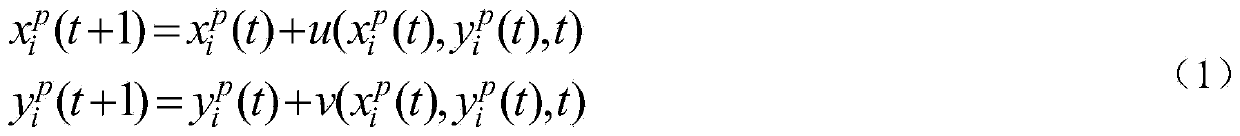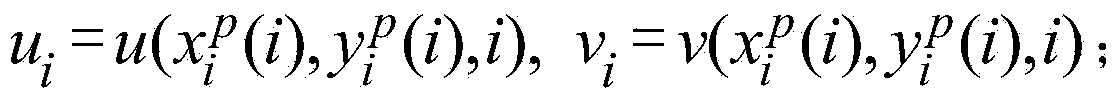Patents
Literature
230 results about "Line flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
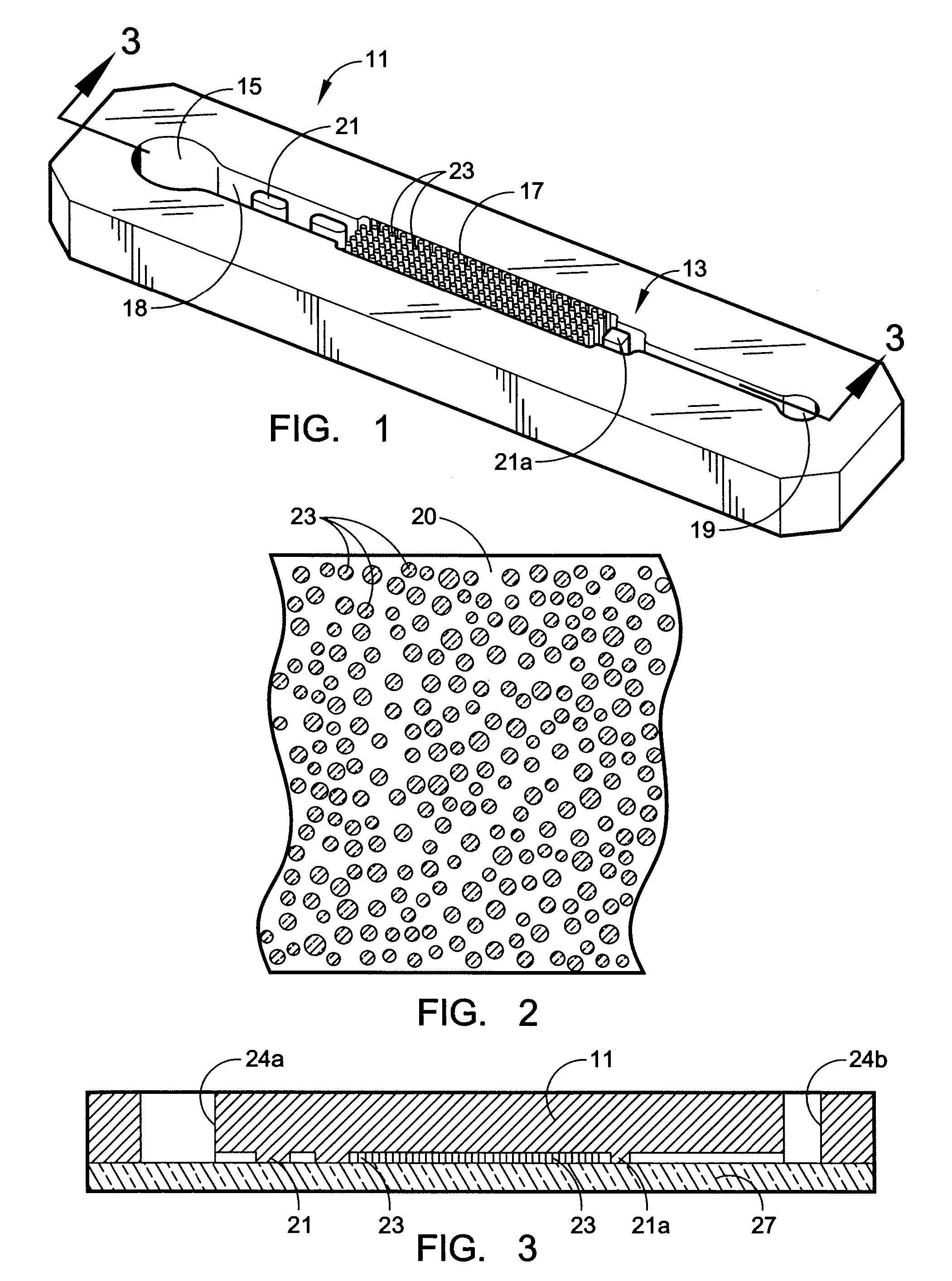
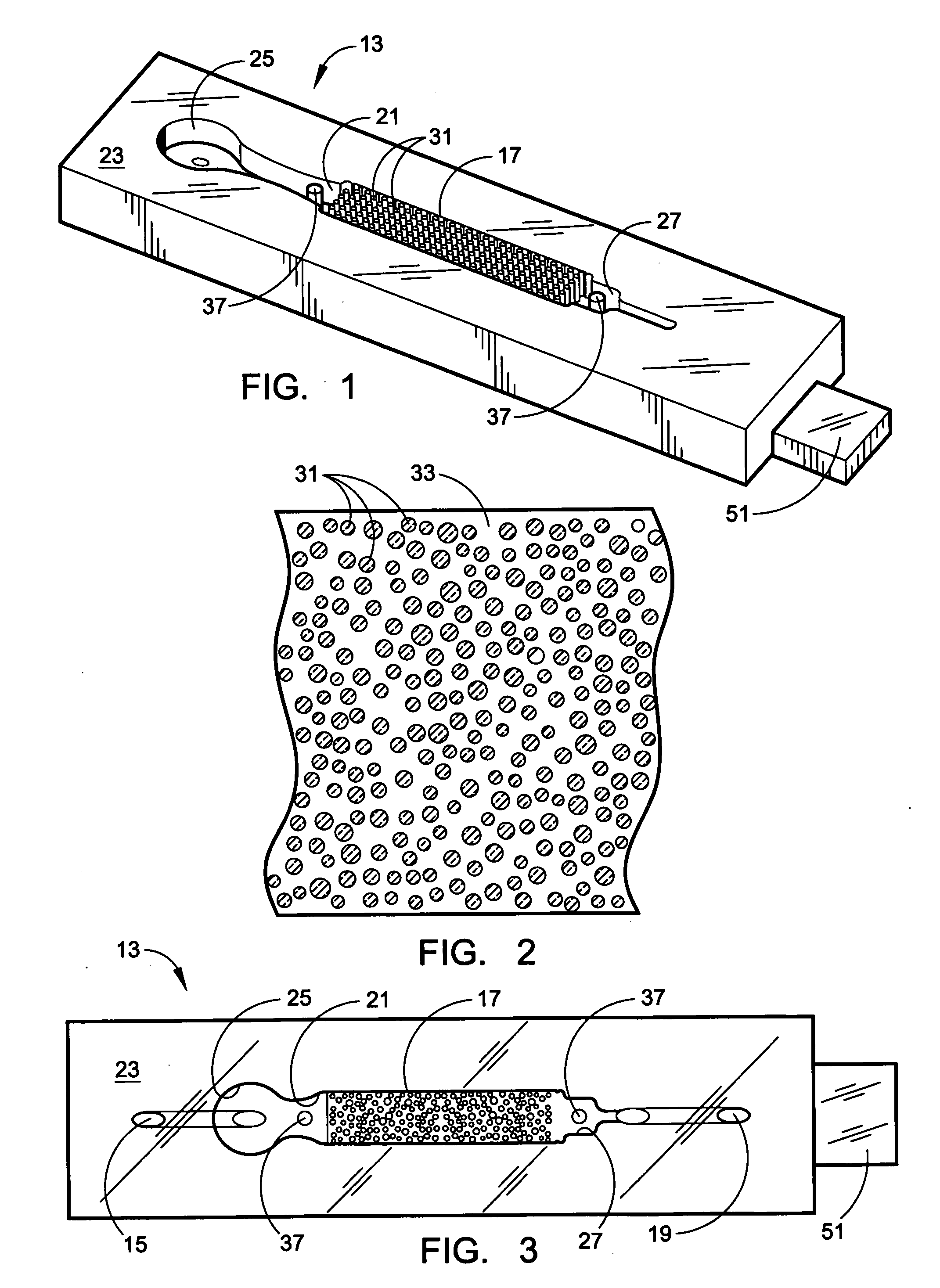
Recovery of rare cells using a microchannel apparatus with patterned posts
ActiveUS20060160243A1Flow interruptionEfficient captureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrophilic coatingFlow disruption
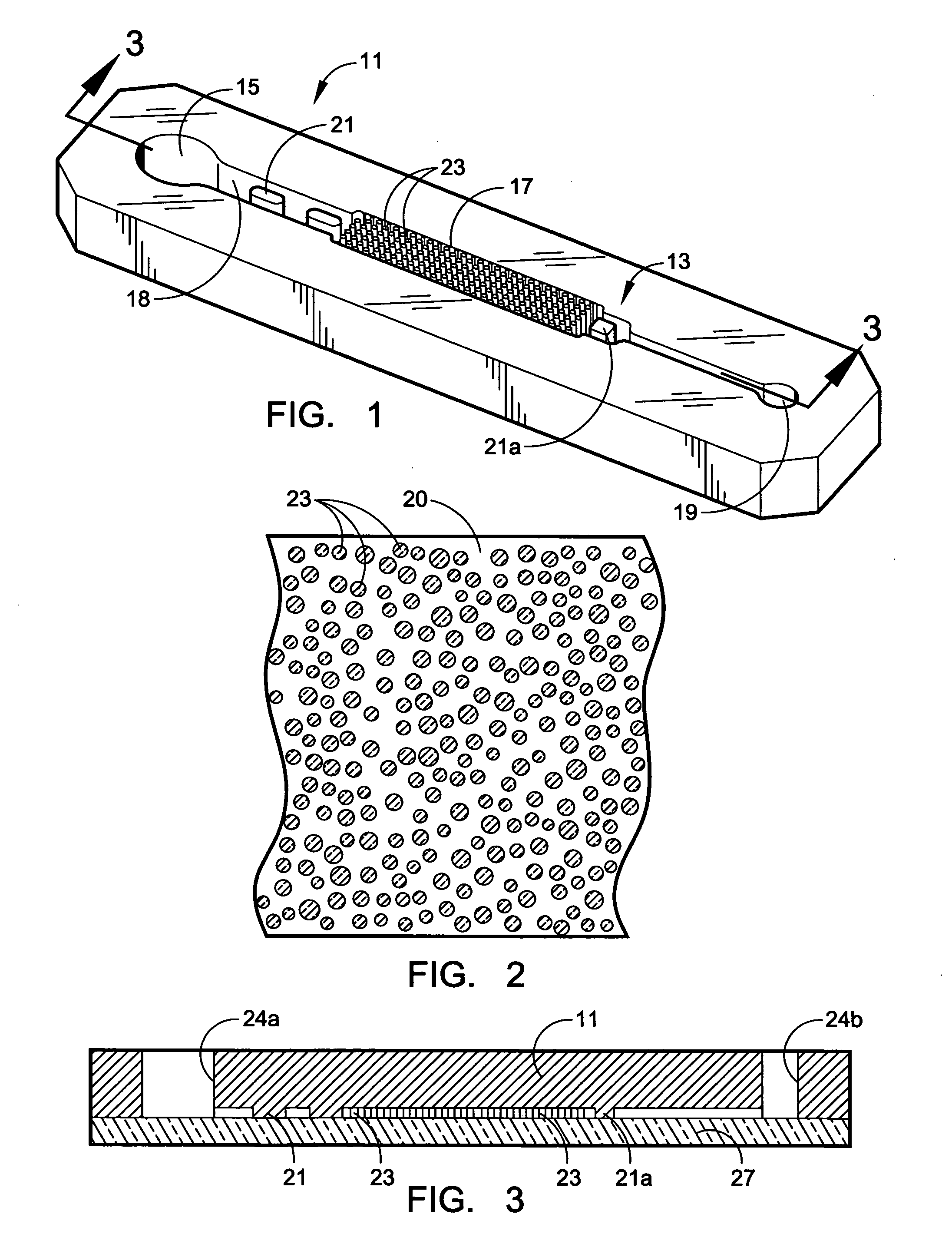
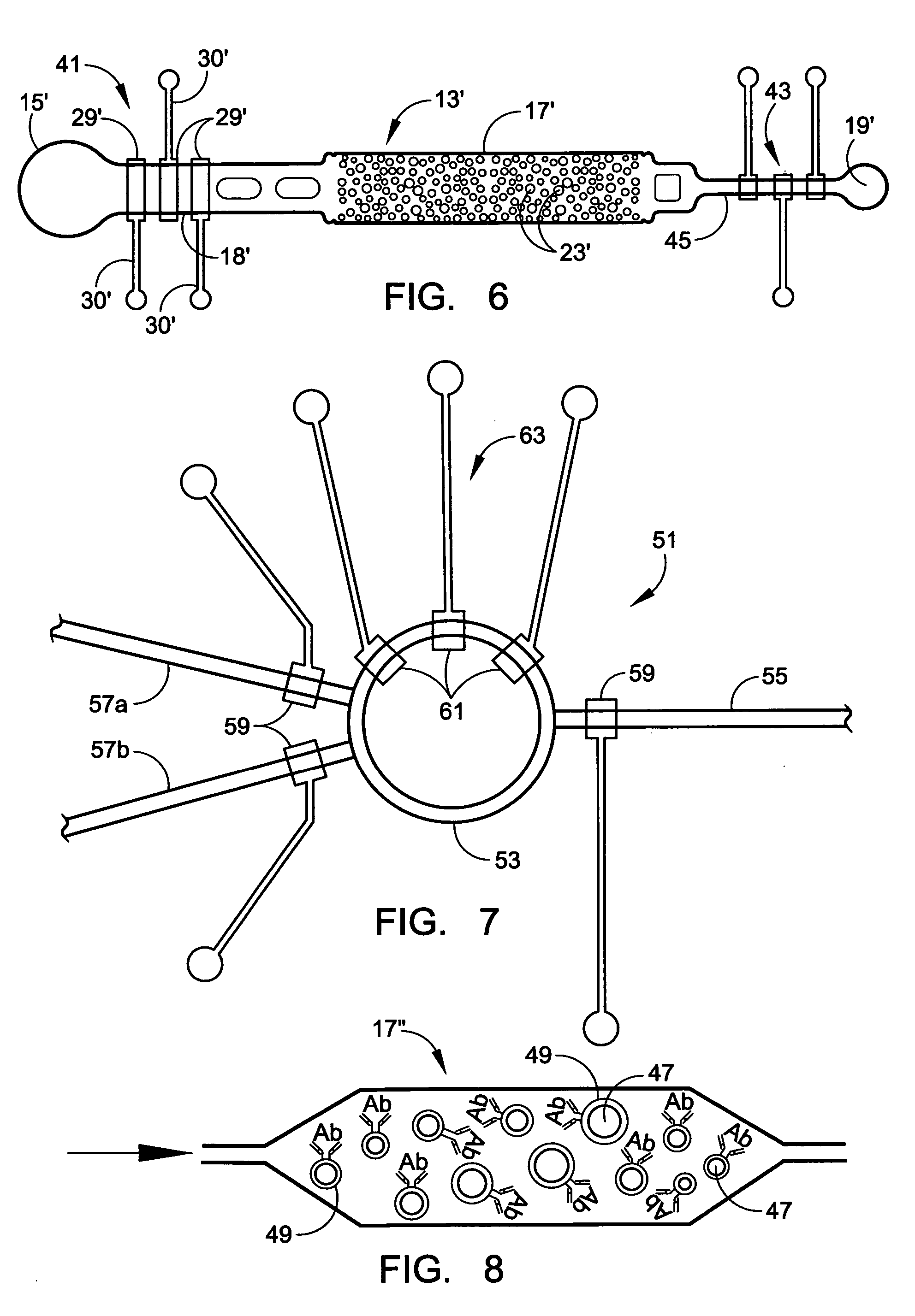
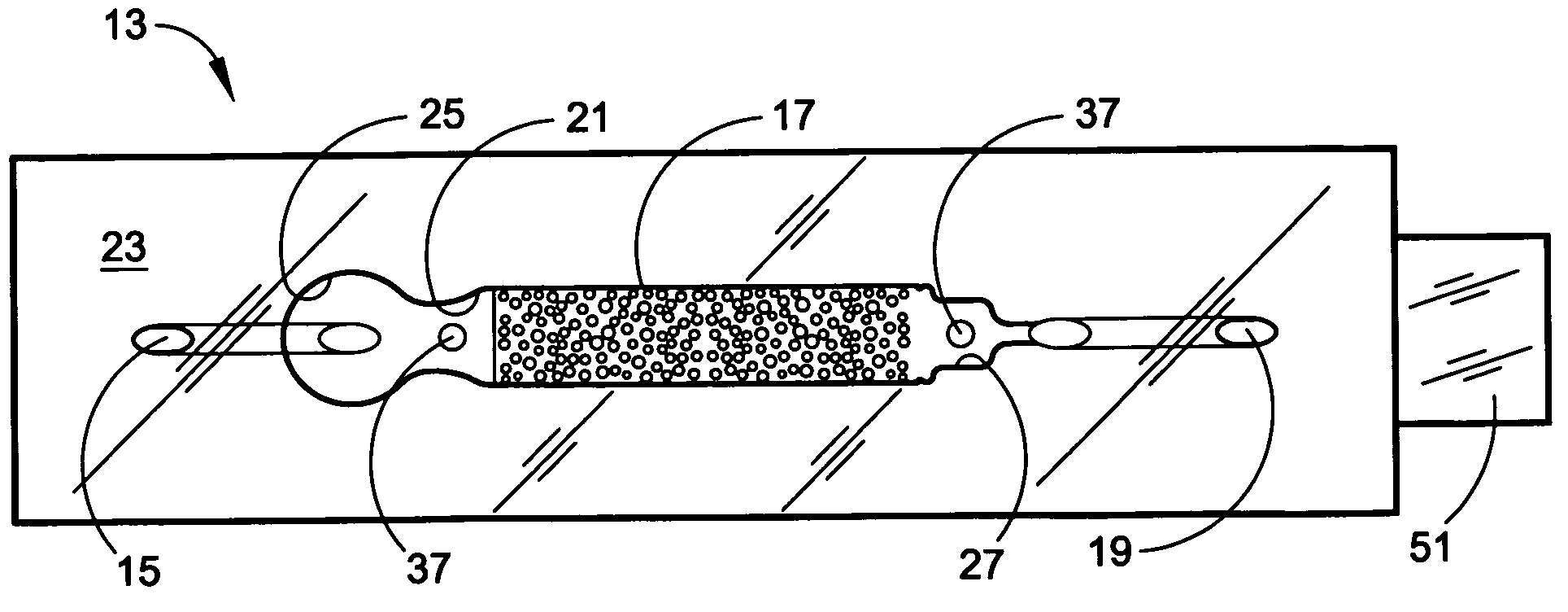
A microflow apparatus for separating or isolating cells from a bodily fluid or other liquid sample uses a flow path where straight-line flow is interrupted by a pattern of transverse posts. The posts are spaced across the width of a collection region in the flow path, extending between the upper and lower surfaces thereof; they have rectilinear surfaces, have arcuate cross-sections, and are randomly arranged so as to disrupt streamlined flow. Sequestering agents, such as Abs, are attached to all surfaces in the collection region via a hydrophilic coating, preferably a hydrogel containing isocyanate moieties or a PEG or polyglycine of substantial length, and are highly effective in capturing cells or other targeted biomolecules as a result of such streamlined flow disruption.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
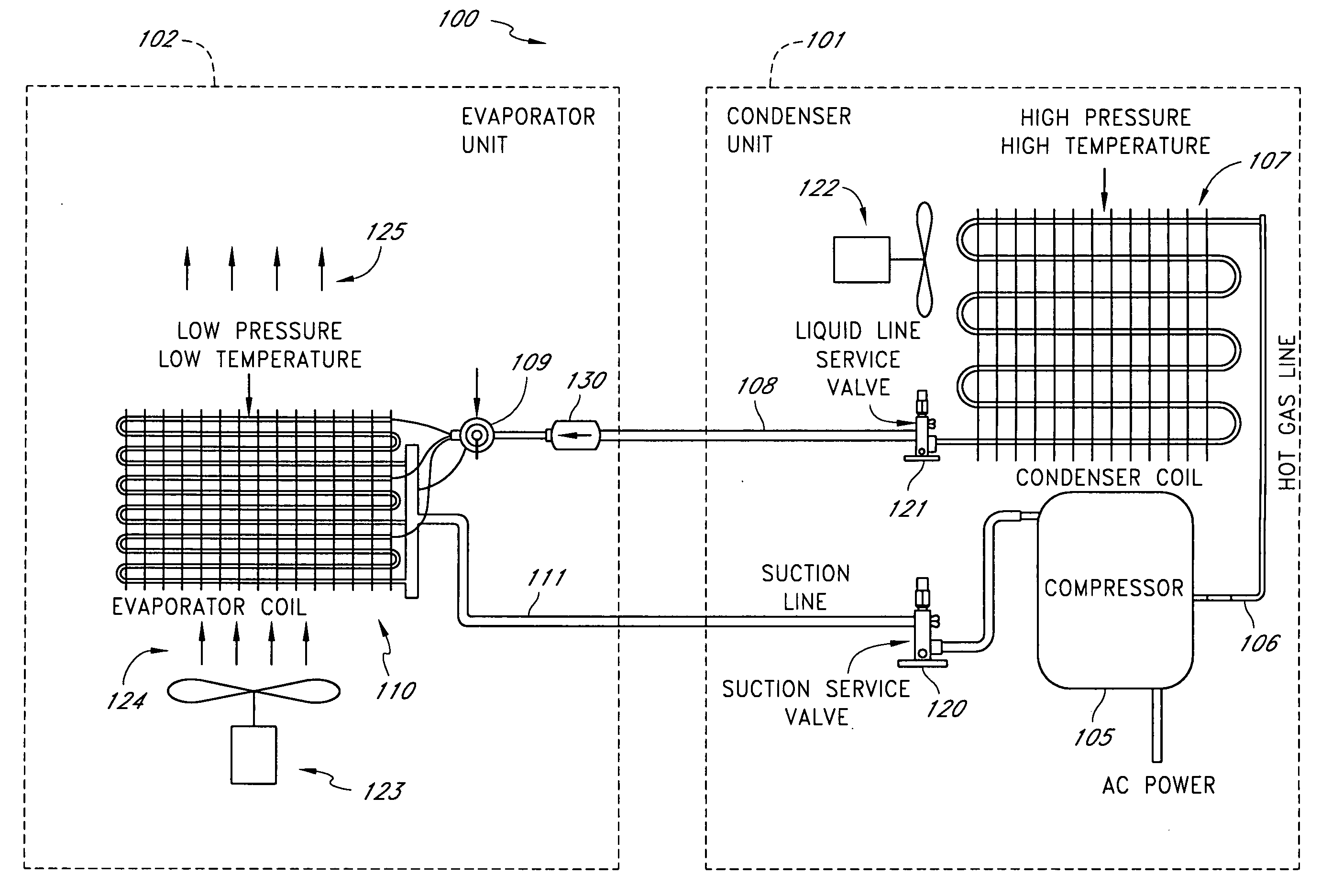
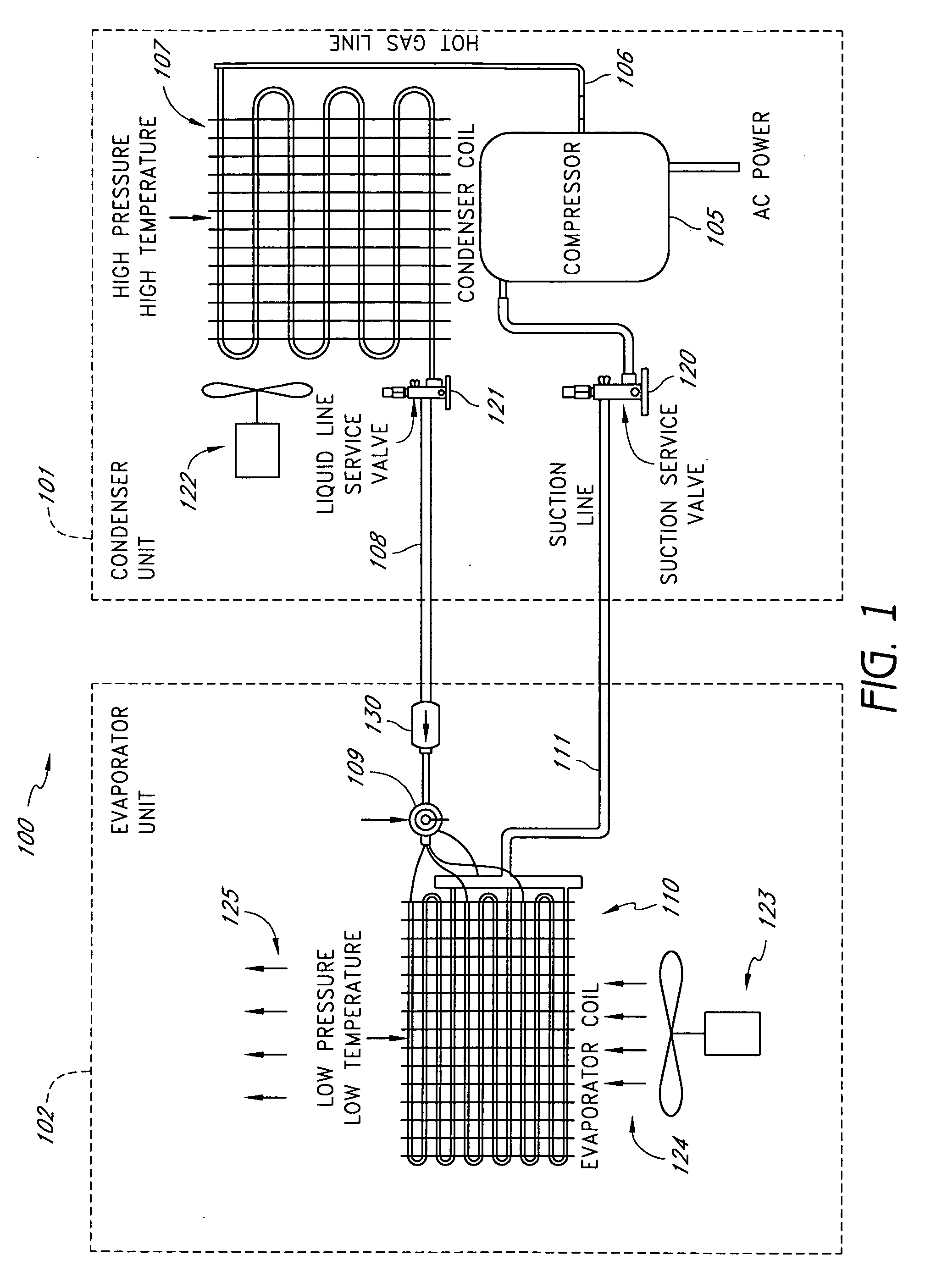
Air filter monitoring system
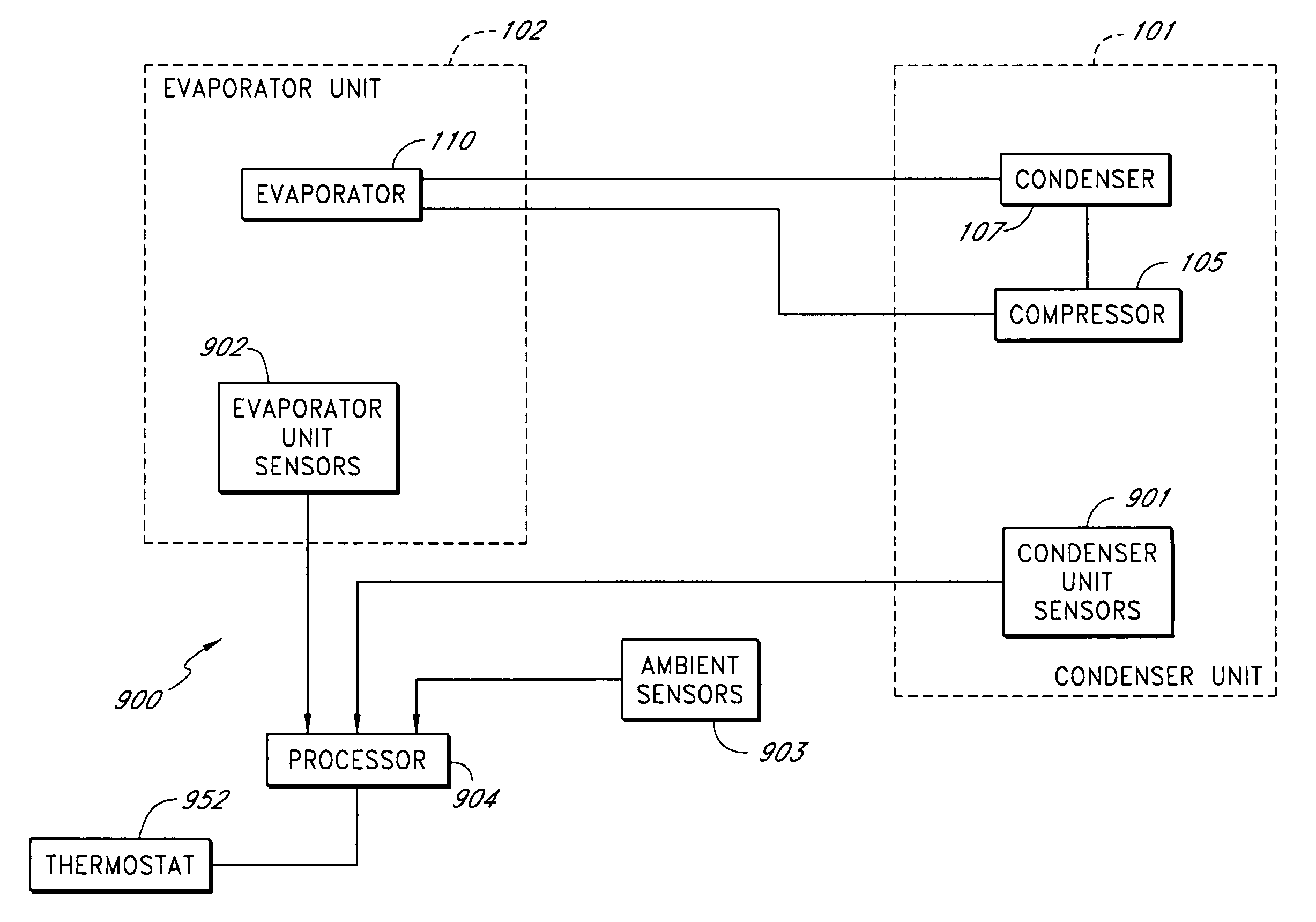
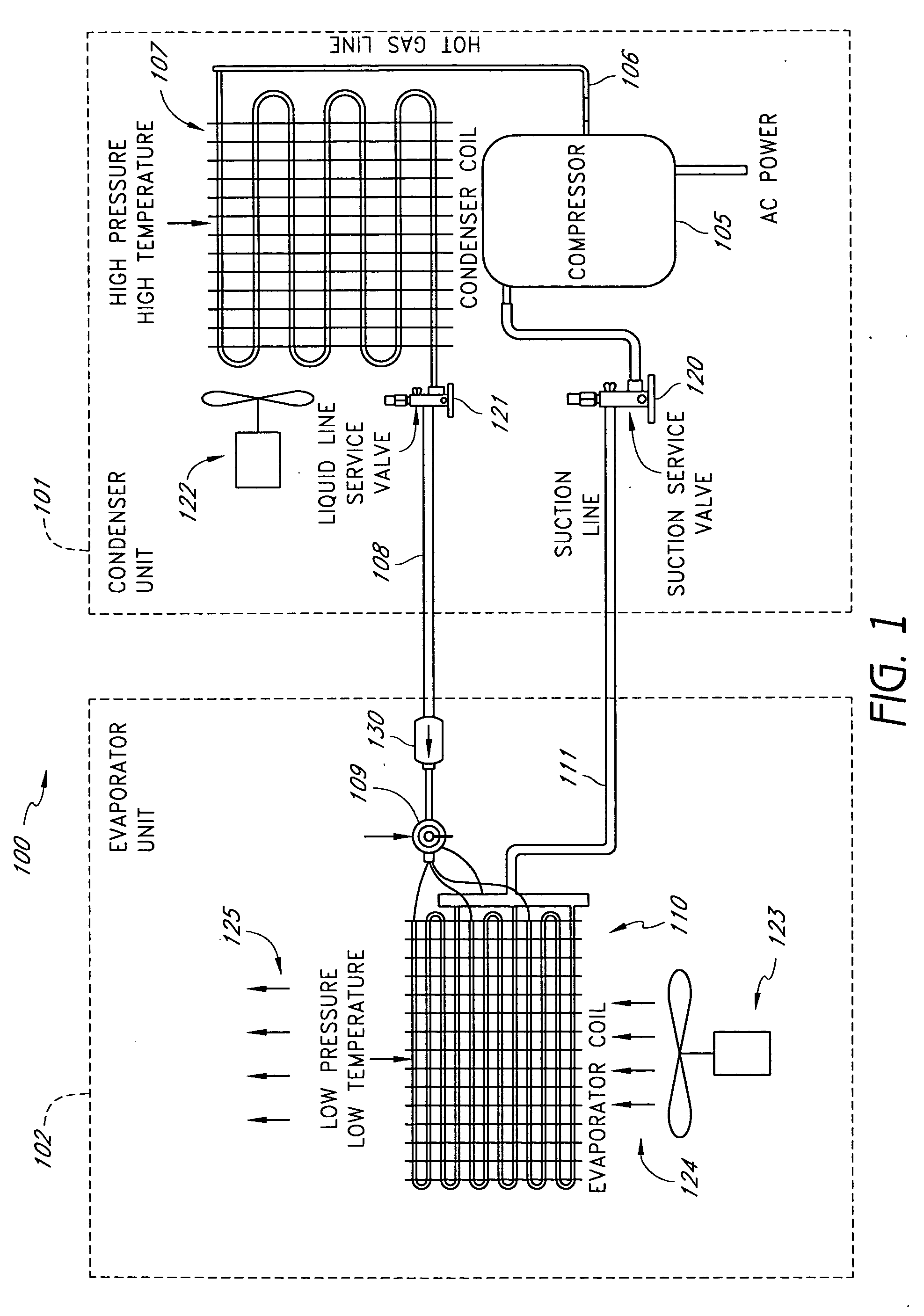
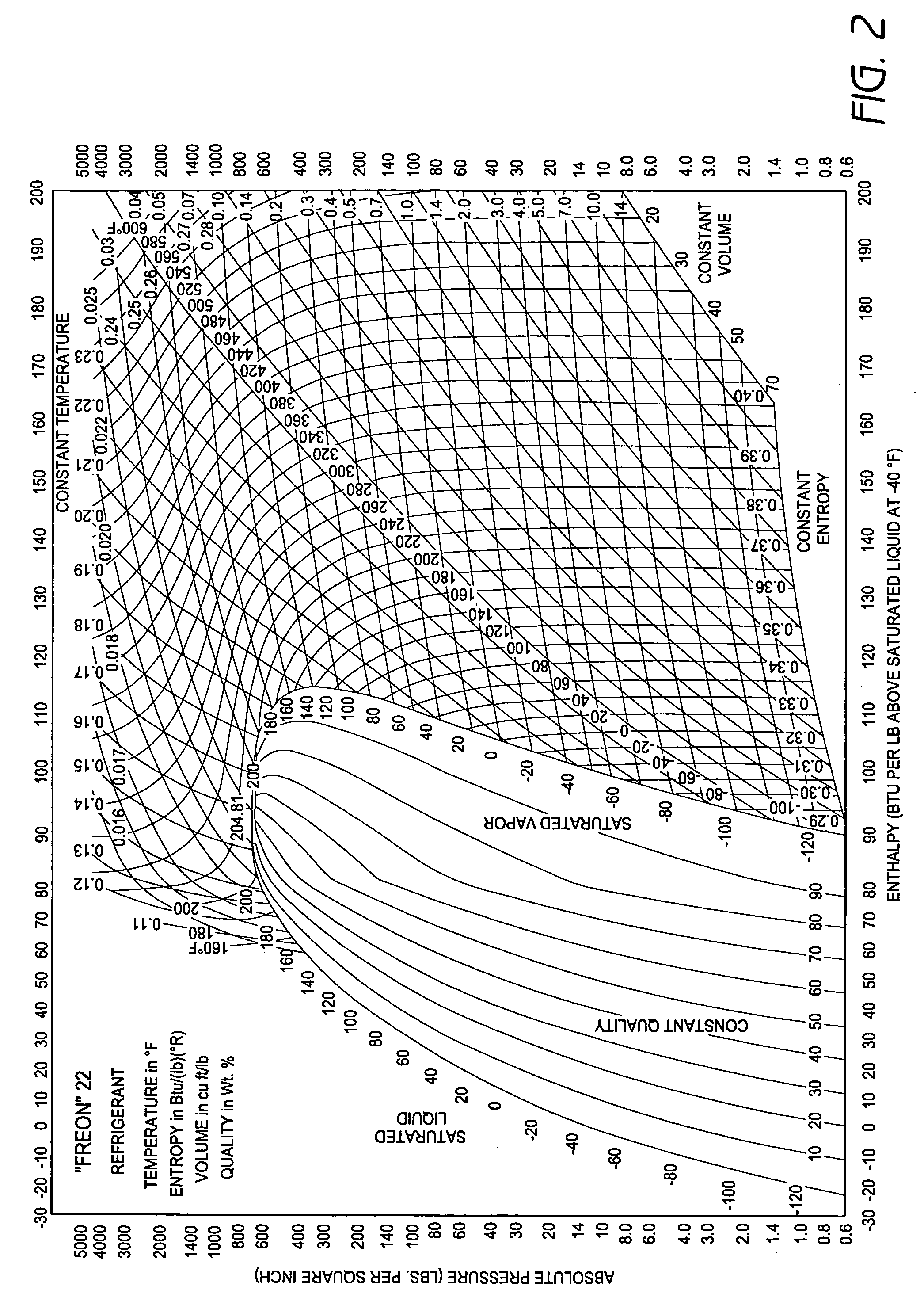
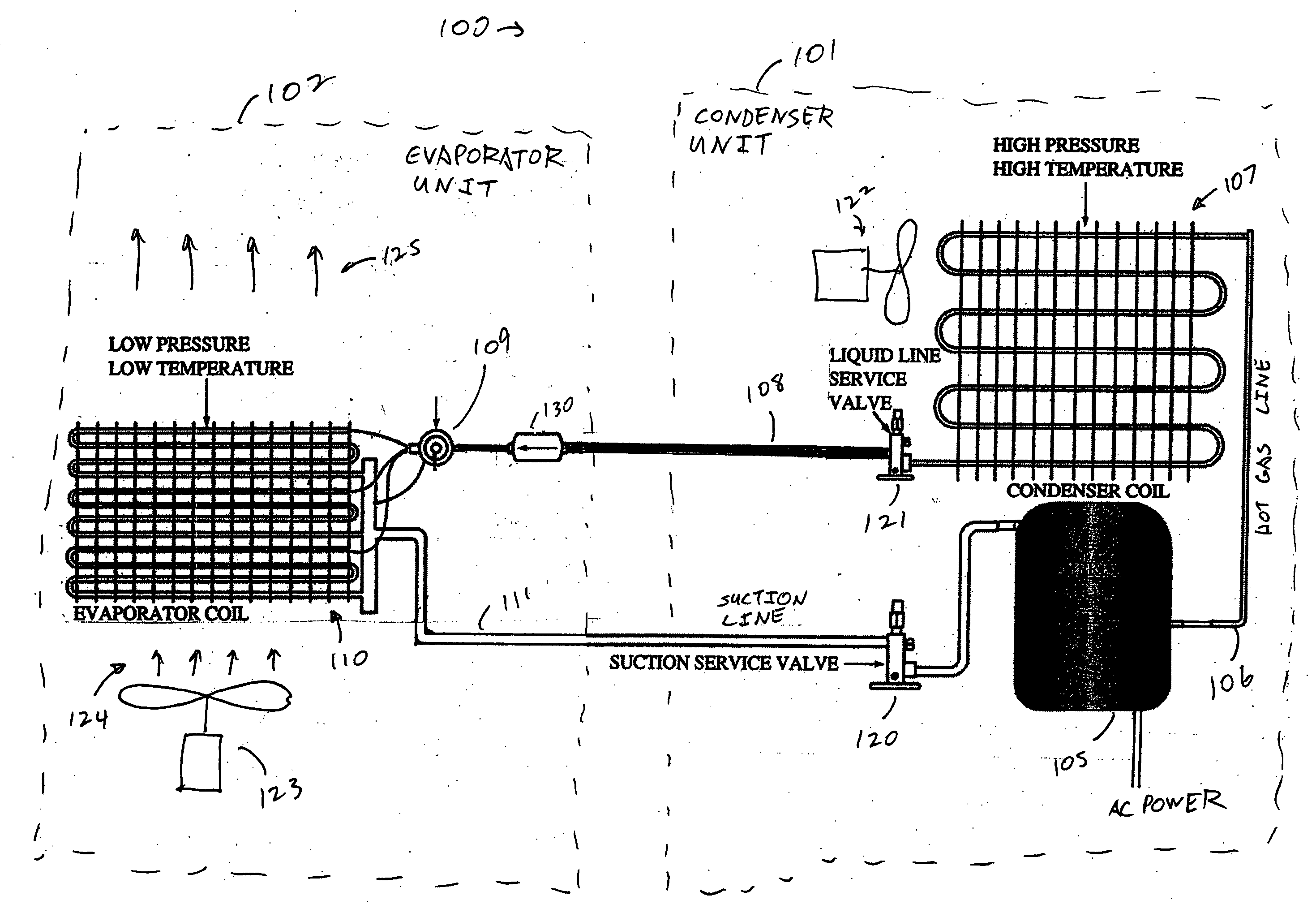
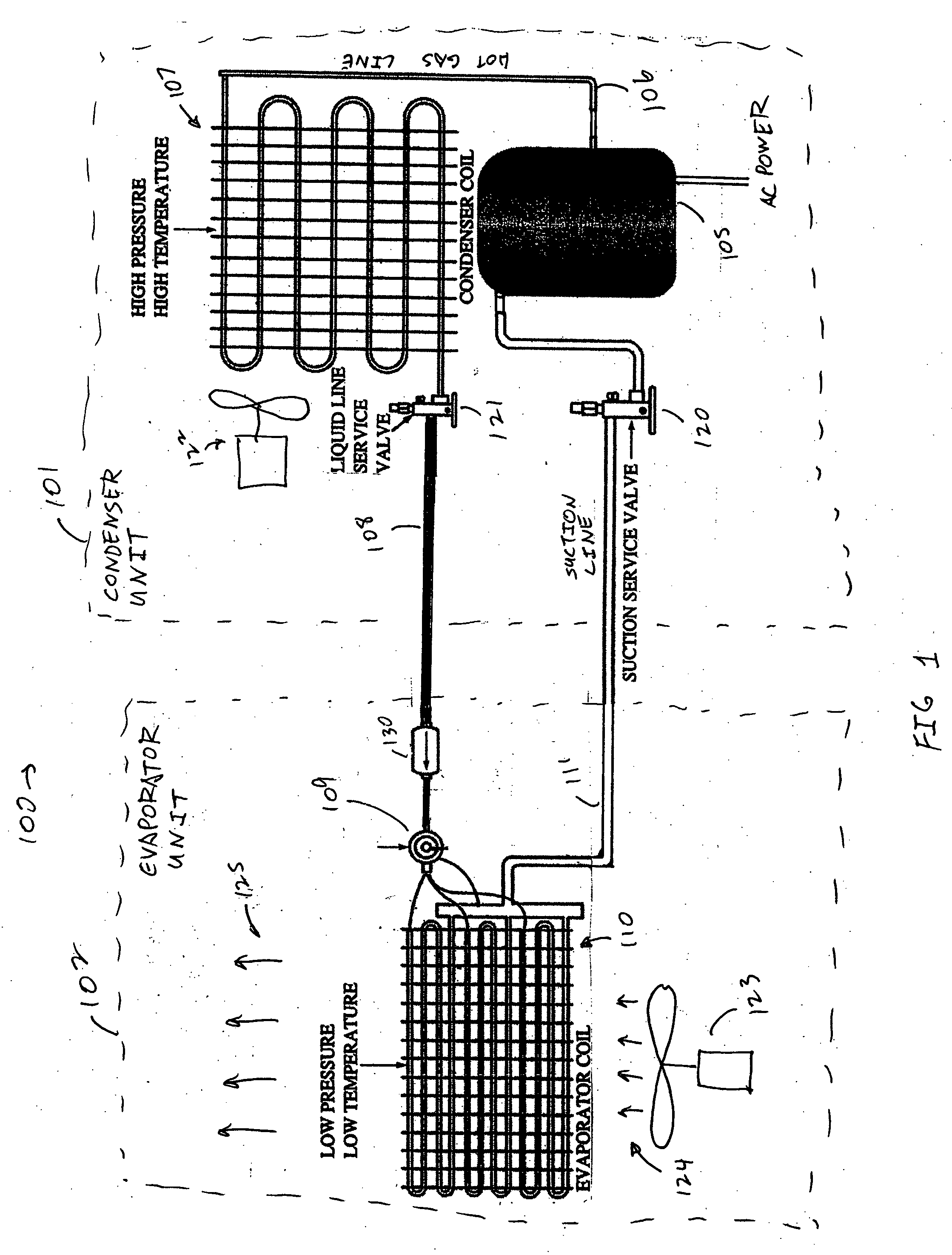
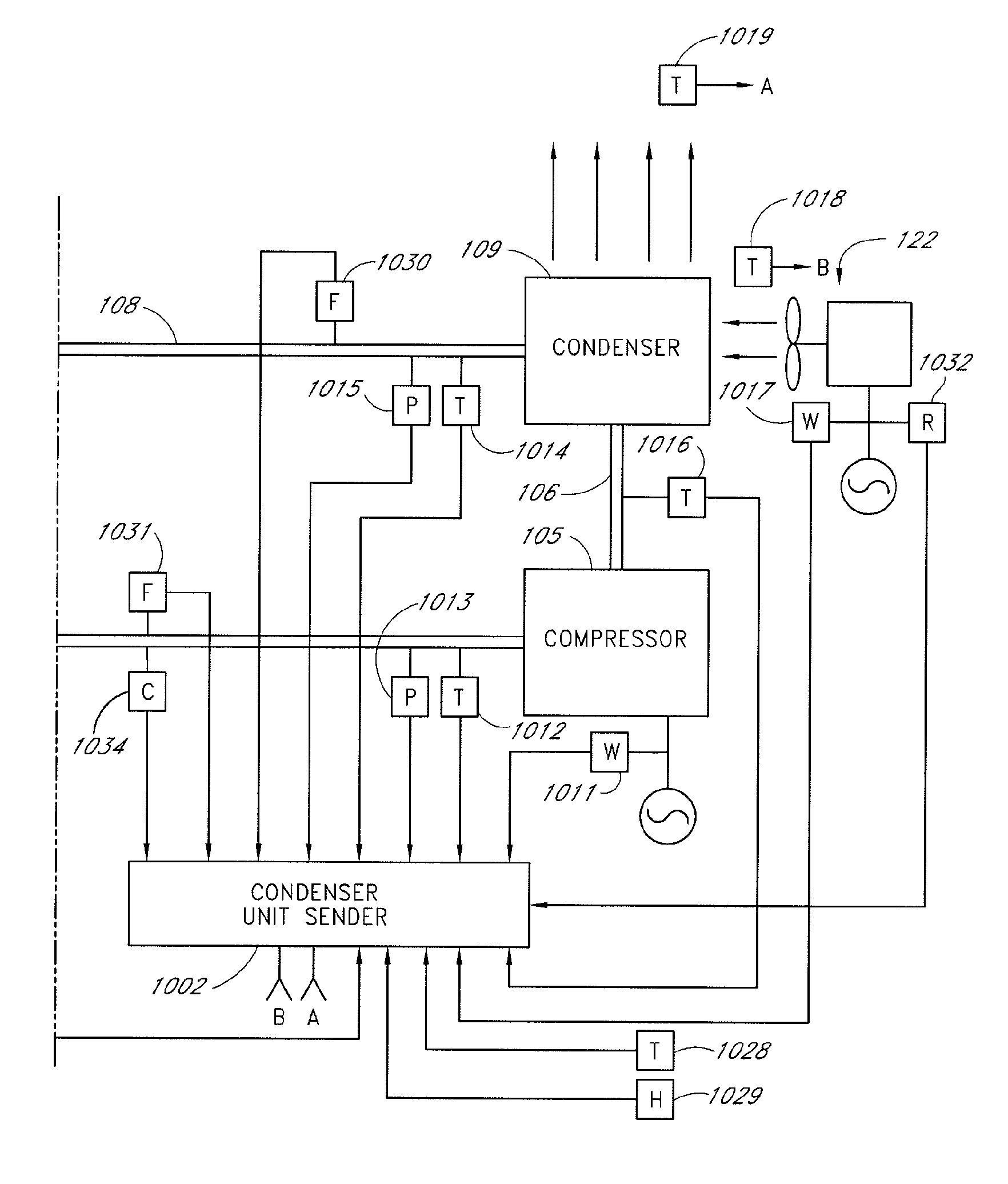
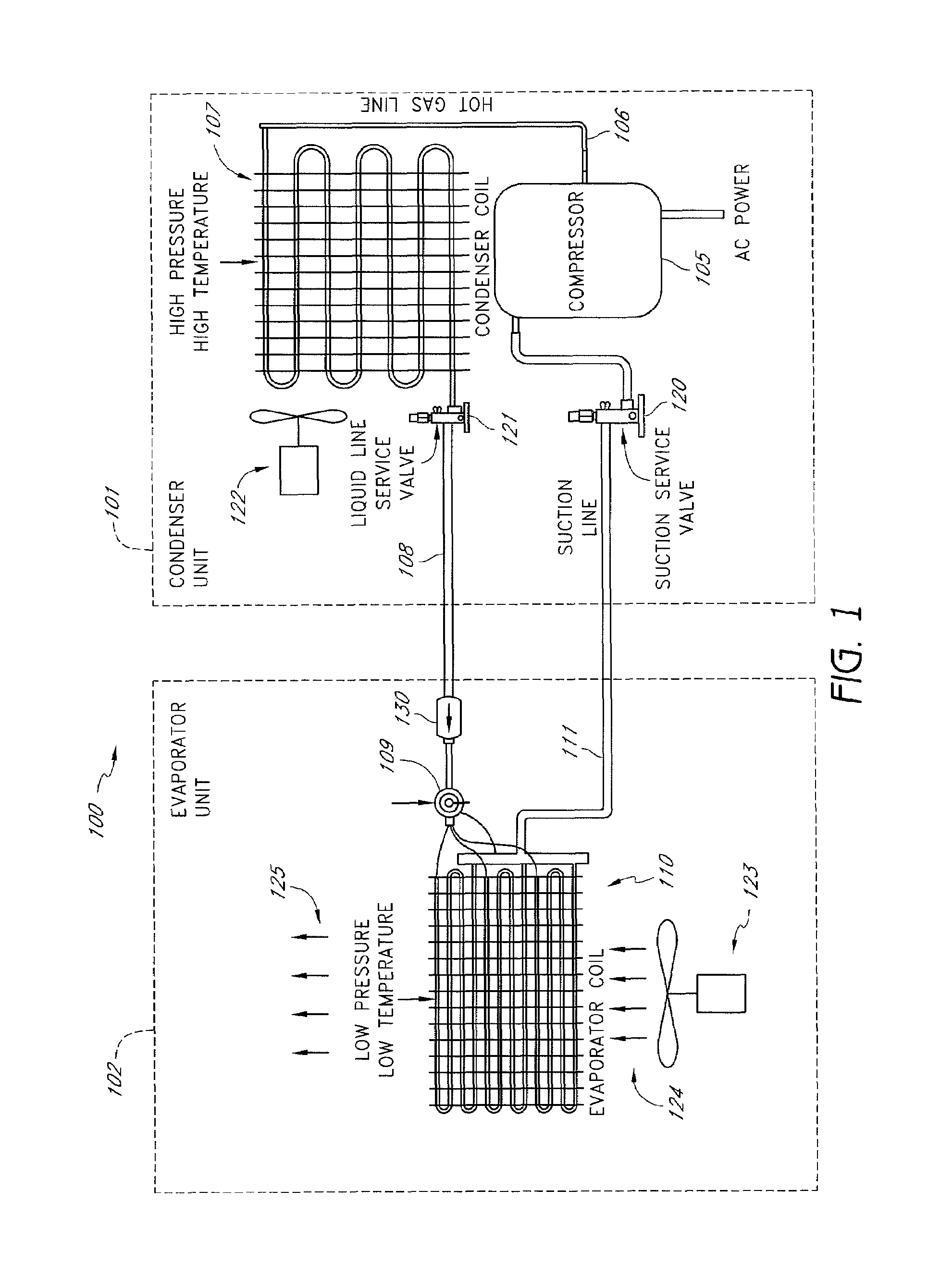
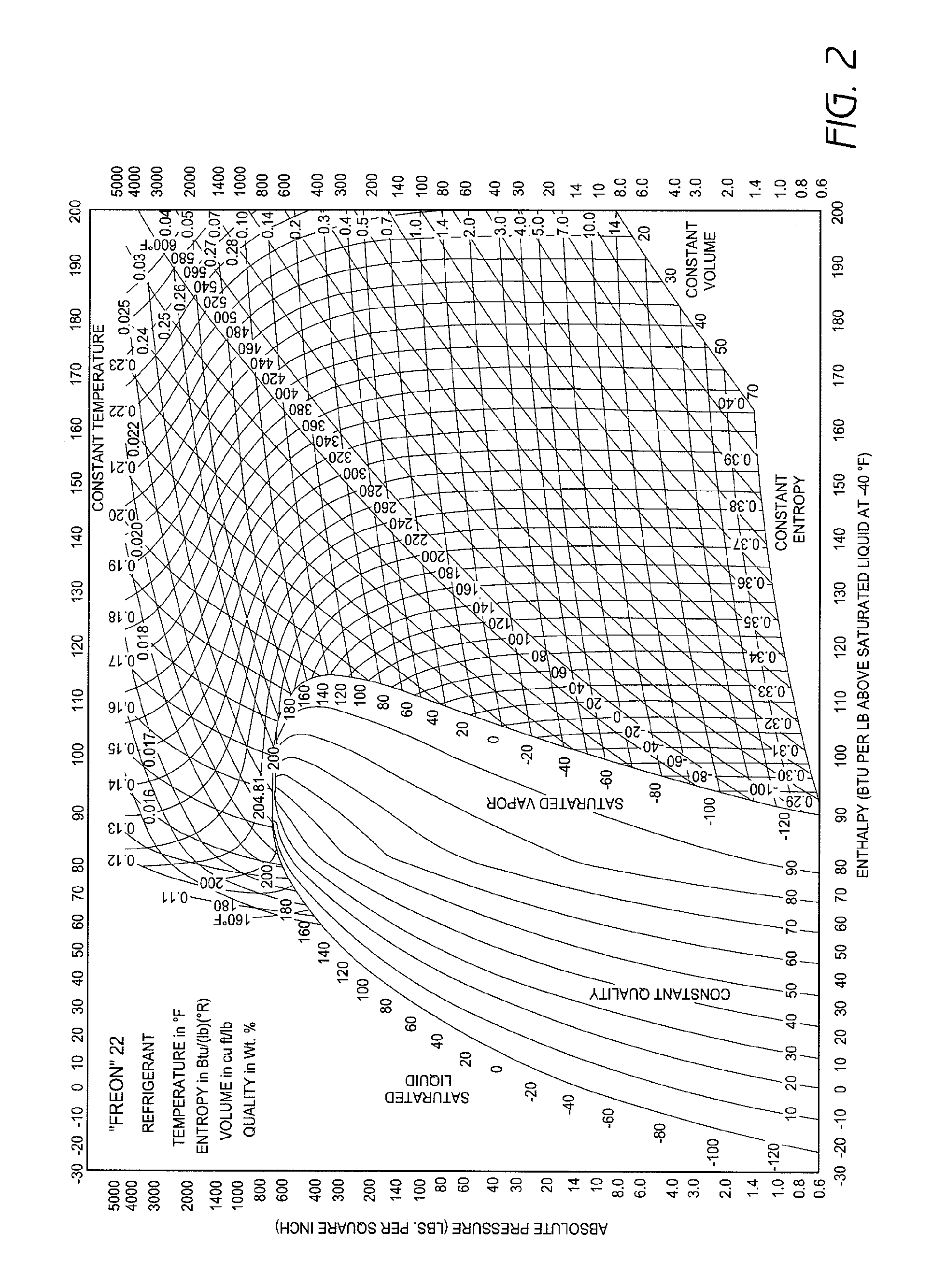
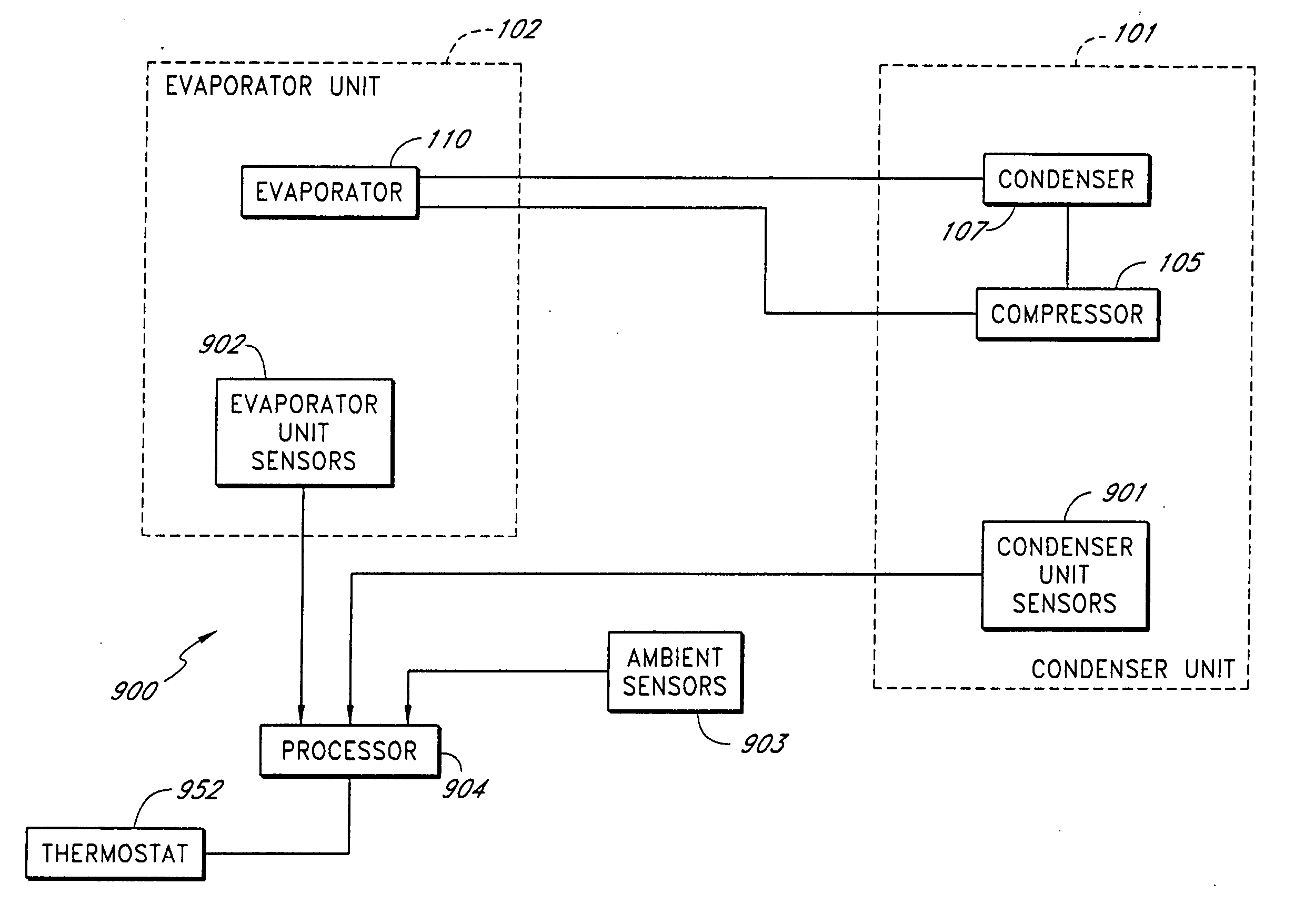
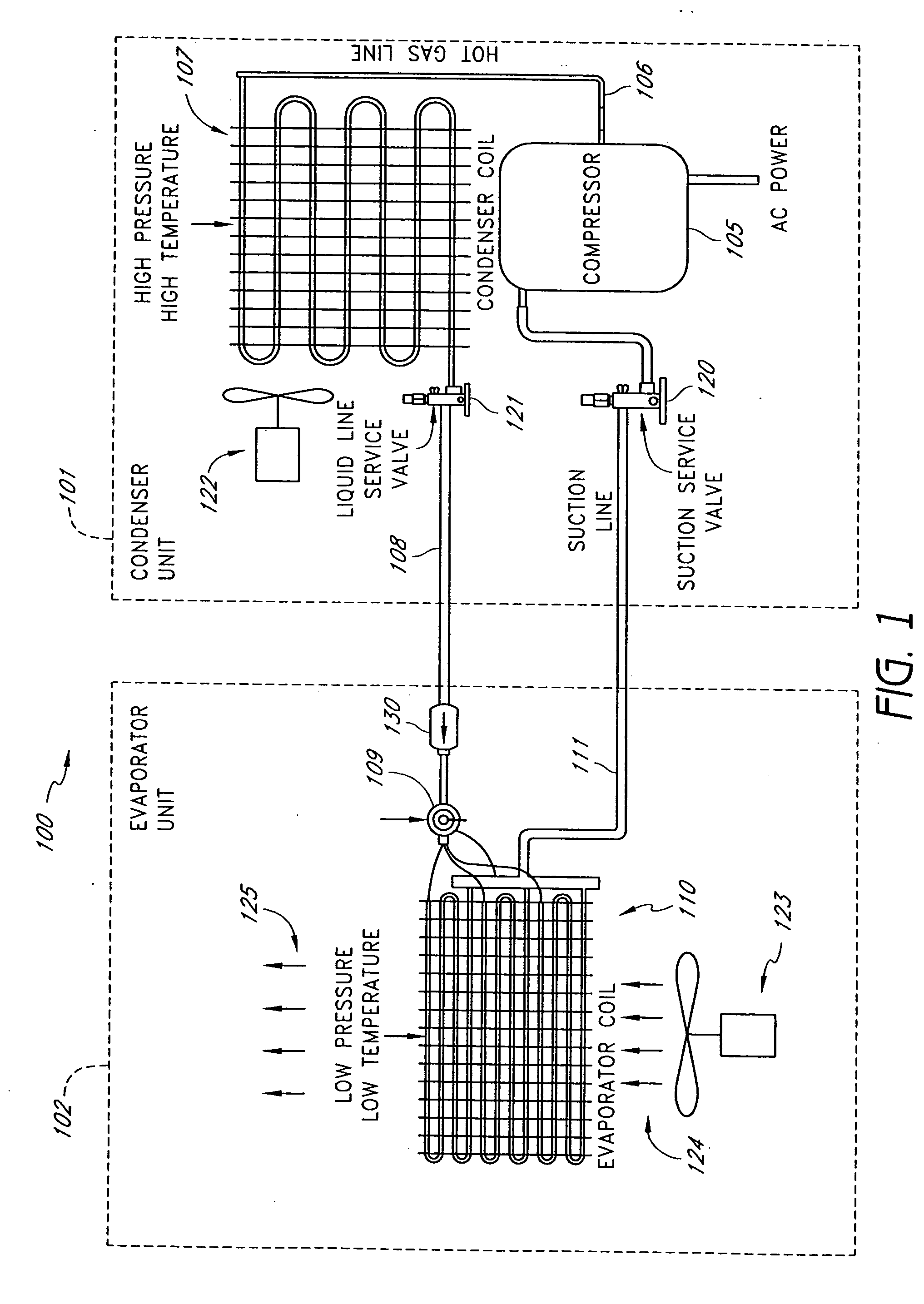
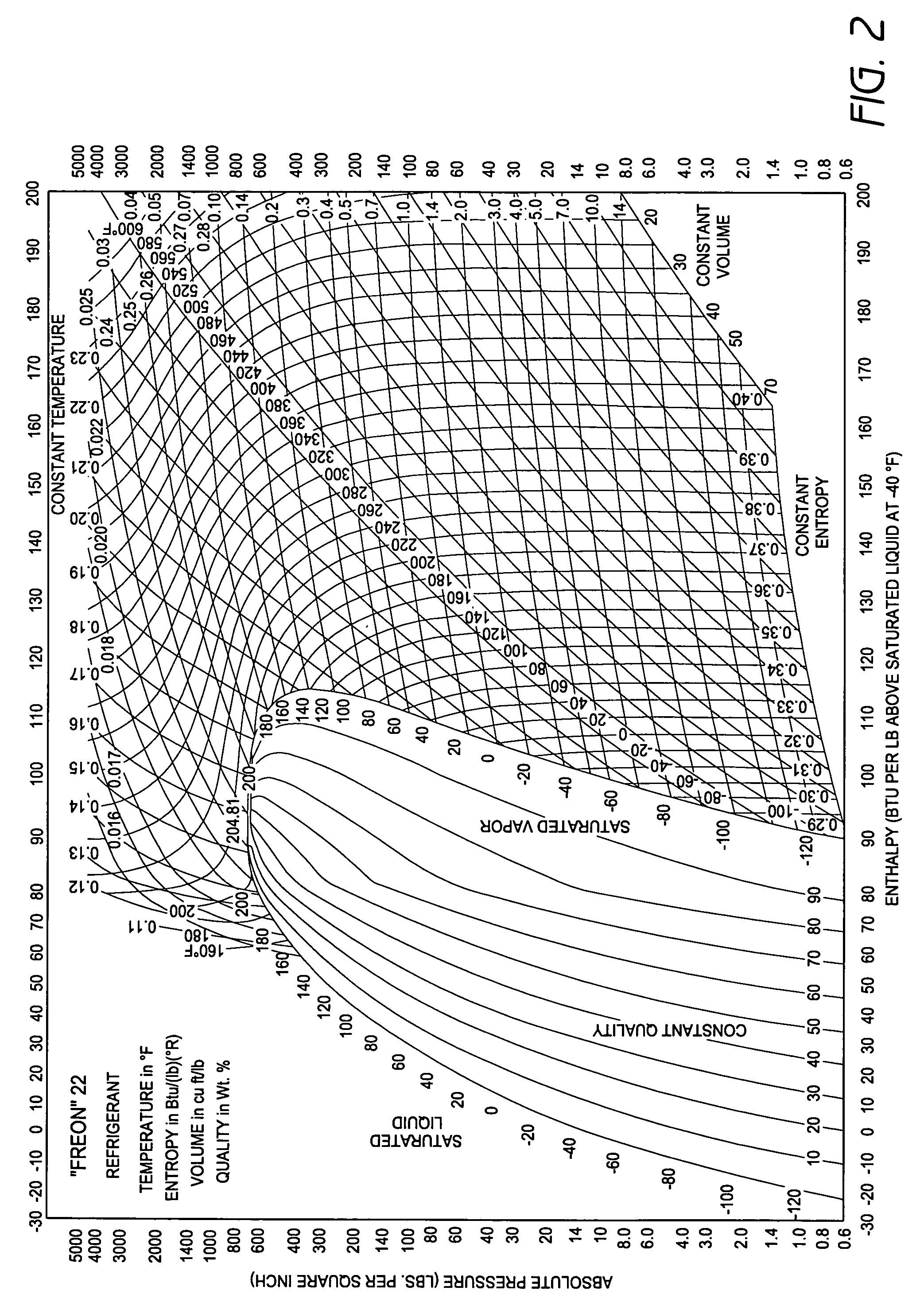
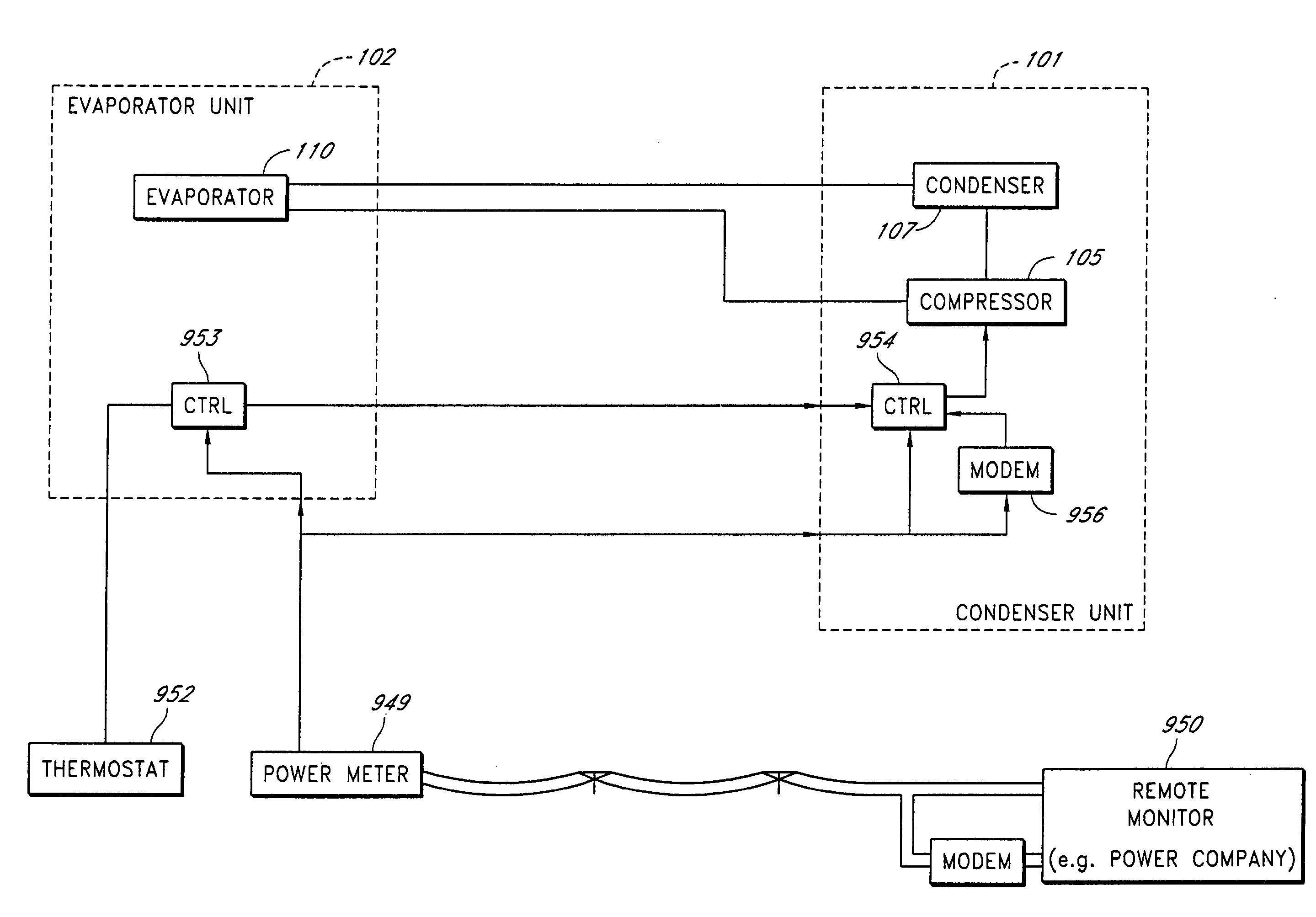
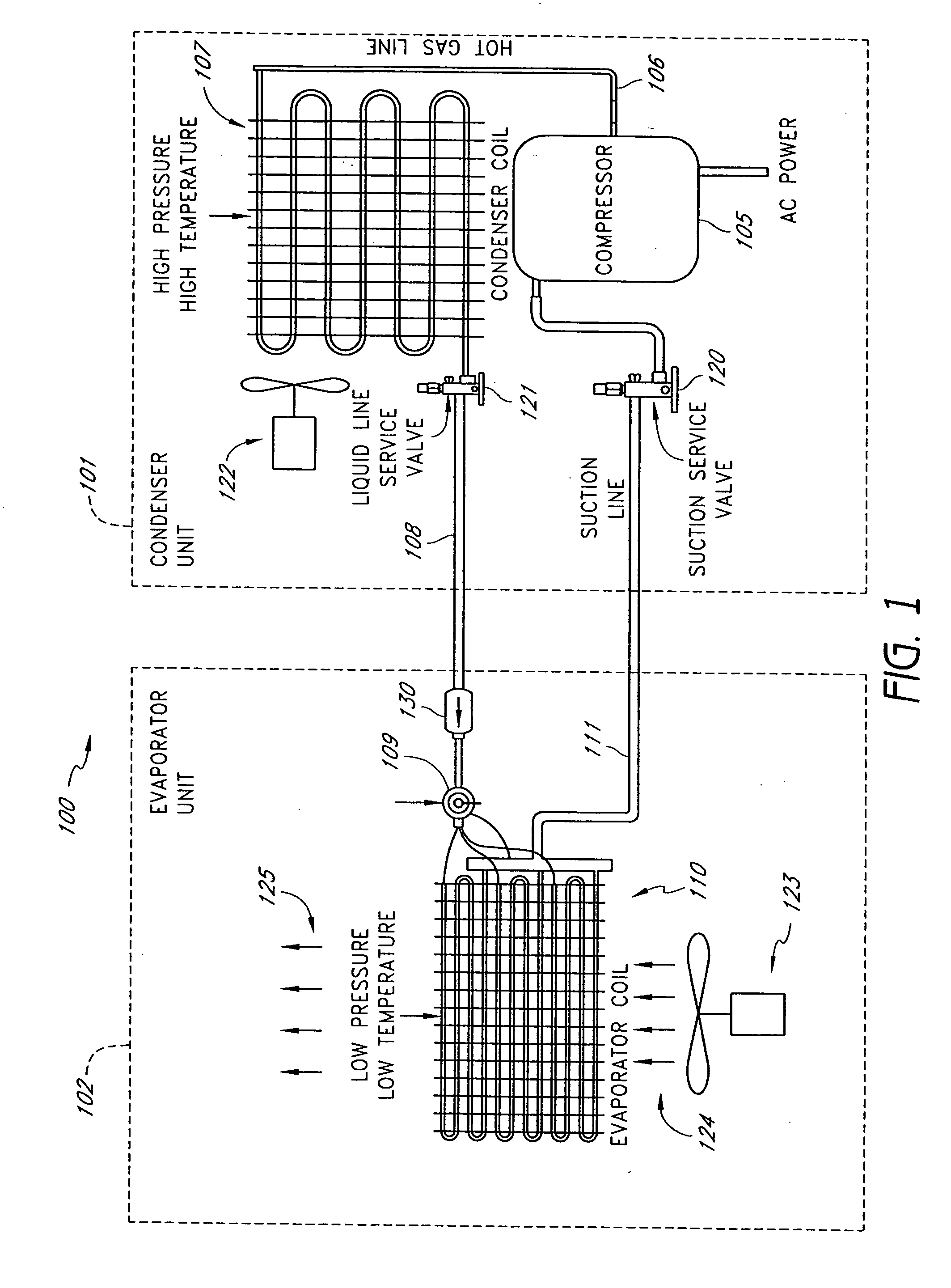
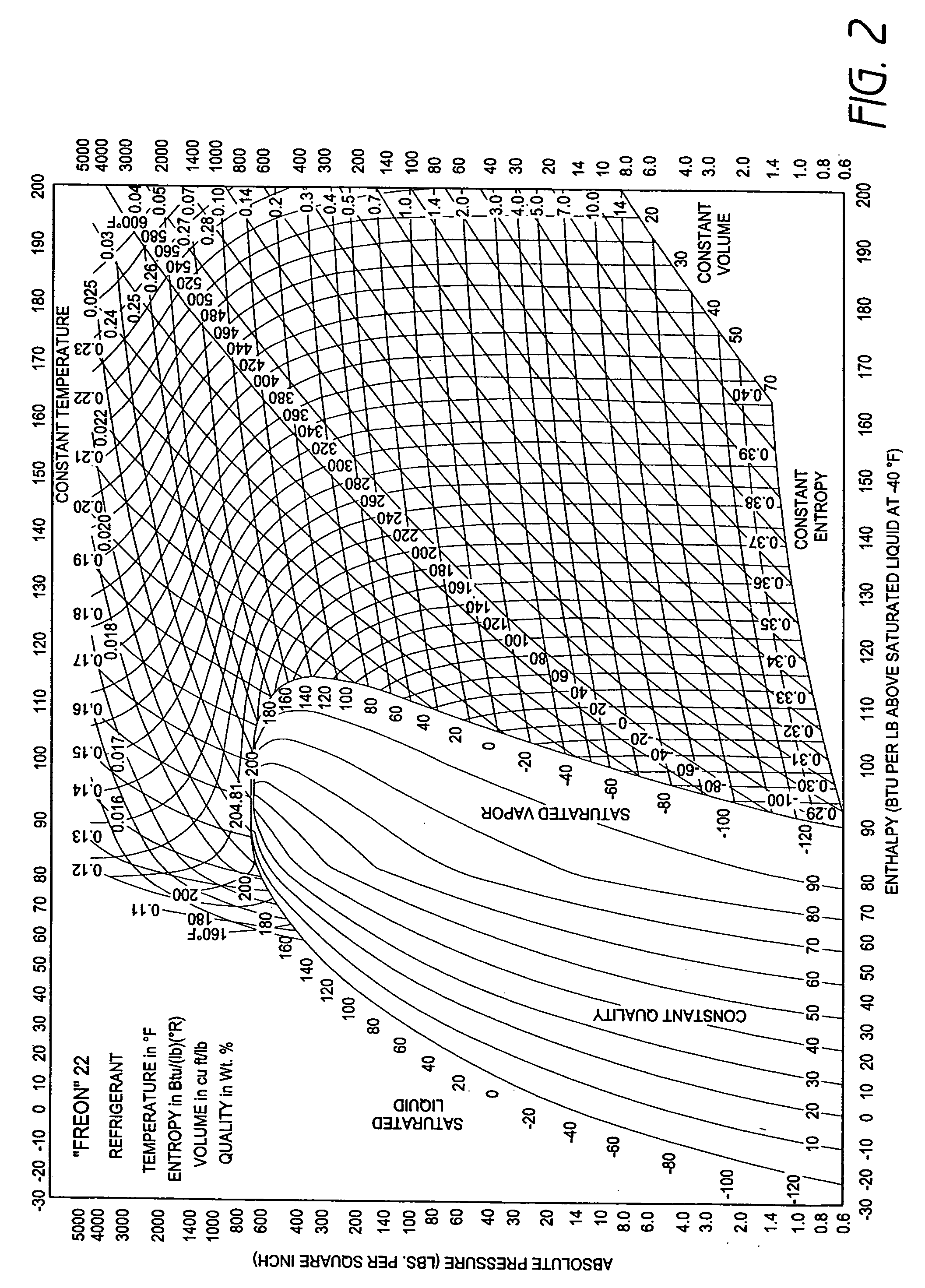
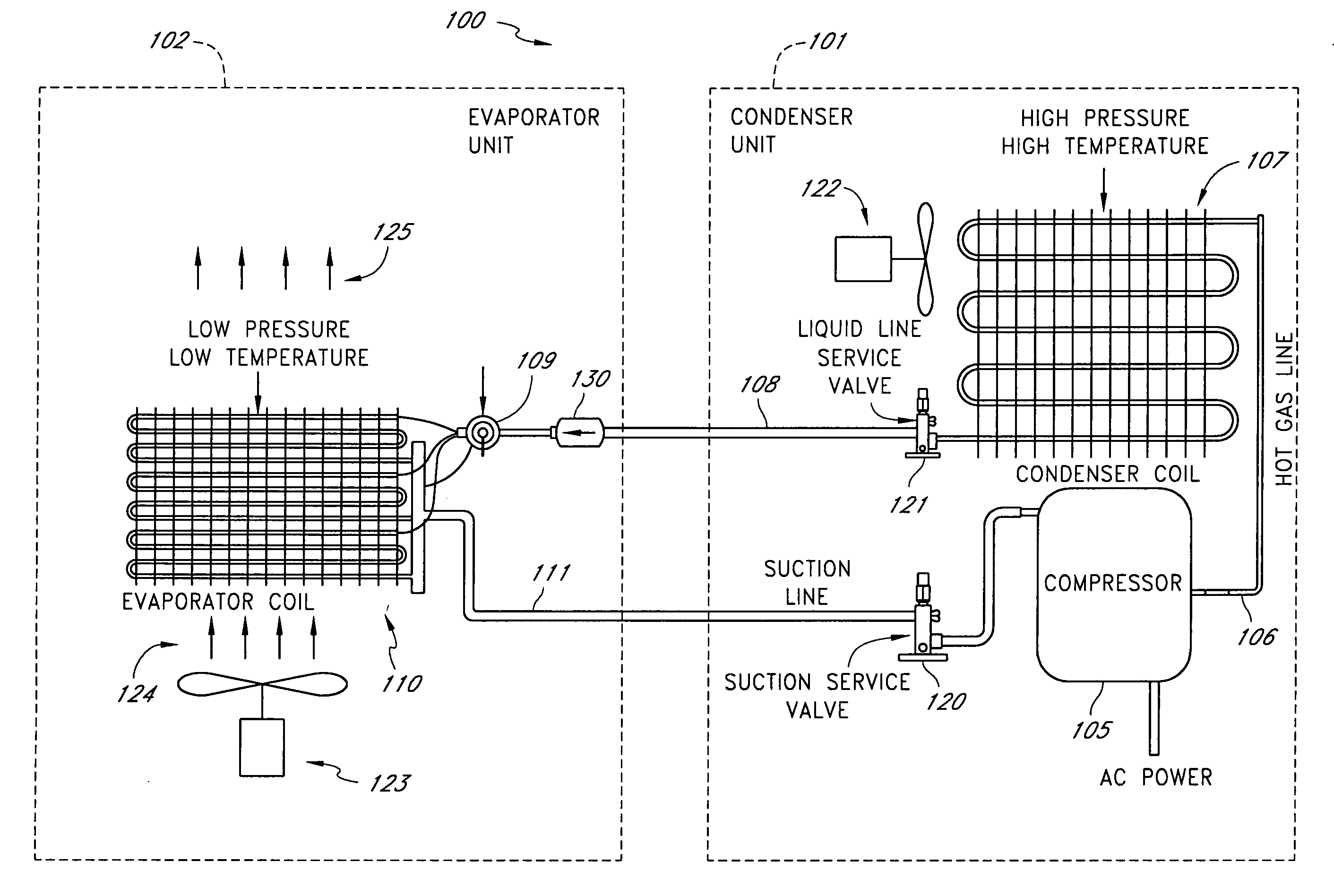
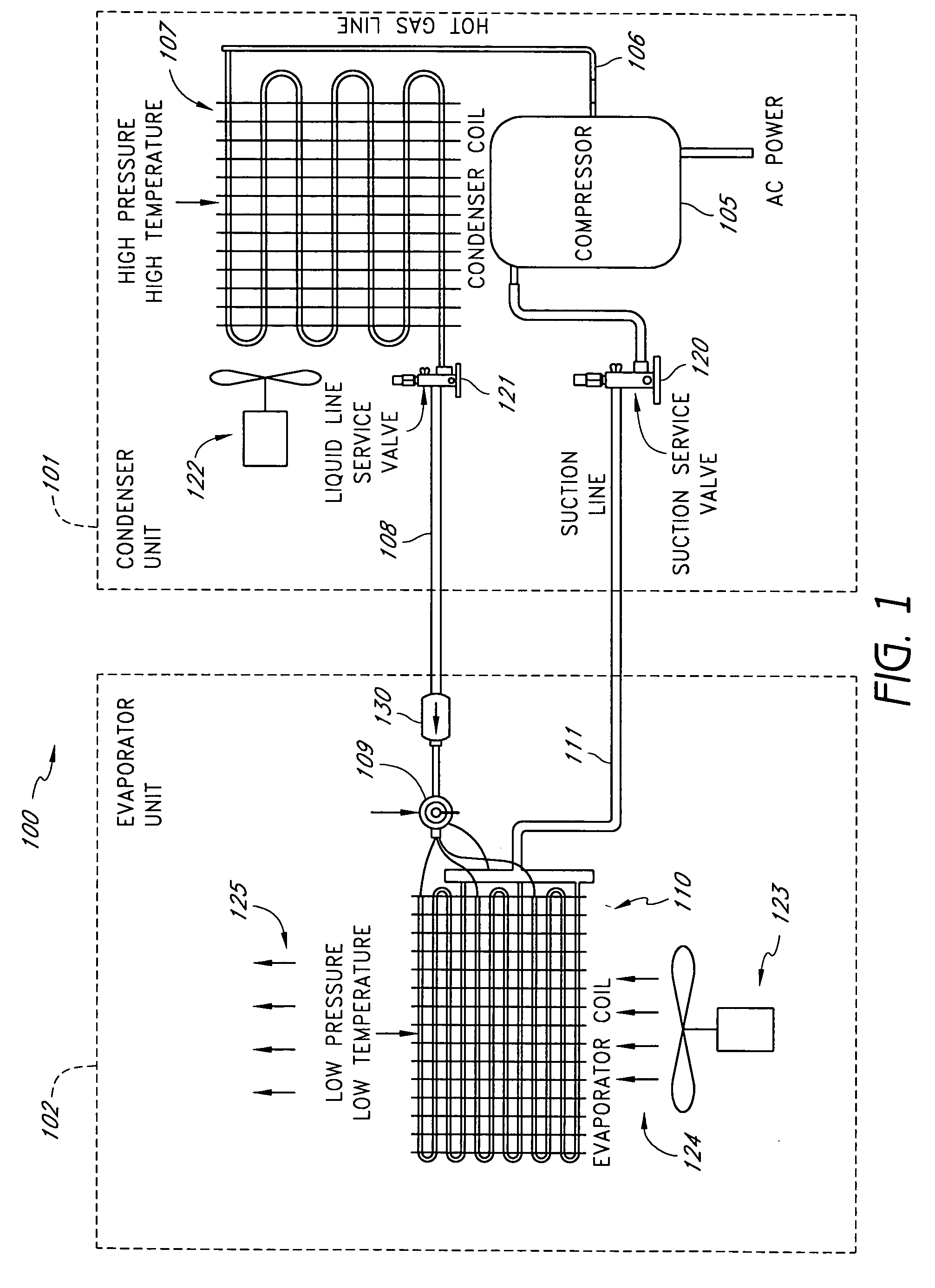
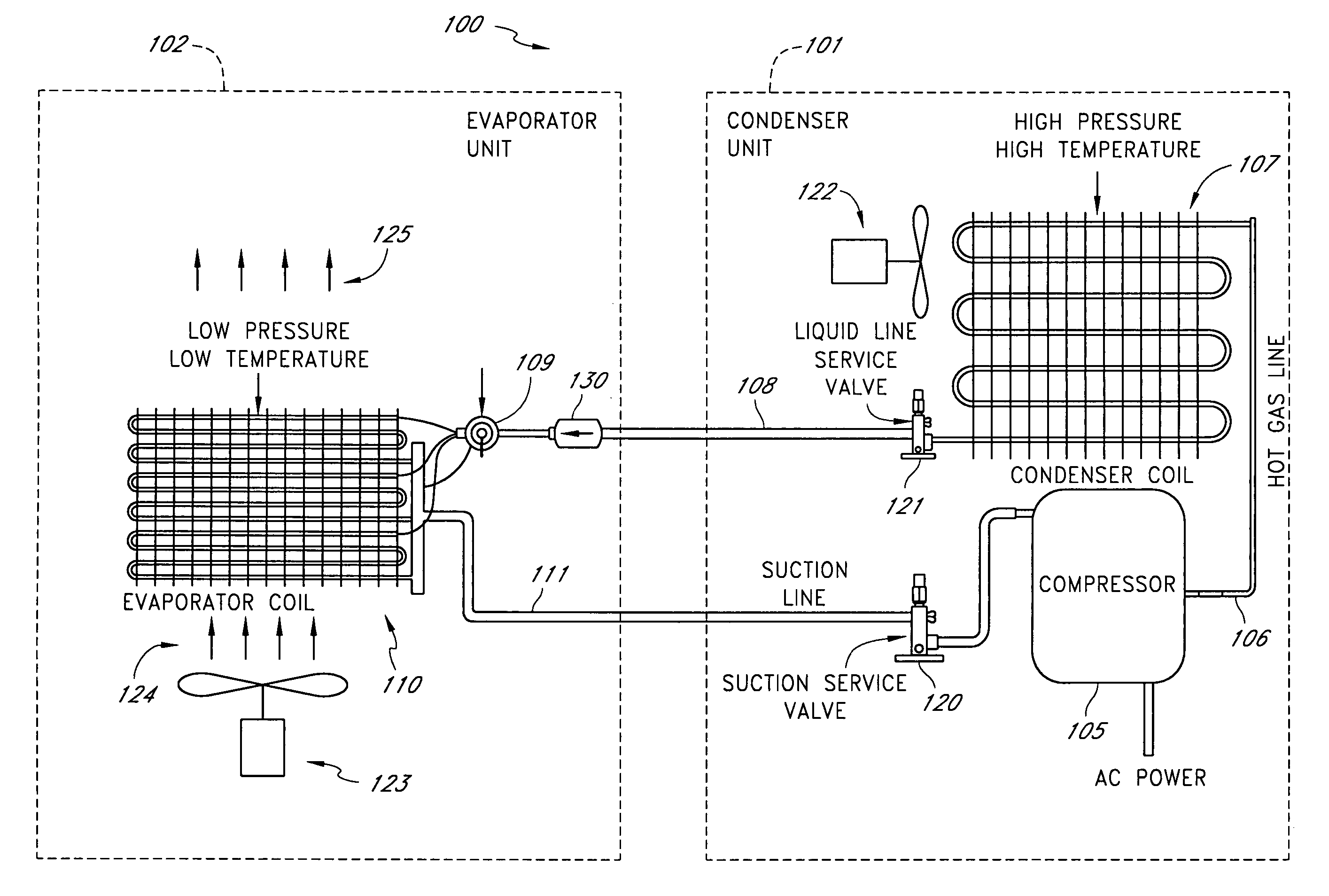
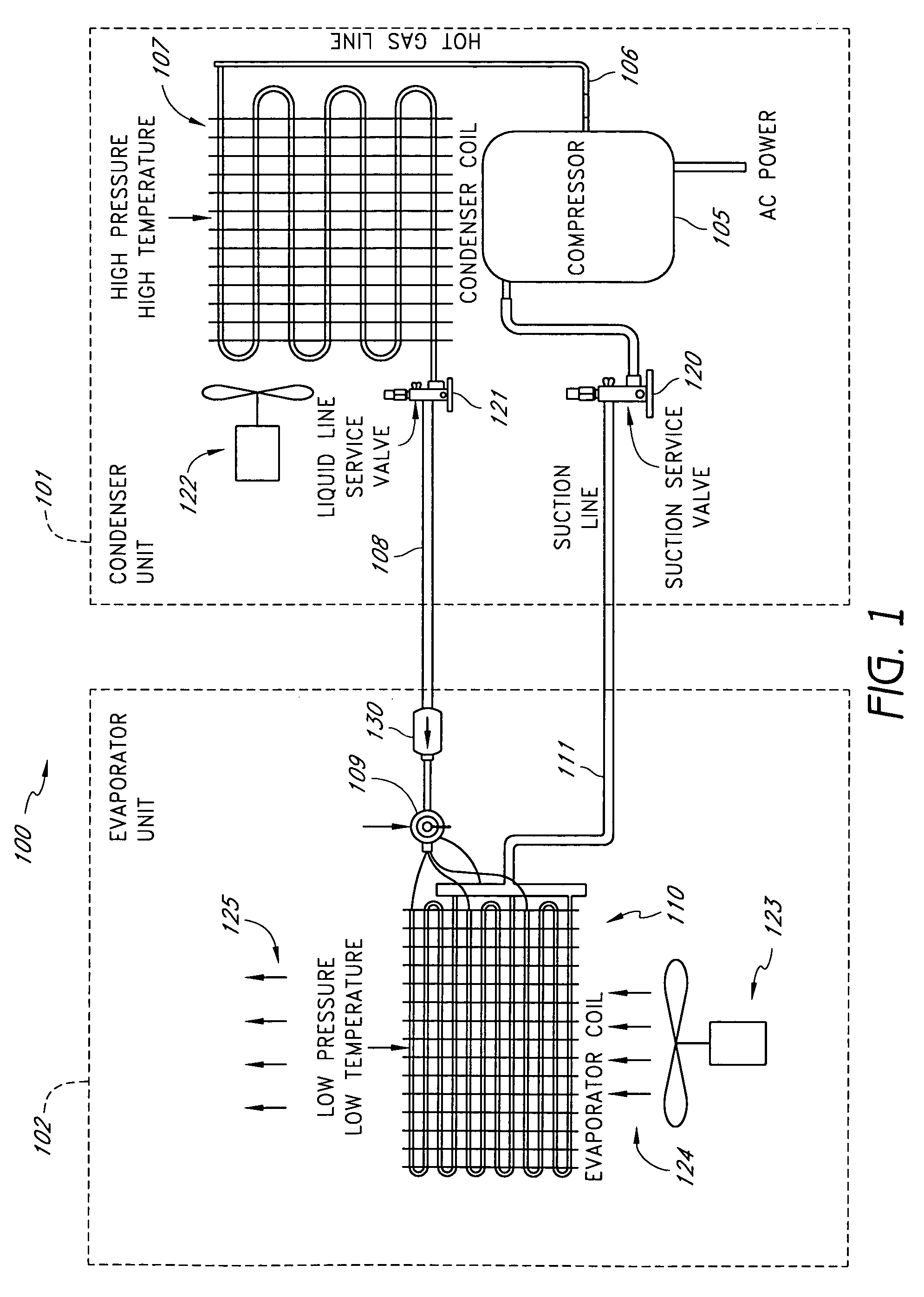
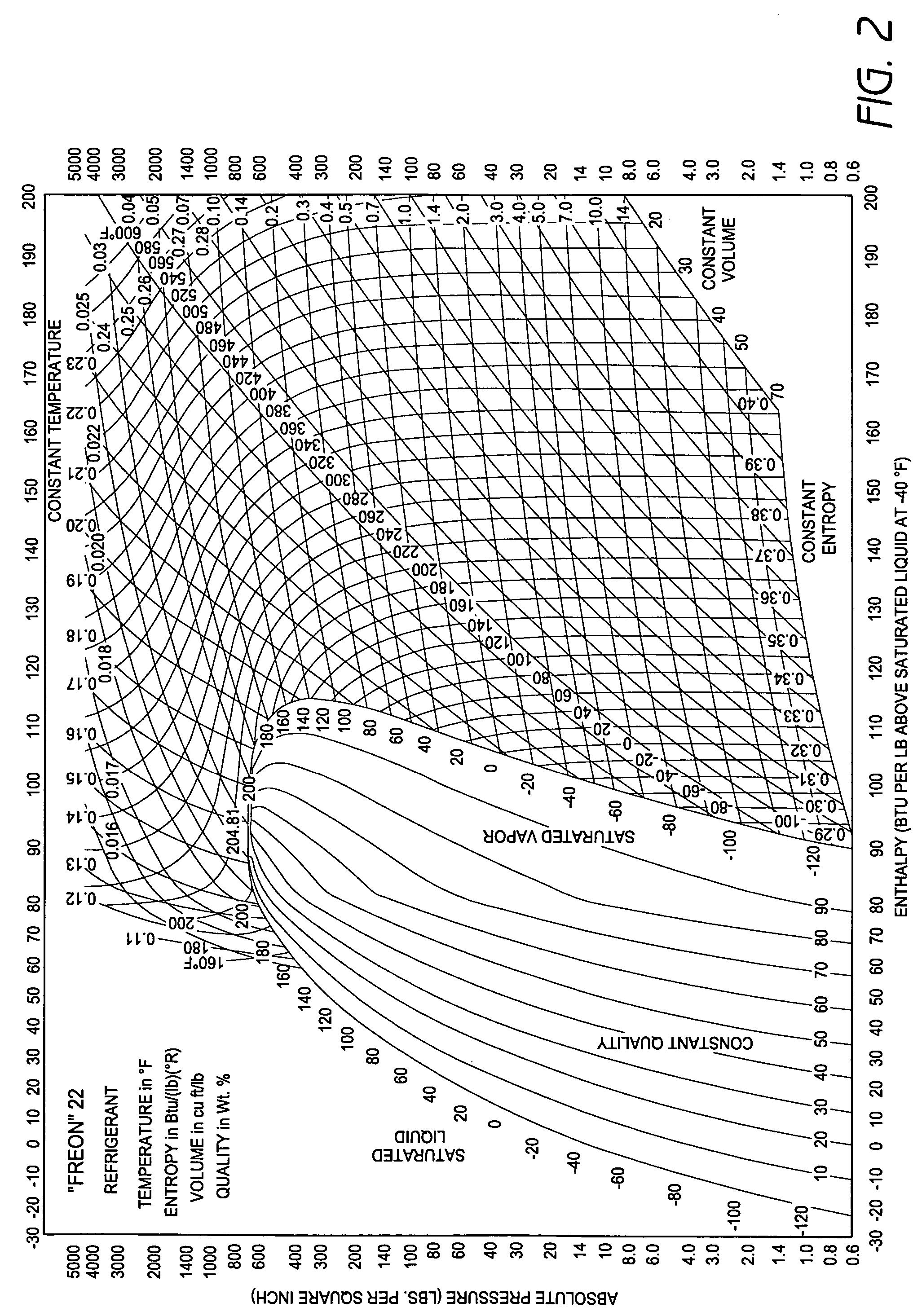
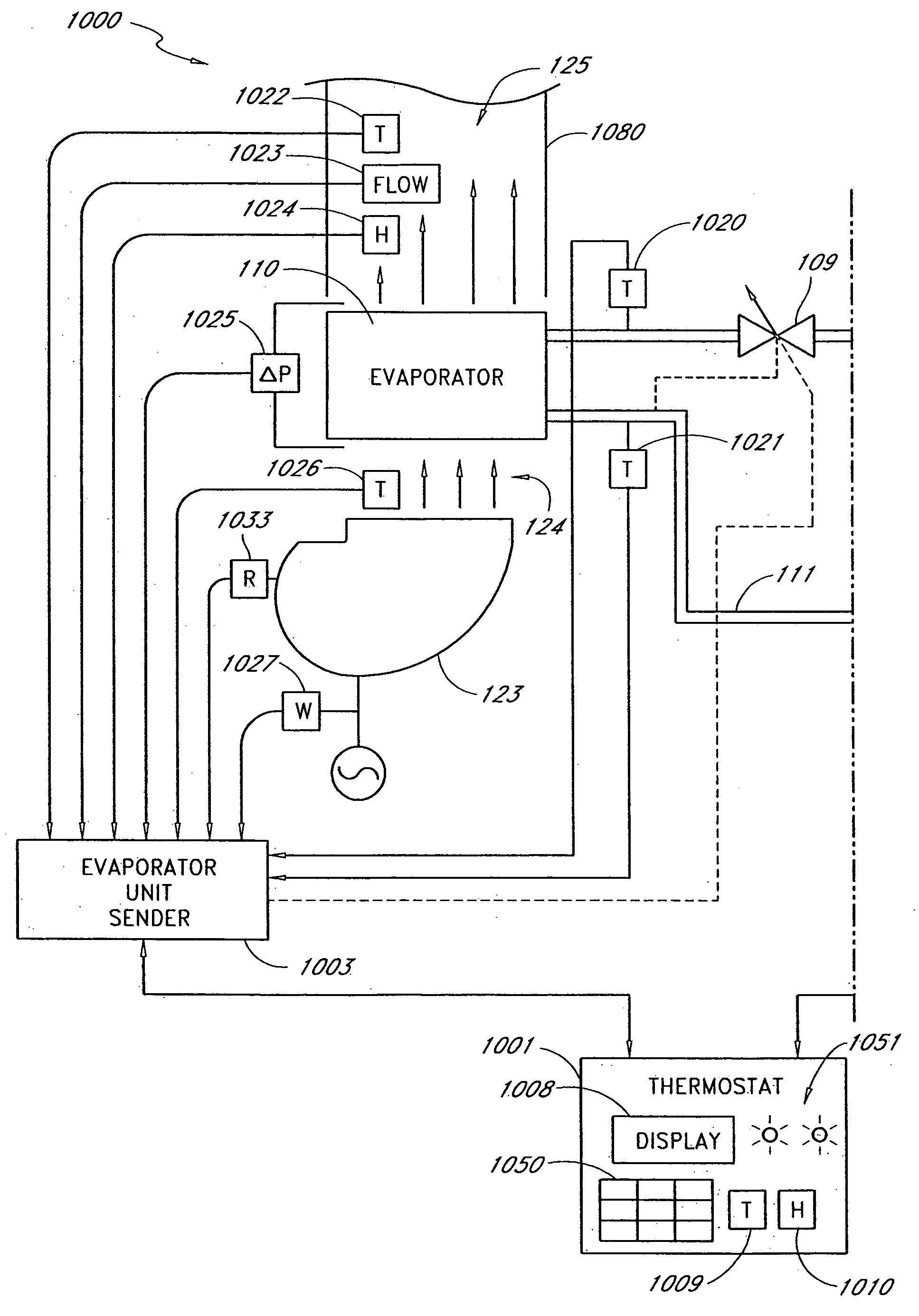
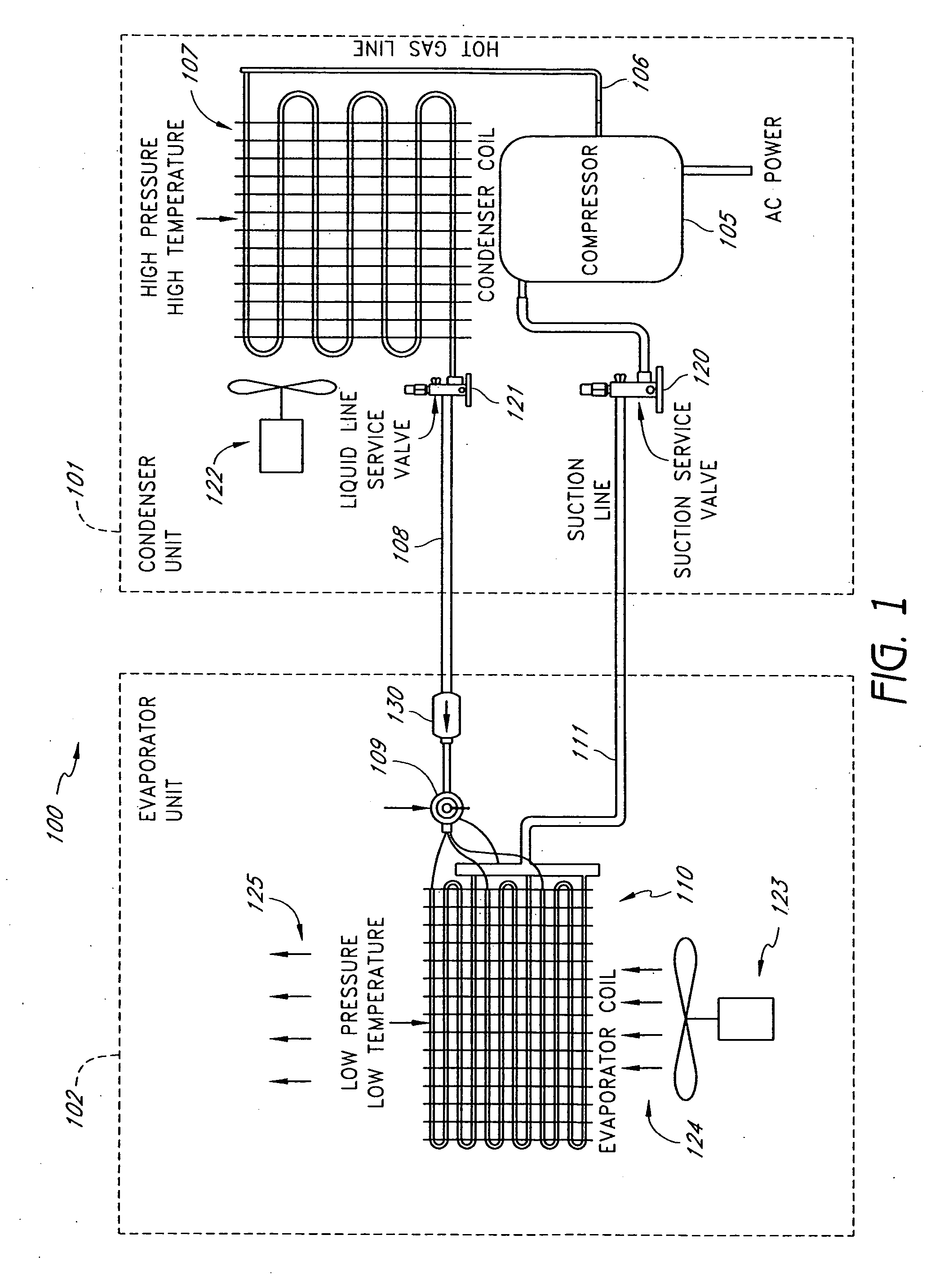
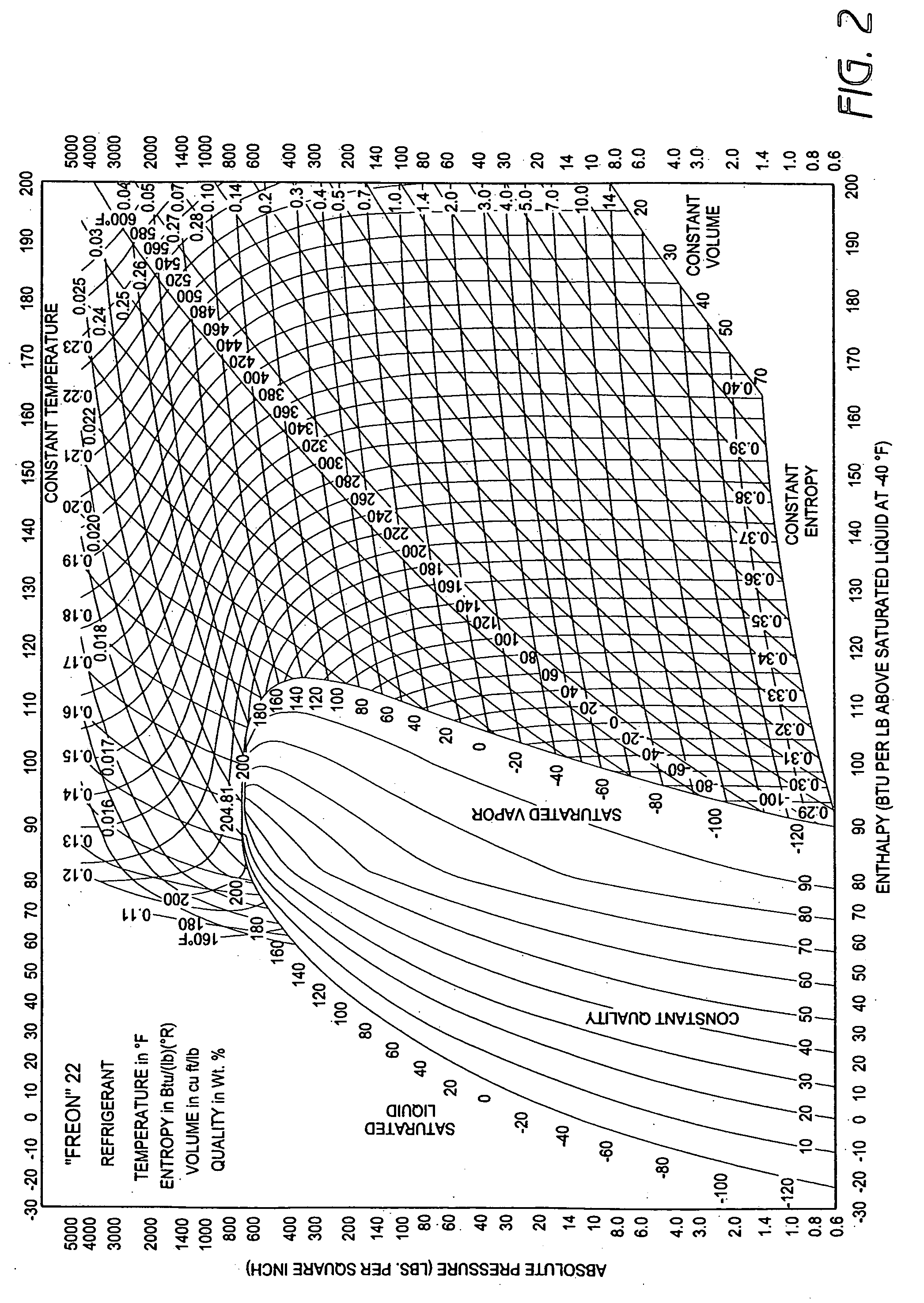
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:EMERSON CLIMATE TECH INC
Method and apparatus for monitoring refrigerant-cycle systems
ActiveUS20060032245A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Recovery of rare cells using a microchannel apparatus with patterned posts
InactiveUS20060252087A1Useful in detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlow disruptionHydrophilic coating
A microflow apparatus for separating or isolating cells from a bodily fluid or other liquid sample uses a flow path where straight-line flow is interrupted by a pattern of transverse posts. The posts are spaced across the width of a collection region in the flow path, extending between the upper and lower surfaces thereof; they have rectilinear surfaces, have arcuate cross-sections, and are randomly arranged so as to disrupt streamlined flow. Sequestering agents, such as Abs, are attached to all surfaces in the collection region via a hydrophilic coating, preferably a hydrogel containing isocyanate moieties or a PEG or polyglycine of substantial length, and are highly effective in capturing cells or other targeted biomolecules as a result of such streamlined flow disruption.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
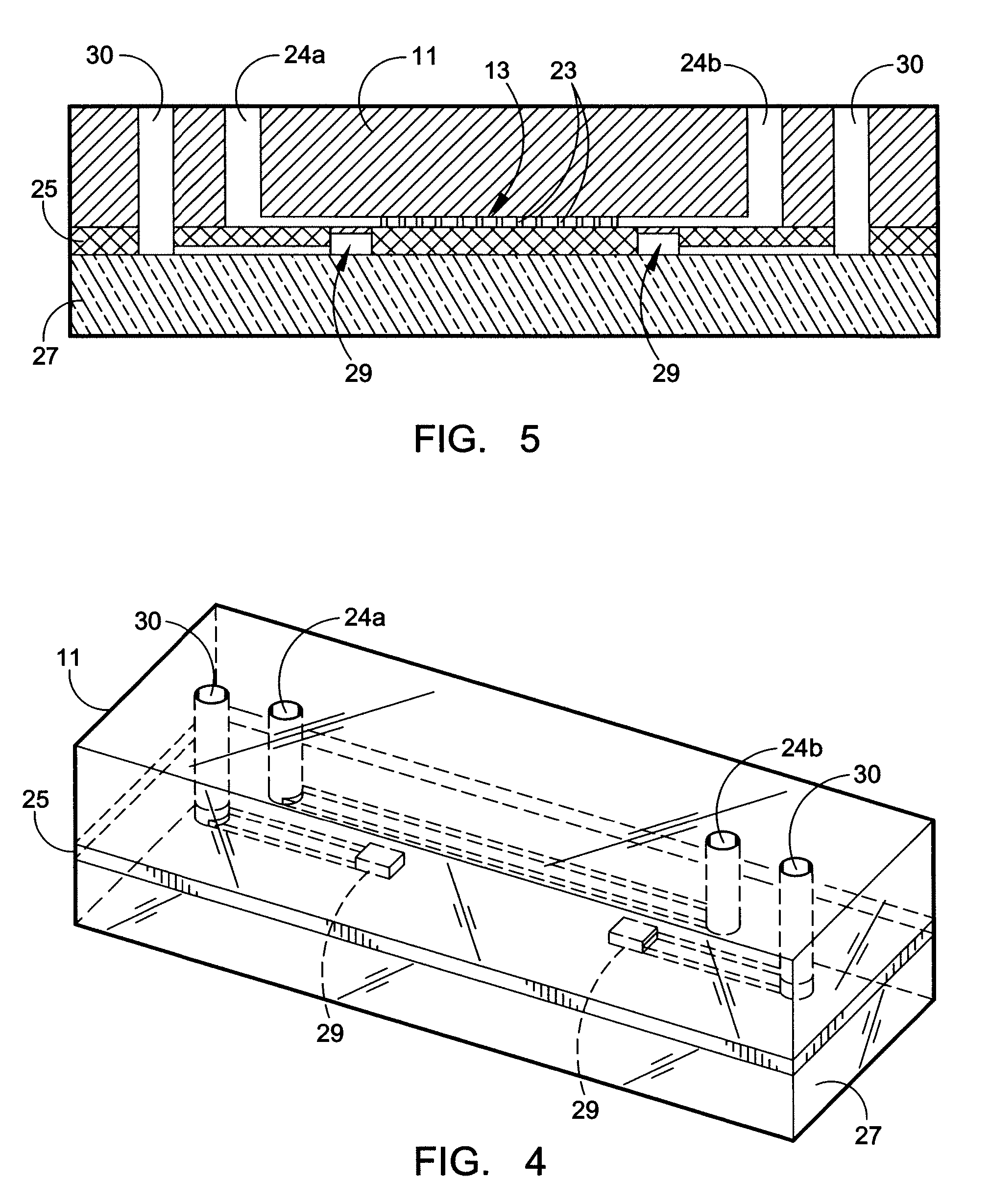
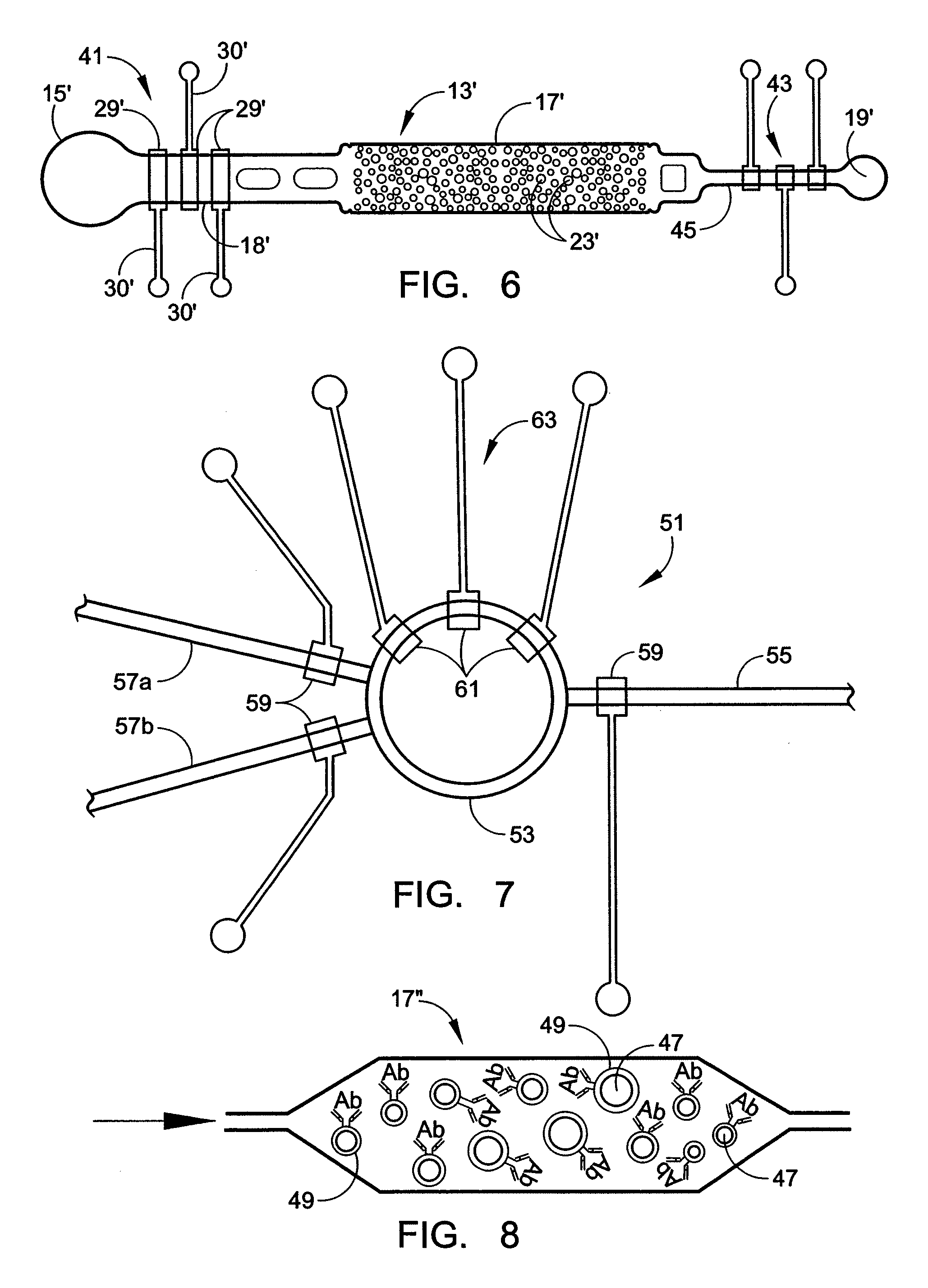
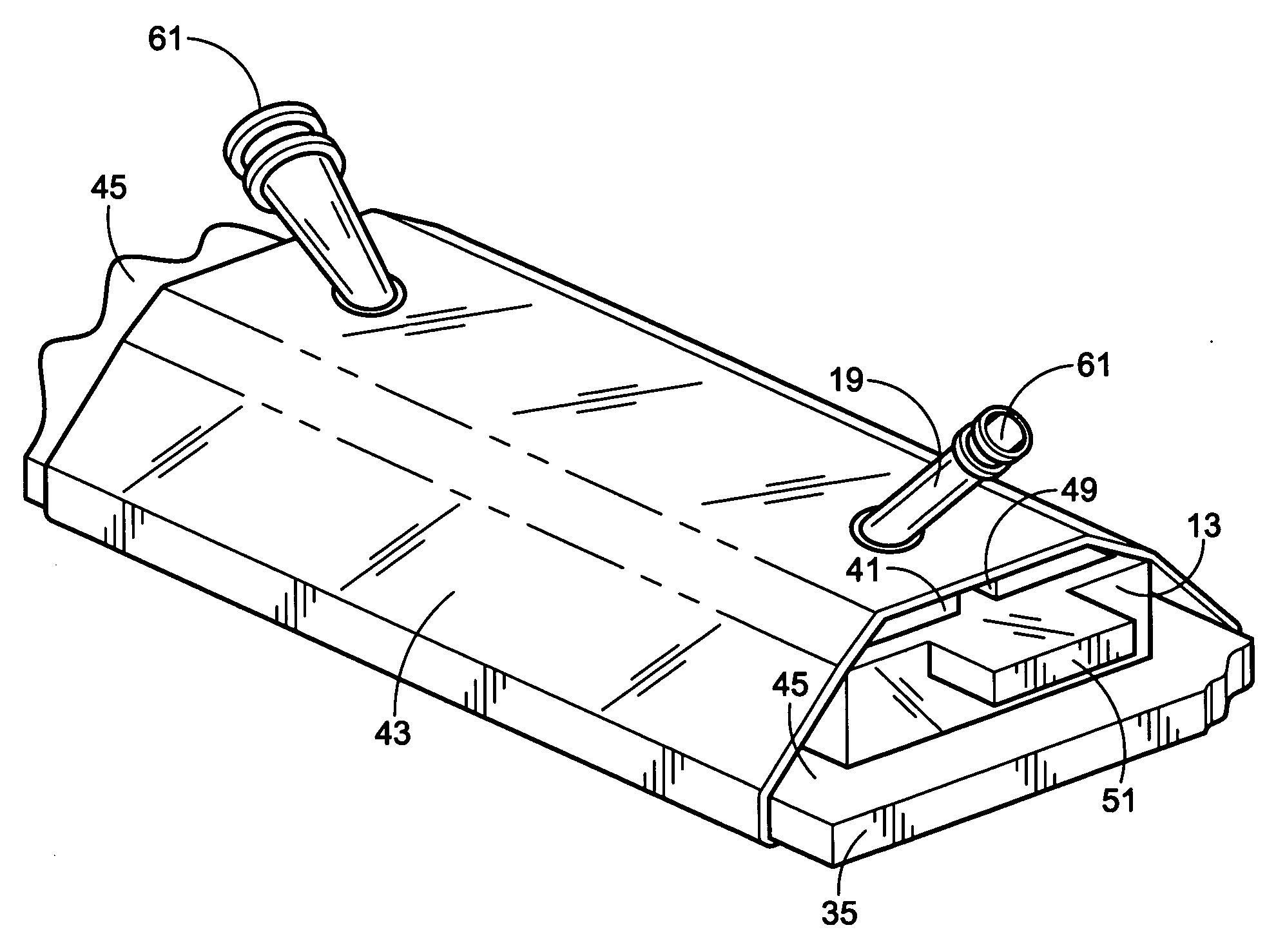
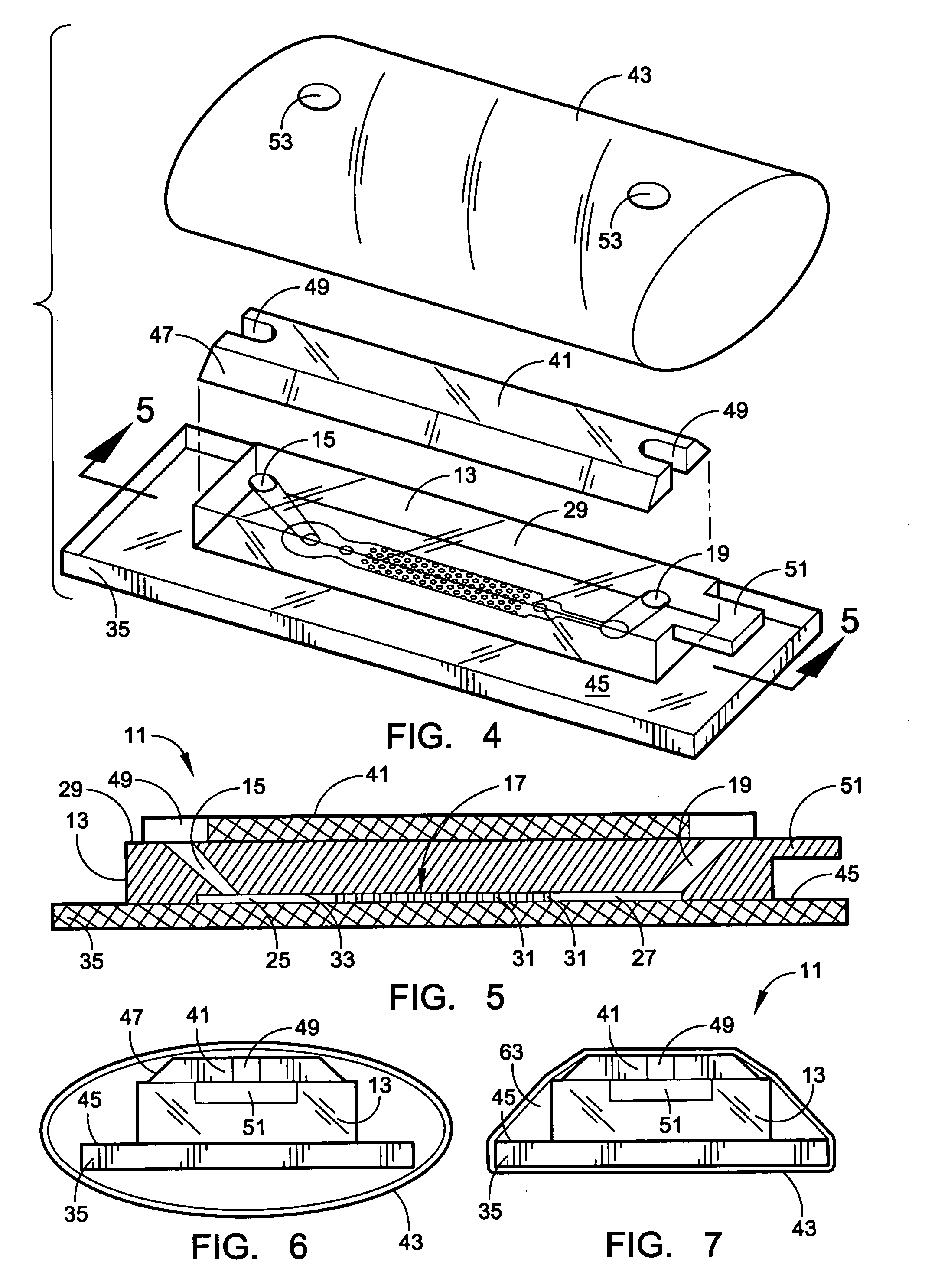
Device for cell separation and analysis and method of using
ActiveUS20070161051A1Disrupt flowEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMicroscopic exam
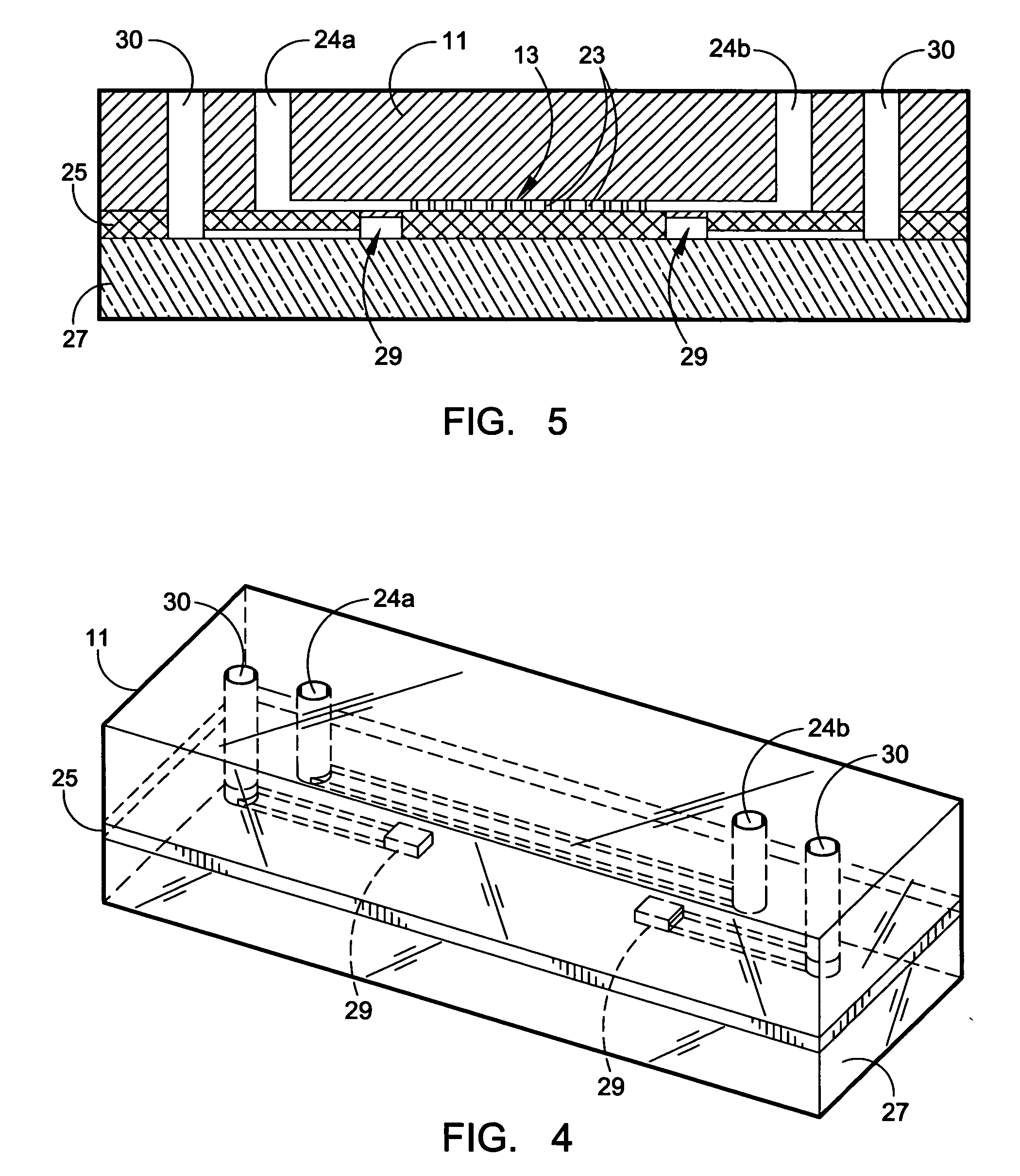
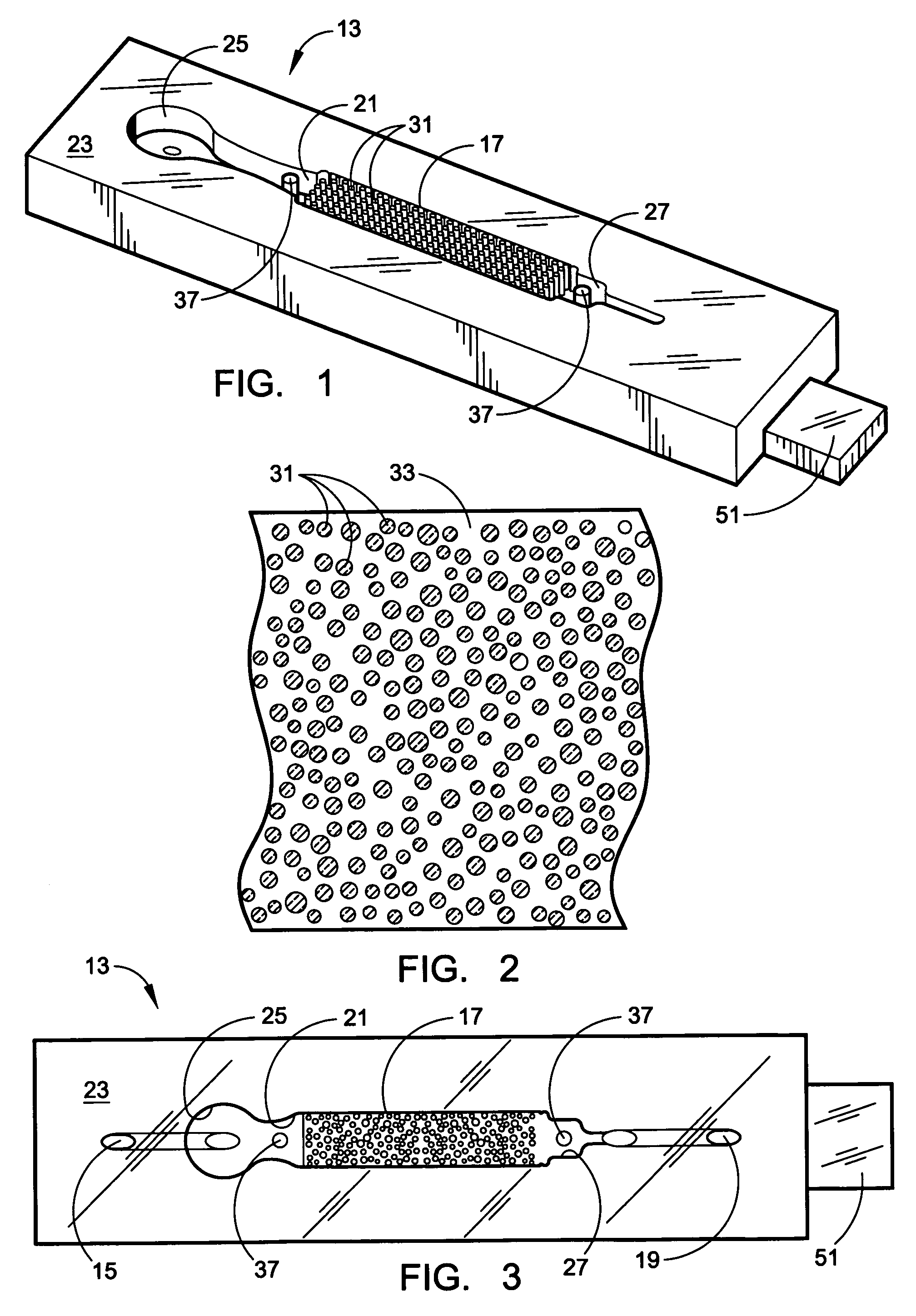
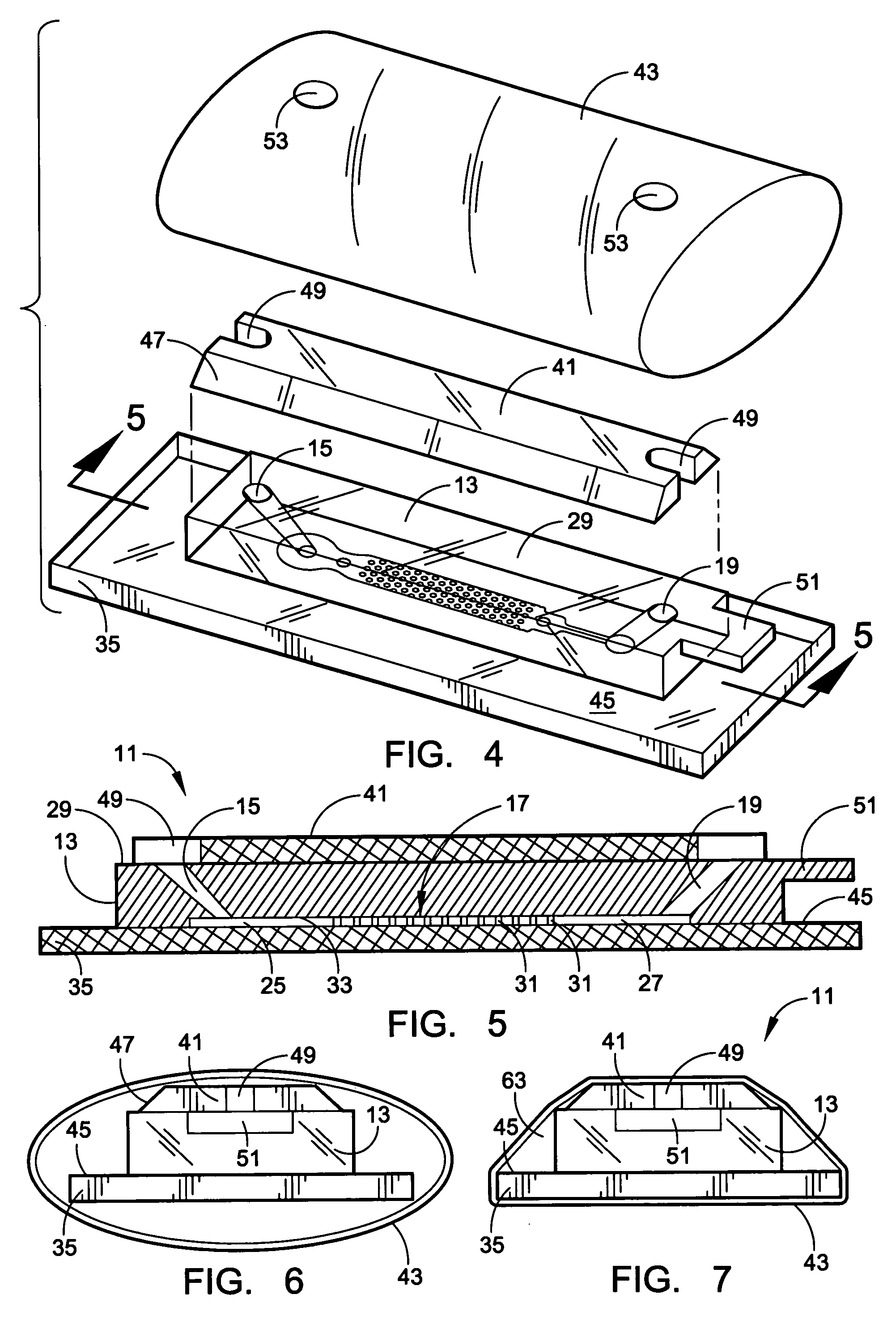
A microflow device for separating or isolating cells from a bodily fluid or other liquid sample uses a flow path where straight-line flow is interrupted by a pattern of transverse posts which are arranged across the width of a collection region in an irregular or set random pattern so as to disrupt streamlined flow. Sequestering agents, such as Abs, are attached to all surfaces in the collection region via a hydrophilic permeable hydrogel coating. The collection region is formed as a cavity in a body molded from PDMS, which flexible body is sandwiched between a glass slide or comparable flat plate and a rigid top cap plate, both of which are pressed into abutting relation with the PDMS body by a heat-shrunk polymeric sleeve. Following cell separation and washing, cells can be released from the sequestering agents and the device centrifuged to force said cells to collect adjacent the hydrogel-coated slide or plate. Slitting the polymeric sleeve allows the body to then be peeled from the slide or plate, using an integral tab, to expose the separated cells on the top surface thereof for ready microscopic examination.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Method and apparatus for monitoring a calibrated condenser unit in a refrigerant-cycle system
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Device for cell separation and analysis and method of using
ActiveUS7695956B2Easy to separateEasy to peelBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscopic examEngineering
A microflow device for separating or isolating cells from a bodily fluid or other liquid sample uses a flow path where straight-line flow is interrupted by a pattern of transverse posts which are arranged across the width of a collection region in an irregular or set random pattern so as to disrupt streamlined flow. Sequestering agents, such as Abs, are attached to all surfaces in the collection region via a hydrophilic permeable hydrogel coating. The collection region is formed as a cavity in a body molded from PDMS, which flexible body is sandwiched between a glass slide or comparable flat plate and a rigid top cap plate, both of which are pressed into abutting relation with the PDMS body by a heat-shrunk polymeric sleeve. Following cell separation and washing, cells can be released from the sequestering agents and the device centrifuged to force said cells to collect adjacent the hydrogel-coated slide or plate. Slitting the polymeric sleeve allows the body to then be peeled from the slide or plate, using an integral tab, to expose the separated cells on the top surface thereof for ready microscopic examination.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Method and apparatus for monitoring a calibrated condenser unit in a refrigerant-cycle system
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
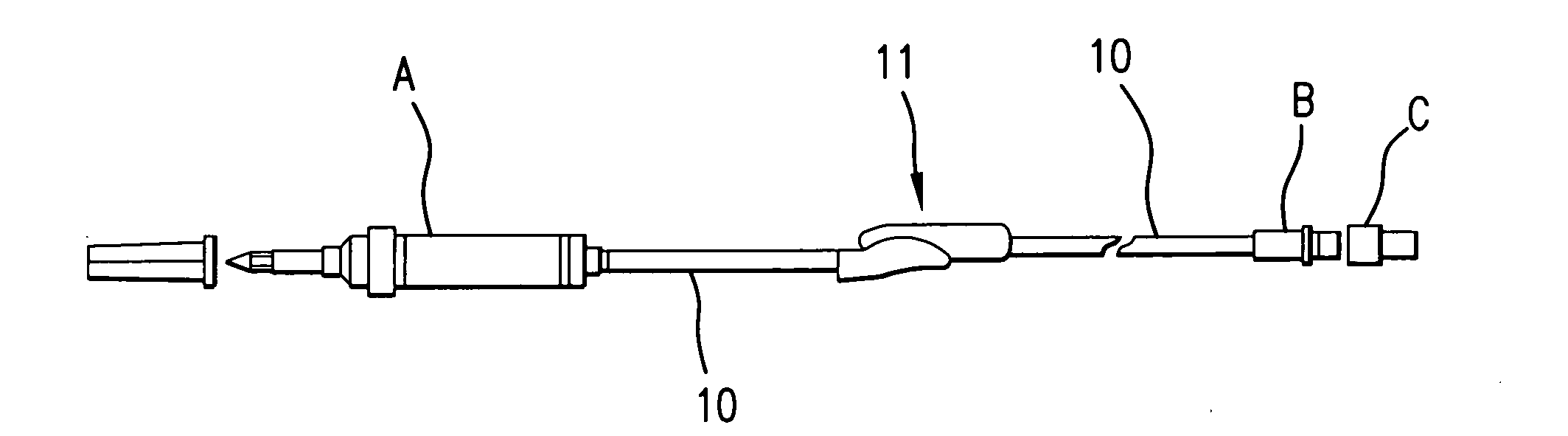
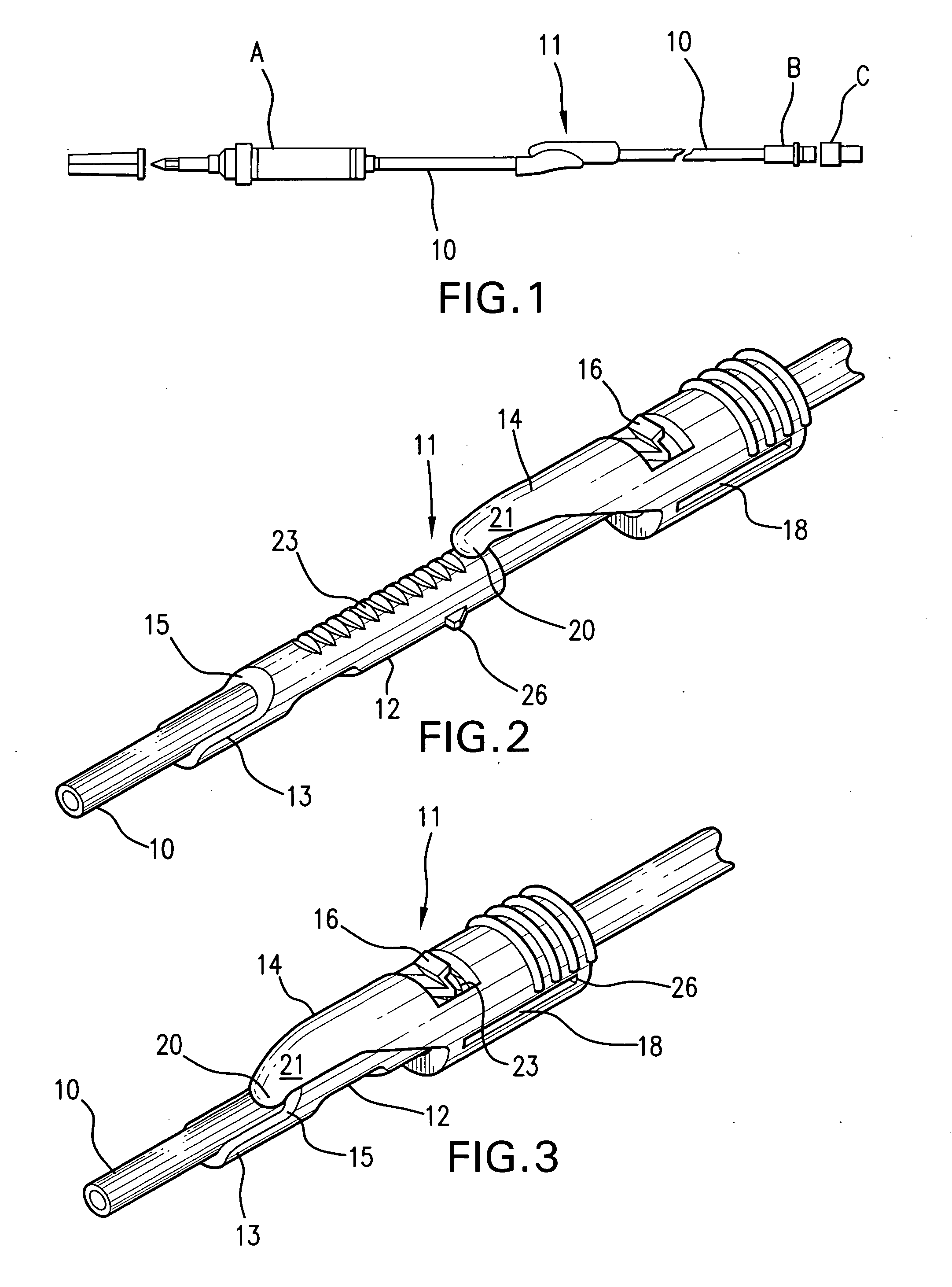
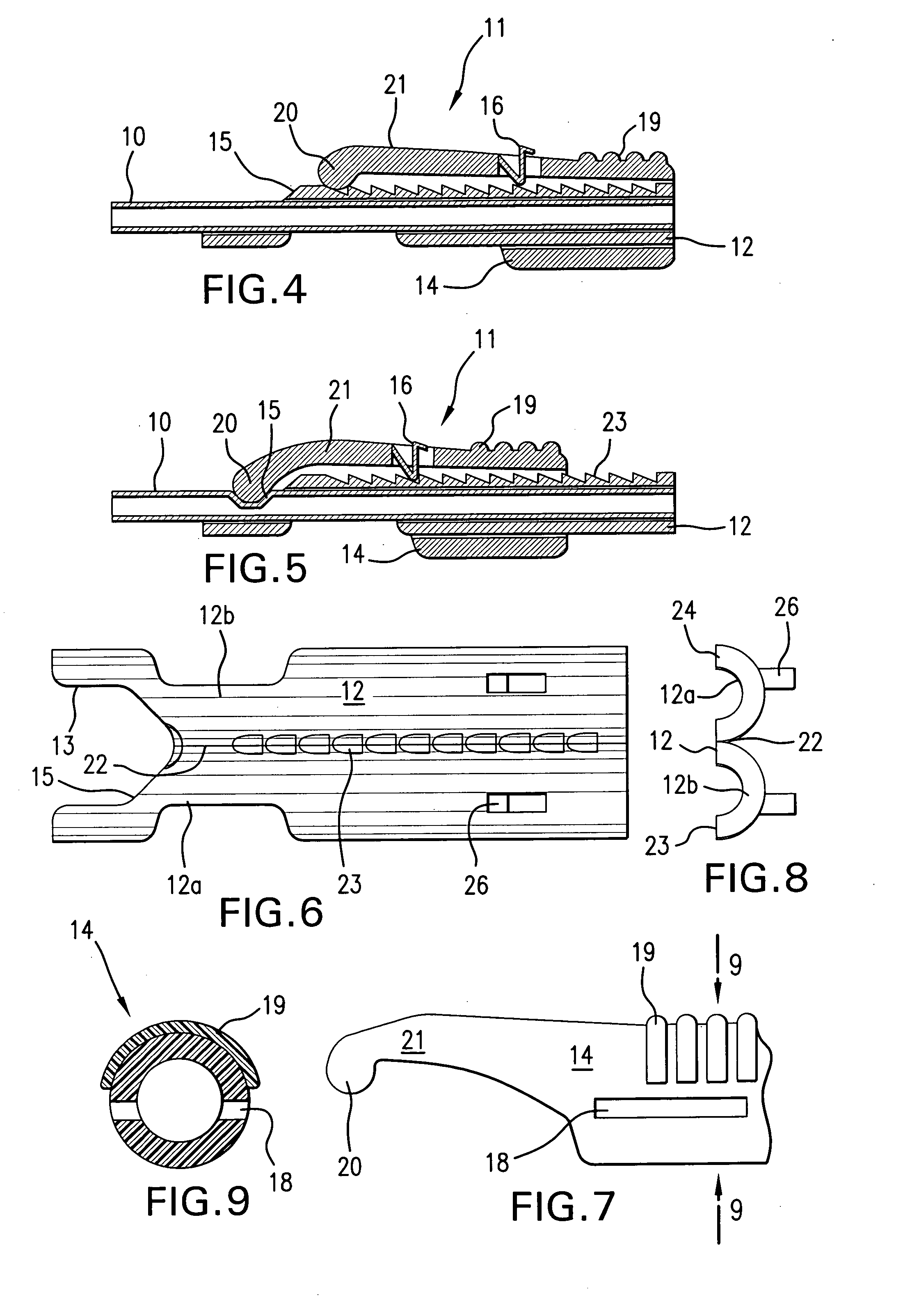
In-line flow rate control device
A readily adjustable flow rate control device having a movable flow control member which includes a plurality of spaced-apart flow restrictors which are adapted to be selectively positioned intermediate a fluid flow path extending between a fluid supply line and a fluid delivery line. The flow restrictors can take the form of porous rate control frits which can be selectively moved into index with the fluid flow path or microbores formed in a rotatable member which can be rotated to selectively move the microbores into index with the fluid flow path.
Owner:PESCADERO BEACH HLDG
Method and apparatus for monitoring air-exchange evaporation in a refrigerant-cycle system
ActiveUS20060032248A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEvaporation
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Intelligent thermostat system for load monitoring a refrigerant-cycle apparatus
ActiveUS20060196197A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Intelligent thermostat system for monitoring a refrigerant-cycle apparatus
ActiveUS20060032246A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureThermostat
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Method and apparatus for monitoring a condenser unit in a refrigerant-cycle system
ActiveUS20060032247A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Method and apparatus for airflow monitoring refrigerant-cycle systems
InactiveUS20060196196A1Mechanical apparatusTemperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsDifferential pressureEngineering
A real-time monitoring system that monitors various aspects of the operation of a refrigerant-cycle system is described. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor that measures power provided to the refrigerant-cycle system and that gathers data from one or more sensors and uses the sensor data to calculate a figure of merit related to the efficiency of the system. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of the following sensors: a suction line temperature sensor, a suction line pressure sensor, a suction line flow sensor, a hot gas line temperature sensor, a hot gas line pressure sensor, a hot gas line flow sensor, a liquid line temperature sensor, a liquid line pressure sensor, a liquid line flow sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an evaporator air temperature input sensor, an evaporator air temperature output sensor, an evaporator air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor, and a differential pressure sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of a condenser air temperature input sensor, a condenser air temperature output sensor, and a condenser air flow sensor, an evaporator air humidity sensor. In one embodiment, the sensors include one or more of an ambient air sensor and an ambient humidity sensor.
Owner:KATES LAWRENCE
Data display using multicolumn scrolling
InactiveUS7320105B1Digital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsScripting languageData display
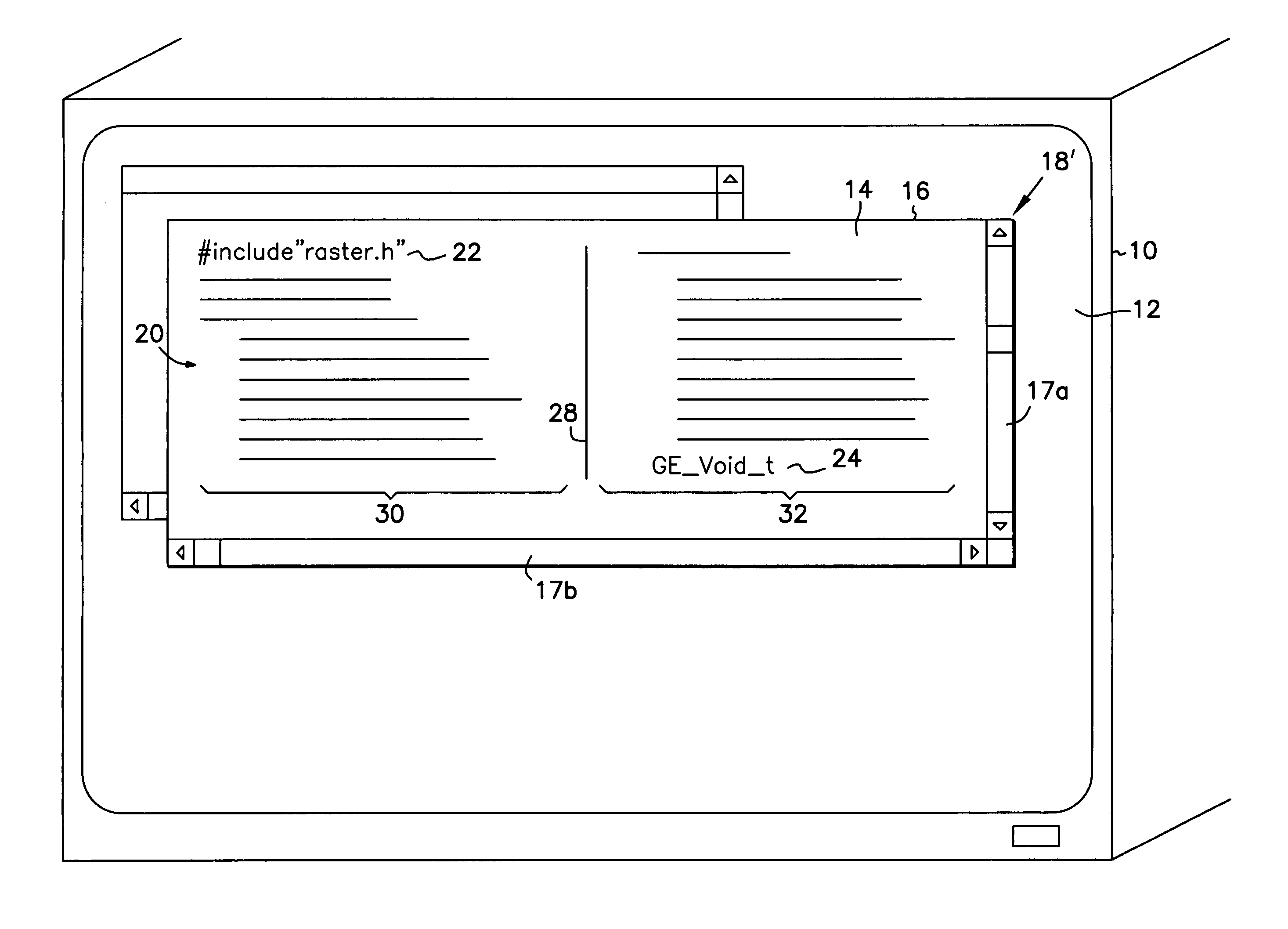
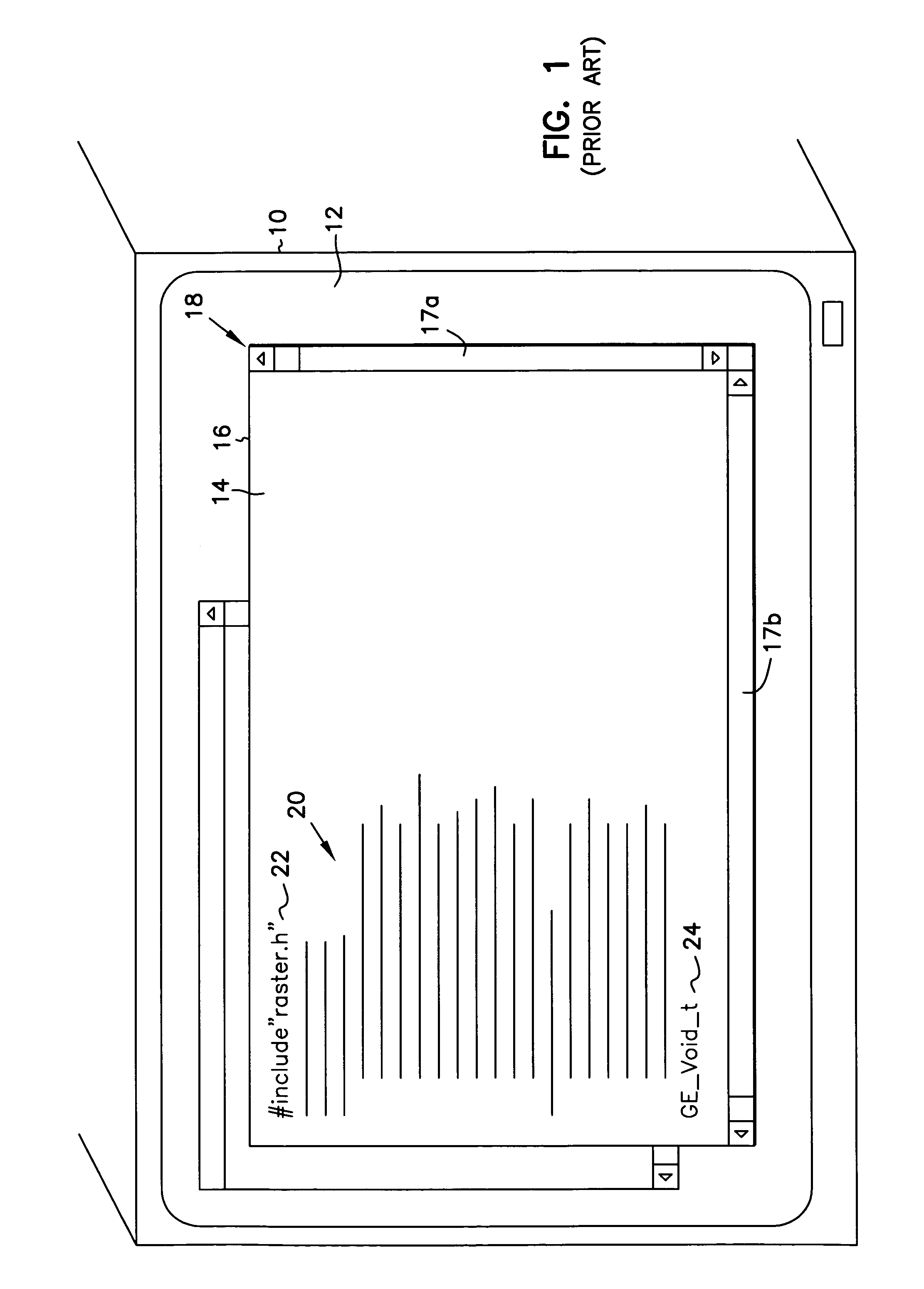
Apparatus, software and method for displaying line-formatted materials in multiple columns of a screen display and providing for scrolling through the materials such that lines spill from one column to another, are disclosed. The columns form a display area for display of contiguous lines of the line-formatted materials, wherein diagonally opposite ends of the rightmost and leftmost columns define the starting and ending lines of the display area, such that when scrolling through line-formatted materials the lines flow into and out of the display area at the starting and ending lines. In another embodiment, Scripting language encoded line-formatted materials are displayed under the control of a web browser using the scrollable columns. In another embodiment, line-formatted materials are encoded with one or more Scripting language codes that specify to a web browser that the line-formatted materials are to be displayed in scrollable columns.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for creating a closed-loop riparian geothermal infrastructure
InactiveUS20080148733A1Other heat production devicesWind motor supports/mountsClosed loopEngineering
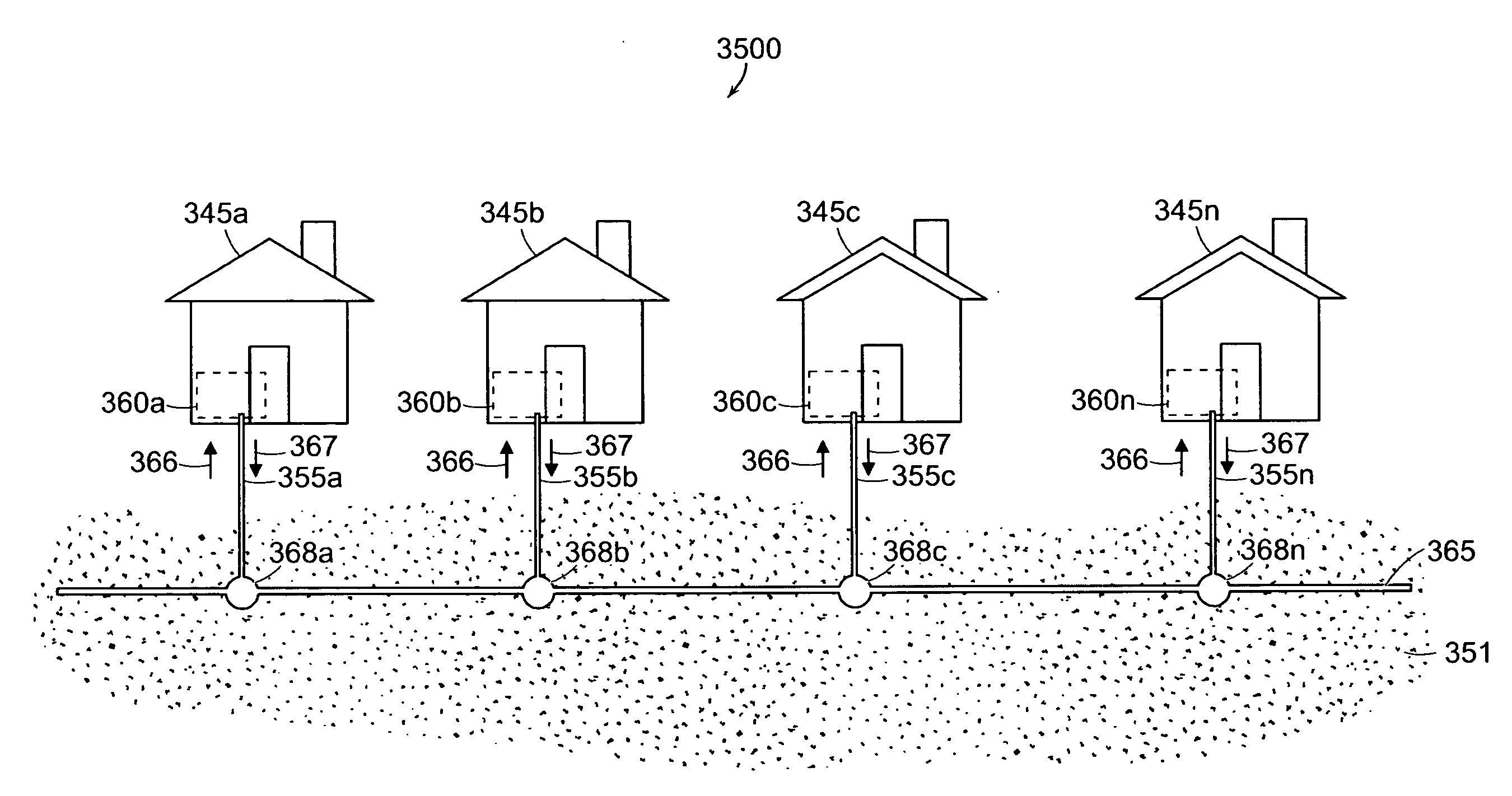
A system and method for generating and distributing a closed loop riparian geothermal energy infrastructure. This system fills the need for the average home to tie into an existing geothermal “grid” constructed along, adjacent to or underneath a riparian body. The user may not need to invest in the geothermal infrastructure necessary outside the home to enable a geothermal system inside a home. The user, instead, is responsible for creating the section of the geothermal system that exists in the interior home infrastructure. In one embodiment of the invention, the infrastructure comprises at least one distribution flow line having a forward line for a first phase and a return flow line for circulatory second phase. The distribution flow line is coupled to any point along a main flow line. The main line flow line is buried to a sufficient depth within a riparian body for converting the first and second phases.
Owner:GLOUSTER APPL L L C
In-line flow through diaphragm tank
An in-line expansion tank. As fluid traverses a pipe within the tank, it may pass into and displace a diaphragm disposed outside of the pipe if the fluid pressure is greater than a tank pressure pushing the diaphragm against the pipe. When the fluid pressure decreases, the fluid passes from the diaphragm back into the pipe.
Owner:FLEXCON INDS
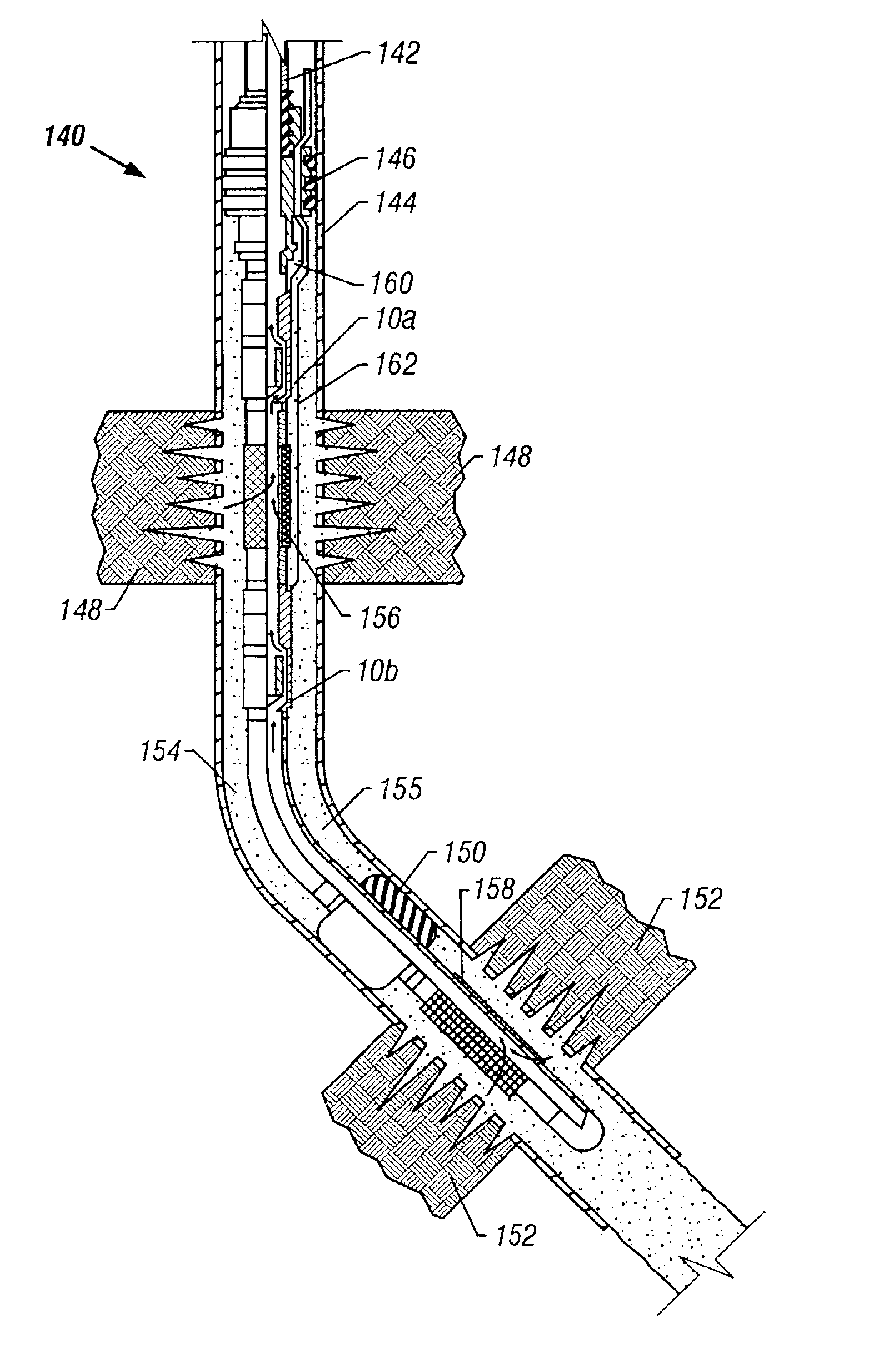
Method & Apparatus for Selective Injection or Flow Control with Through-Tubing Operation Capacity
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for calculating riverway cross-section flow measured by non-contact radar
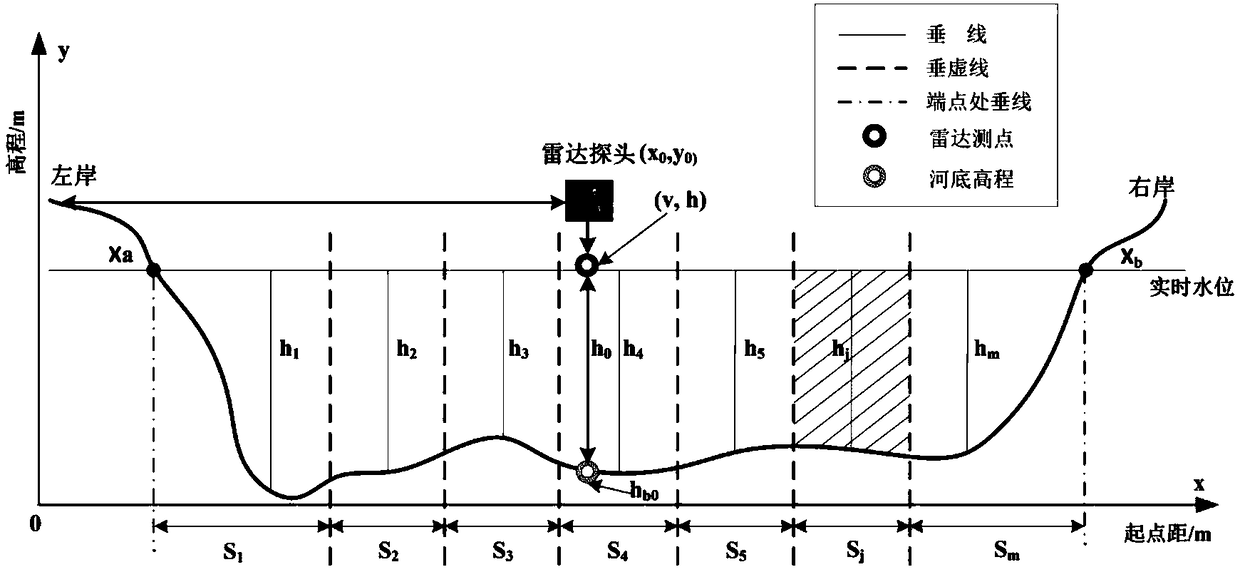
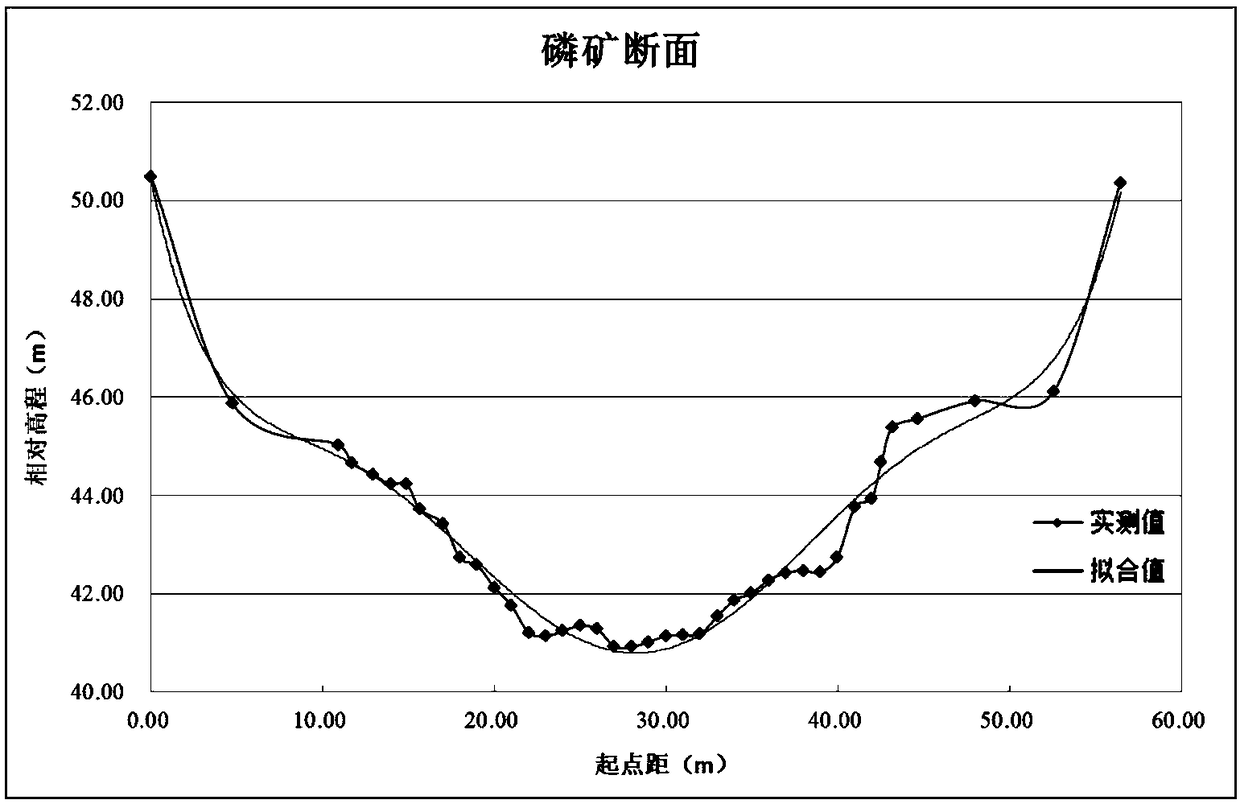
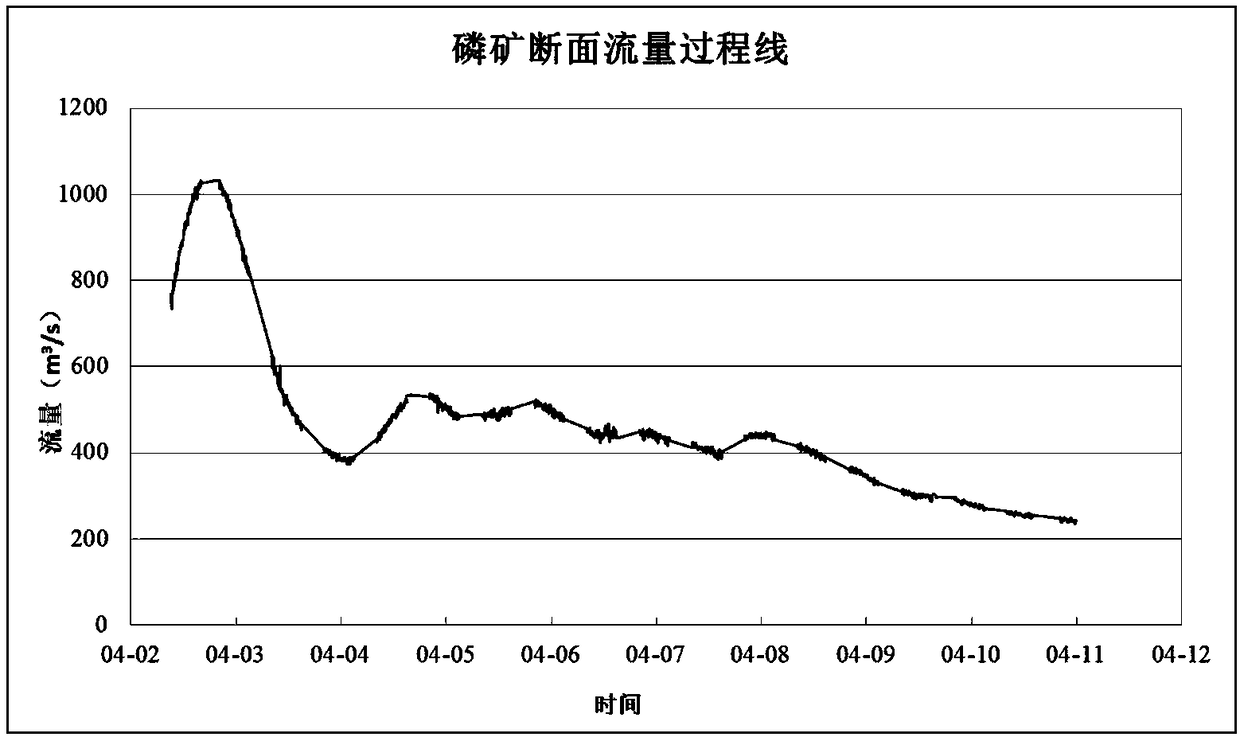
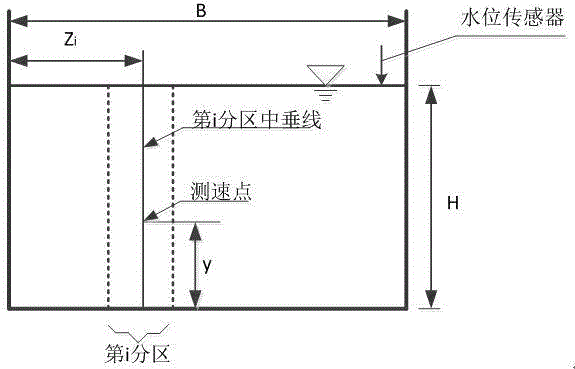
ActiveCN109060056ASolve the problem that it is difficult to obtain cross-sectional flowMeet the requirements of high real-time traffic monitoringVolume/mass flow measurementWater resource assessmentBed roughnessMeasurement point
The invention provides a method for calculating the riverway cross-section flow measured by a non-contact radar. On a riverway cross-section on which a radar probe measurement point is located, cross-section measurement is carried out at a certain distance interval, based on the measured cross-section data, the cross-section polynomial curve fitting is carried out, and the riverway cross-section water surface slope is calculated by combining with a hydraulics manning formula according to the position of a probe, the actually-measured water level, the surface flow velocity and the bed roughness, then based on a hydraulics natural riverway flow calculation principle, a certain number of vertical lines are chosen to divide the riverway cross-section evenly, the depth of water of the verticallines and the corresponding vertical line flow velocity are calculated in sequence, and then virtual vertical lines are made in interval midpoint of each vertical line, a plurality of virtual verticallines and cross-section fitted curves and a riverway water line form a plurality of irregular polygons, the area of each polygon is calculated in sequence, and finally, a weighted area method is usedfor calculating the flow of a riverway large section. The method for calculating the riverway cross-section flow measured by the non-contact radar has important practical value for the popularizationof online flow measurement technology and the high real-time flow monitoring of flood prevention.
Owner:CHANGJIANG RIVER SCI RES INST CHANGJIANG WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
Method and device for identifying traffic of access network
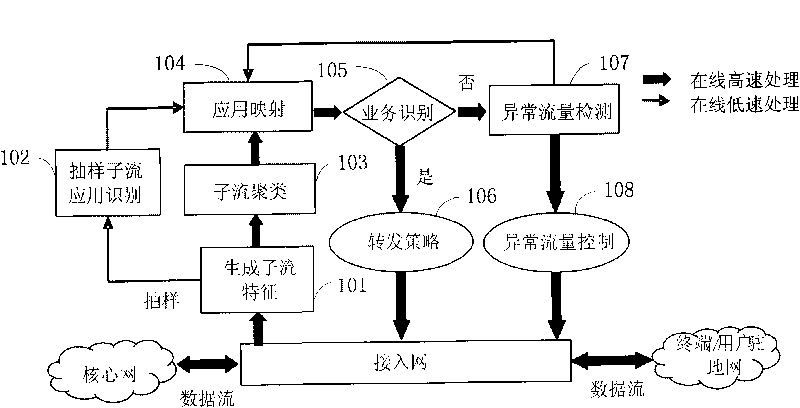
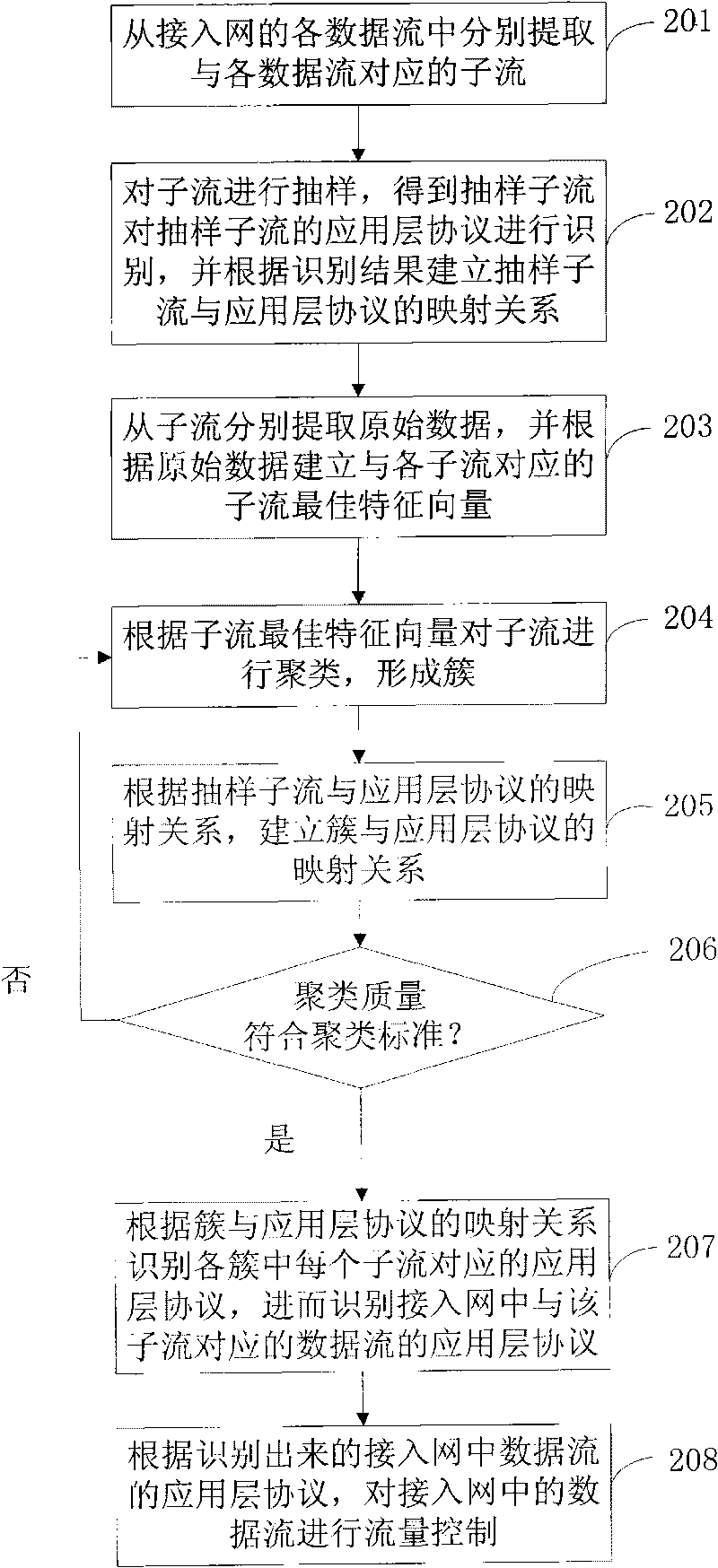
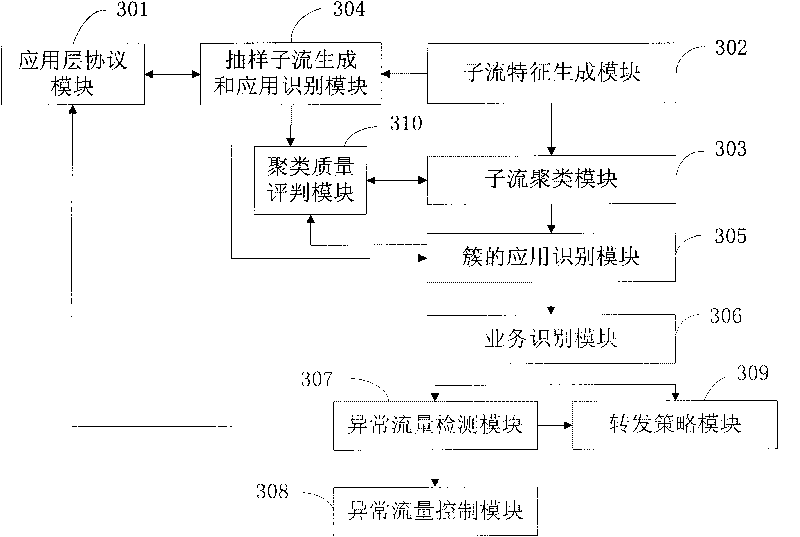
InactiveCN101714952ATraffic identification is validReduce detection workloadData switching networksFeature vectorAccess network
The invention discloses a method and a device for identifying the traffic of an access network. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a sub-stream, which corresponds to each data stream, from each data stream of the access network; sampling all the sub-streams to obtain sampling sub-streams; identifying the application layer protocol of each sampling sub-stream and establishing a mapping relationship between the sampling sub-stream and the application layer protocol according to the identification result; extracting initial data from each sub-stream and establishing sub-stream characteristic vectors which correspond to the sub-streams according to the initial data; clustering the sub-streams according to all the sub-stream characteristic vectors to form a plurality of clusters; establishing a mapping relationship between the clusters and the application layer protocols according to the mapping relationship between the sampling sub-stream and the application layer protocol; and identifying the application layer protocol, which each sub-stream in each cluster corresponds to, according to the mapping relationship between the clusters and the application layer protocols so as to identify the application layer protocol of the data stream which correspond to the sub-stream in the access network. The method and the device for identifying the traffic of the access network can perform high-speed on-line flow identification for the access network and can identify the application layer protocol of an encrypted data stream in the access network.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Online automatic channel flow measuring method
InactiveCN104535123ARealize automatic measurementEasy to operateVolume/mass flow by mechanical effectsMicrocontrollerMeasurement point
The invention discloses an online automatic channel flow measuring method. Measuring parameters are set on an upper computer, a microcontroller automatically subdivides a fracture surface into a plurality of zones, feature measuring points are automatically selected, after the flow speed of one point of the fracture surface and the water level of the fracture surface are measured, the average flow speed of a vertical line where the flow speed point is located is worked out according to the flow speed distribution rule in the vertical line direction of the fracture surface, the measuring point position, the measuring point flow speed and the water depth value, the average vertical line flow speed in each zone is obtained according to the transverse distribution rule of the average flow speed, the average flow speeds in the zones are represented through the average vertical line flow speeds in the zones, summing is conducted after the flow of the zones is obtained, and then the total flow of the fracture surface can be obtained. The feature measurement points can be accurately, reliably and automatically positioned, the detection precision is improved, the automatic flow measurement is achieved, and labor input is reduced.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Multi-point water inlet aeration anoxic-aerobic high-efficient nitrogen and phosphorus removal method
ActiveCN103241904ALow investment costLow running costMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a multi-point water inlet aeration anoxic-aerobic high-efficient nitrogen and phosphorus removal method. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: (1) introducing sewage to be treated into a grille regulating tank through a water inlet pipe; (2) dividing the water after pretreatment by the grille regulating tank into two lines, wherein one line leads to an aeration tank and the other line leads to an anoxic tank; (3) sending the water in the anoxic tank into an aerobic tank; (4) dividing nitrified water after nitrification treatment in the aerobic tank into two lines, wherein one line returns to the anoxic tank, and the other line flows into a precipitation tank to perform mud-water separation; and (5) lifting sludge through a sludge lifting device, transporting the residual sludge to the outside through a sludge discharge pipe after passing through a sludge treatment system, and returning the sludge after lifting into the aeration tank. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for new and transformation upgrading projects of high-ammonia nitrogen village and small town / industrial sewage treatment works, has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in management and maintenance, low cost, good treatment effects, strong nitrogen removal effect and the like, and is less affected by climatic conditions.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Process for improving inline tailings treatment
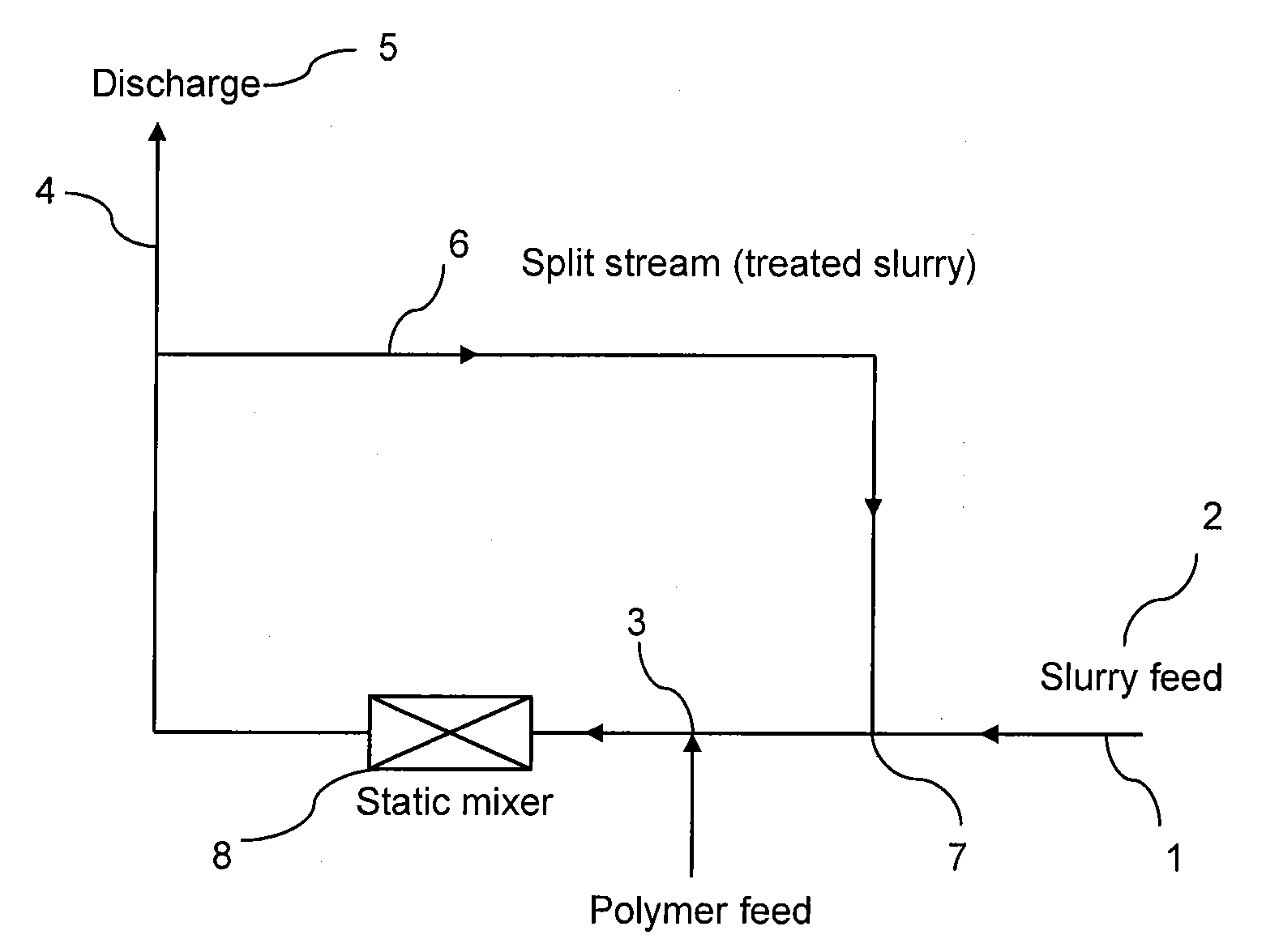
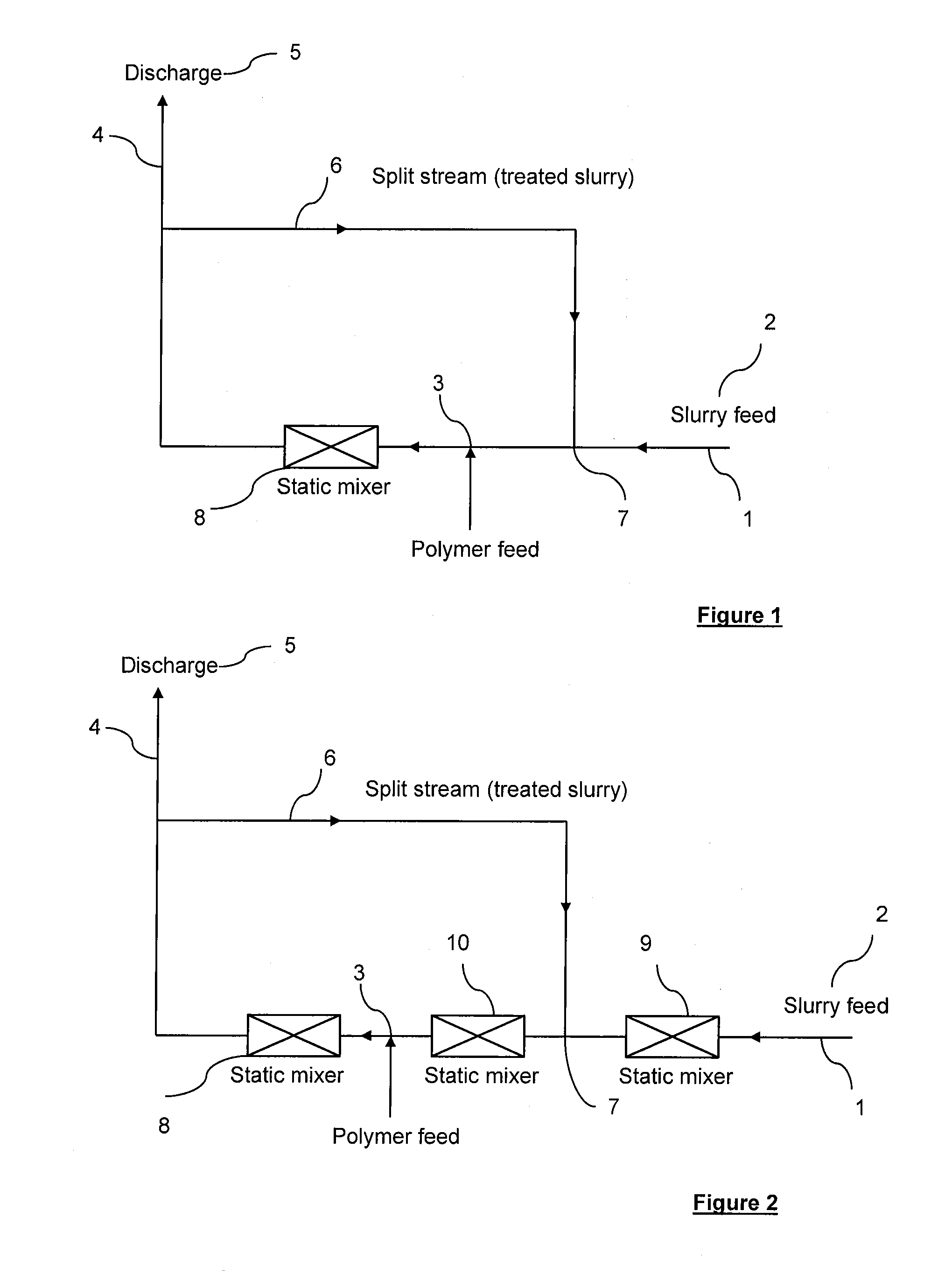
InactiveUS20120138542A1Improve processing efficiencyEasily improve performanceTransportation and packagingSolid waste disposalFlocculationPolymer science
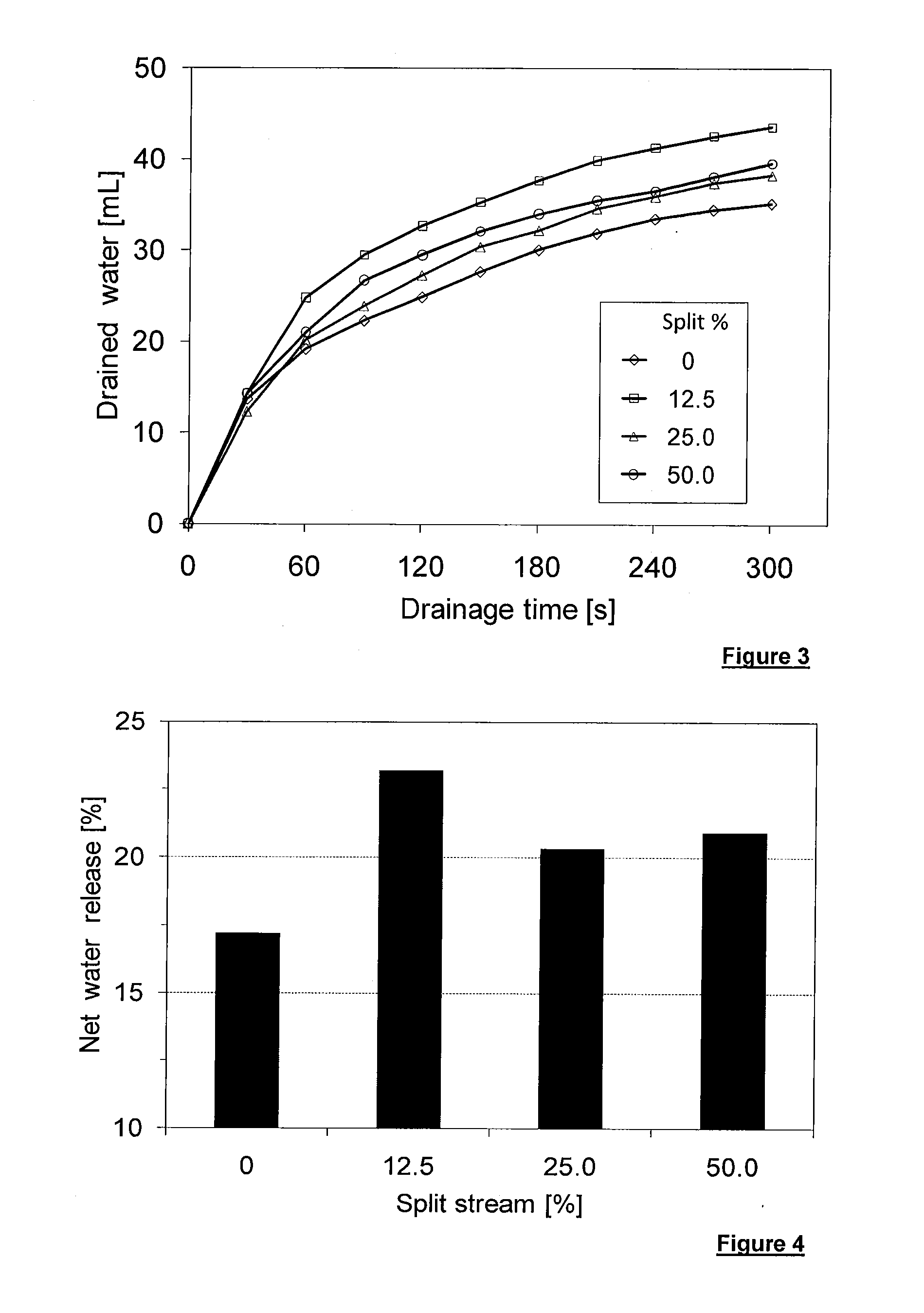
A process for improving inline mineral slurries treatment comprises successively: providing an in-line flow of slurries in a main stream; introducing at least one polymer into the main stream through at least one polymer injection point to cause dispersion of the polymer and to start the coagulation and / or the flocculation of slurries to produce treated slurries; and splitting the main stream containing treated slurries into two streams respectively: a discharge stream which directly transfers a part of treated slurries to the deposit area, and a split stream which reintroduces the other part of treated slurries into the main stream through at least a reinjection point in a location prior to the at least one polymer injection point.
Owner:S P C M SA
Off-line dynamic QR code generation method, and payment method and device
InactiveCN107180351ASolve the problem that one code at a time cannot be realizedReduce interaction timeKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationInteraction timeProgramming language
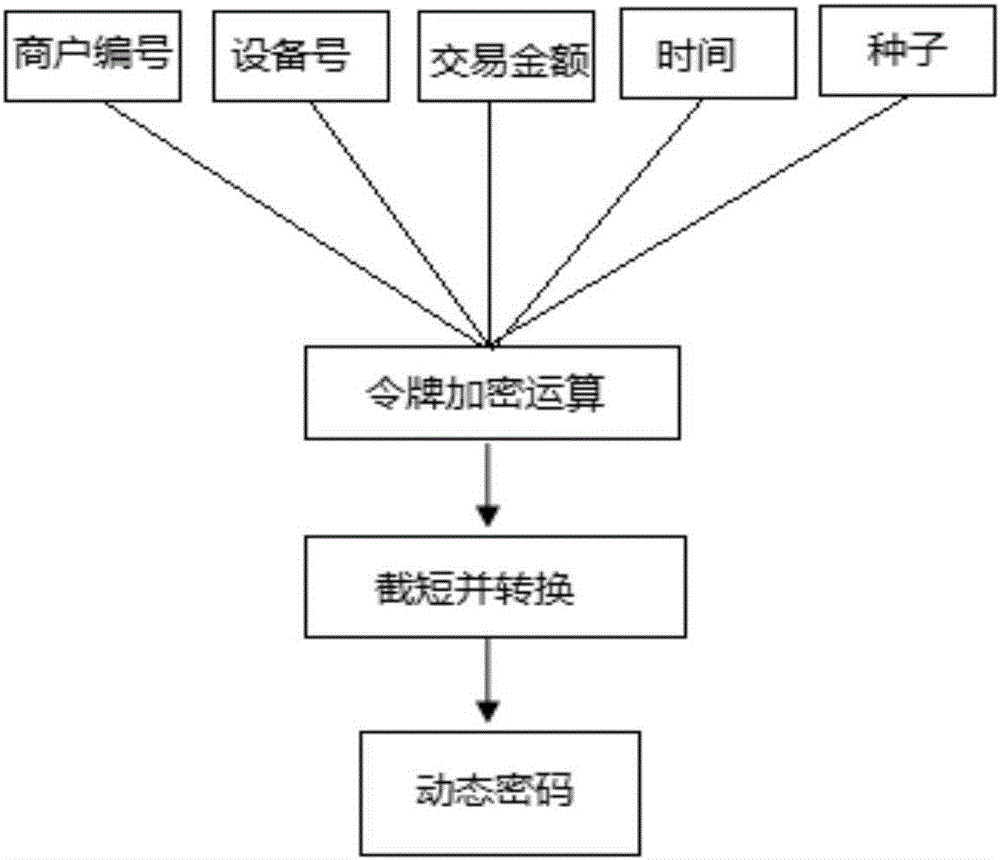
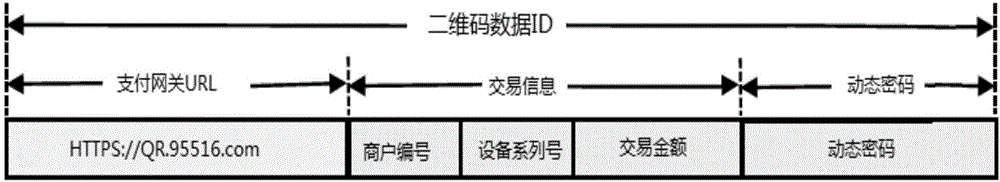
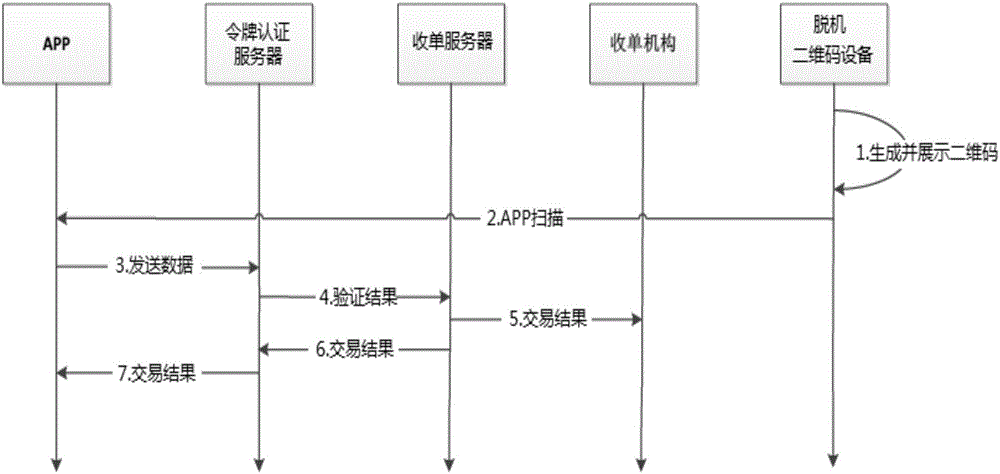
The invention discloses an off-line dynamic QR code generation method, and a payment method and device. For the scheme of the off-line dynamic QR code generation method, a dynamic password token technology based on time is used to perform encrypted operation to calculate the dynamic keyword of this time, according to a token seed key and a time factor, by means of combination with the transaction information containing the transaction amount, and a dynamic QR code pattern is generated according to the dynamic keyword of this time. The scheme applies to the dynamic password token technology to the dynamic QR code generation technology, thus being able to preferably solving the problem that a static QR code cannot realize one code for one time. Besides, in the scheme, the dynamic token and a certificate server are synchronous in time and are consistent in the algorithm, thus not depending on on-line and using the off-line mode to guarantee that the generated QR code data can be identified and authenticated by the background. And at the same time, the advantages of off-line are reduction of the on-line flow, reduction of network interaction time, reduction of transaction flow and steps, and improvement of transaction efficiency.
Owner:DYNAMICODE
Method and apparatus for selective injection or flow control with through-tubing operation capacity
An in-line flow control device for a well chokes flow through a conduit while allowing access therethrough.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
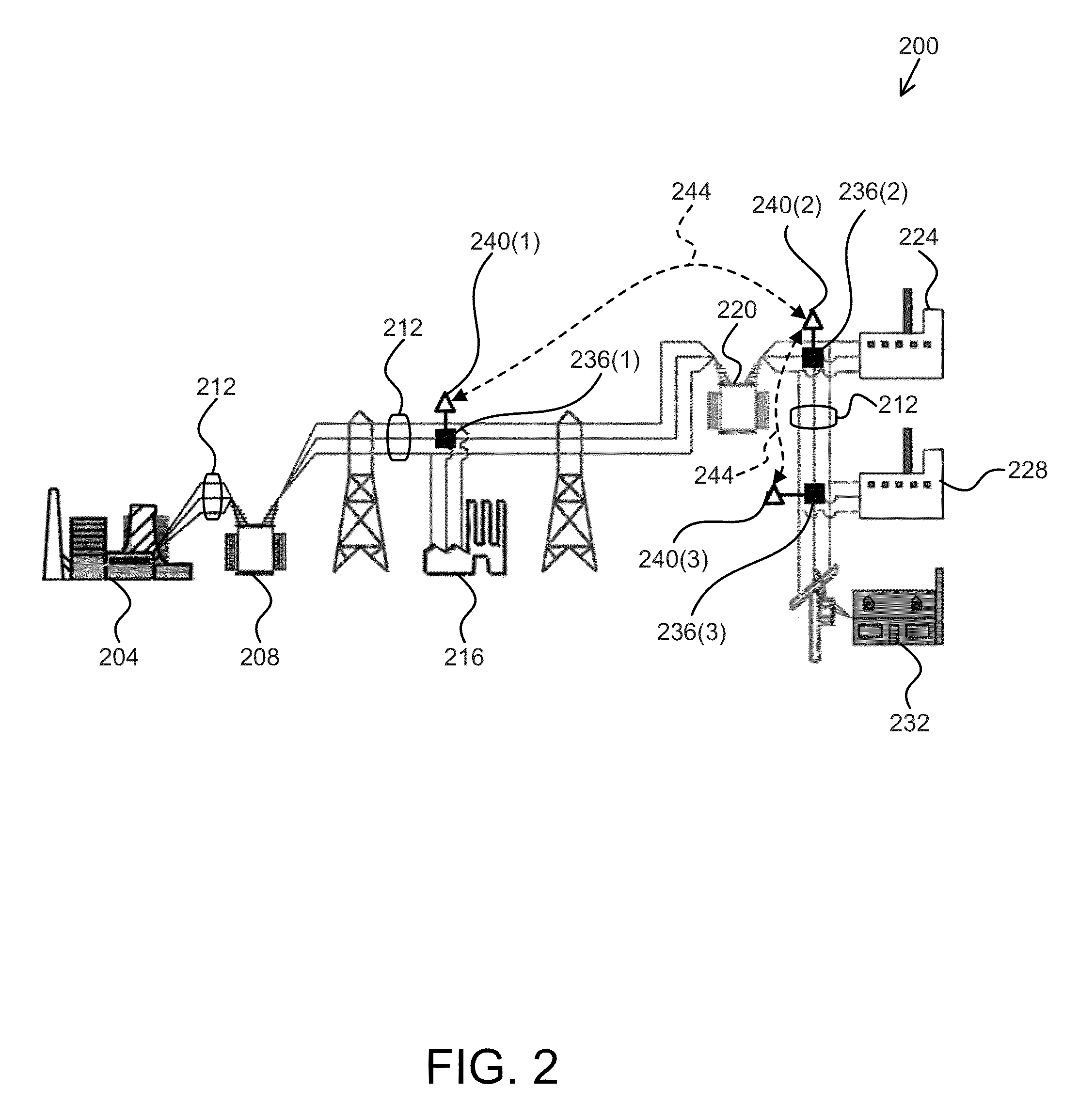
Distributed Methods and Software For Balancing Supply and Demand In An Electric Power Network
ActiveUS20150025696A1Mechanical power/torque controlData processing applicationsEngineeringPhysical system
Methods and software for managing electric power networks in a distributed manner. A supply and demand balancing scheme is used across a network of agents to facilitate agreement on the optimal incremental price for energy provision in an electric power network subject to the constraint that the total generation in the electric power network matches the total network demand. A multi-step optimization approach is provided that incorporates inter-temporal constraints, allowing for optimal integration of flexible power loads and power storage entities and taking into account power generation ramp rate constraints at individual generation entities. The approach is extended to cope with line flow constraints imposed by the physical system topology and transmission line limits / capacities.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
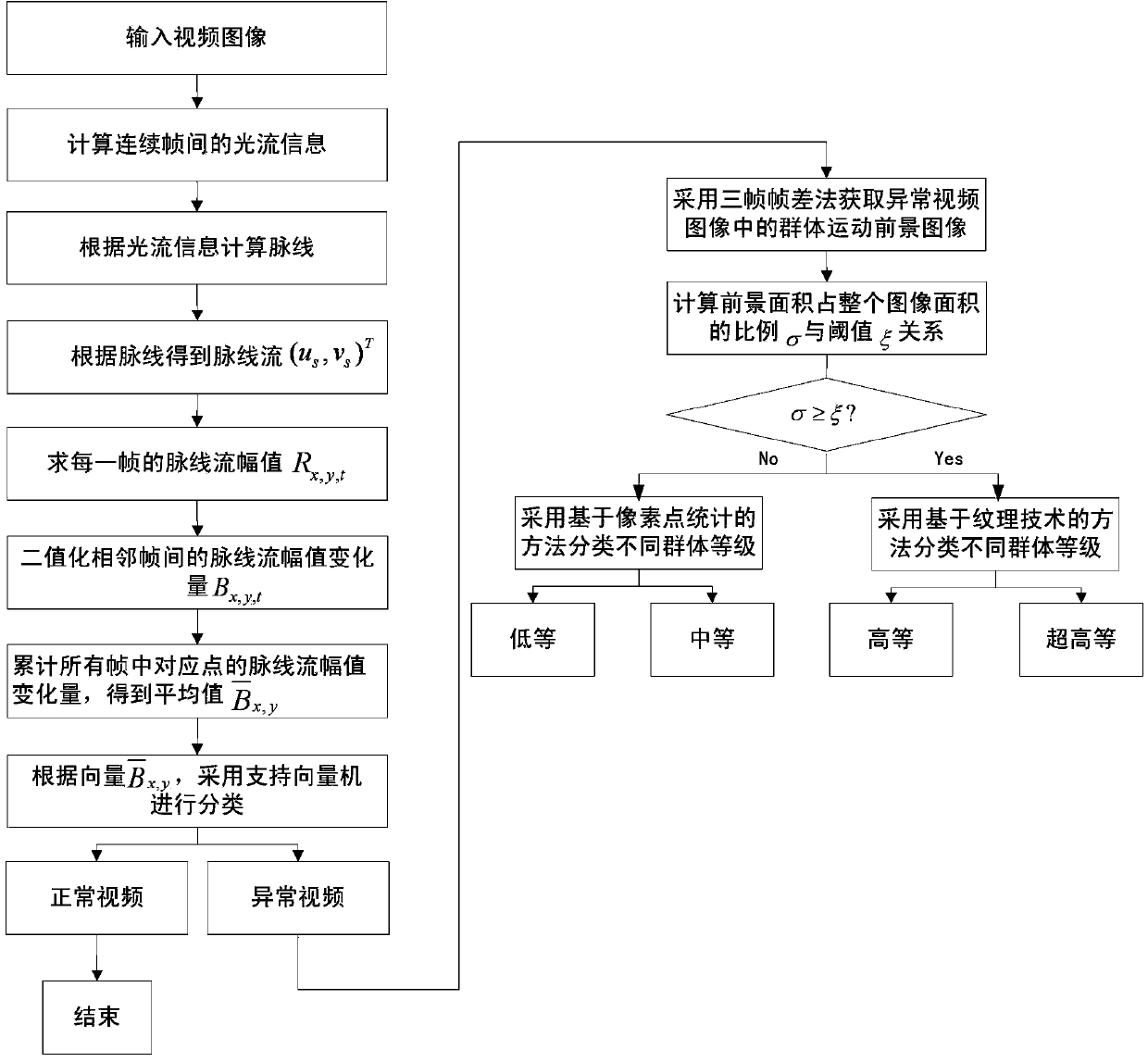
Adaptive abnormal crowd behavior analysis method
ActiveCN103745230AAccurate detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionAnomalous behavior
The invention discloses an adaptive abnormal crowd behavior analysis method, which is used for analyzing crowd behaviors in a video image. The method comprises the following steps of performing streak line calculation on the video image; calculating a streak line flow; detecting abnormal behaviors; performing foreground detection on the video image of abnormal crowd behaviors; performing adaptive crowd density estimation comprising pixel-counting-based density estimation and texture-analysis-based density estimation, and finally dividing estimated density into four density levels, i.e. a low density level, a medium density level, a high density level and an ultrahigh density level, thereby finishing grading the abnormal crowd behaviors. According to the method, the concepts of streak line and streak line flow are introduced to analyze whether a crowd in the video image is abnormal or not; the method has the advantage of detection accuracy; the densities of crowds involved in the abnormal crowd behaviors in different density scenarios are estimated in an adaptive way, and the detected abnormal crowd behaviors are graded by using density estimation results as main characteristics; the method is used for accurately grading the abnormal behaviors (such as mass brawl) in crowded public places, and giving alarms.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Medical in-line flow control clamp device
A medical in-line flow control clamp device which is arranged coaxially along the longitudinal axis of an infusion tube or the like, and which has a sleeve connected to the tube and a slide having an arm movably mounted on and having a part biased toward the sleeve in a manner where the arm bears against and pinches the tube when the slid is moved relative to the sleeve. The sleeve may have a ramp and support directed toward the tube which causes the arm to move against the tube. The slide may be fabricated from a plastic material, such as acrylic, which causes the arm to bind against the tube. The sleeve may have one or more stops and latch means to receive and secure the arm in tube pinching relation. The sleeve and slide may have a track and projection parts which train the slide in a predetermined direction toward the tube as the slide is moved to pinching position on the sleeve. Bars may be arranged on the slide transverse to the sleeve and tube for manipulating the slide on the sleeve by finger pressure. The sleeve may be fabricated in portions connected by a web so they may be folded and held around the tube in a selected position.
Owner:GARCIA JR RAUL
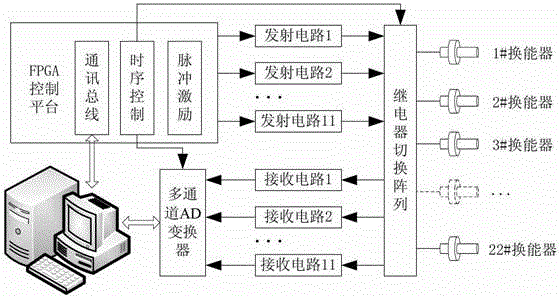
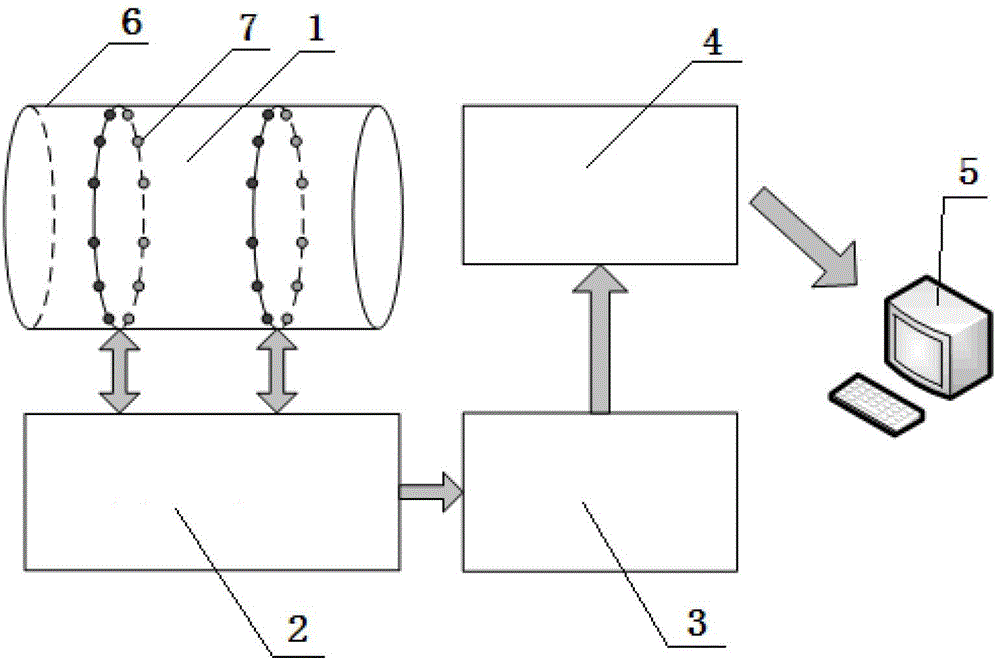
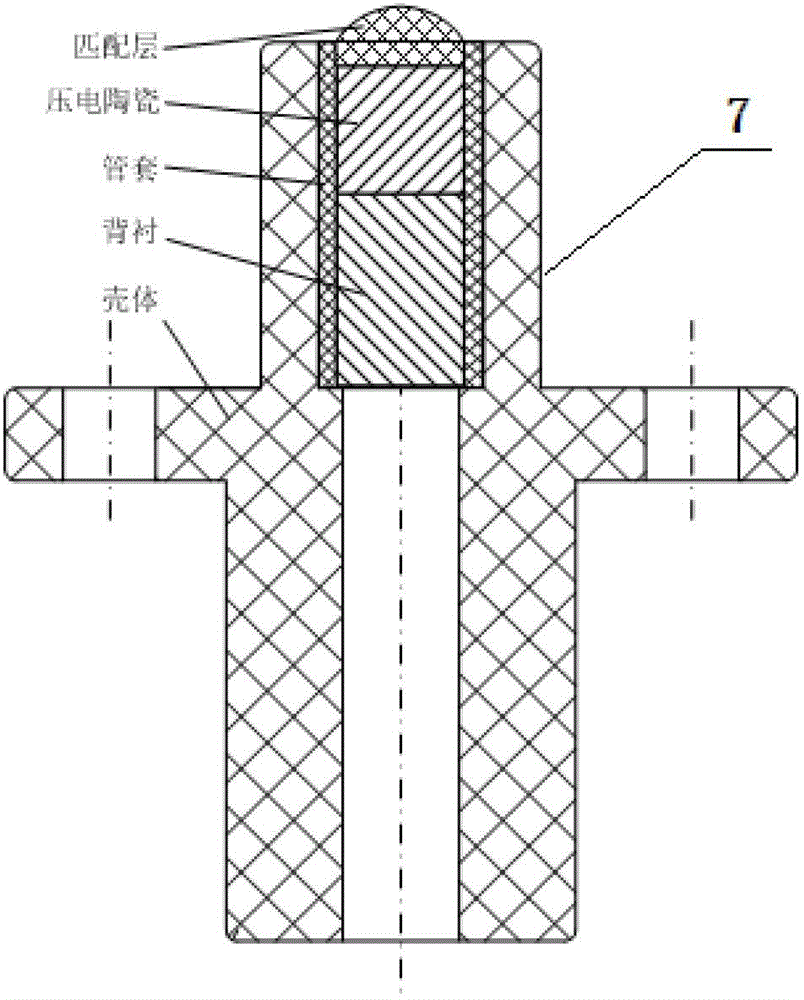
Ultrasonic imaging method and device for axial flow field of fluid in pipeline
The invention provides an ultrasonic imaging method and device for an axial flow field of fluid in a pipeline. The method comprises the following steps: distributing a plurality of ultrasonic transducers on the two cross sections at the upstream and the downstream, and detecting the axial flow field by using a tone channel network woven by the transducers; stimulating each transducer in sequence, electronically scanning and collecting ultrasonic signals transmitted by fair current and counter current of each tone channel; calculating average line flow velocity, and obtaining projection integration of the axial flow field on each tone channel; parallelly dividing the tone channels, and subdividing projection data of each tone channel group in an interval manner; using the chromatography imaging algorithm, rebuilding the axial flow field by using the subdivided projection data, and outputting and displaying the axial flow field. The device comprises a flow field detection pipe segment, an ultrasonic signal stimulation and collection module, a tone channel line flow velocity measuring module, an axial flow field reconstruction module and an output and display module. According to the device and the method provided by the invention, quick and accurate no-blind zone detection of the axial flow field on the cross sections of the pipeline can be realized, so that high-precision two-dimensional rebuilding of the axial flow field can be realized accordingly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
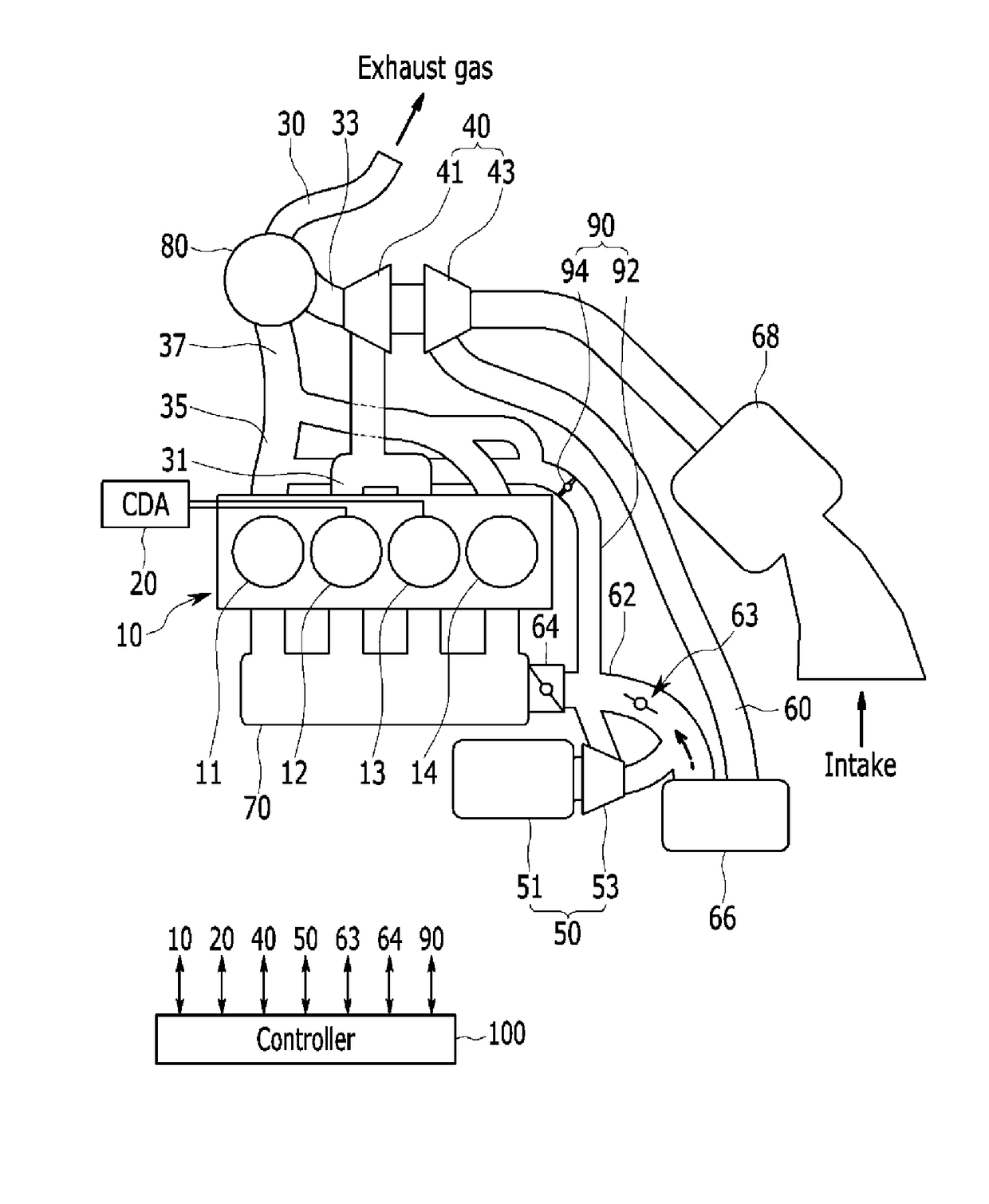
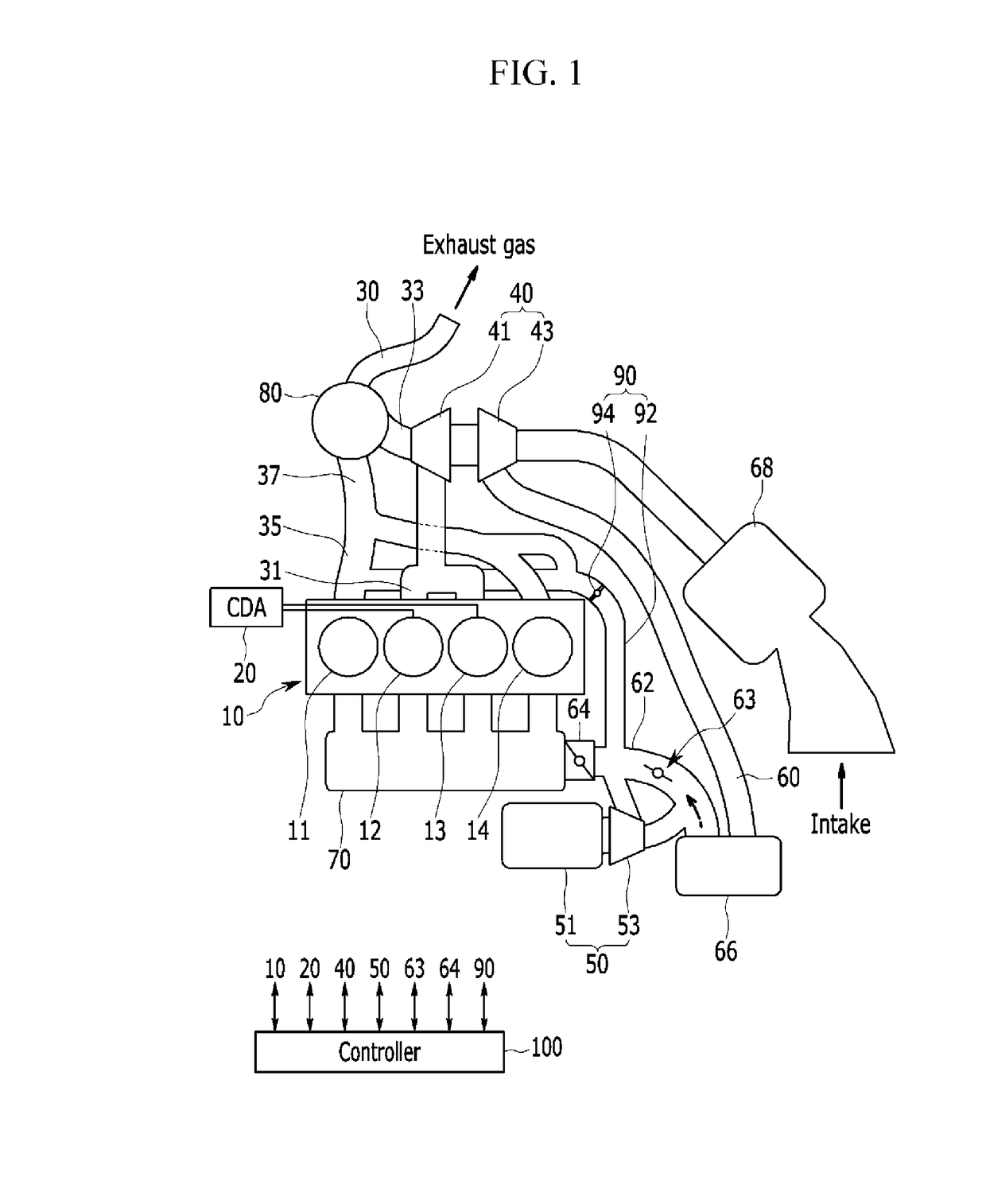
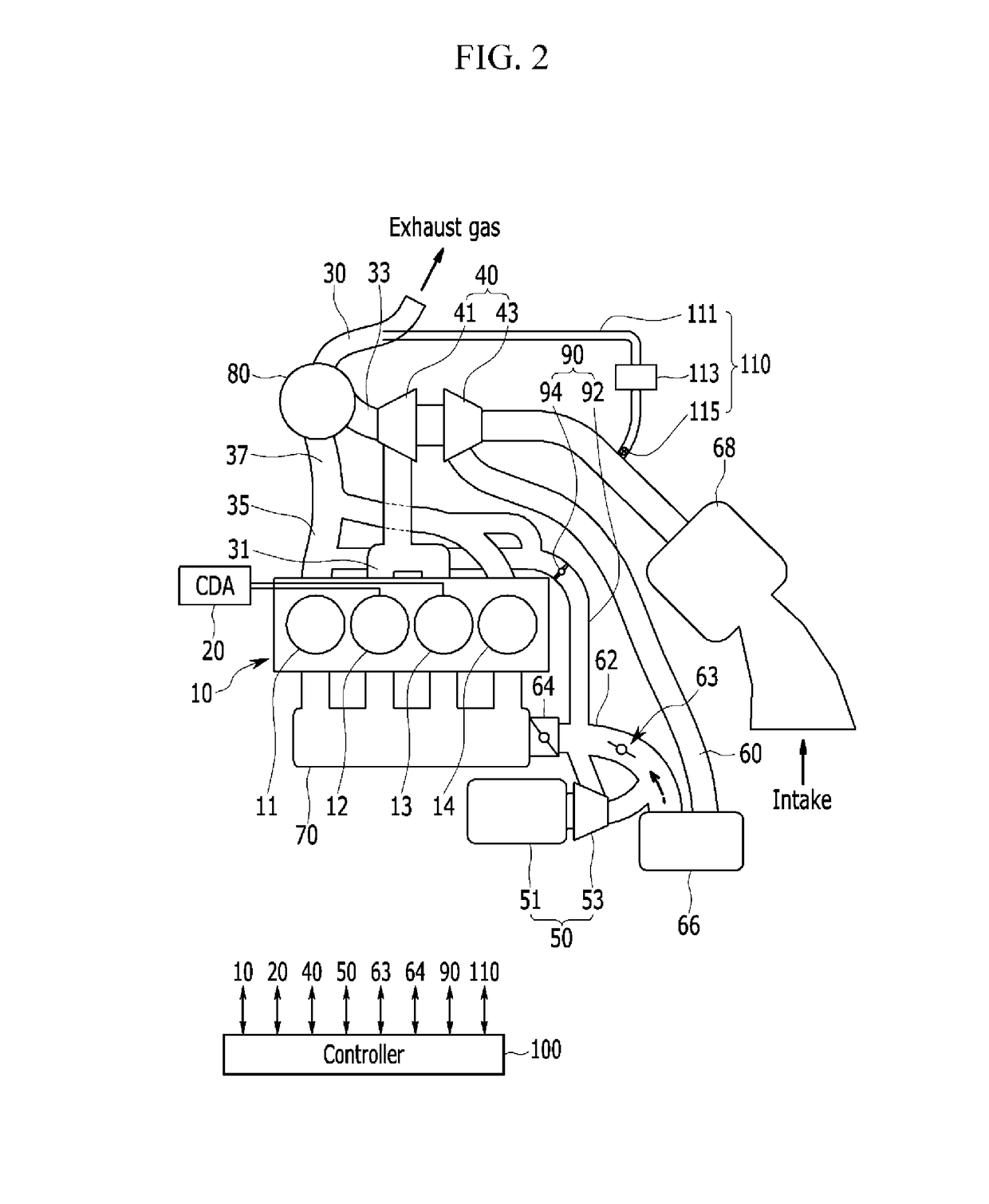
Engine system
ActiveUS20180058289A1Reduce back pressureIncrease the compression ratioElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberTurbocharger
An engine system may include an engine, an intake line, a cylinder deactivation (CDA) device mounted at a portion of combustion chambers, a first exhaust manifold connected to combustion chambers mounted with the CDA device, a second exhaust manifold connected to combustion chambers without the CDA device, a first exhaust line flowing exhaust gas exhausted from the first exhaust manifold, a second exhaust line flowing exhaust gas exhausted from the second exhaust manifold, a main exhaust line to which the first exhaust line and the second exhaust line are joined, an exhaust gas processing device at which the main exhaust line is installed, a turbocharger mounted at the first exhaust line, an electric supercharger installed at the intake line to supply supercharged air to the combustion chamber and an electric compressor, and an air injection device supplying the fresh air to the second exhaust manifold or the second exhaust line.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com