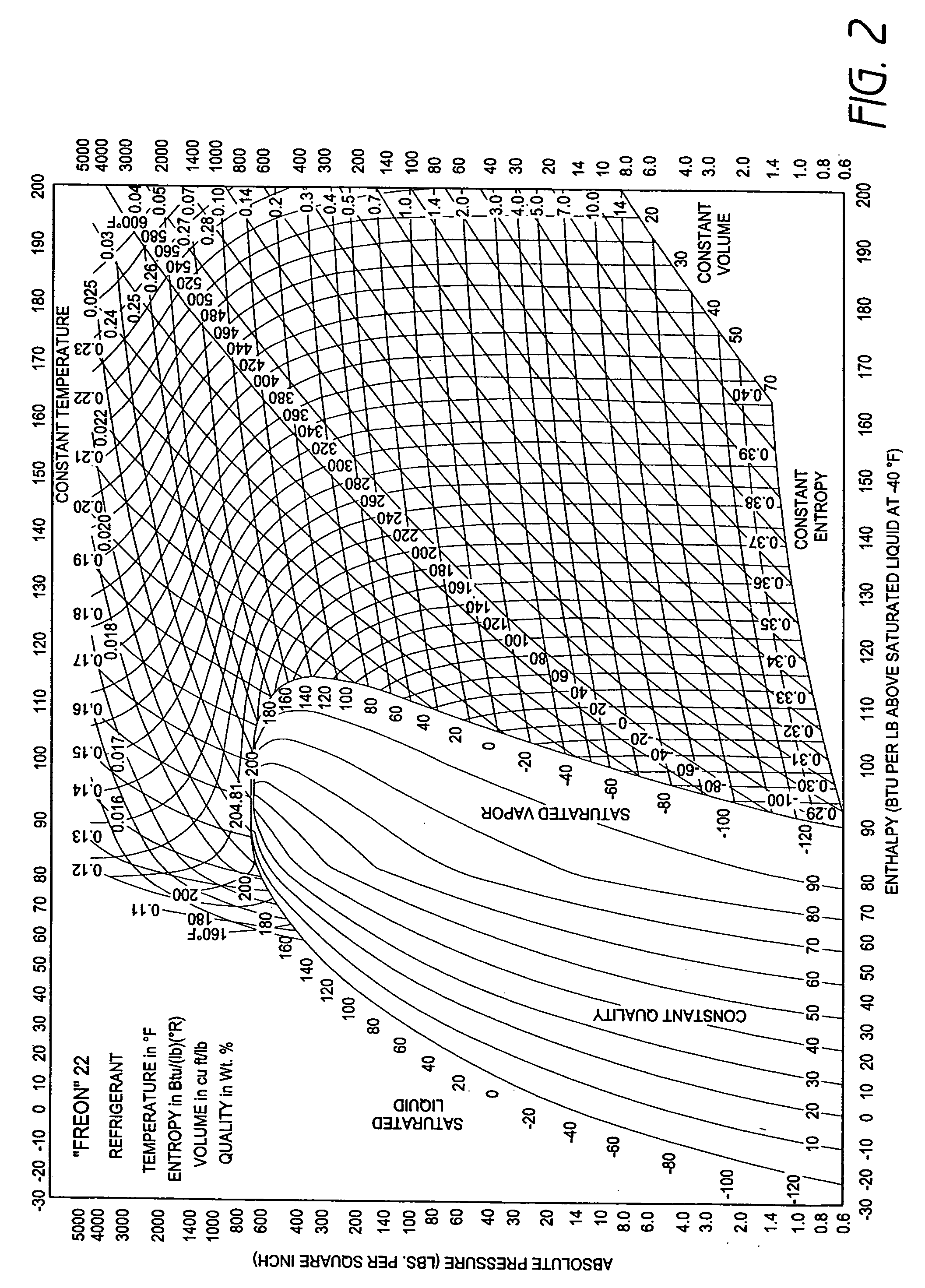
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
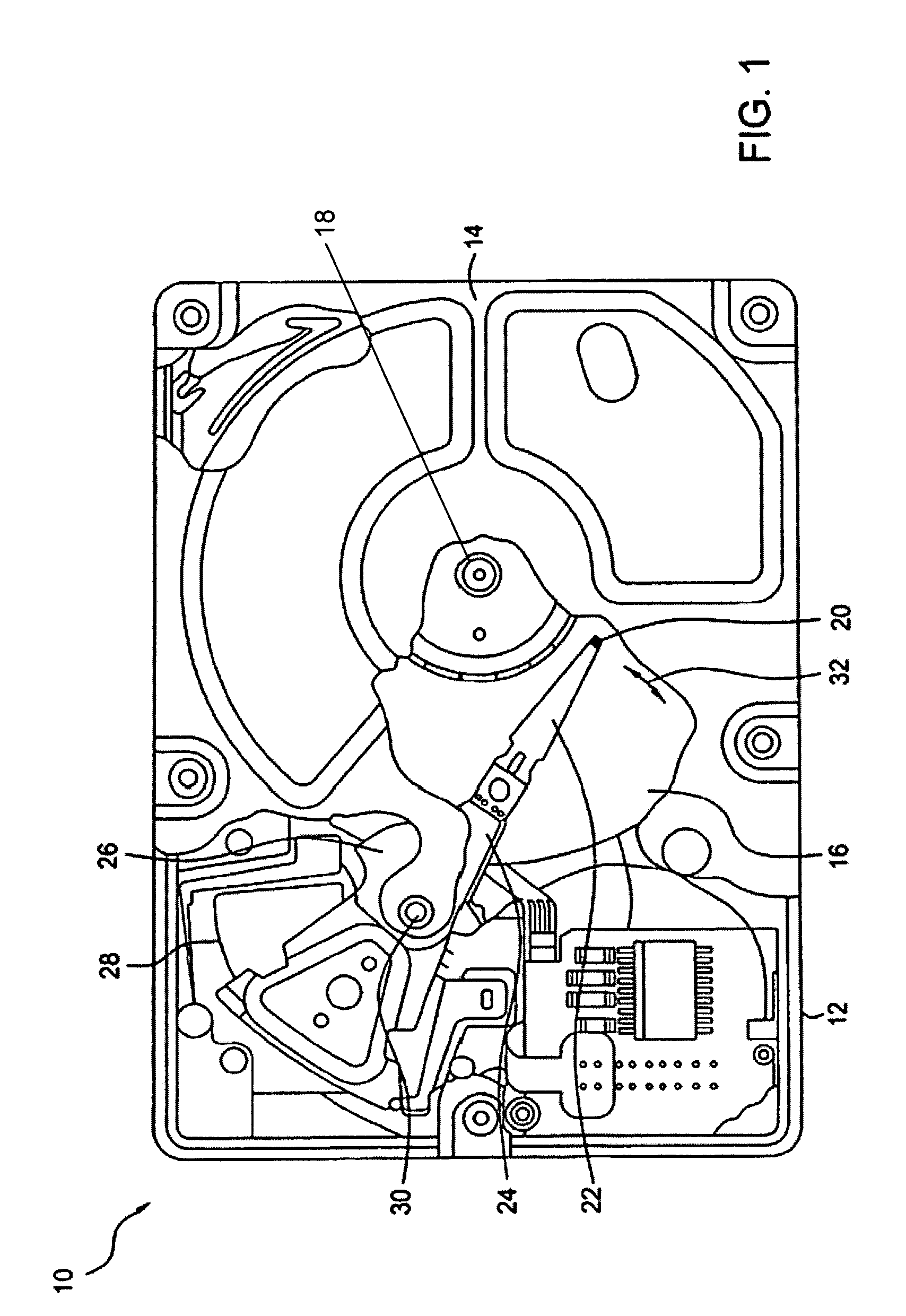
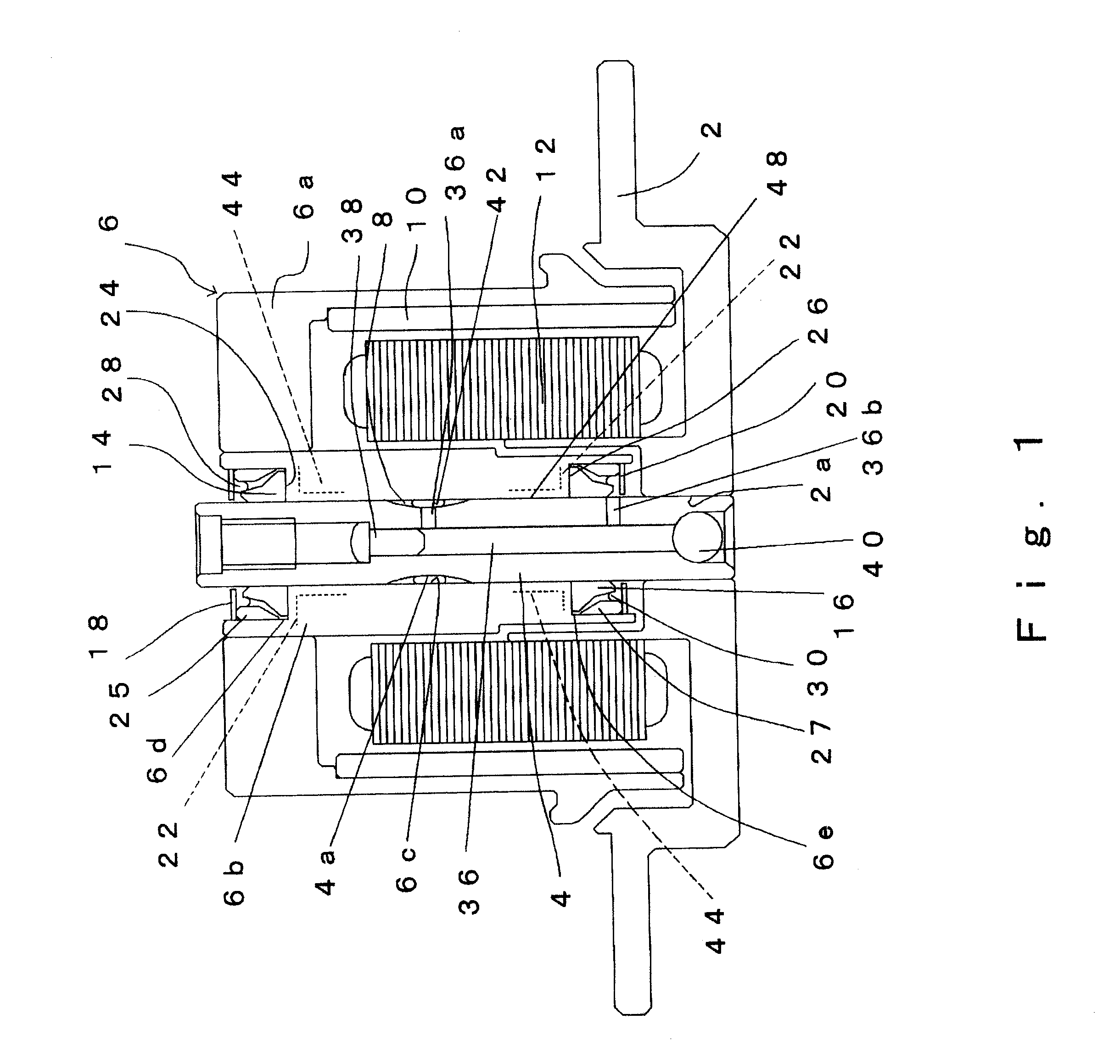
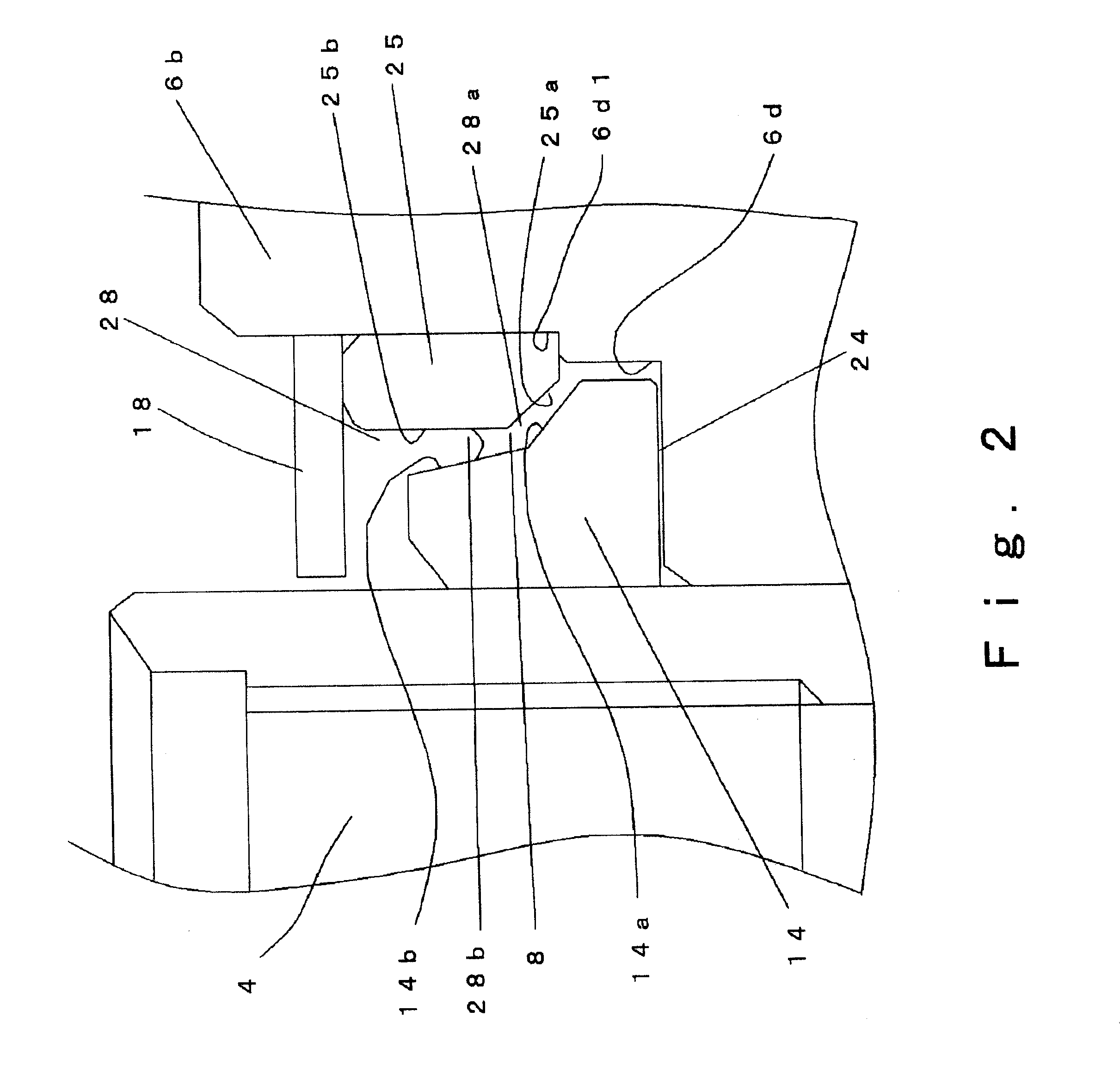
Low profile fluid dynamic bearing motor having increased journal span
InactiveUS6991376B2Reduce dependenceIncrease stiffnessBearing assemblyShaftsEngineeringElectric motor
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Spindle motor
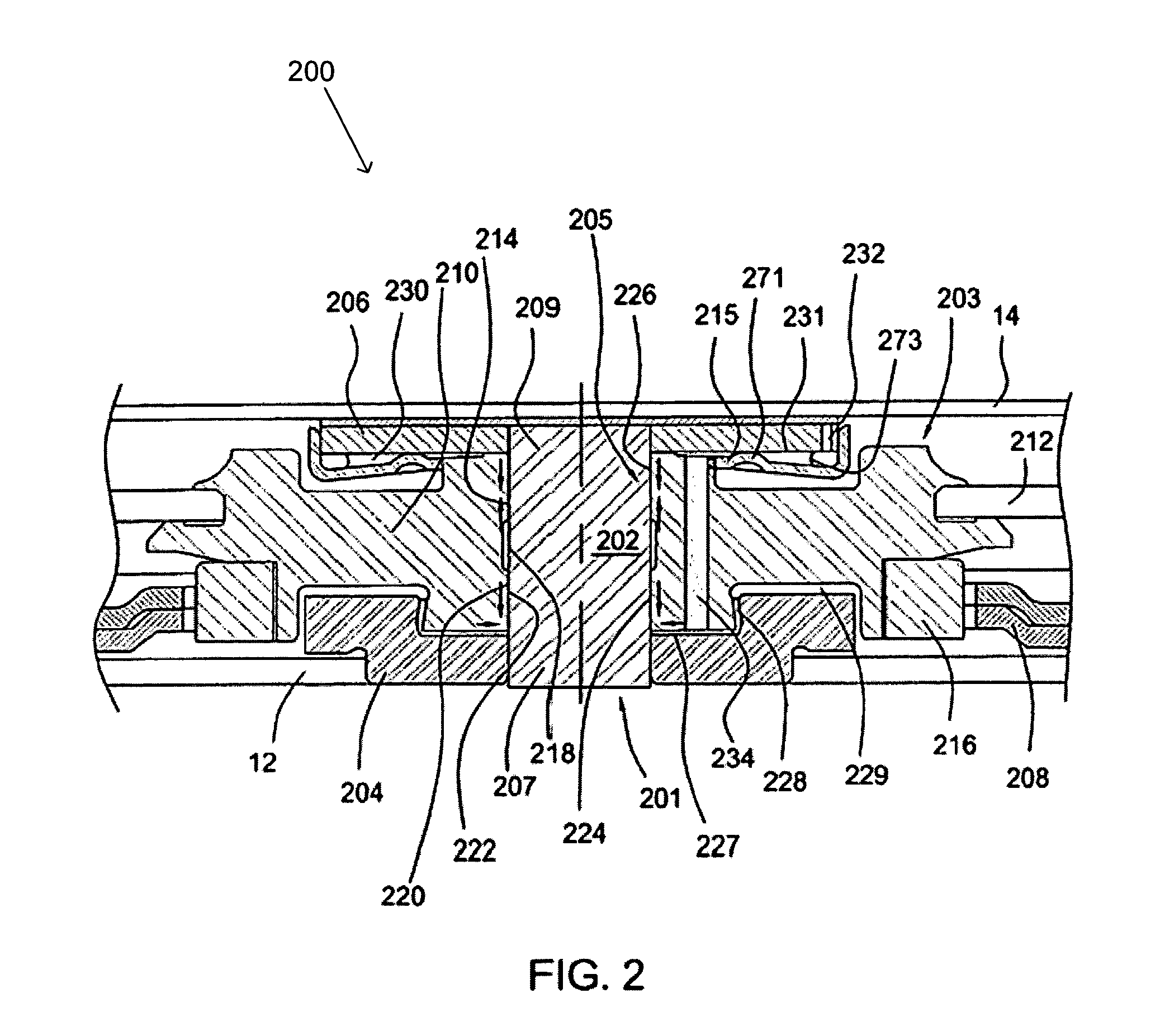
InactiveUS20100207470A1Easily and intuitively control interfaceMore fluidShaftsRecord information storageElectric machineThrust bearing
Disclosed herein is a spindle motor including a journal bearing and a thrust bearing, thus preventing the lack of fluid occurring as a result of the evaporation or scattering of fluid, and making it easy to control the injected amount of fluid. The spindle motor includes a rotating shaft having a thrust plate inserted perpendicularly into the upper portion thereof. A sleeve accommodates and rotatably supports the rotating shaft. A plate is provided such that the sleeve is secured to the plate. An inner cap is secured to the sleeve in such a way as to face the upper surface of the thrust plate, and a first fluid sealing part is defined between the thrust plate and the inner cap. An outer cap is secured to the upper portion of the inner cap, and a second fluid sealing part is defined between the inner and outer caps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Spindle motor having a fluid dynamic bearing system and a stationary shaft
ActiveUS20090140587A1Easy to manufactureEasy dischargeShaftsBearing componentsEngineeringElectromagnetic drive
The invention relates to a spindle motor having a fluid dynamic bearing system comprising axial and radial bearings that contains a rotor component (14) which encloses a stationary shaft (12), which in turn is connected at both its ends to axially aligned bearing parts (16; 18) that are fashioned such that they form capillary sealing gaps (32; 34), a recirculation channel (28) filled with bearing fluid that connects the remote regions of the bearing to each other, and an electromagnetic drive system (42, 44) for driving the rotor component.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
Fluid Dynamic-Pressure Bearing Device and Spindle Motor
ActiveUS20060051001A1Easy maintenanceReduce the overall heightBearing assemblyShaftsEngineeringDynamic pressure
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Motor unit, manufacturing method therefor and recording disk driving apparatus
ActiveUS7088023B1Increase production capacityHigh bonding strengthBearing assemblyShaft assemblyAdhesiveEngineering
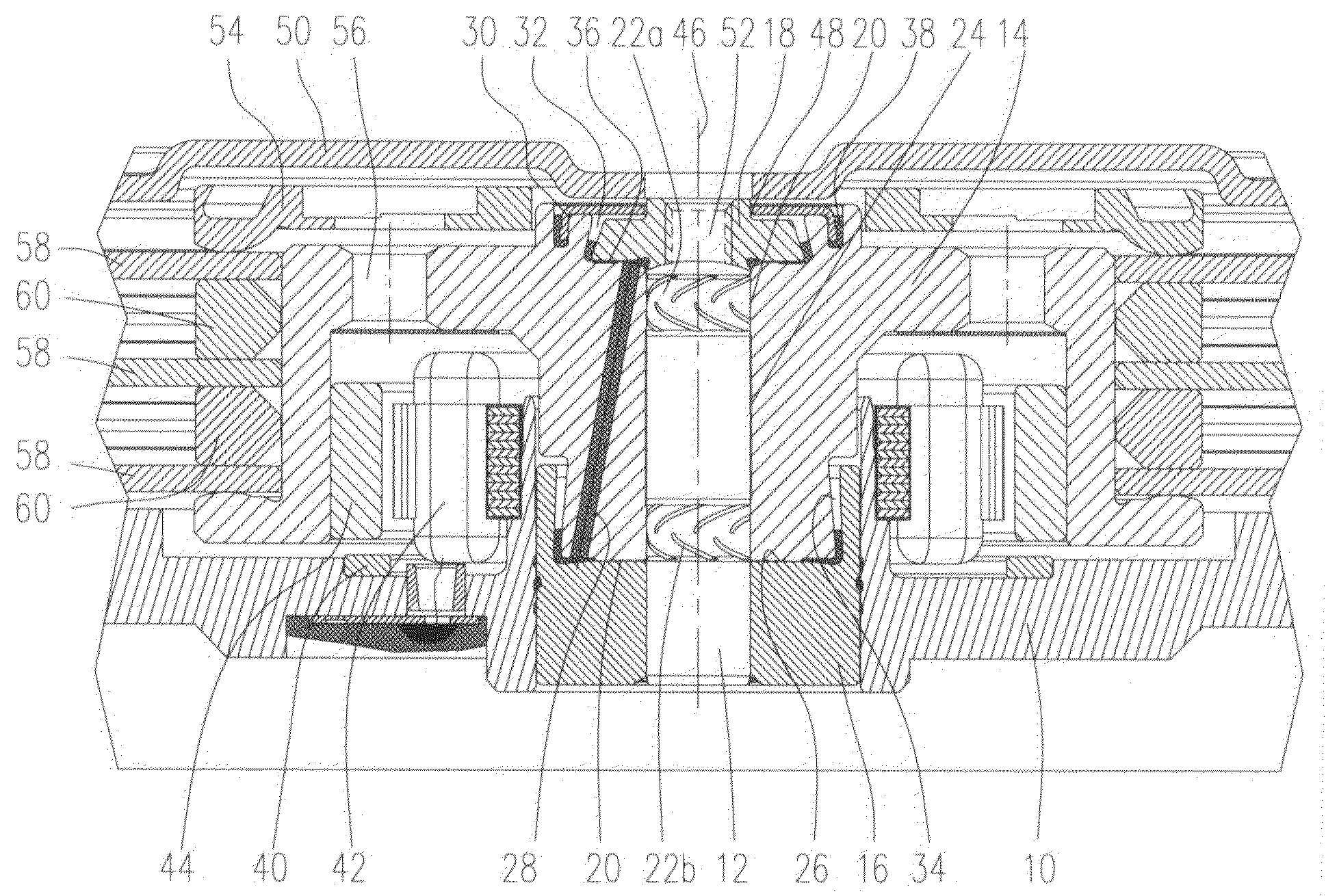
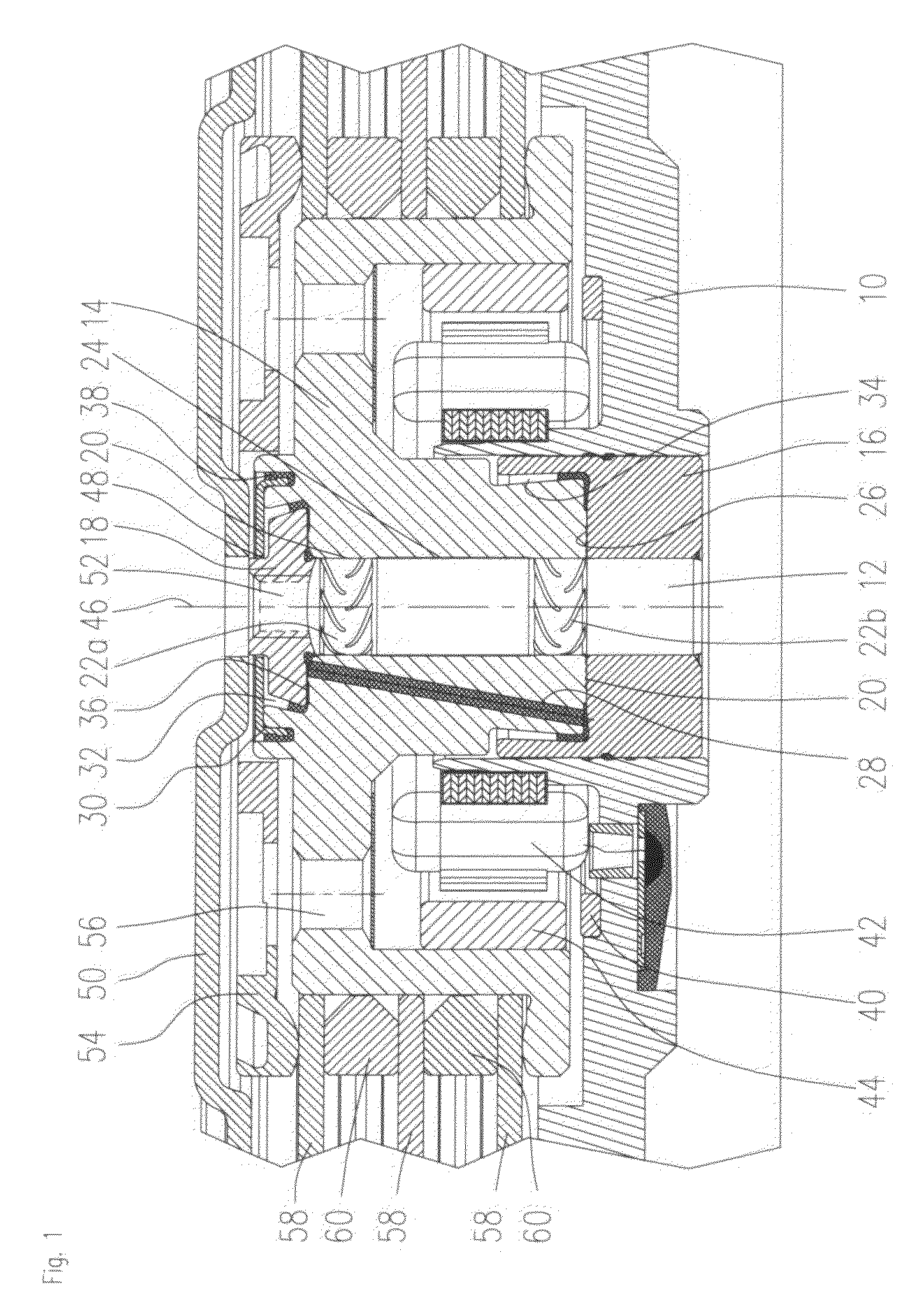
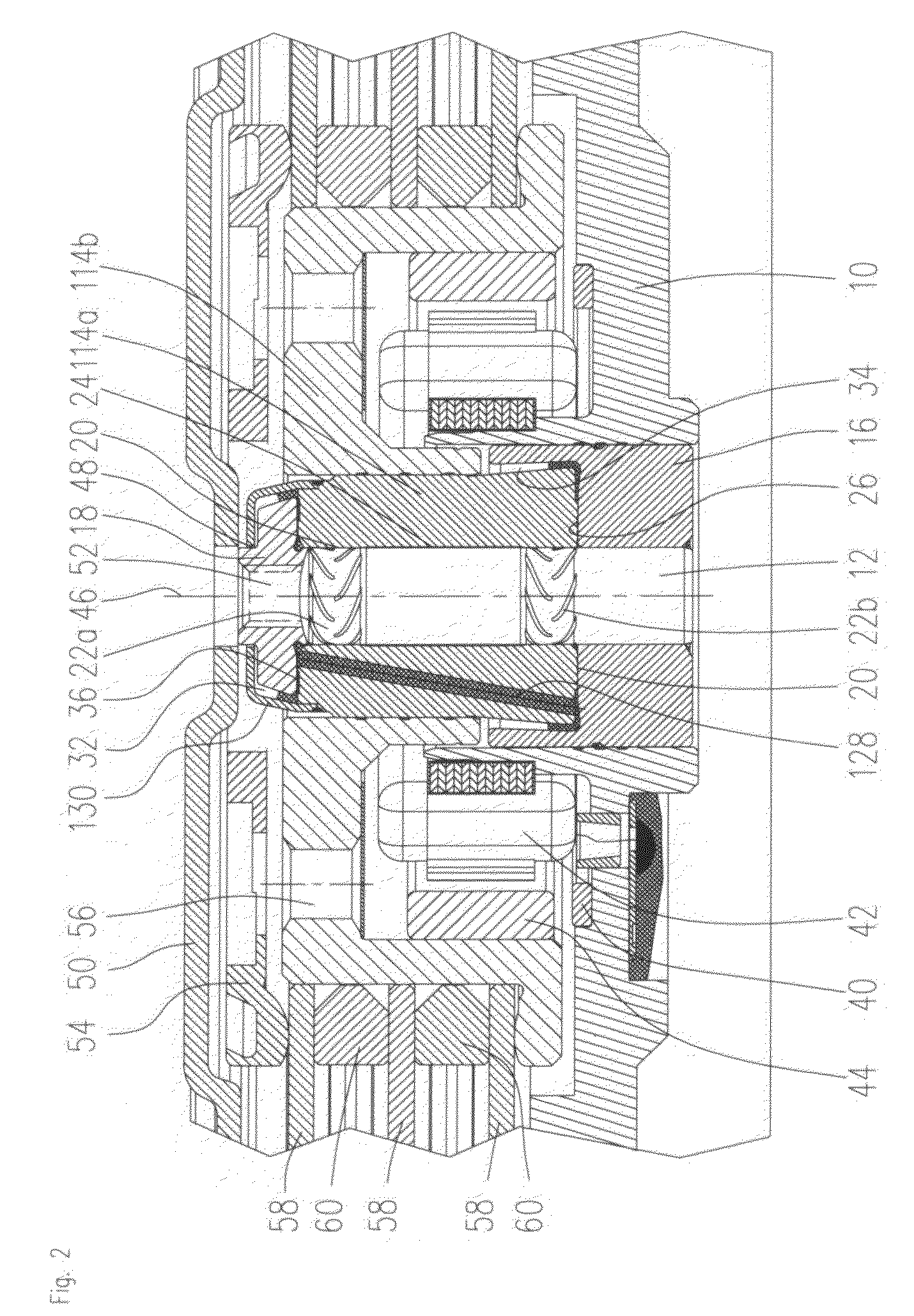
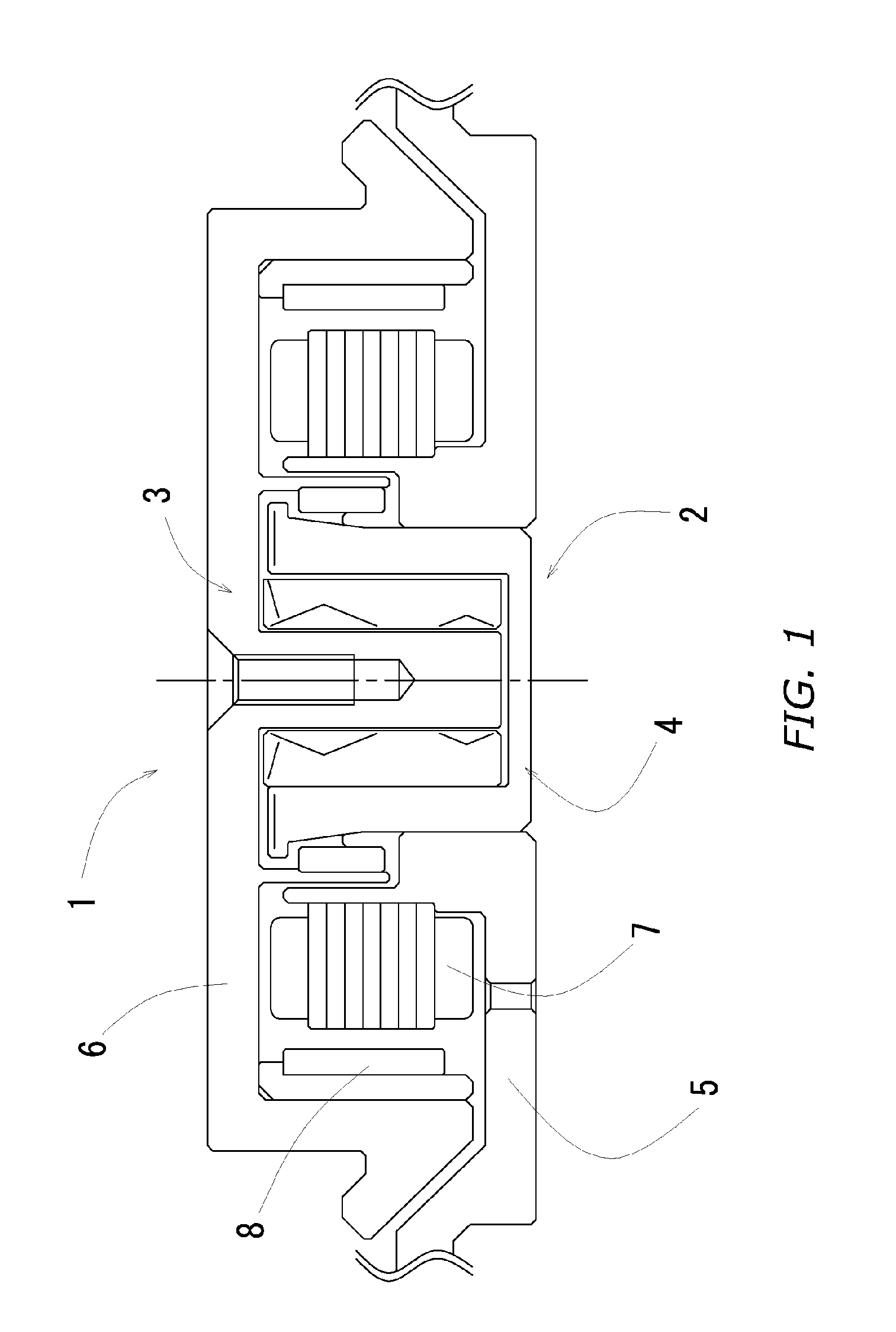
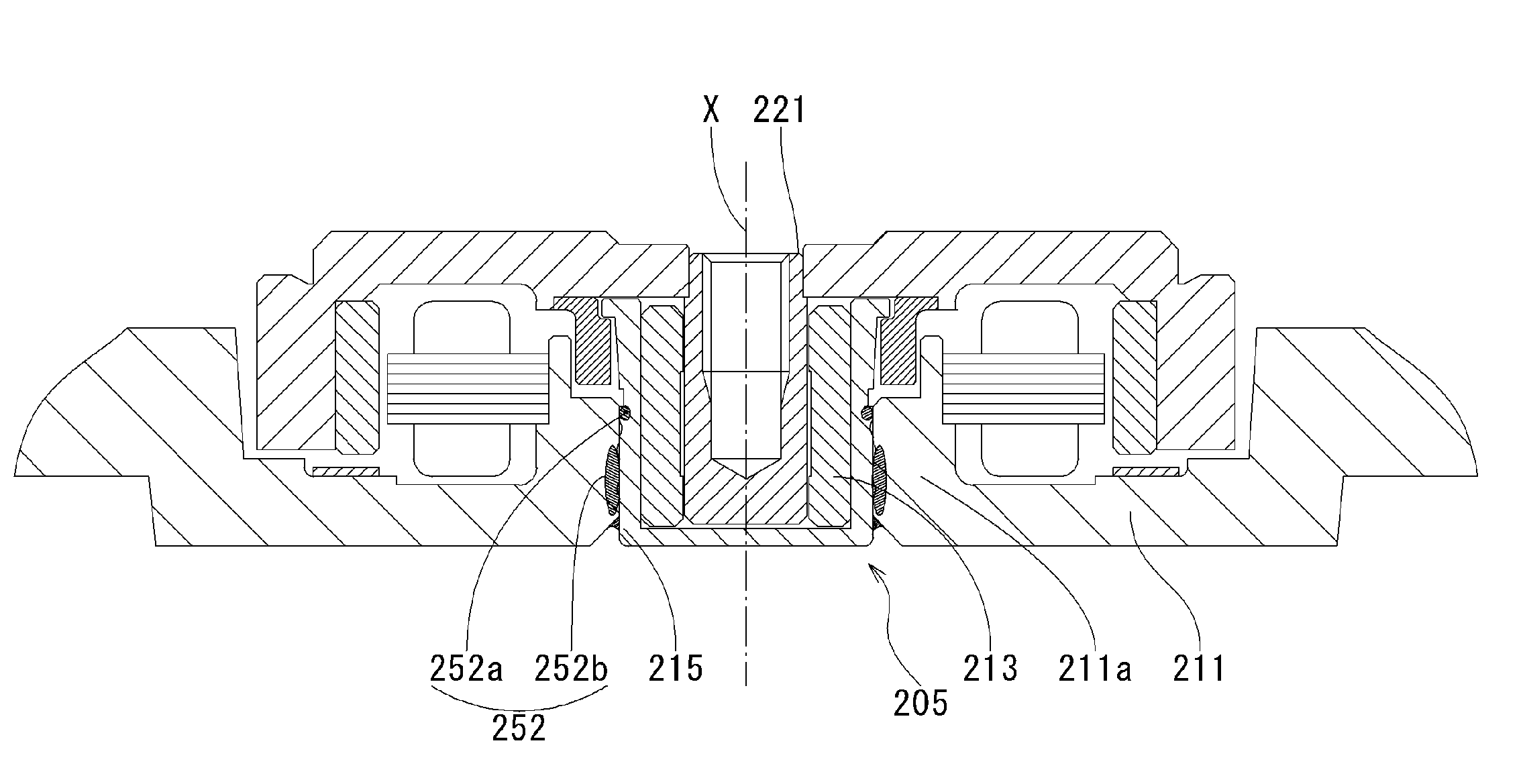
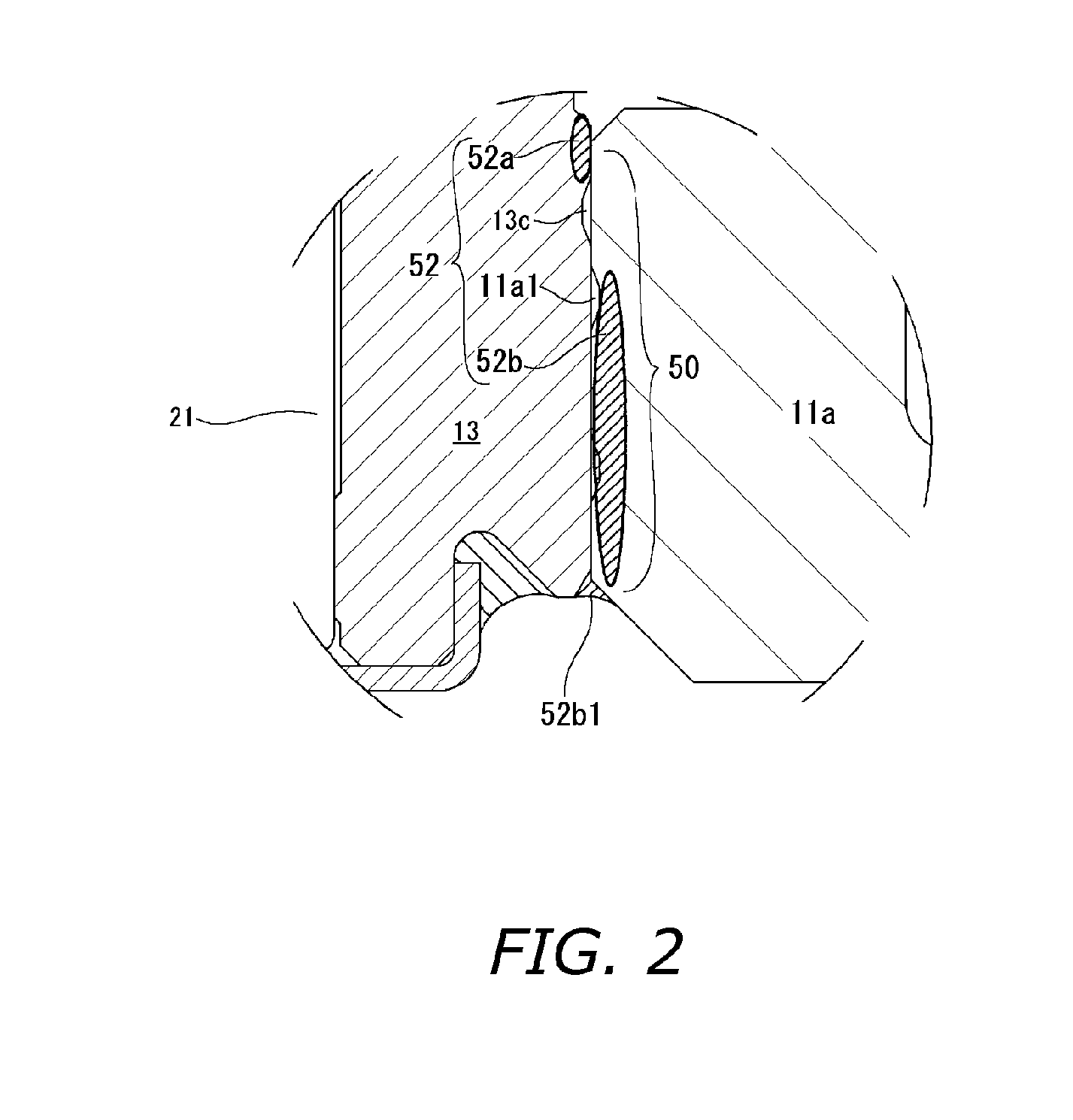
In a motor unit as an example of the invention, a bearing assembly 5 is securely held on an inner circumferential portion of a hollow cylindrical section 11a of a first housing member 11 with an adhesive section 52 interposed therebetween. The adhesive section 52 includes: a first adhering subsection 52a in which an anaerobic adhesive is present and a second adhering subsection 52b in which an externally stimulated curing type adhesive cured by heating or ultraviolet irradiation is present. Inserting the bearing assembly 5 into the hollow cylindrical section 11a produces a temporarily fixed state by the first adhering subsection 52a, thereby enabling the external stimulated curing type adhesive to be stably cured in the temporarily fixed state.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
Method and apparatus for monitoring air-exchange evaporation in a refrigerant-cycle system
ActiveUS20060032248A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEvaporation
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Mounting assembly
ActiveUS20080199254A1Less sensitiveEasy to controlRecord information storagePivotal connectionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
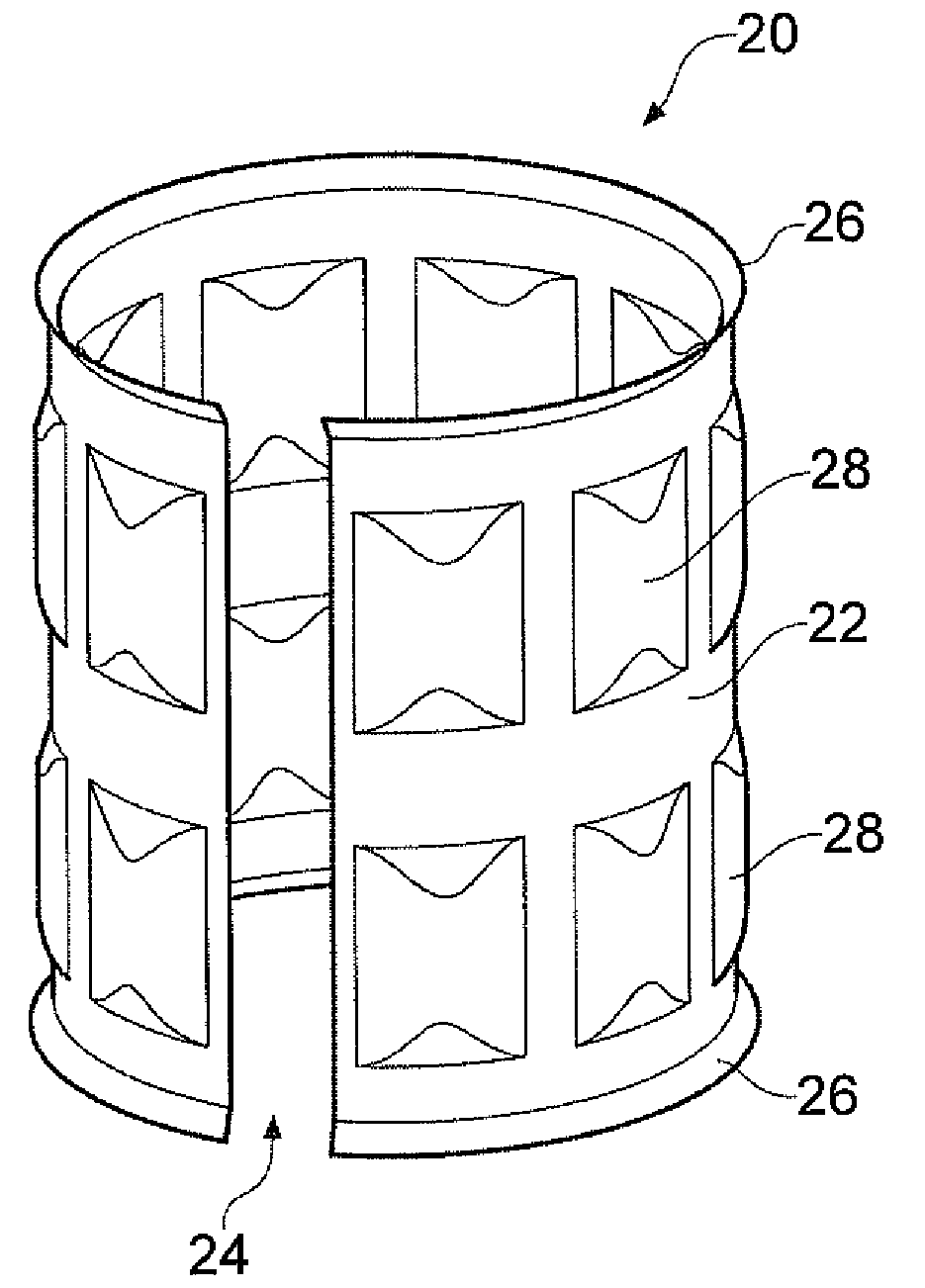
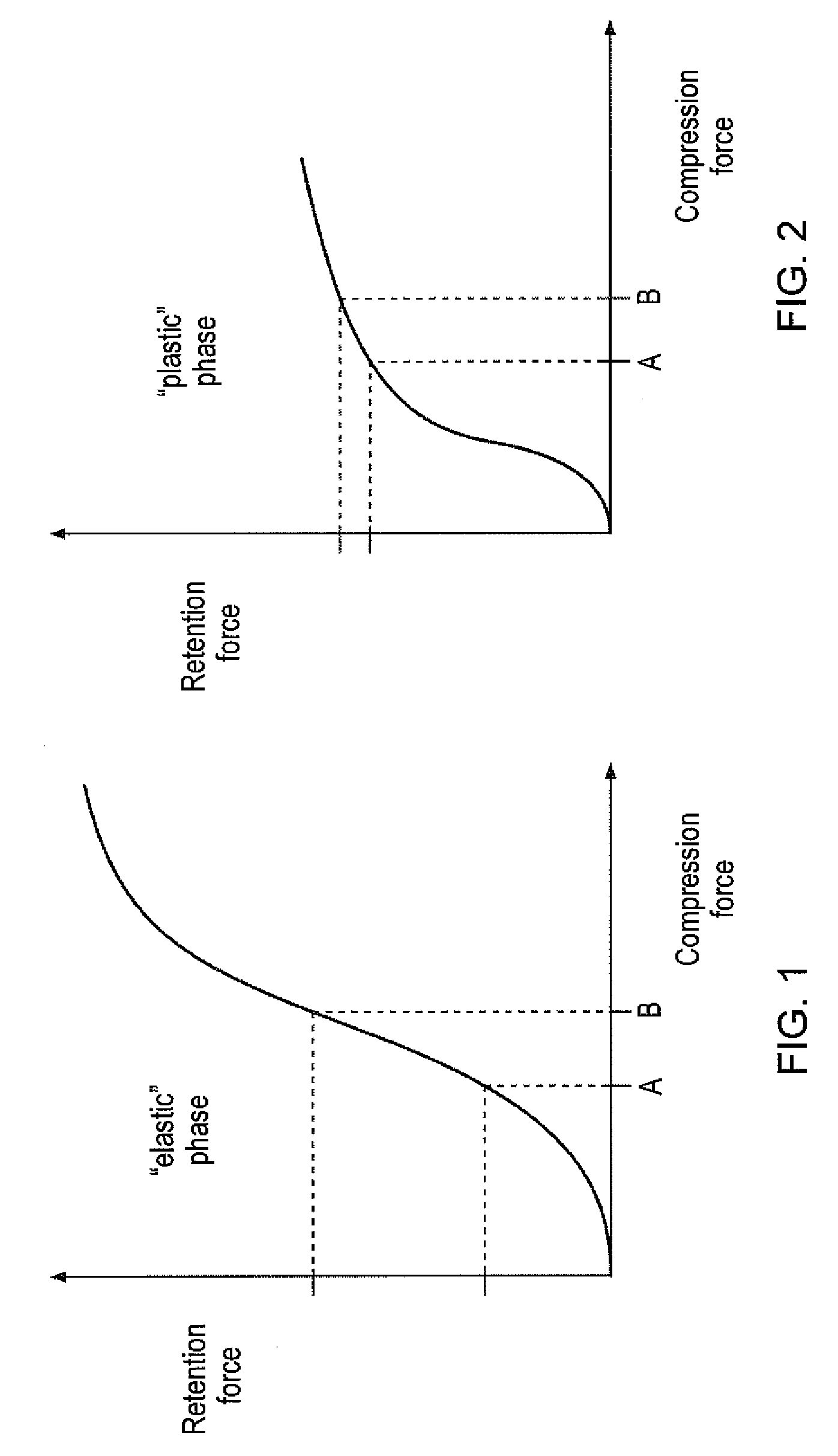
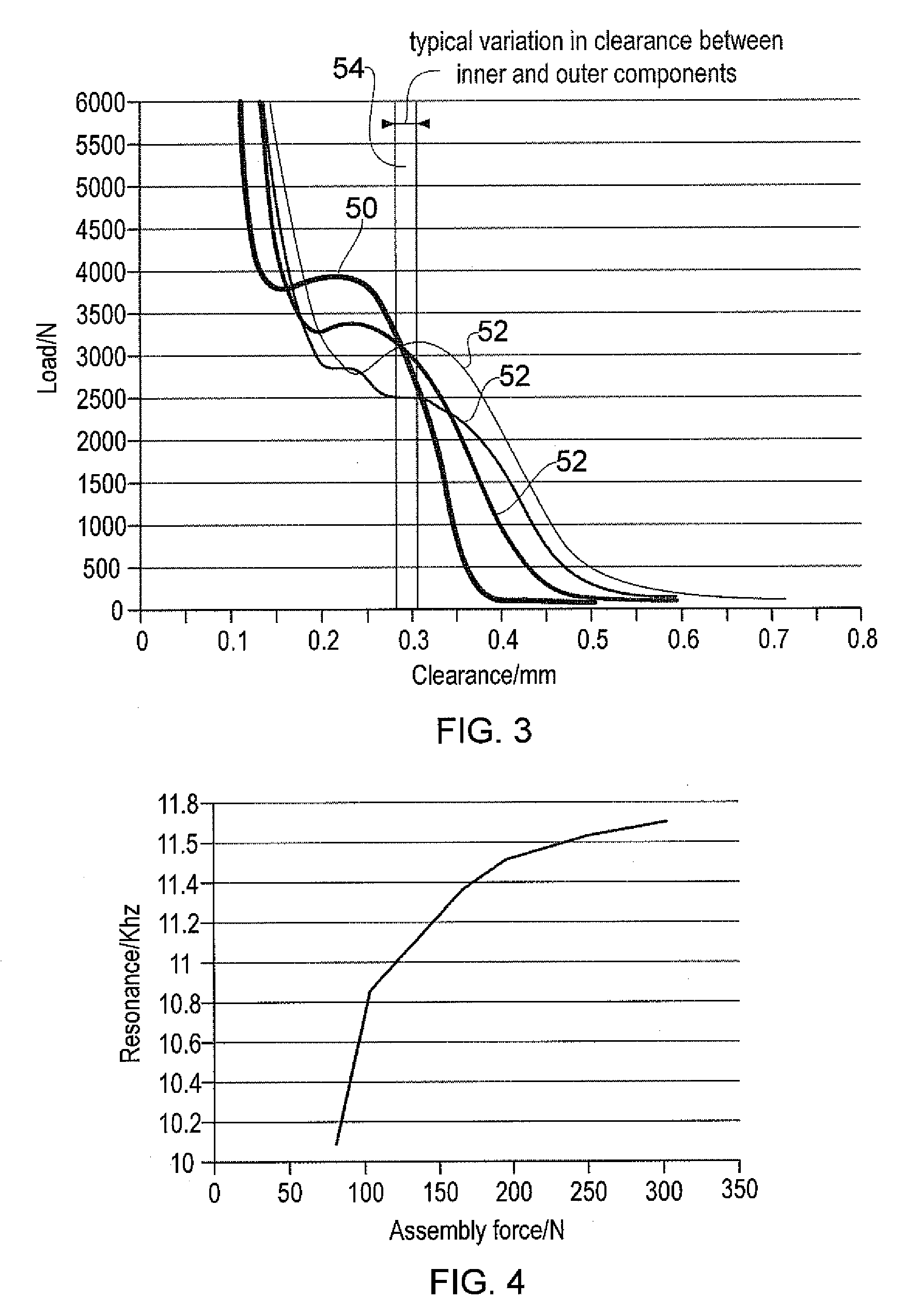
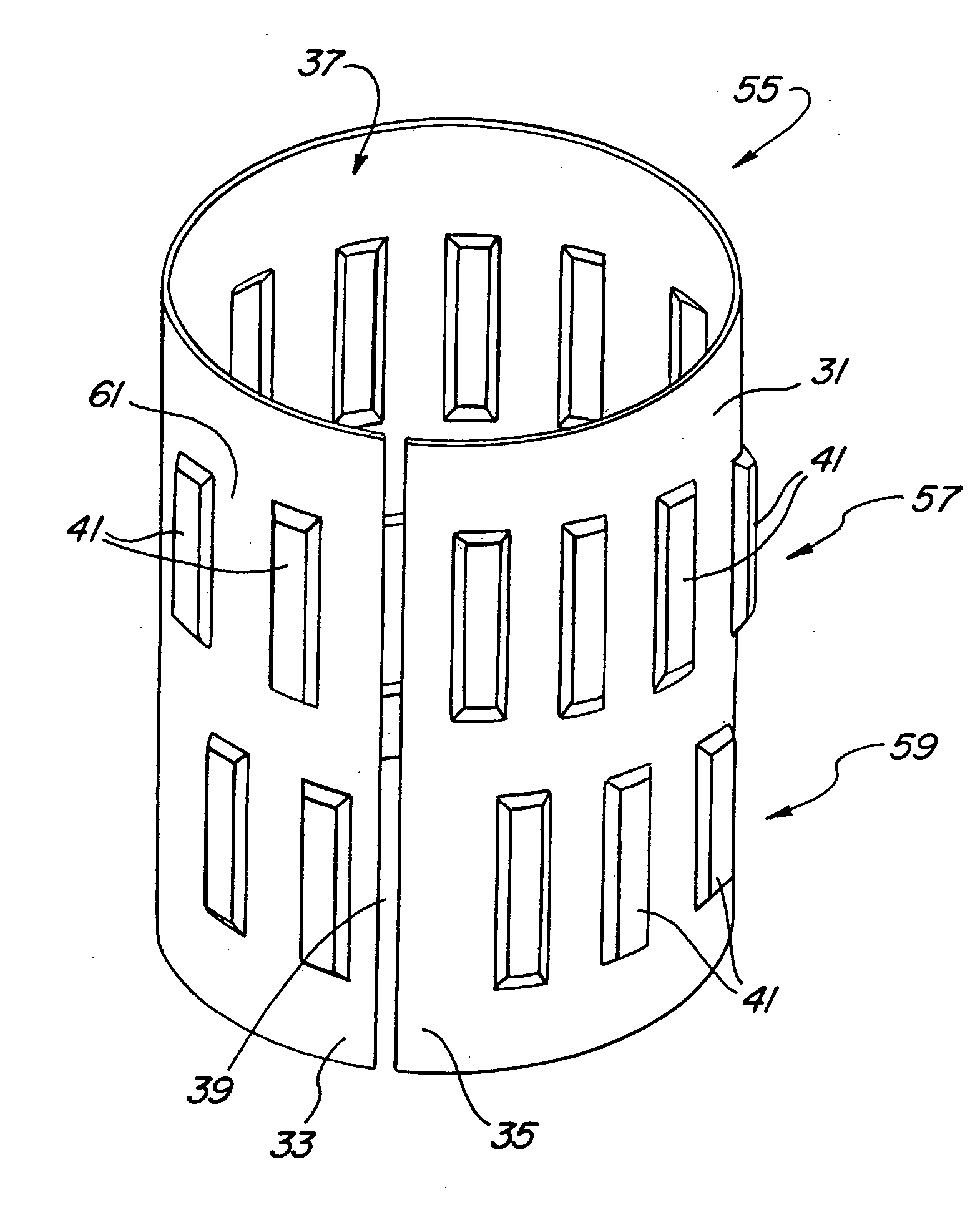
A mounting assembly comprising mating inner and outer components (36, 38) mounted together using a tolerance (20) is disclosed. The tolerance ring (20) has radially extending projections (28) that are configured to cause the tolerance ring (20) to operate into the plastic phase of its compression force / retention force characteristic. This can be achieved by using softer projections than those found in conventional tolerance rings. The force required to mount the tolerance ring and a range of retention forces exhibited by it for a given variance in sizes of mating components is thereby stabilised.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS RENCOL
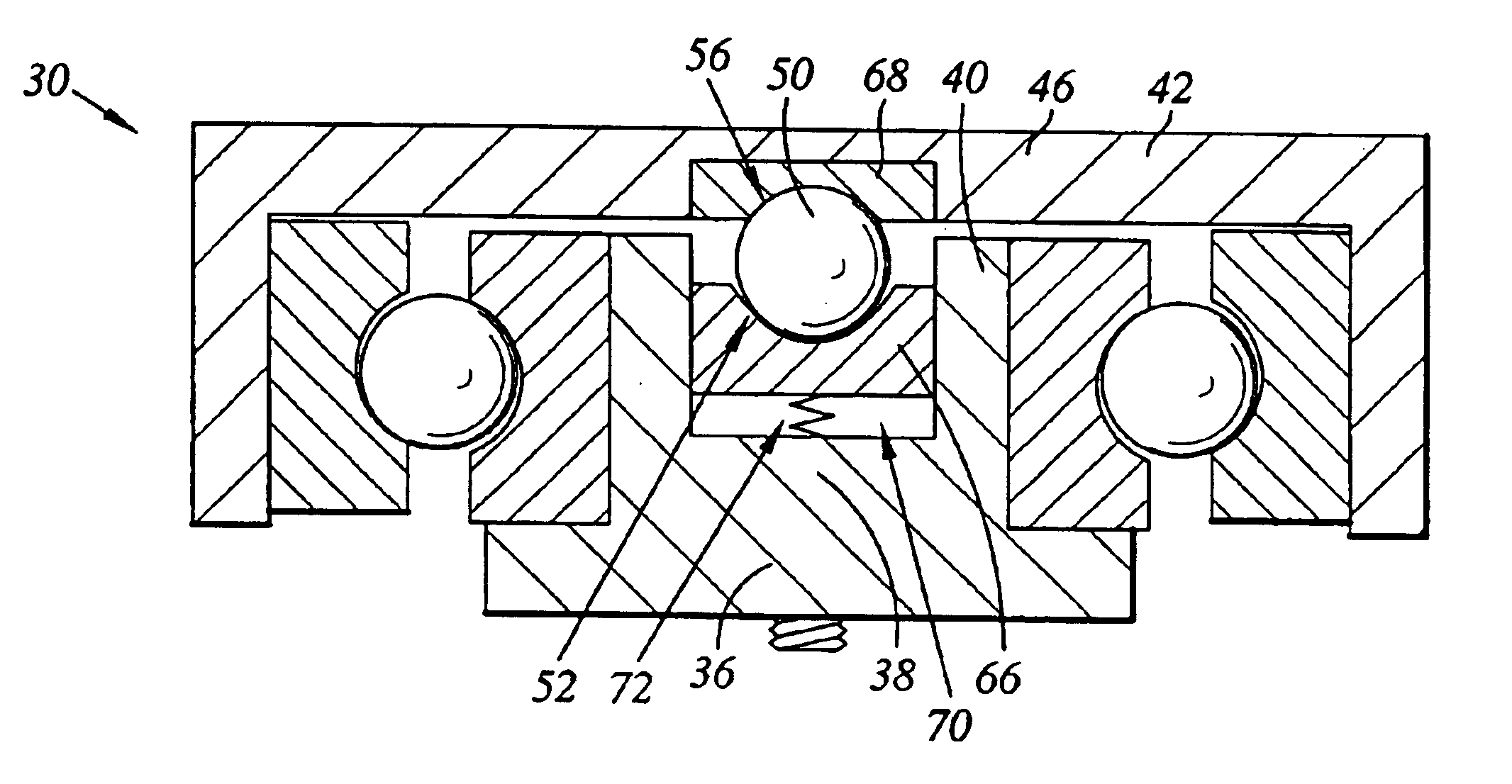
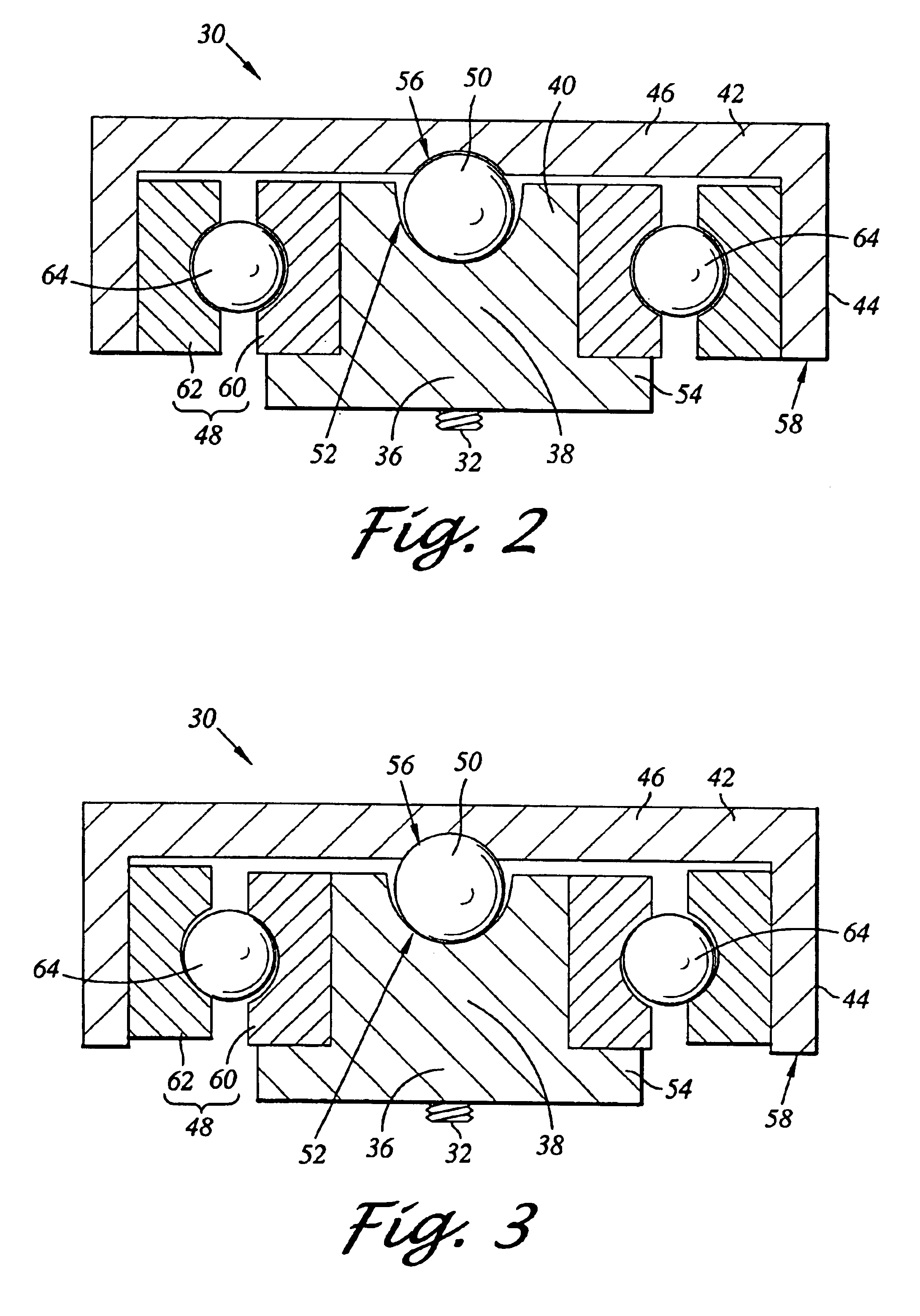
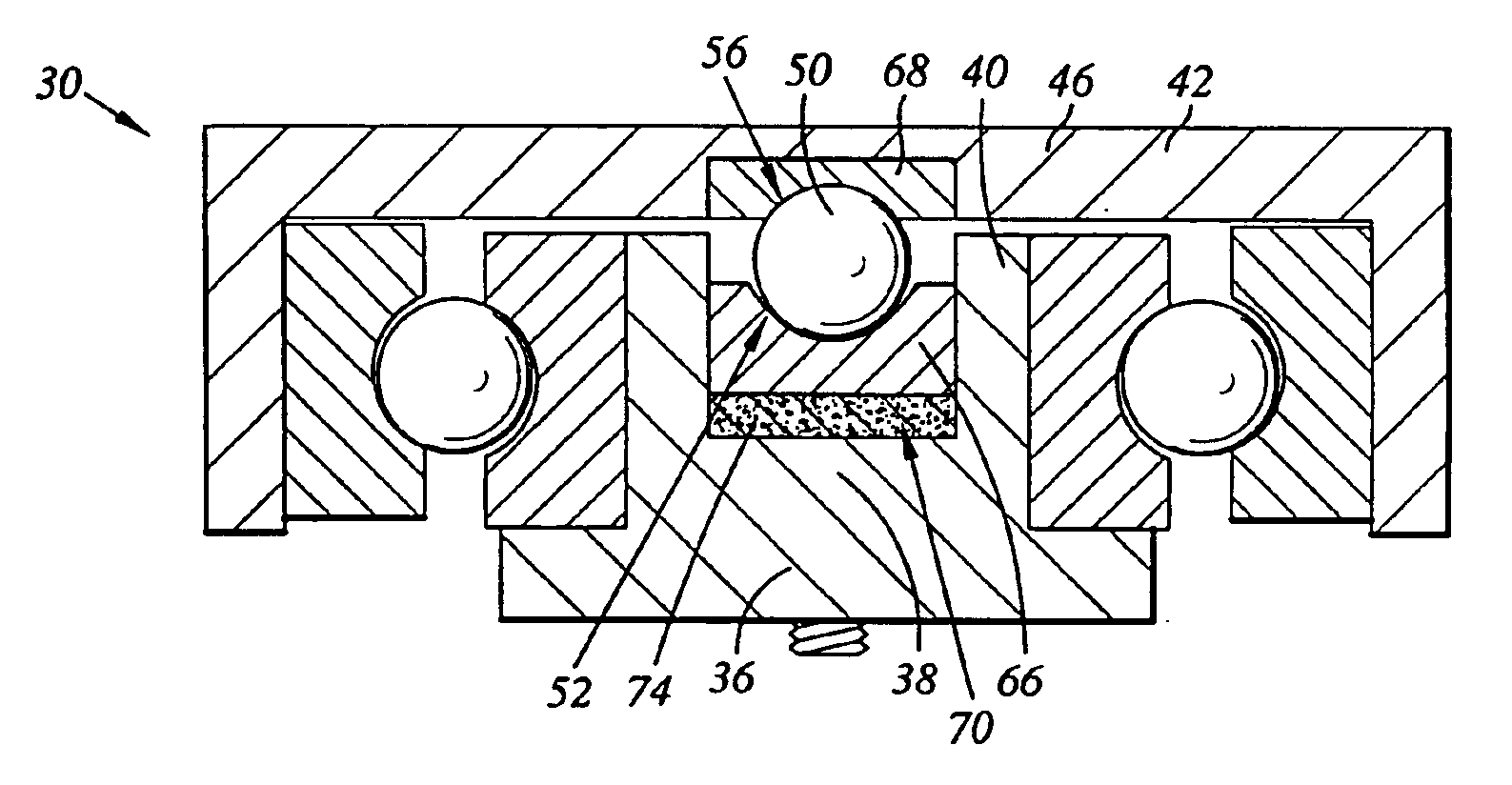
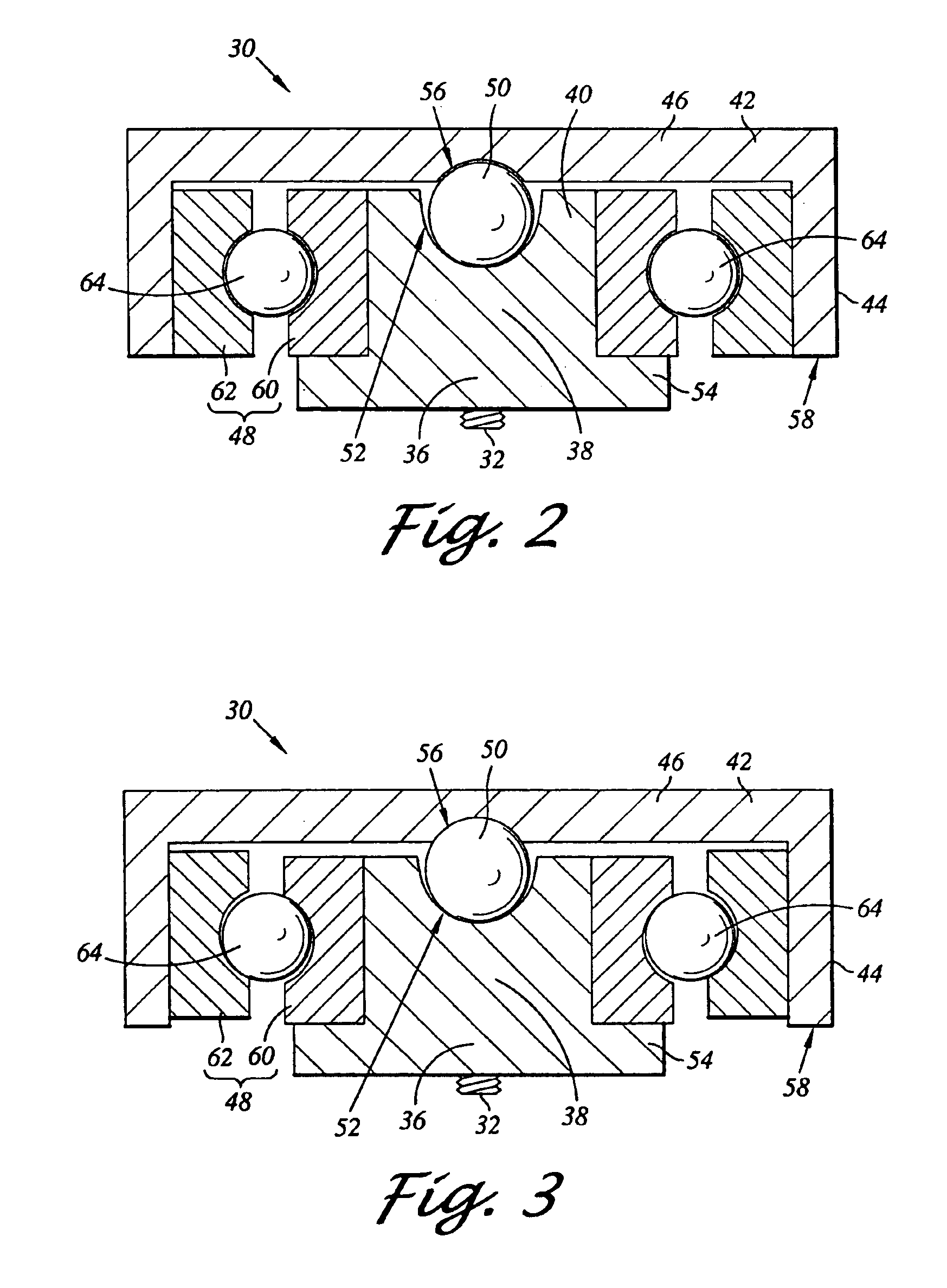
Tolerance ring having variable height and/or assymmetrically located bumps
A tolerance ring configured to reduce torque ripple for a pivot bearing in an actuator arm assembly. The tolerance ring comprises a cylinder having a predetermined length, and a first and a second row of contacting portions arranged around the surface of the cylinder, the contacting portions of the second row are circumferentially displaced with respect to the first row by a distance greater than zero but less than the distance of the contacting portion and the spacing between adjacent contacting portions in the first row.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
Tolerance ring with debris-reducing profile
A tolerance ring for applications requiring cleanliness has contacting portions having a novel profile that reduces debris generation during installation of the tolerance ring while still providing adequate stiffness after installation. The tolerance ring is suitable for cylindrical interface applications where both a reduction in debris generation and high interface stiffness are desirable, such as the interface between an actuator pivot bearing and an actuator arm in a magnetic hard disk drive.
Owner:INTRL PLEX TECH INC
Intelligent thermostat system for load monitoring a refrigerant-cycle apparatus
ActiveUS20060196197A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Intelligent thermostat system for monitoring a refrigerant-cycle apparatus
ActiveUS20060032246A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureThermostat
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Method and apparatus for monitoring a condenser unit in a refrigerant-cycle system
ActiveUS20060032247A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
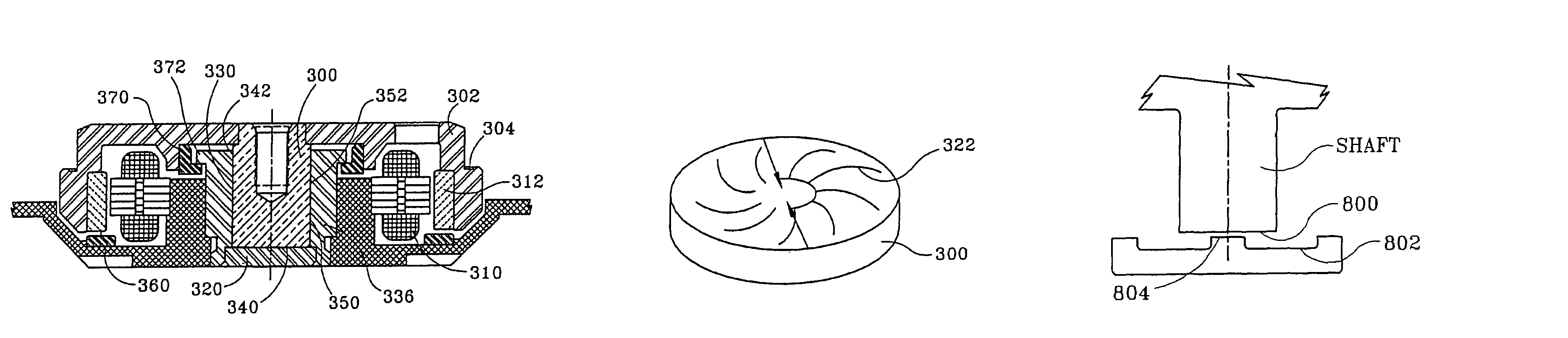
Low profile fluid dynamic bearing
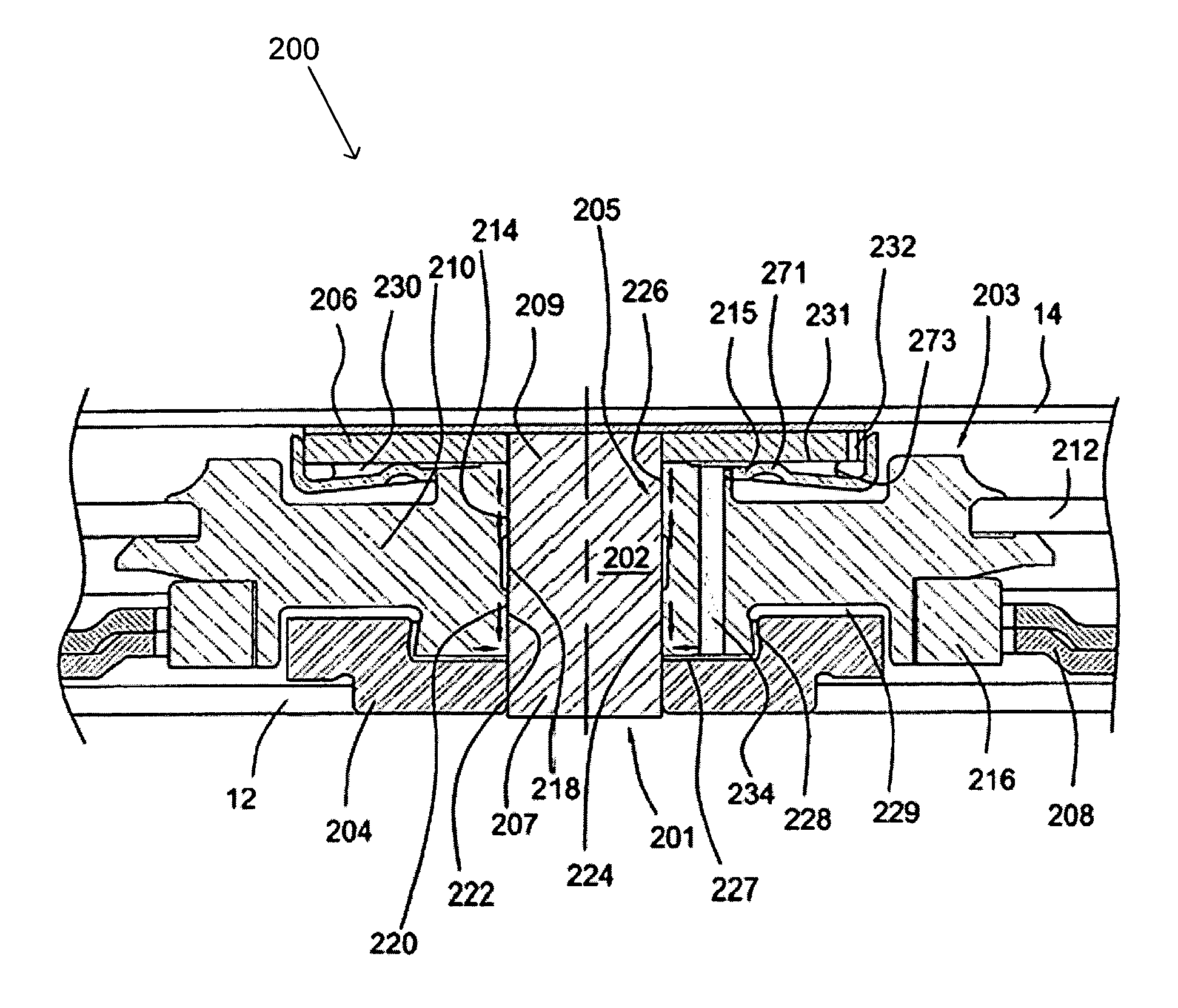
InactiveUS6982510B1Simple and scalable in designReduce the amount of powerShaftsRecord information storageAxial displacementThrust bearing
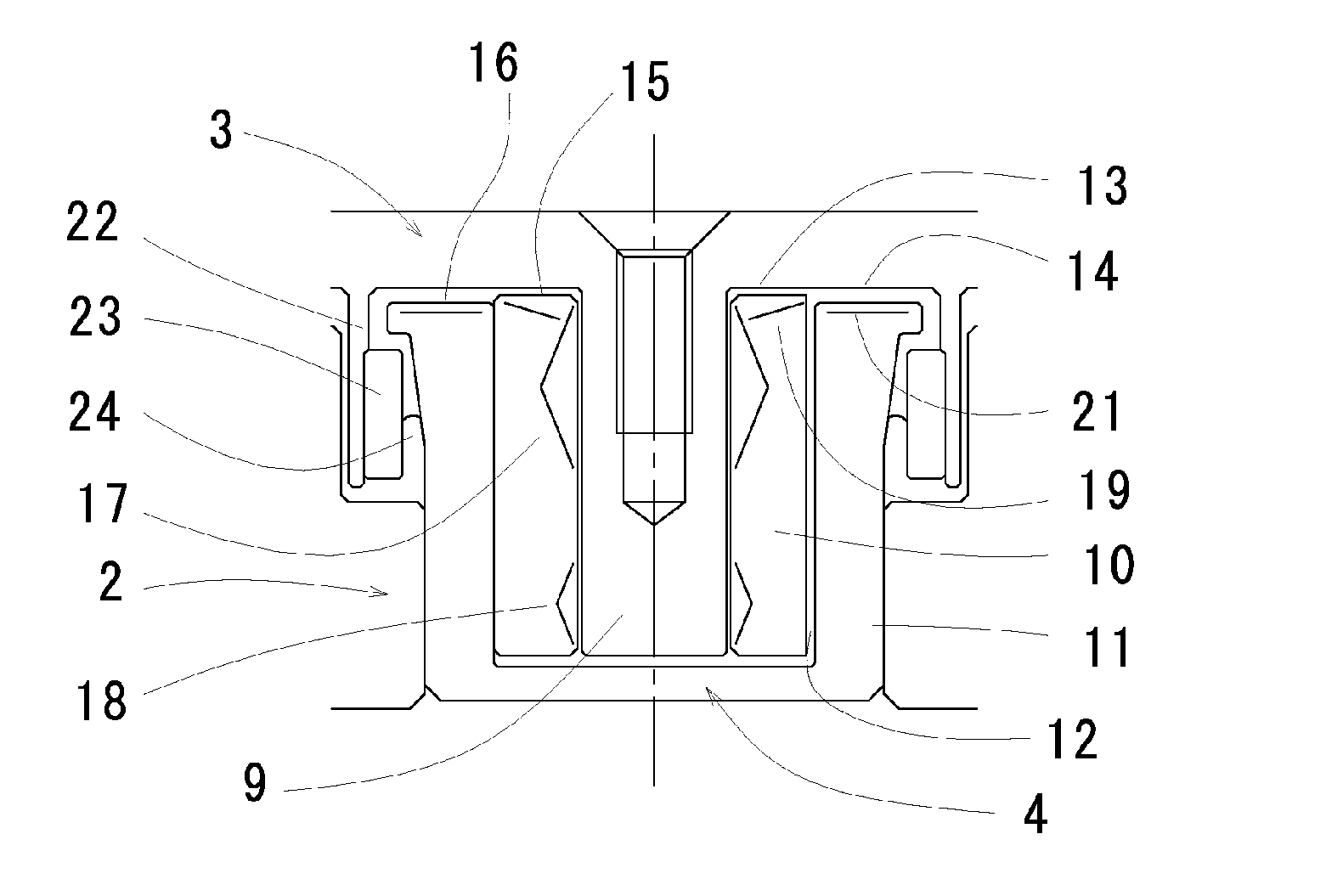
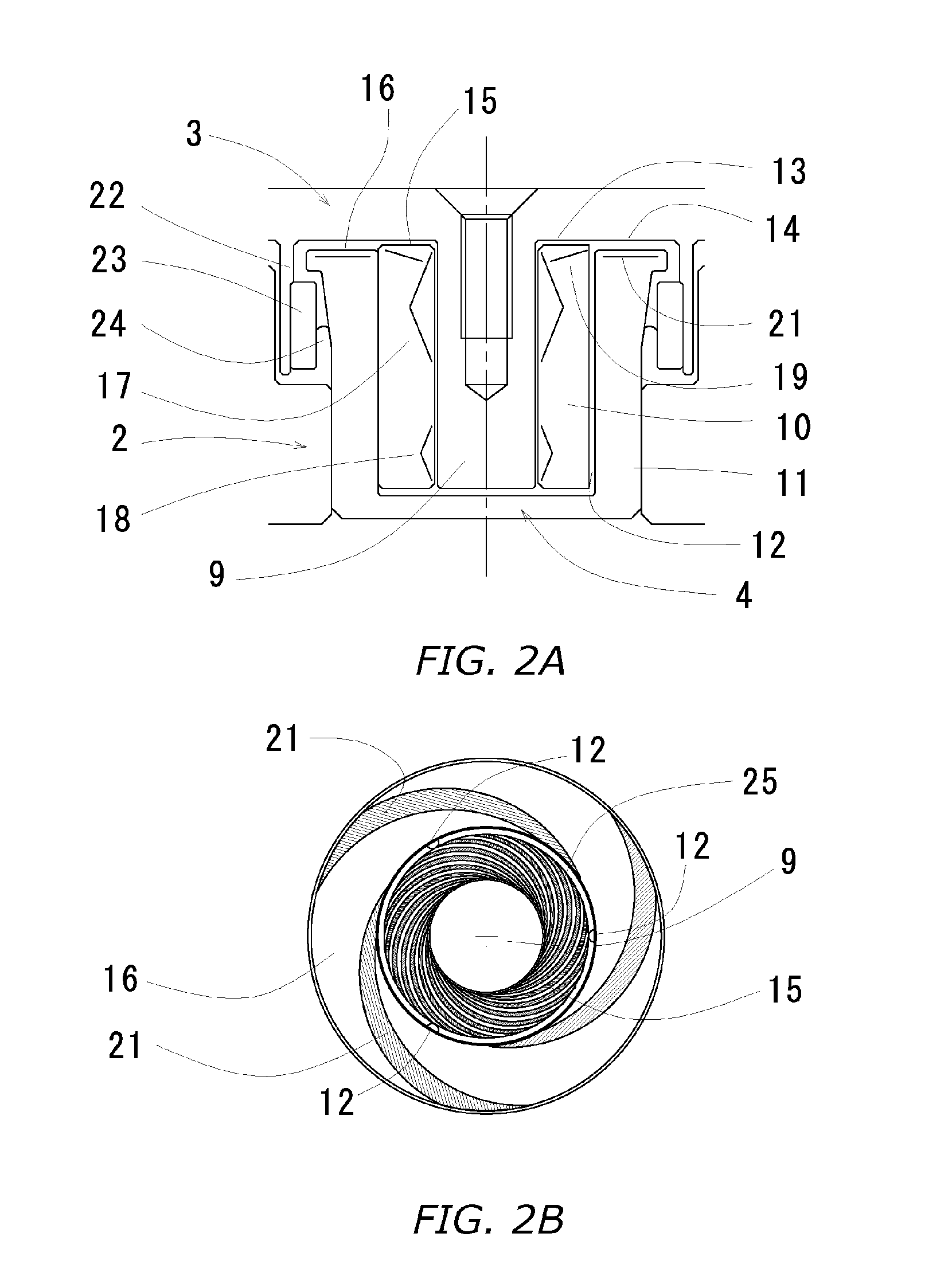
The design comprises a shaft and sleeve supported for relative rotation by a journal type fluid dynamic bearing utilizing grooves on one of the shaft or sleeve surfaces. A grooved pattern of a design similar to that usually found on a thrust plate is defined on an axial end surface of the shaft or the counterplate facing the axial end of the shaft, so that thrust is created to maintain separation of the end of the shaft and the facing thrust plate during relative rotation.In one embodiment, to establish and maintain the gap between the shaft end and the facing counterplate, the journal bearing has an asymmetry to pump toward the shaft end having the bearing. In a further refinement, to maintain the shaft and gap within an optimum spacing, a magnet is mounted to provide an axially directed magnetic force on the shaft which works against the axial force created by shaft end thrust bearing.To prevent separation of the shaft and sleeve or hub, the hub which is integrated with a rotating shaft, further incorporates a shoulder which extends axially beneath a cooperating shoulder on the sleeve surrounding the shaft to prevent any more than a limited axially displacement of the hub and shaft relative to the sleeve.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
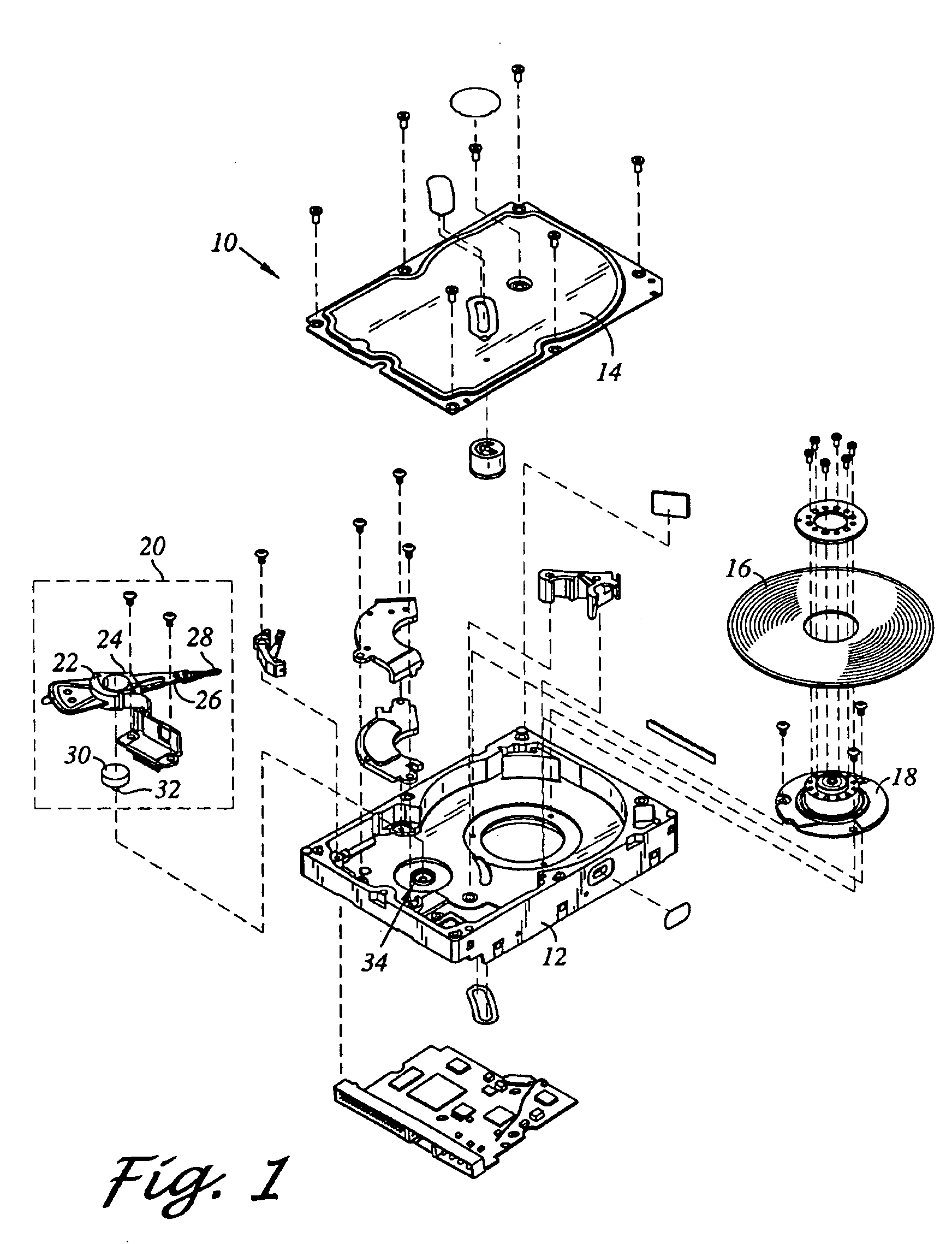
Pivot bearing cartridge including central pivot element and ball bearing set
A pivot bearing cartridge for use in a head stack assembly. The pivot bearing cartridge includes a pivot shaft including a shaft body and a shaft distal end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a cap disposed about the pivot shaft. The cap includes a cap annular body and a cap closed end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a ball bearing set in mechanical communication with the pivot shaft and the cap annular body. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a central pivot element disposed between and in mechanical communication with the shaft distal end and the cap closed end for facilitating rotation of the cap relative to the pivot shaft.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Hydrodynamic bearing device, spindle motor including the same, and recording and reproducing apparatus
A cylindrical sleeve is rotatably fitted over a fixed shaft erected on a base, the sleeve including an outer collar part at an outer periphery of the lower end portion thereof, a slip-out preventing member for preventing the slip-out from the fixed shaft while allowing the sleeve to rotate is provided on the base, the slip-out preventing member including an inner collar part that engages with the outer collar part in the slip-out direction. A hub is provided on the upper end portion of the sleeve, a pair of upper and lower radial bearings formed with a dynamic pressure generating groove are provided on the inner peripheral surface of the sleeve, and a thrust bearing formed with a dynamic pressure generating groove is provided at the lower end face of the sleeve.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for airflow monitoring refrigerant-cycle systems
InactiveUS20060196196A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:KATES LAWRENCE
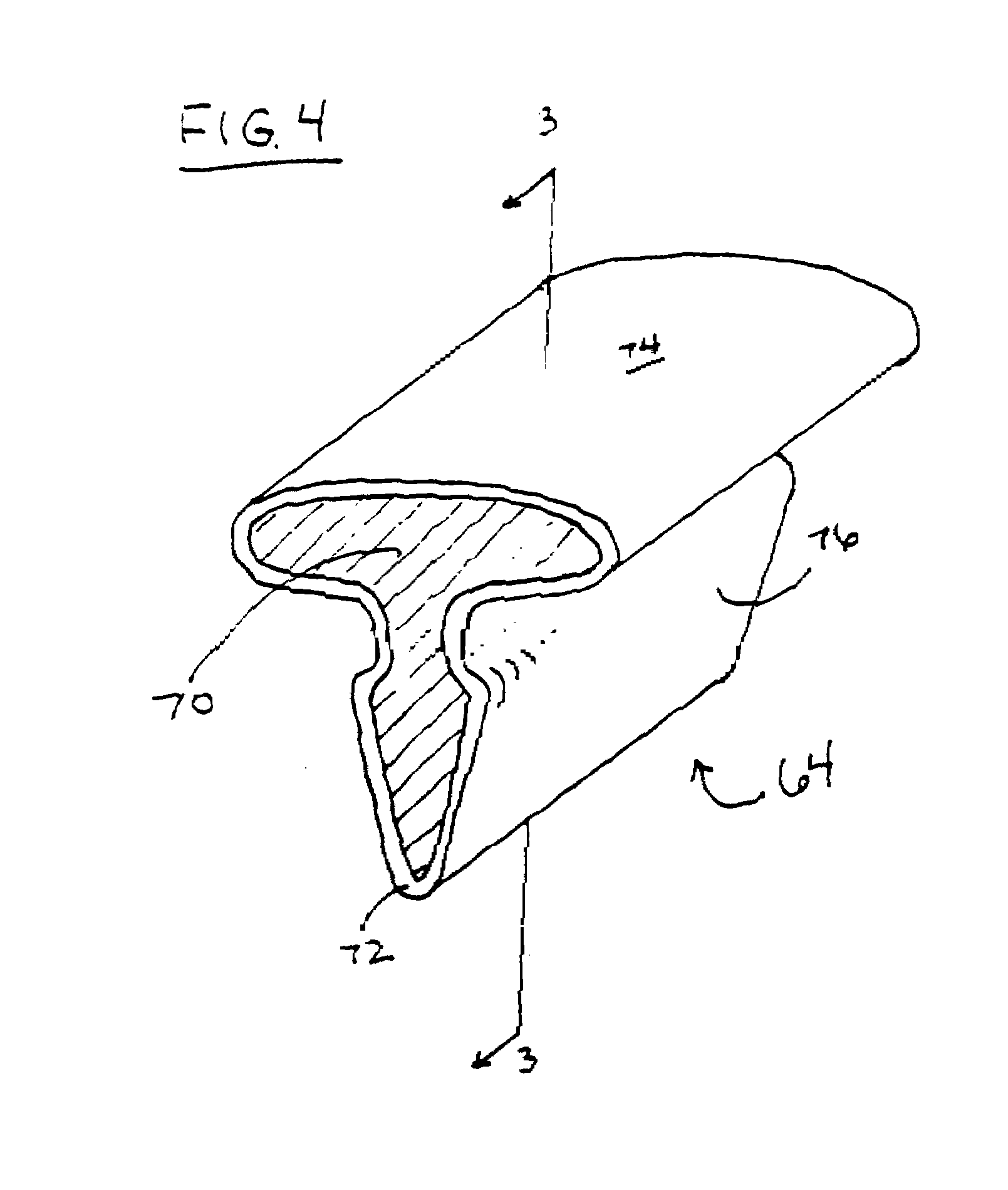
Method for detecting a fault in an HVAC system
A bypass factor of an evaporator is used to indicate when an air filter of an HVAC is clogged. The bypass factor represents the amount of air that is bypassed without direct contact with the evaporator. As the air filter clogs, the bypass factor decreases. The bypass factor can also be used for early detection of clogging of the air filter. A first bypass factor is calculated by using the temperature measurements, and a second bypass factor is calculated by using the airflow rate of the air. The difference between the two bypass factors determines the error. An increase in the error indicates that the air filter is clogged. A coefficient of performance of the evaporator can also be calculated to detect if the air filter is clogged. A decrease in the coefficient of performance indicates that the air filter is clogged.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
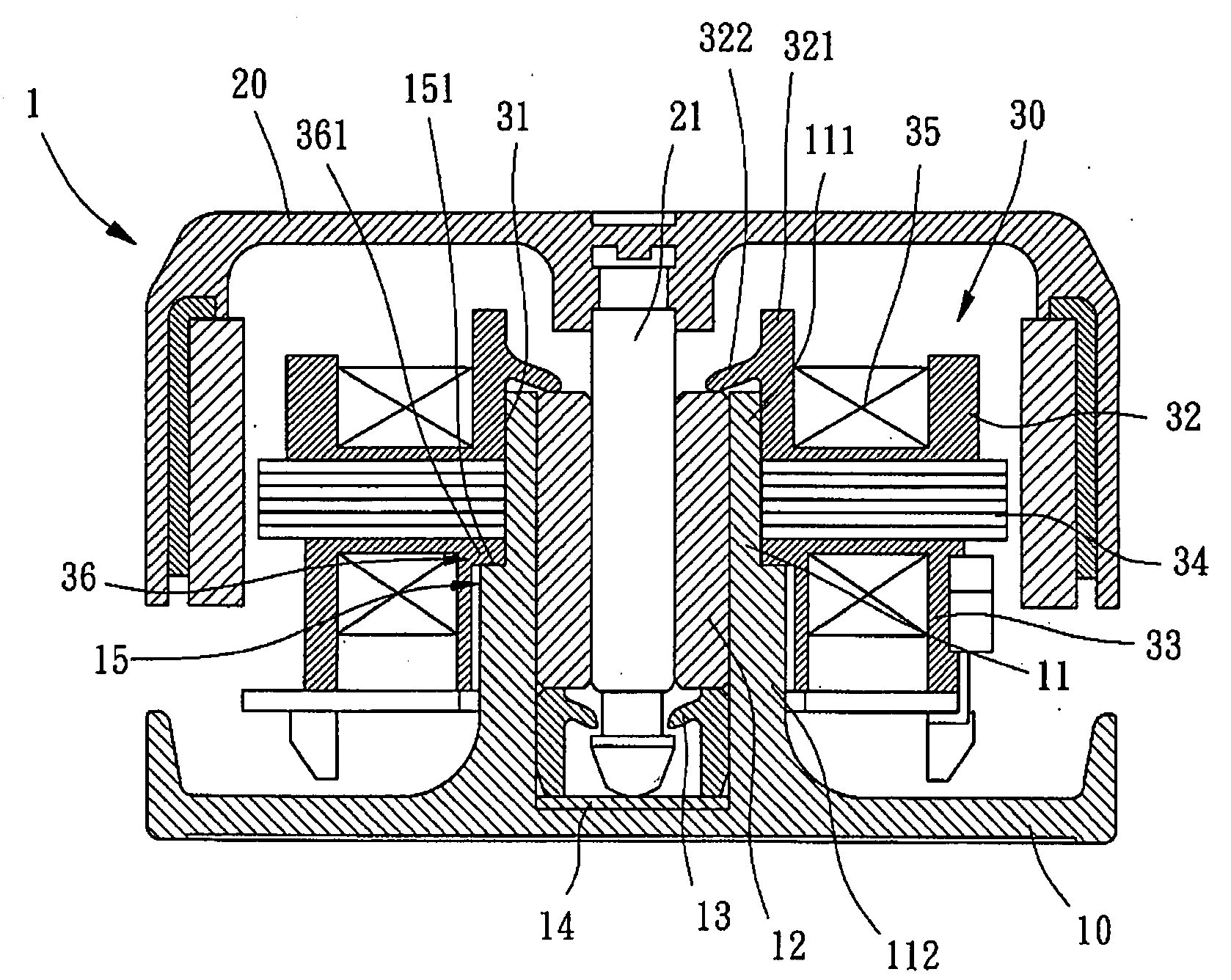
Motor Structure
A motor structure includes a housing having a shaft tube receiving a bearing. The shaft tube includes a positioning section on an outer periphery thereof. A rotor includes a shaft rotatably extending through the bearing. A stator is mounted around the shaft tube and includes an upper bobbin having an abutting portion and a lower bobbin having an engaging portion. The positioning section of the shaft tube provides the engaging portion of the lower bobbin with an axial supporting force along a longitudinal axis of the shaft tube to position the stator in a fixed axial position relative to the bearing along a longitudinal axis of the shaft tube. Also, the abutting portion of the upper bobbin abuts the bearing to prevent the bearing from disengaging from the shaft tube.
Owner:SUNONWEALTH ELECTRIC MACHINE IND
Pivot bearing cartridge including central pivot element and ball bearing set
A pivot bearing cartridge for use in a head stack assembly. The pivot bearing cartridge includes a pivot shaft including a shaft body and a shaft distal end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a cap disposed about the pivot shaft. The cap includes a cap annular body and a cap closed end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a ball bearing set in mechanical communication with the pivot shaft and the cap annular body. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a central pivot element disposed between and in mechanical communication with the shaft distal end and the cap closed end for facilitating rotation of the cap relative to the pivot shaft.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
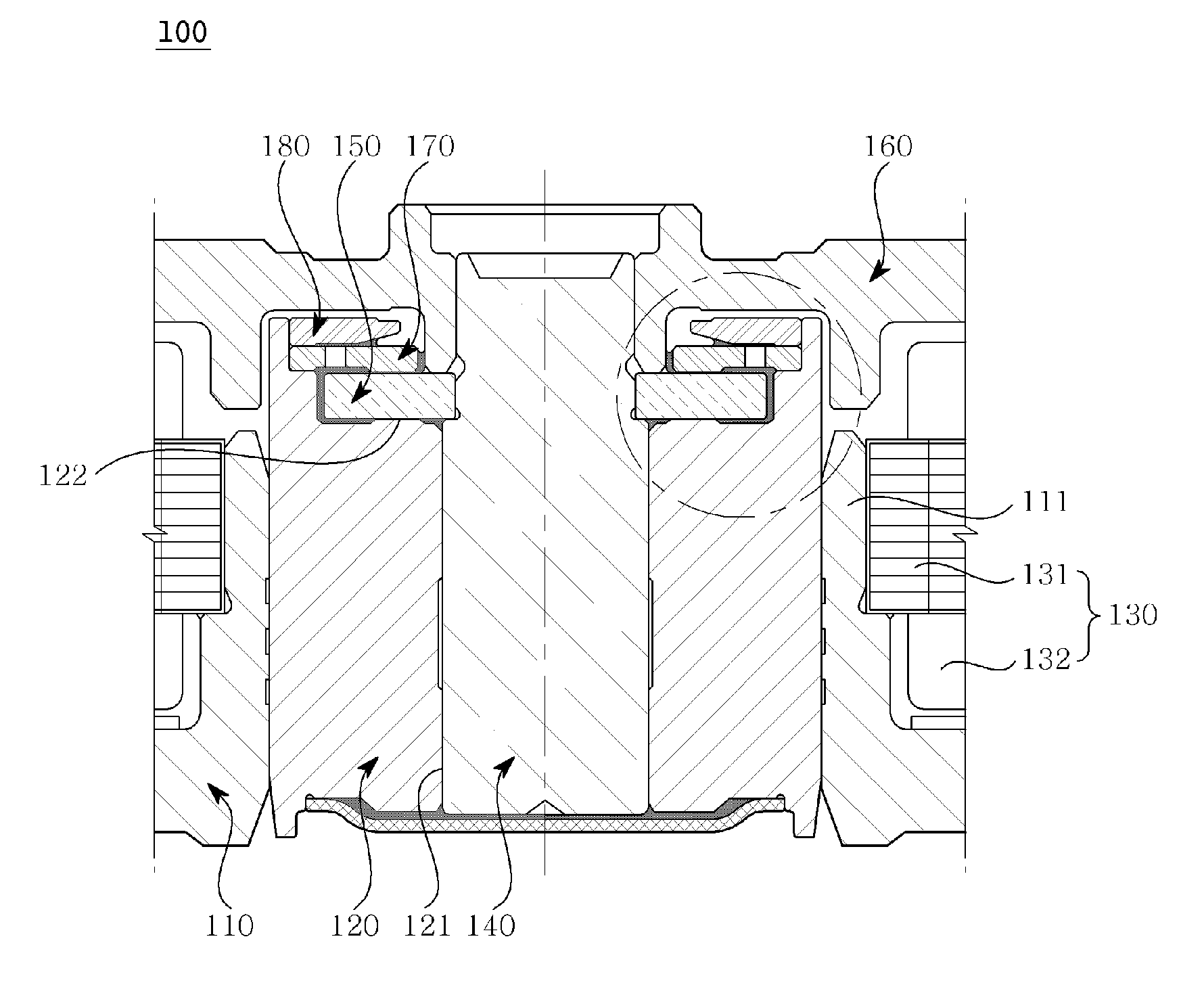
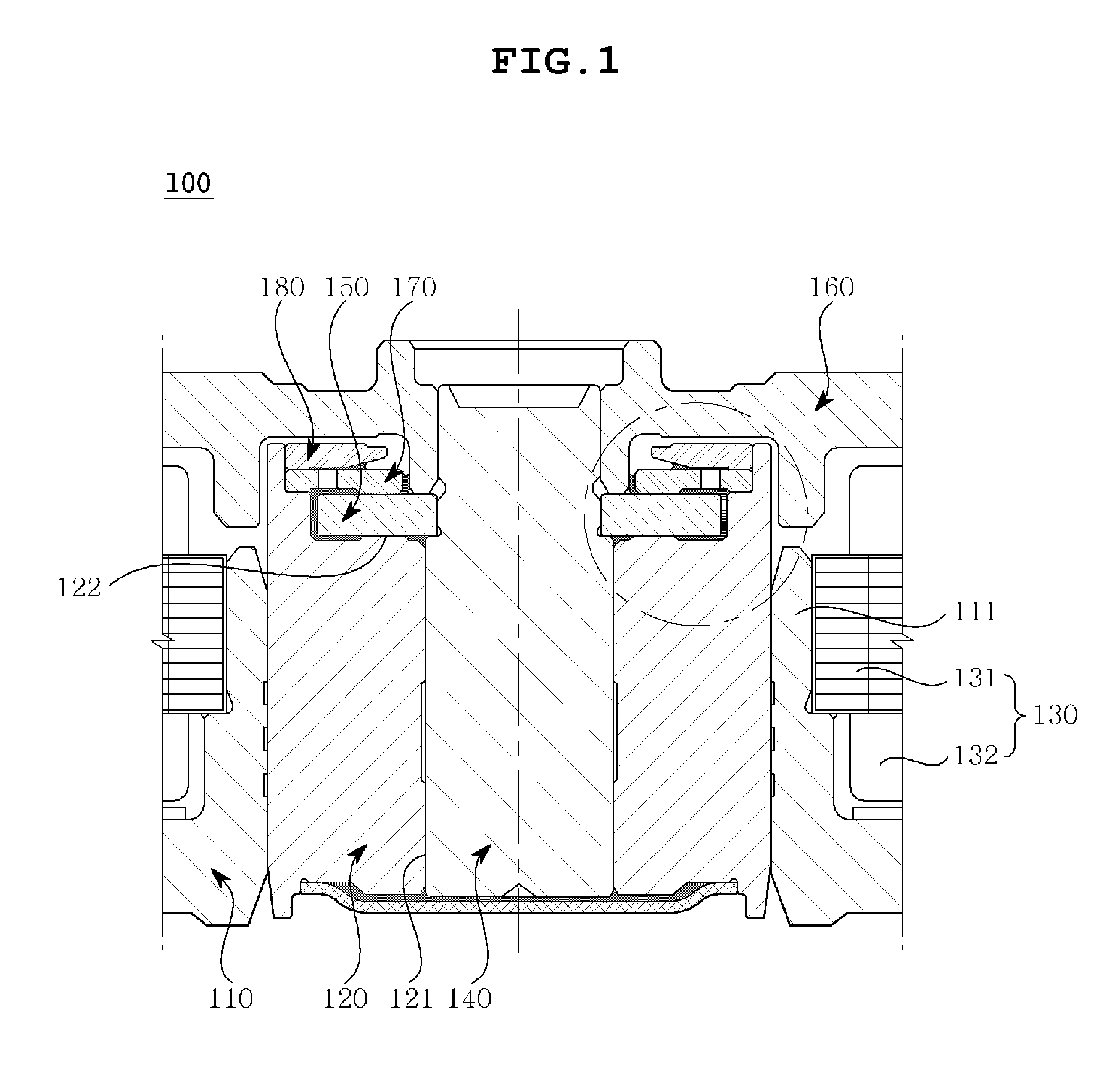
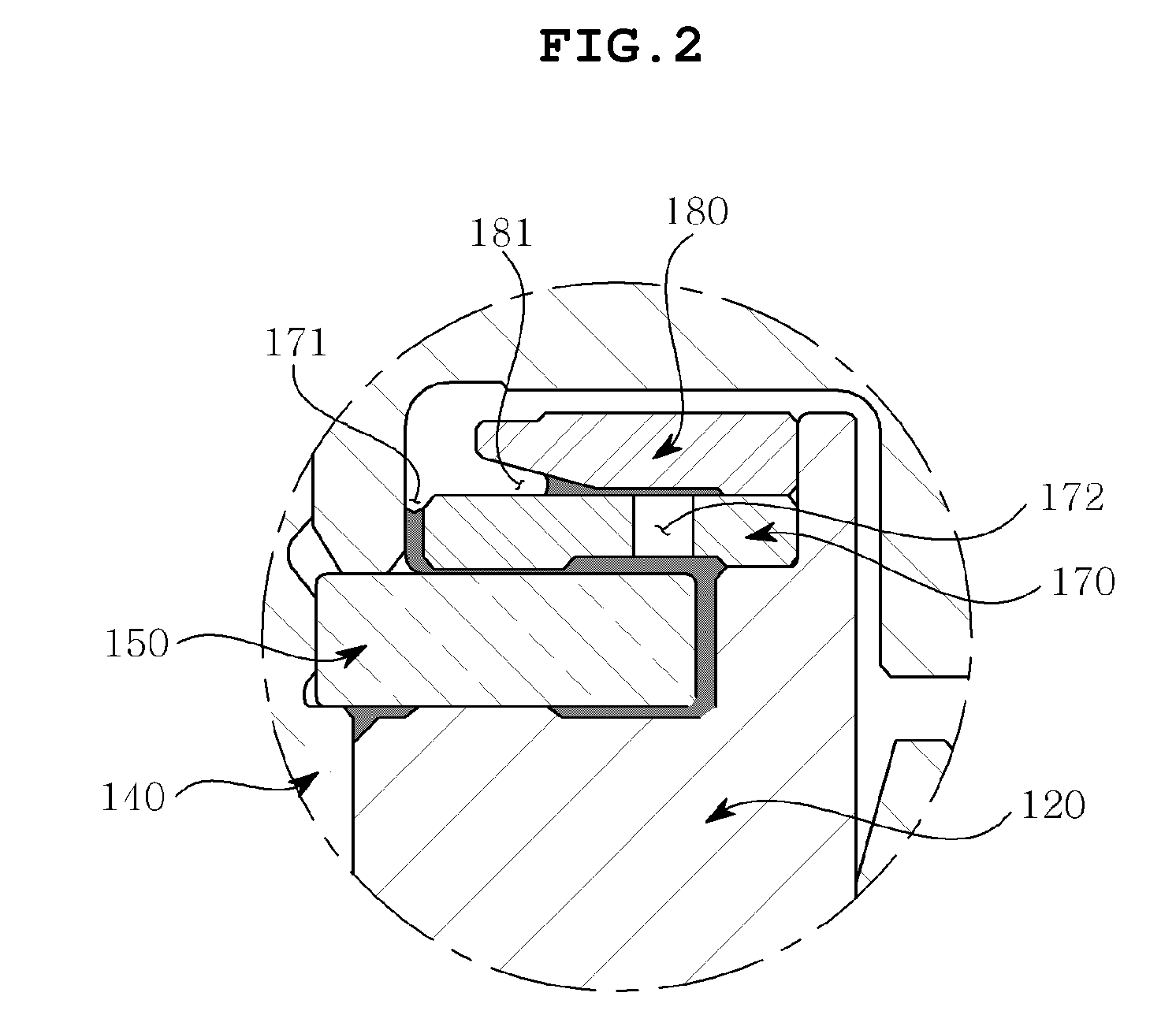
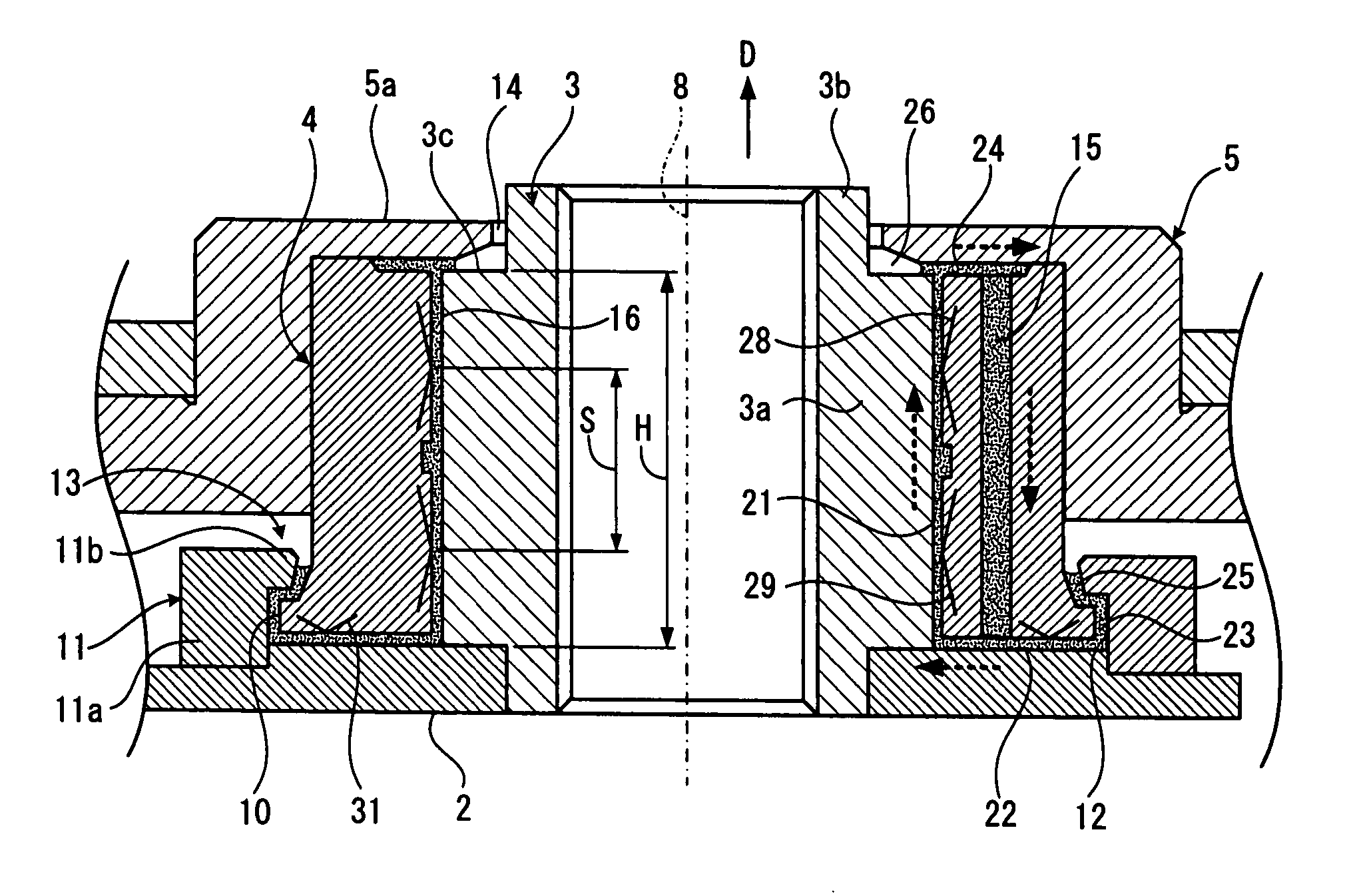
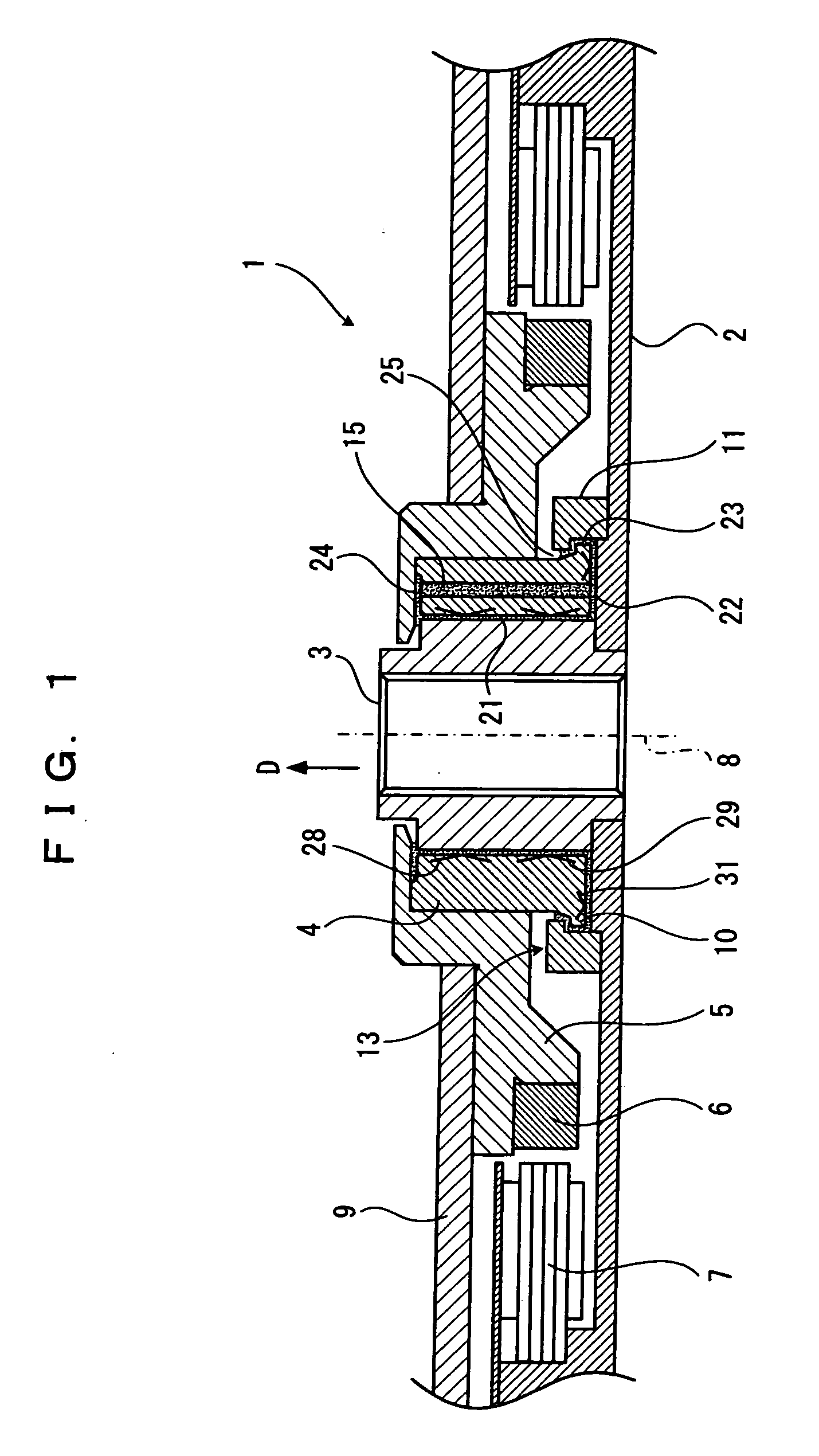
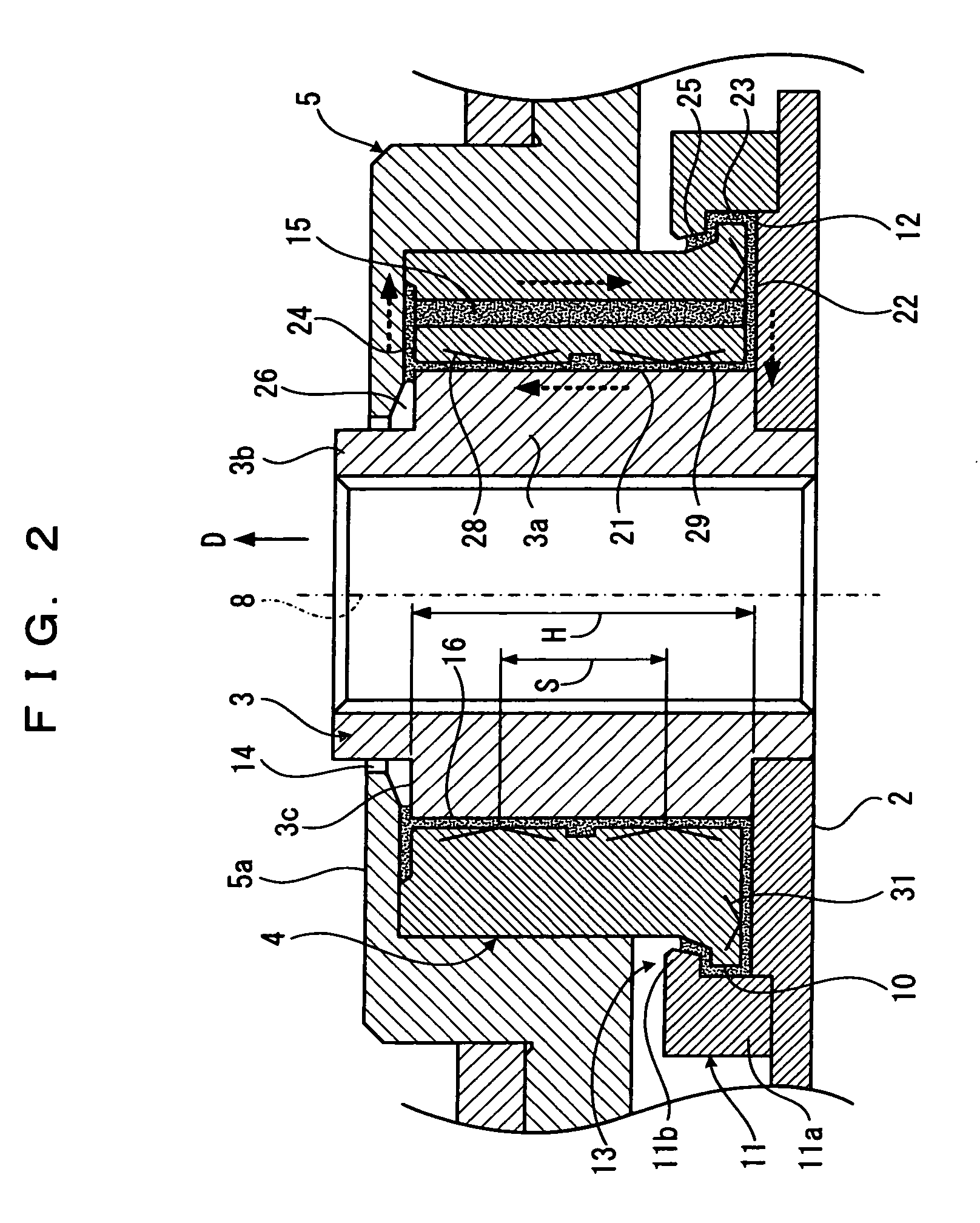
Hydrodynamic bearing, spindle motor using the same and disc drive apparatus provided with spindle motor
ActiveUS20040165797A1Increase capacitySufficient amount can be retainedShaftsRecord information storageWorking fluidCapillaria obsignata
The present invention relates to a hydrodynamic bearing supporting a shaft and a sleeve so as to relatively rotate with respect to a rotation axis. In accordance with one example of the present invention, there is provided a hydrodynamic bearing in which a capillary seal portion is formed continuously in a bearing portion having a lubricating oil retained in a micro gap as a working fluid. The capillary seal portion is provided with a first capillary seal portion having a first radial gap, a dimension of the first radial gap being getting at least wider in accordance with increasing a distance from the bearing portion in the rotation axis, and a second capillary seal portion adjoining the first capillary seal portion and having a second radial gap, a dimension of the second radial gap being getting at least wider in accordance with increasing a distance from the bearing portion in the rotation axis. The second capillary seal portion is expanded progressively in accordance with getting toward an outer side in an axial direction.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
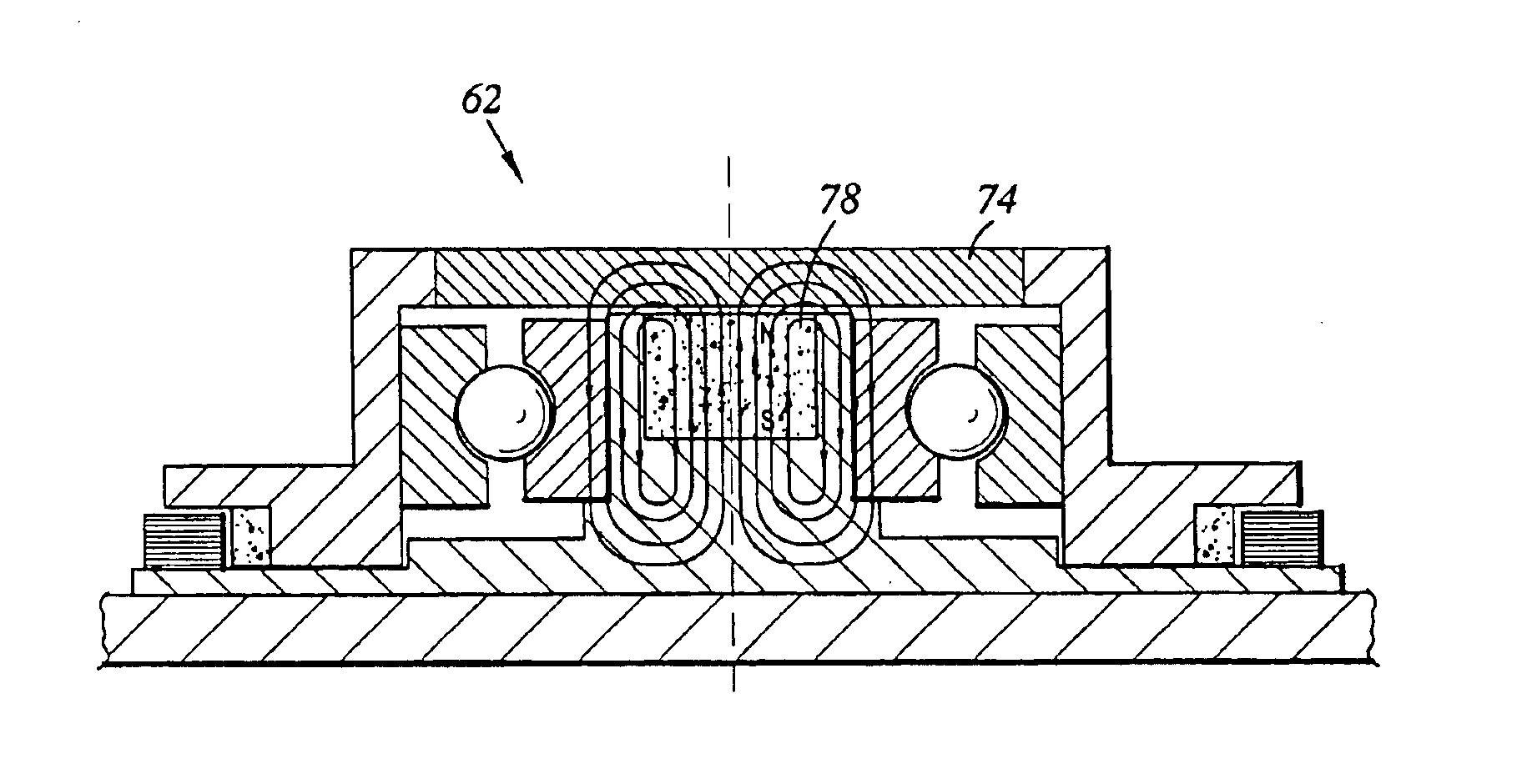
Spindle motor including magnetic element for pre-loading a ball bearing set
A spindle motor for use in a disk drive includes a spindle motor base and a motor shaft. The motor shaft has a central axis. The spindle motor includes a spindle motor hub rotatably coupled to the spindle motor base, the spindle motor hub including a central magnetic metal portion disposed adjacent a distal end of the motor shaft. The spindle motor includes a ball bearing set disposed between and in mechanical communication with the spindle motor hub and the motor shaft for rotatably coupling the spindle motor hub to the spindle motor base. The spindle motor includes a shaft magnetic element attached to the motor shaft at the distal end adjacent the central magnetic metal portion, the shaft magnetic element being sized and configured to apply an attractive magnetic force to the central magnetic metal portion in a direction along the central axis for pre-loading the ball bearing set.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spindle motor and disk drive furnished therewith
ActiveUS6914358B2Avoid Bubble ProblemsShaftsRecord information storageInternal pressureAtmospheric air
In a spindle motor utilizing dynamic-pressure bearings having a full-fill structure, a bearing configuration that balances and sustains at or above atmospheric pressure the internal pressure of the bearing oil. Thrust and radial bearing sections are configured within oil-filled bearing clearances in between the rotor, the shaft, and a shaft-encompassing hollow bearing member. A communicating passage one end of which opens on, radially inwardly along, the thrust bearing section is formed in the bearing member. Either axial ends of the bearing clearance in between the bearing member and shaft communicate through the passage. The communicating passage enables the oil to redistribute itself within the bearing clearances. Pressure difference between the axial upper and lower ends of the oil retained in between the bearing member and the shaft is compensated through the communicating passage, preventing incidents of negative pressure within the oil and of over-lift on the rotor.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
Method and apparatus for enabling cold temperature performance of a disk
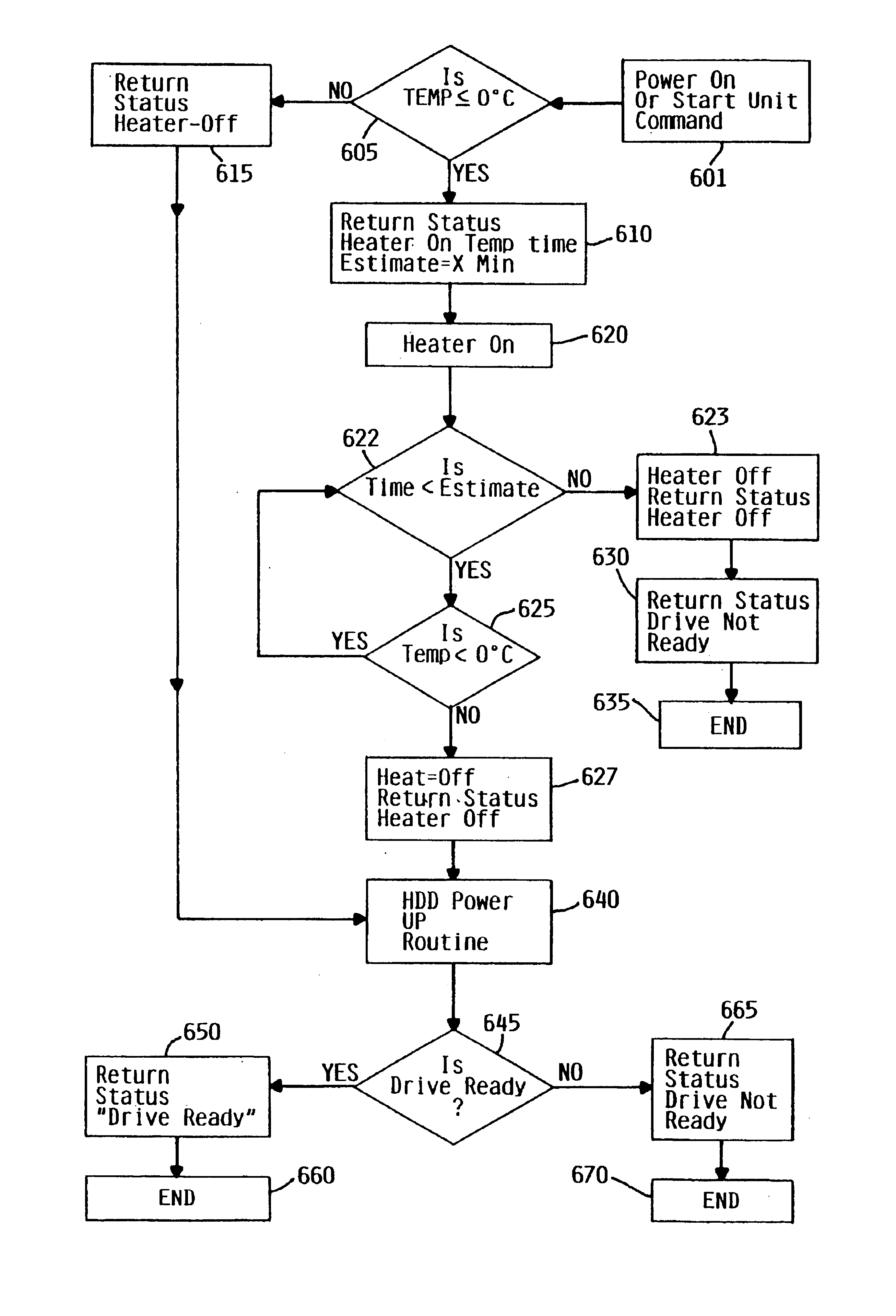
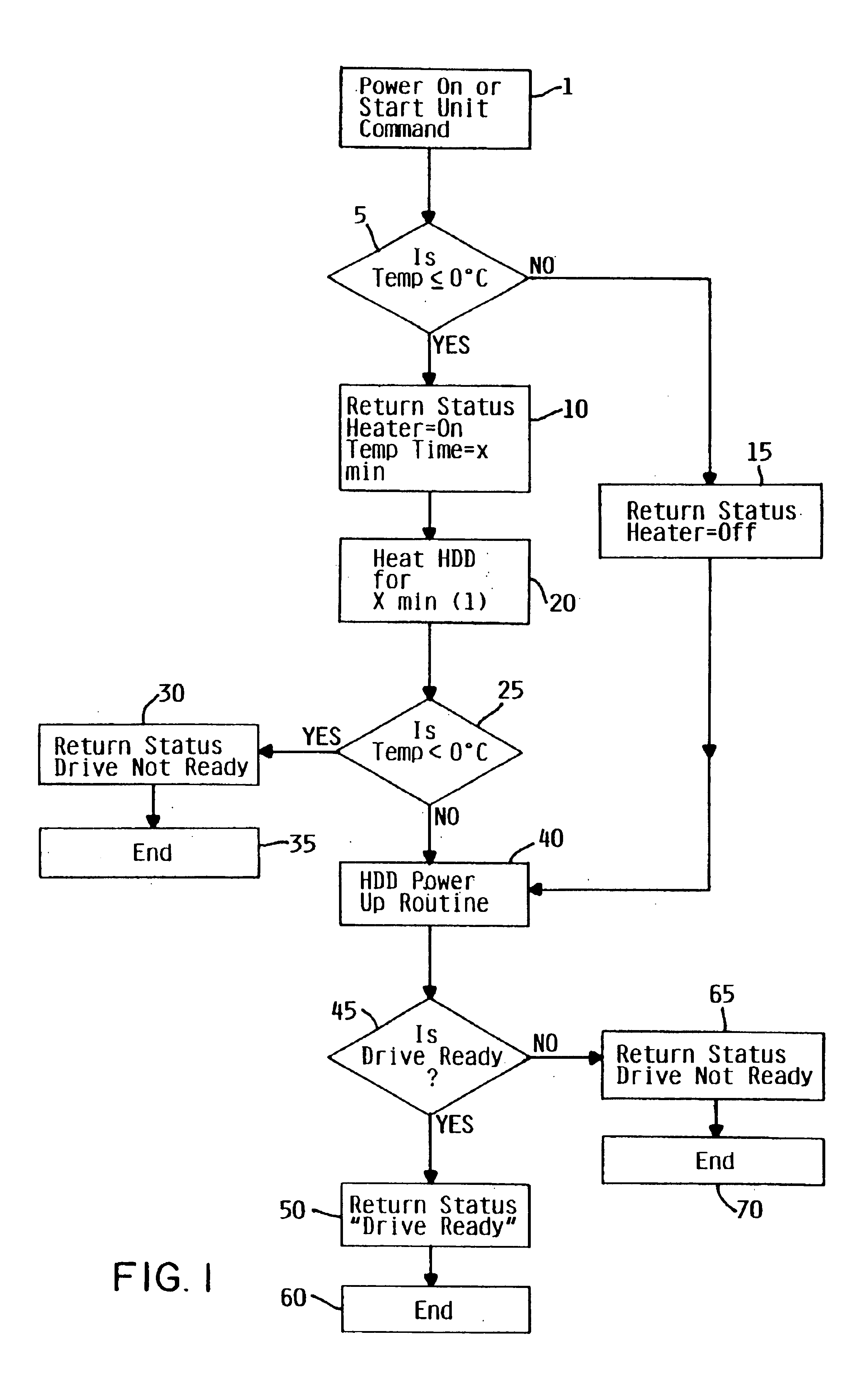
InactiveUS6735035B1High torqueHigh viscosityCommutation monitoringApparatus for flat record carriersDirect-access storage deviceEngineering
In cold weather, the higher torque required for normal spinning operation of a spindle motor assembly in a direct access storage device due to the increased viscosity of the grease, is overcome by localizing the heating to the spindle motor assembly to reduce the viscosity of the grease, and then let a disk driven self heat during and after spin-up of the spindle motor assembly.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Fluid dynamic bearing motor attached at both shaft ends
InactiveUS20060039636A1Improve accuracyLow profileShaftsRecord information storageEngineeringCentrifugal force
Owner:KURA LAB
Hydrodynamic bearing device, motor, recording disc driving apparatus and assembly jig
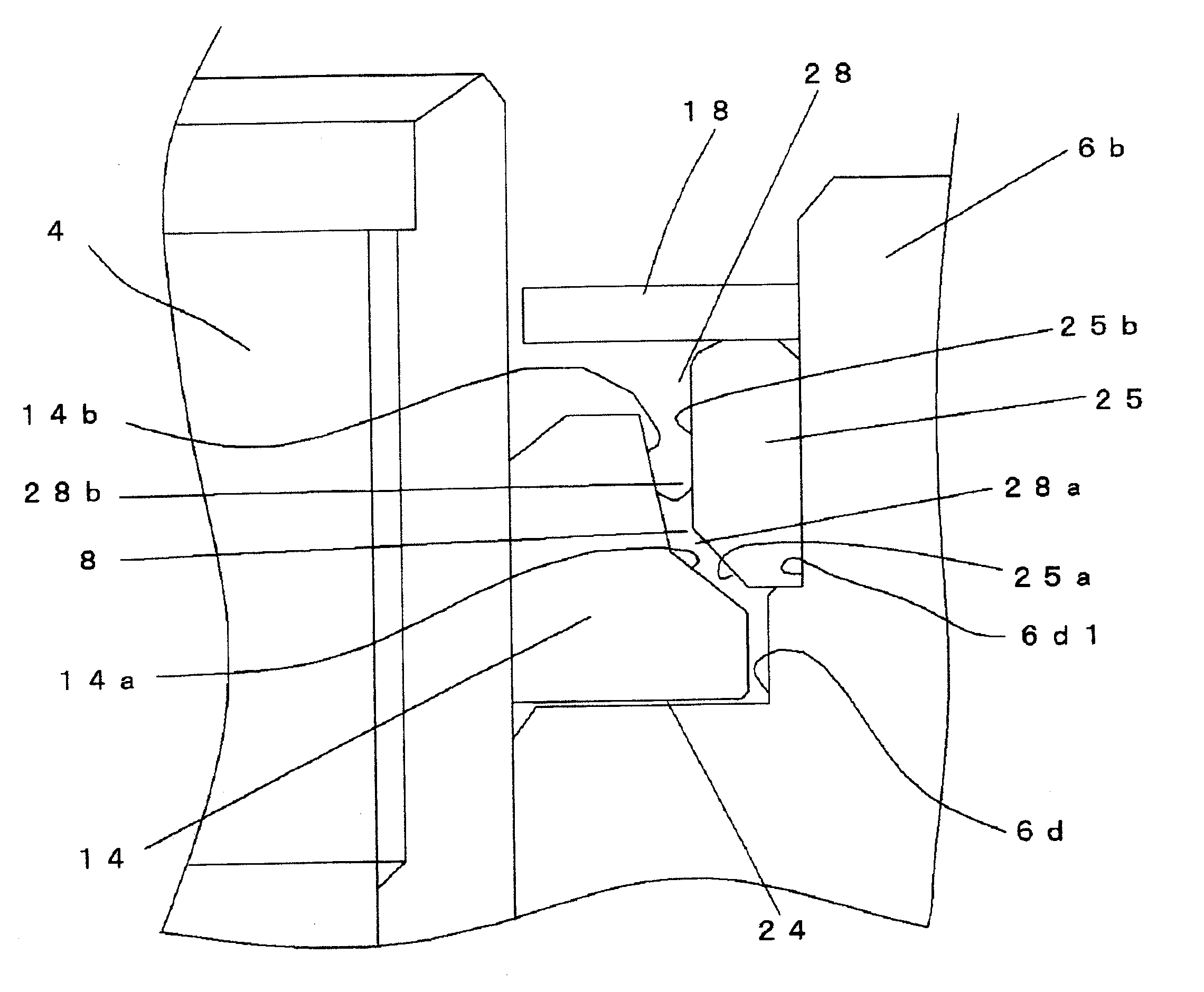
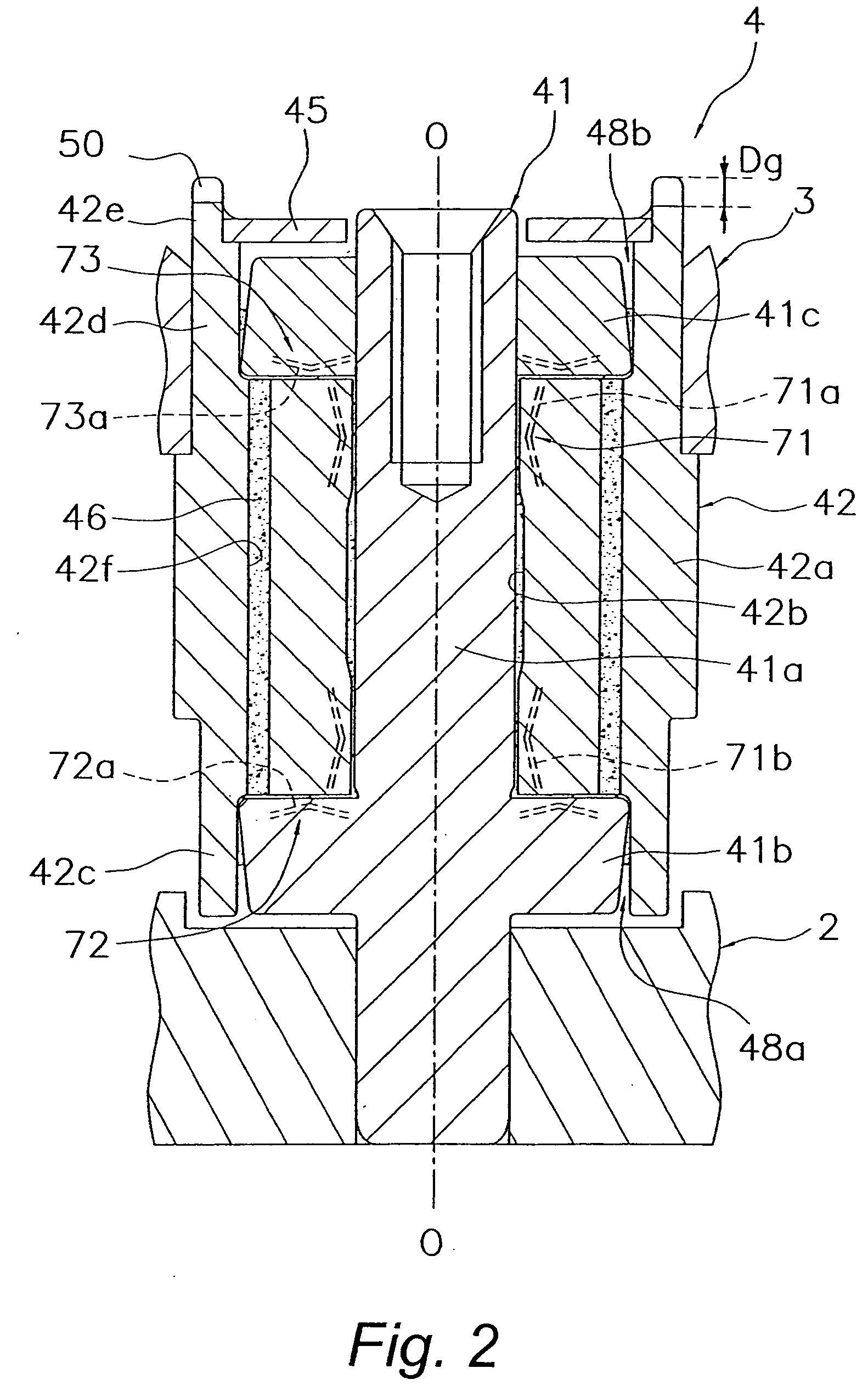
ActiveUS20070133911A1Avoid paddingPrevent air bubbles from infiltrating the bearingsShaftsBearing componentsThrust bearingAssembly line
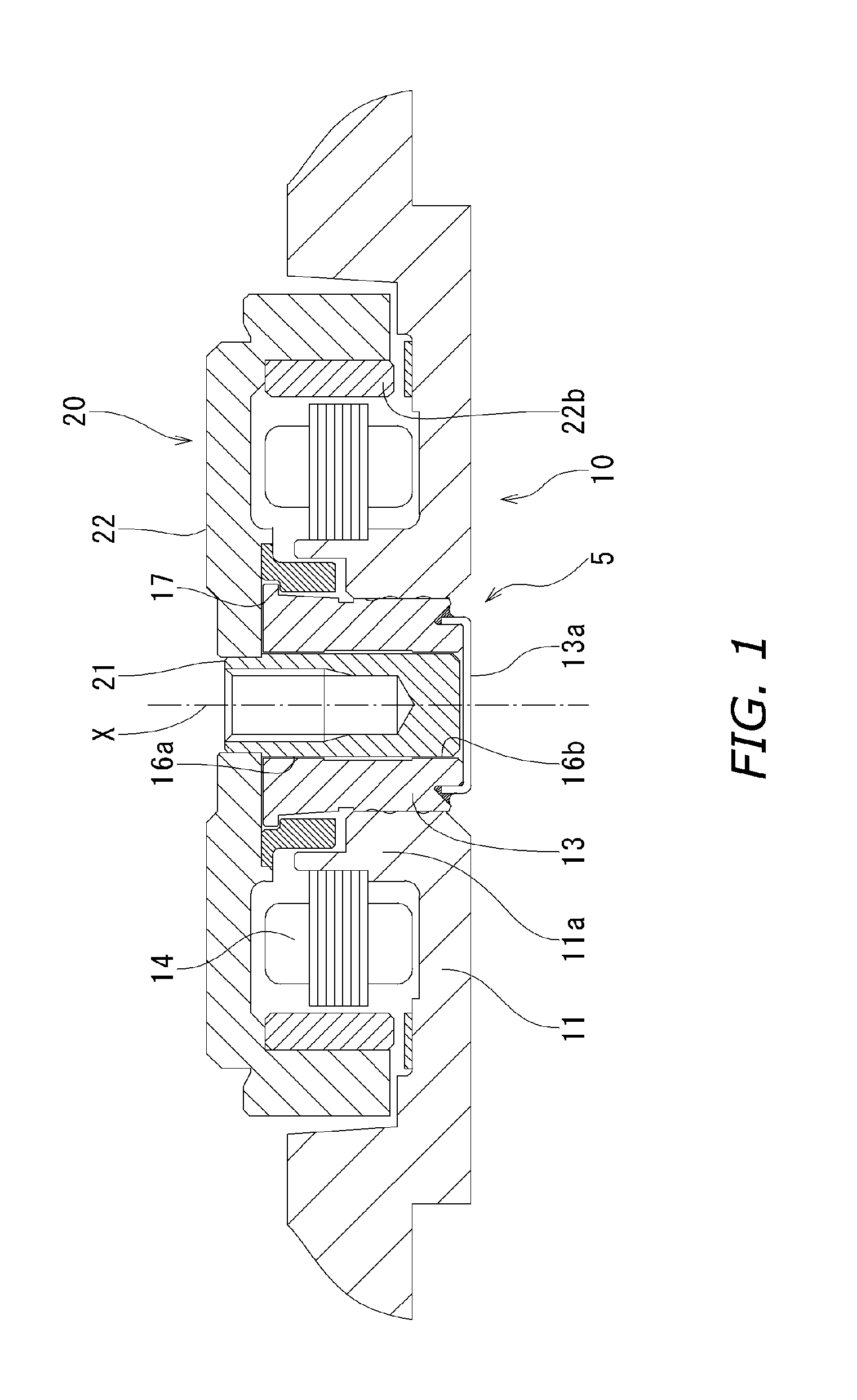
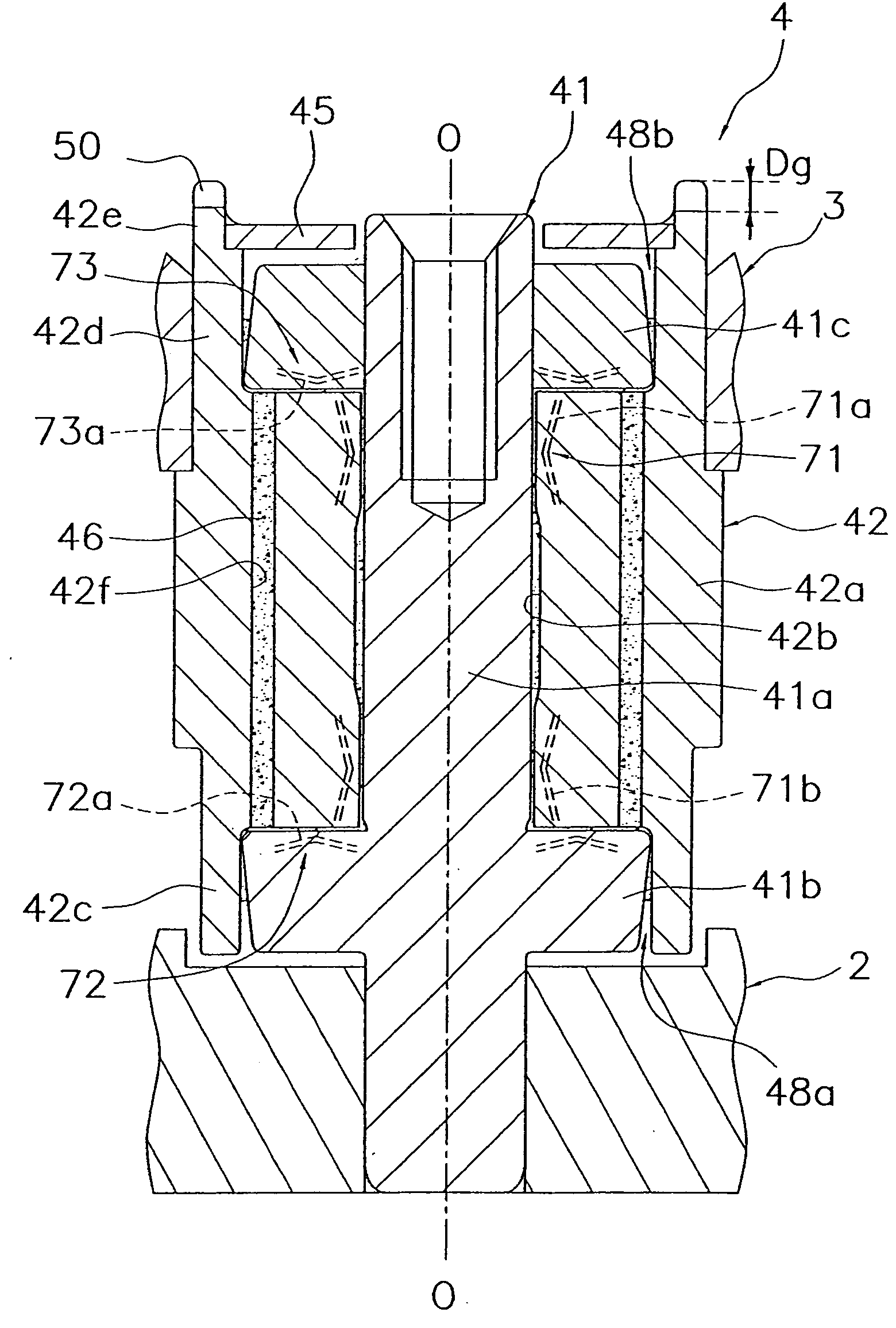
Object: To prevent the lubricant that fills a bearing from leaking out, and prevent air bubbles from infiltrating the bearing, even if the open end of a bearing should be blocked off by a finger or the like in the course of assembling a hydrodynamic bearing device, etc. Means for Solution: A hydrodynamic bearing device 4 comprises a shaft 41, a second thrust flange 41c, a sleeve 42, a radial bearing 71, and a thrust bearing 73. The second thrust flange 41c is fixed near one end of the shaft 41. A third cylindrical protrusion 42e that protrudes farther in the axial direction than the second thrust flange is fixed to or integrally machined at one end of the sleeve 42. A notch 50 that communicates between a radial inner space and a radial outer space separated by the third cylindrical protrusion 42e is provided to the third cylindrical protrusion 42e.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com