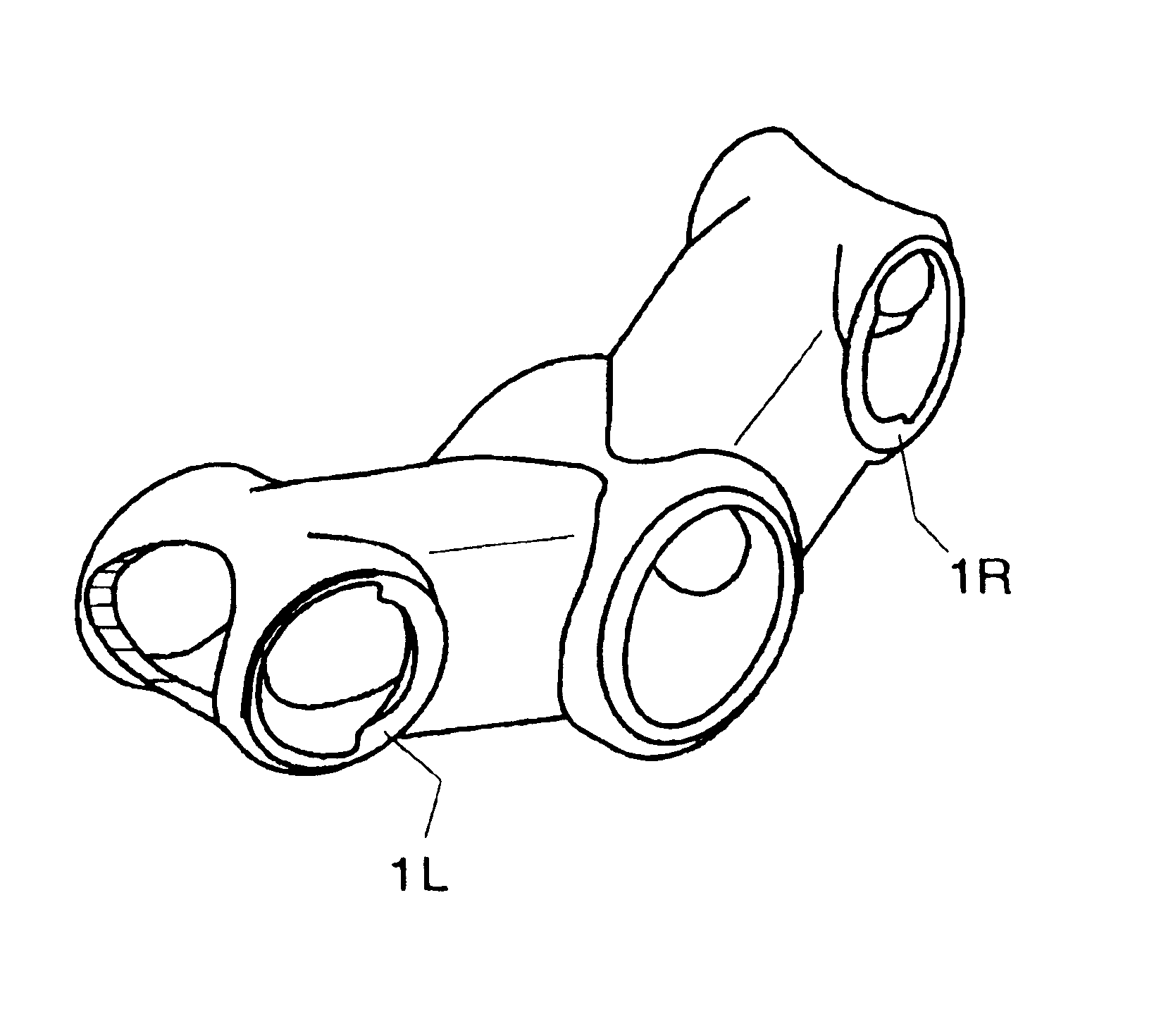
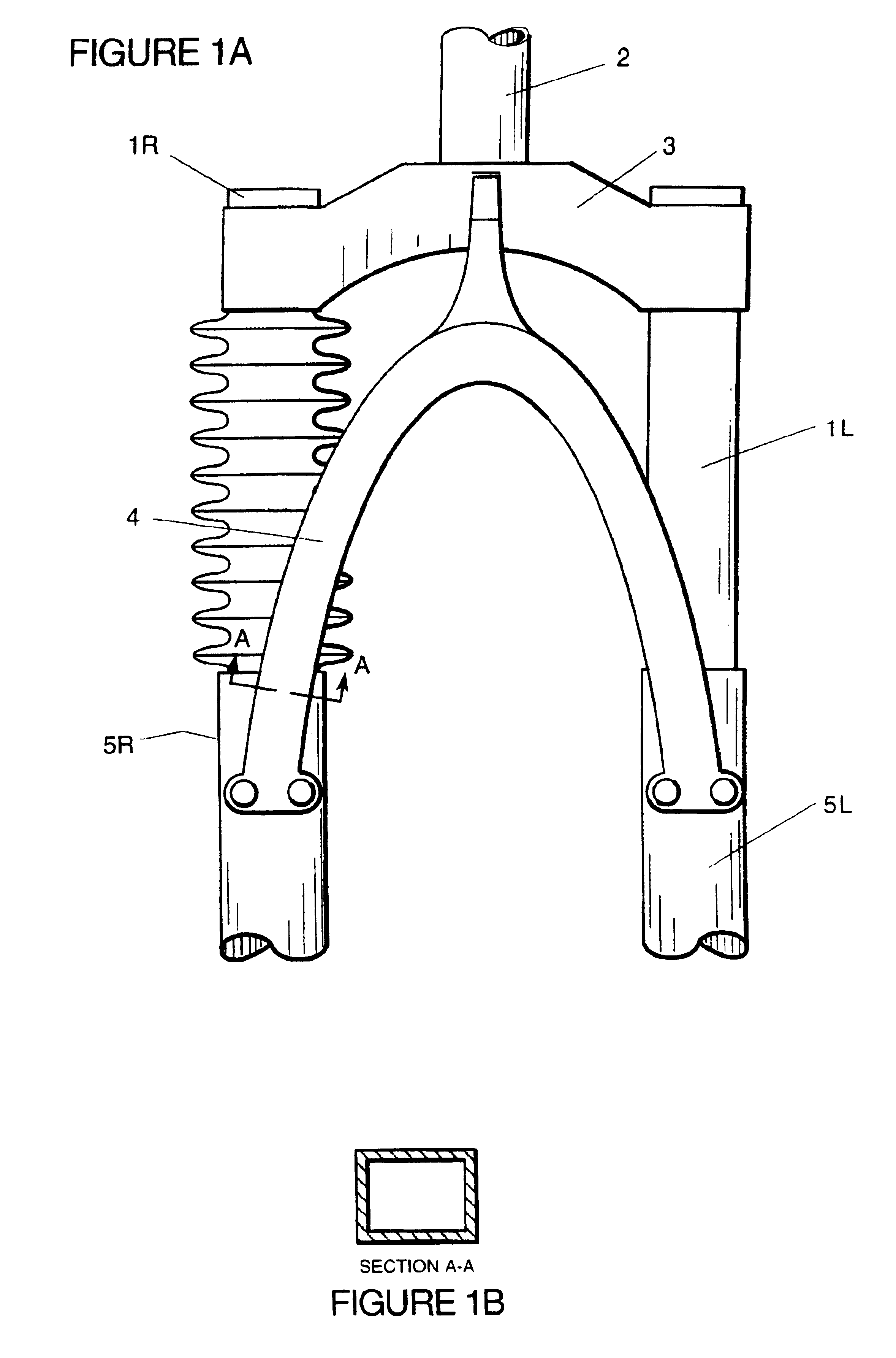
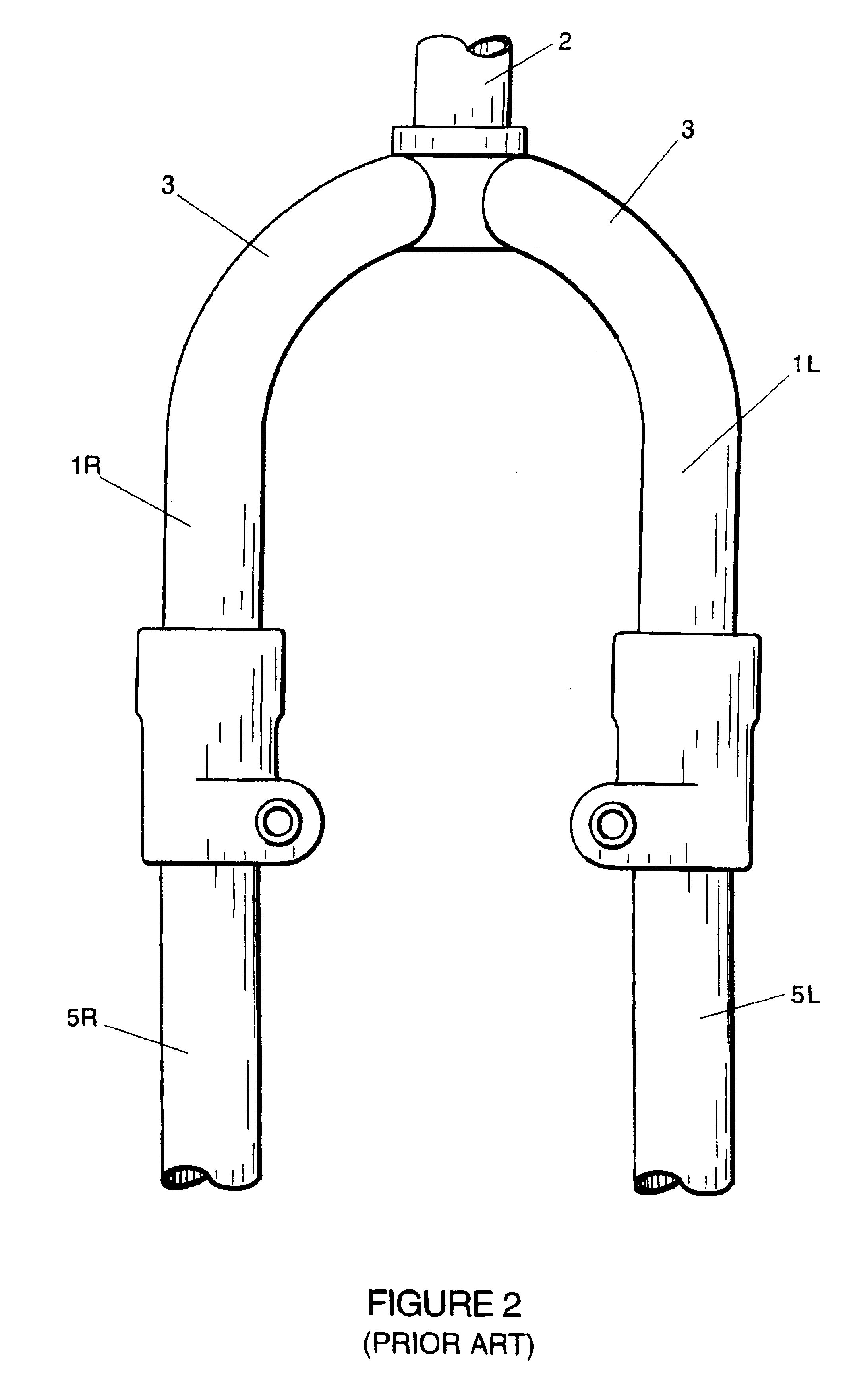
Telescoping-type front fork bicycle suspensions
a technology of front fork and suspension system, which is applied in the direction of friction roller based transmission, steering device, cycle equipment, etc., can solve the problems of design that must operate at relatively high stress, close to the strength limits of materials being used, and critical weight and stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment b (
FIG. 6b) illustrates an end fitting design using adhesive bonding. Both the stanchion socket (6-10) and the bridge (6-9) are designed for bonding. This option has the advantage of lightness and improved fatigue strength but it does not provide an easy means for disassembly.
embodiment c (fig.6c)
Embodiment C (FIG. 6c) uses a collet assembly CA to make the connection. The collet assembly has an inner taper (6-11), internal threads IT, a sliding compression wedge .[.(6-12).]. .Iadd.(6-17) .Iaddend.and a ring adjuster screw (6-13) engageable with thread IT to lock and drive the collet wedge finger into position. The compression wedge .[.(6-12).]. .Iadd.(6-17) .Iaddend.can be made with or without machined slots. The slots boring the fingers tend to make the wedge conform more closely to the mating surfaces thereby giving a more uniform locking force. The inner taper and the sliding wedge piece can be of any angle from 0.1 degrees to 18 degrees, relative to the axis of the stanchion tube. The compression wedge can be made of metal, an engineering plastic or reinforced plastic material. The collet assembly works by using the adjuster screw to force the wedge piece between the inner taper and the external surface of the stanchion tube, until the desired locking force is generated....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com