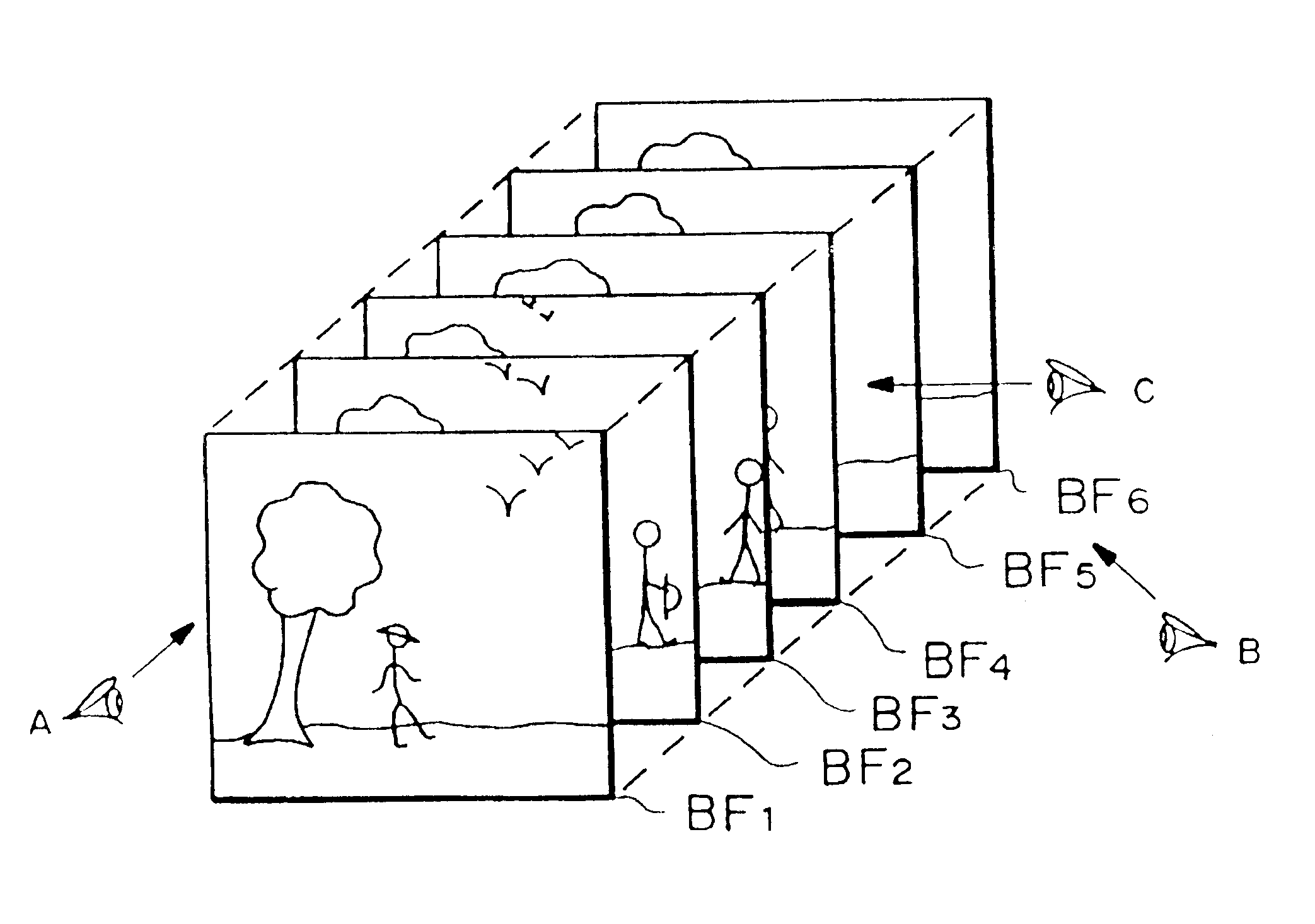
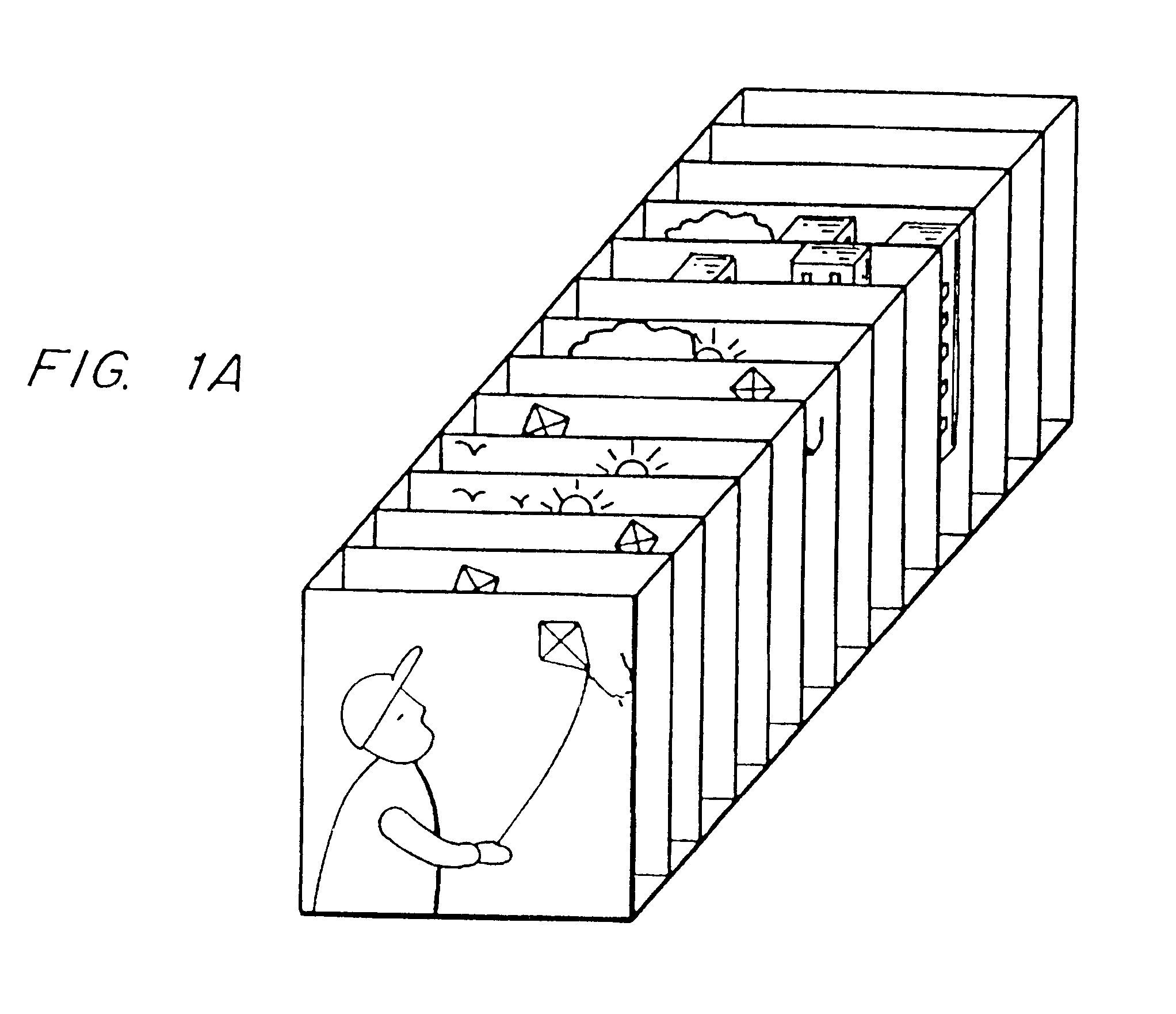
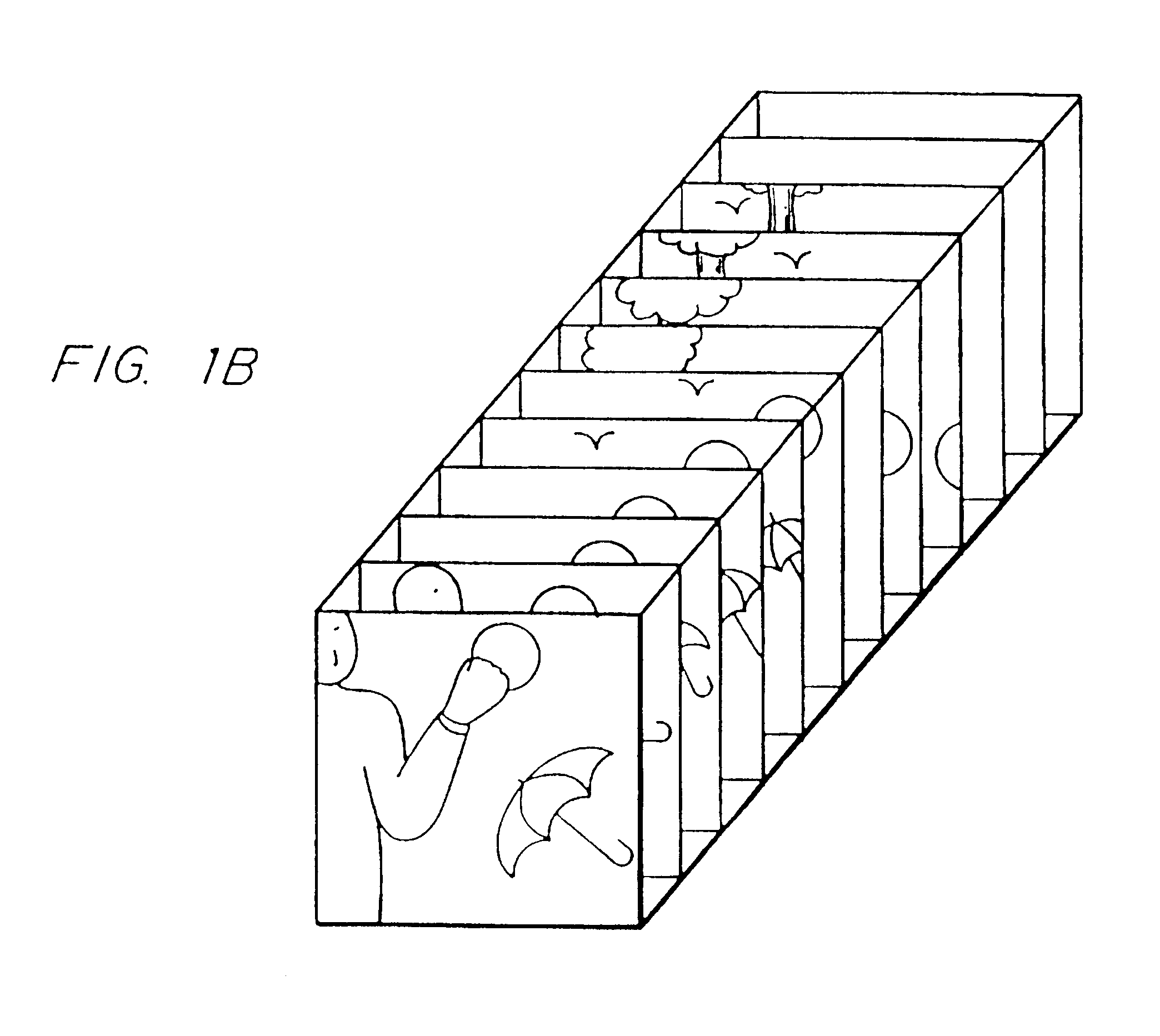
In a "video icon", as illustrated in FIG. 1A, the scene is represented by a number of frames selected from the sequence and which are displayed as if they were stacked up one behind the other in the z-direction and are viewed in perspective. In other words, each individual frame is represented by a plane and the planes lie one behind the other with a slight offset. Typically the first frame of the stack is displayed in its entirety whereas underlying frames are partially occluded by the frames in front. The envelope of the stack of frames has a parallelepiped shape. The use of a number of frames, even if they are partially occluded, gives the user a more complete view of the scene and, thus, a better visual understanding. Furthermore, with some such icons, the user can directly access any frame represented in the icon.
The present invention provides a novel type of interface to video information which allows the user to access information concerning a
video sequence in a highly versatile manner. In particular,
interactive video interfaces of the present invention enable a user to obtain deeper levels of information concerning an associated video sequence at positions in the sequence which are designated by the user as being of interest.
In a reduced form, the present invention can provide non-interactive interfaces to video sequences, in which the root image information is packaged with an associated script defining a routine for automatically displaying a sequence of different views of the root image and performing a set of manipulations on the displayed image, no user manipulation being permitted. However, the full benefits of the invention are best seen in interactive interfaces where the viewing position of the root image is designated by the user, as follows. When the user first accesses the interface he is presented with a displayed image which represents the root image seen from a particular viewpoint (which may be a predetermined reference viewpoint). As he designates different viewing angles, the displayed image represents the root image seen from different perspectives. When the user designates viewing positions at greater or lesser distances from the root image, the displayed image increases or reduces the size and, preferably, resolution of the displayed information, accessing image data from additional video frames, if need be.
In certain embodiments of the present invention, the root image corresponds to an "object-based video icon." In other words, certain of the basic frames included in the root image are not included therein in full; only those portions corresponding to selected objects are included. Alternatively, or additionally, certain basic frames may be included in full in the root image but may include "hot objects," that is, representations of objects selectable by the user. In response to selection of such "hot objects" by the user, the corresponding basic frames (and, if necessary, additional frames) are than displayed as if they had become transparent at all portions thereof except the portion(s) where the selected object or objects are displayed. The presence of such selectable objects in the root image allows the user to selectively isolate objects of interest in the video sequence and obtain at a glance a
visual impression of the appearance and movement of the objects during the video sequence.
In preferred embodiments, the interfaces of the present invention allow the user to generate a displayed image corresponding to a
distortion of the root image. More especially, the displayed image can correspond to the root image subjected to an "accordion effect", where the root image is "cracked open", for example, by bending around a bend line so as to "
fan out" video frames in the vicinity of the opening point, or is modified by linearly spreading apart video frames at a point of interest. The accordion effect can also be applied repetitively or otherwise in a nested fashion according to the present invention.
Thus, the present invention provides a toolkit for use in creation of customized interfaces. In preferred embodiments, the toolkit enables a designer to tailor the configuration and content of the root image, as well as to specify which objects in the video sequence are "hot objects" and to control the way in which the displayed interface image will change in response to manipulation by an
end user. Thus, among other things, the toolkit enables the interface designer to determine which frames of the video sequence should be used as basic frames in the root image, and how many additional frames are added to the displayed image when the user designates a viewing position close to the root image.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More