Compensation method of a bias magnetic field in a storage surface of a magnetoresistive storage cell, and semiconductor device
A technology for memory cells and semiconductors, applied in the field of compensating this bias field, can solve problems such as reducing the stability of the reference layer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
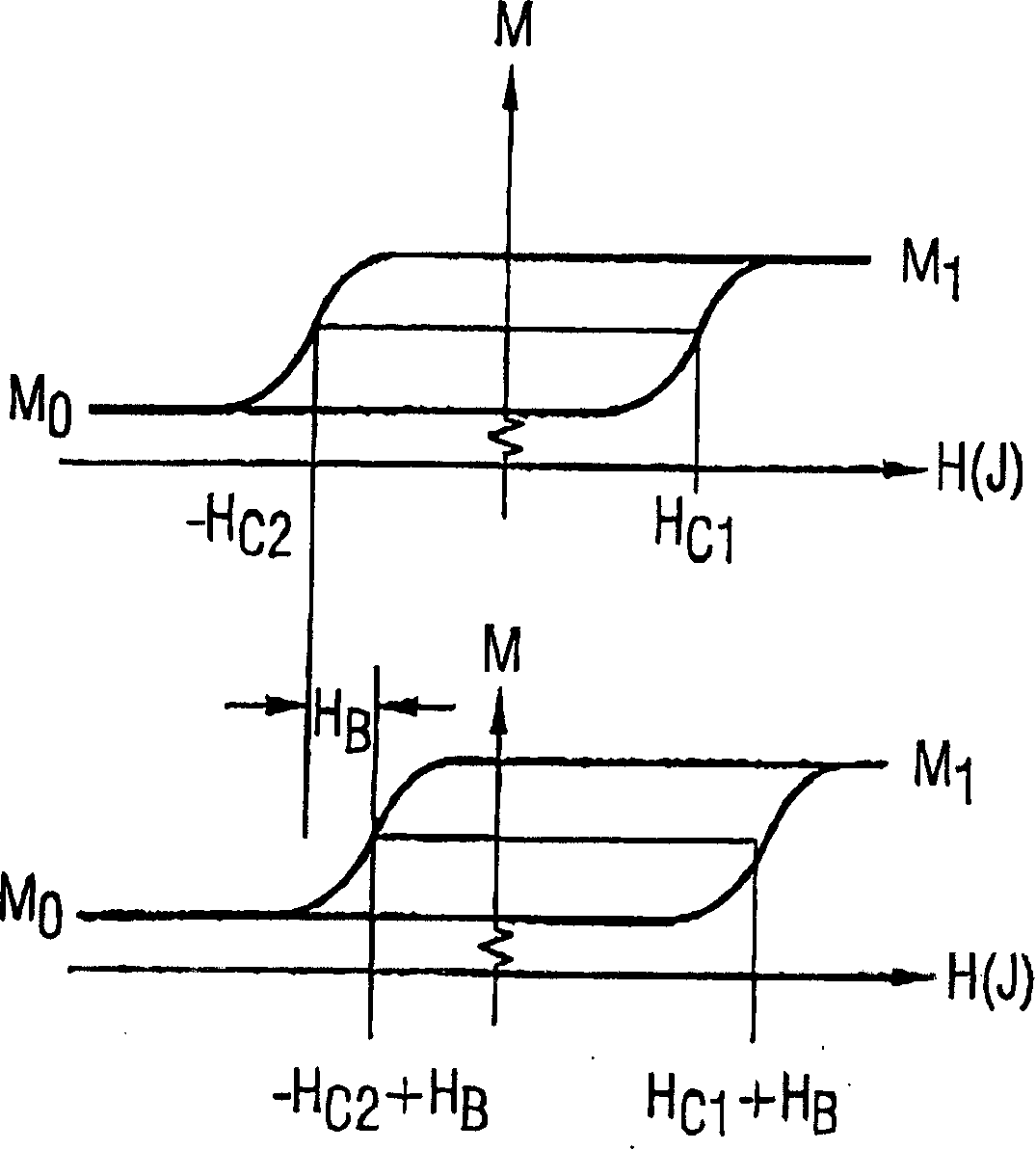
[0060] Figures 2 and 3 have been described in the introduction.
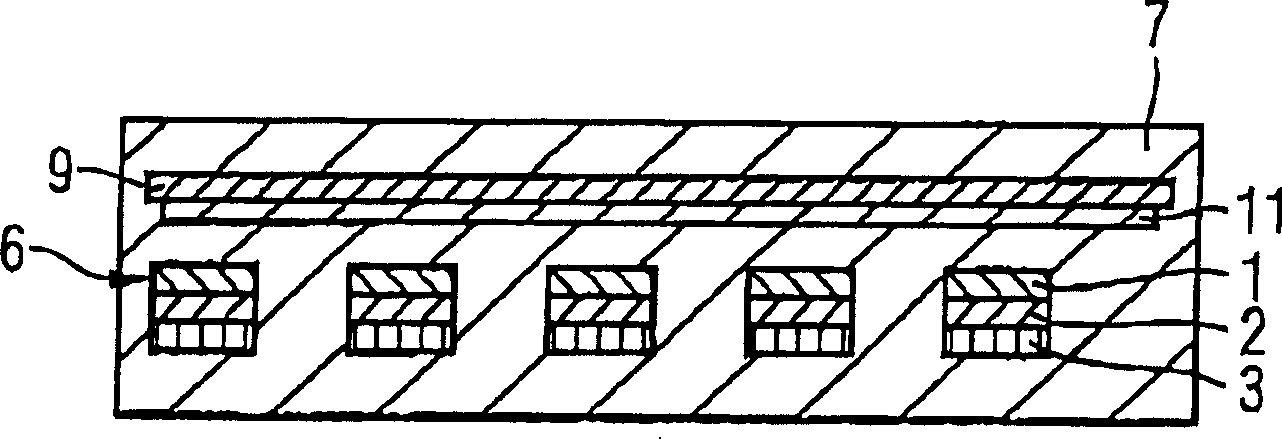
[0061] FIG. 1 is a simple cross-sectional schematic diagram illustrating a semiconductor device 7 with a magnetoresistive memory cell 6. The cross-sectional schematic diagram is not to scale, and the illustration does not limit the features of the present invention.
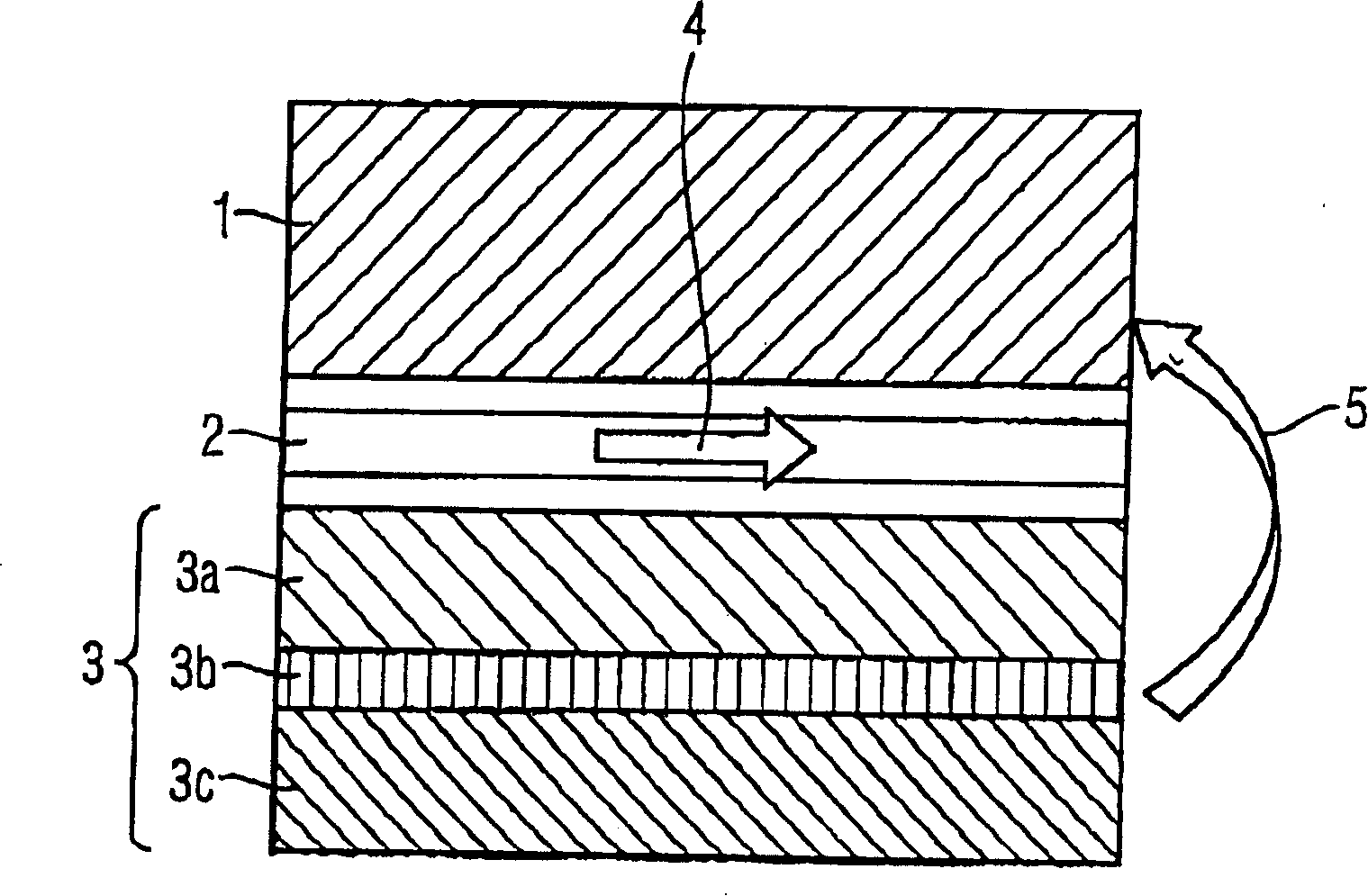
[0062] The memory cell 6 is structured by storage, isolation and reference layers 1 , 2 , 3 , and in the illustrated example, the memory cell 6 is mounted on a single layer of the semiconductor device 7 . A passive layer 11 is used parallel to a memory cell layer formed from the memory cells 6 .
[0063] Between the reference of the memory cell 6 and the storage layers 1, 3, ferromagnetic coupling generates a magnetic bias field.
[0064] The components indicated by the dotted lines have the compensation layer 7 provided by the semiconductor device 7, which is omitted in the first embodiment. In the first embodiment, the compensation layer 9 is u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com