Motion controller and system identifying method
A motion control device and system identification technology, applied in control systems, general control systems, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve problems such as inability to calculate inertia, inability to remove viscous friction or Coulomb friction fixed interference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
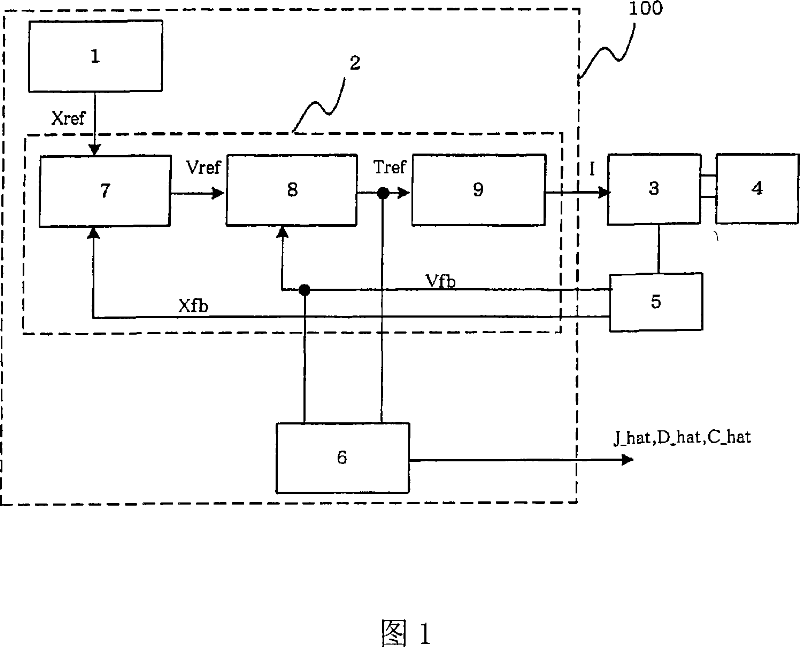
[0100] FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the structure of a motion control device implementing the method of the present invention. In the figure, 1 is a command generator that issues a position command Xref. 2 denotes a controller, which performs a control operation and outputs a current I according to a position command, a position detection value Xfb, and a speed detection value Vfb. The operation inside the controller 2 can be in any form. In this specific embodiment, it is the position controller 7 that outputs the speed command Vref according to the position command Xref and the position detection value Xfb, and outputs the speed command Vref and the speed detection value Vfb The speed controller 8 for the torque command value Tref and the current controller 9 for controlling to output current according to the torque command value are constituted. Here, the speed detection value may be a value obtained by time-differentiating the position detection value, and in the cas...
Embodiment 2
[0162] The second method of the present invention will be described below.
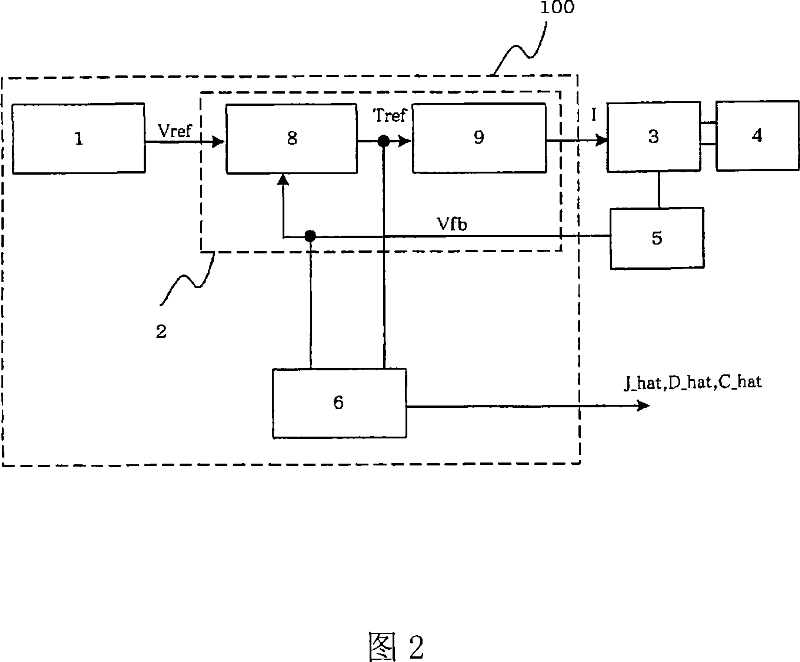
[0163] FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of a motion control device implementing the method of the present invention. Since this figure was described in Embodiment 1, its description is omitted.
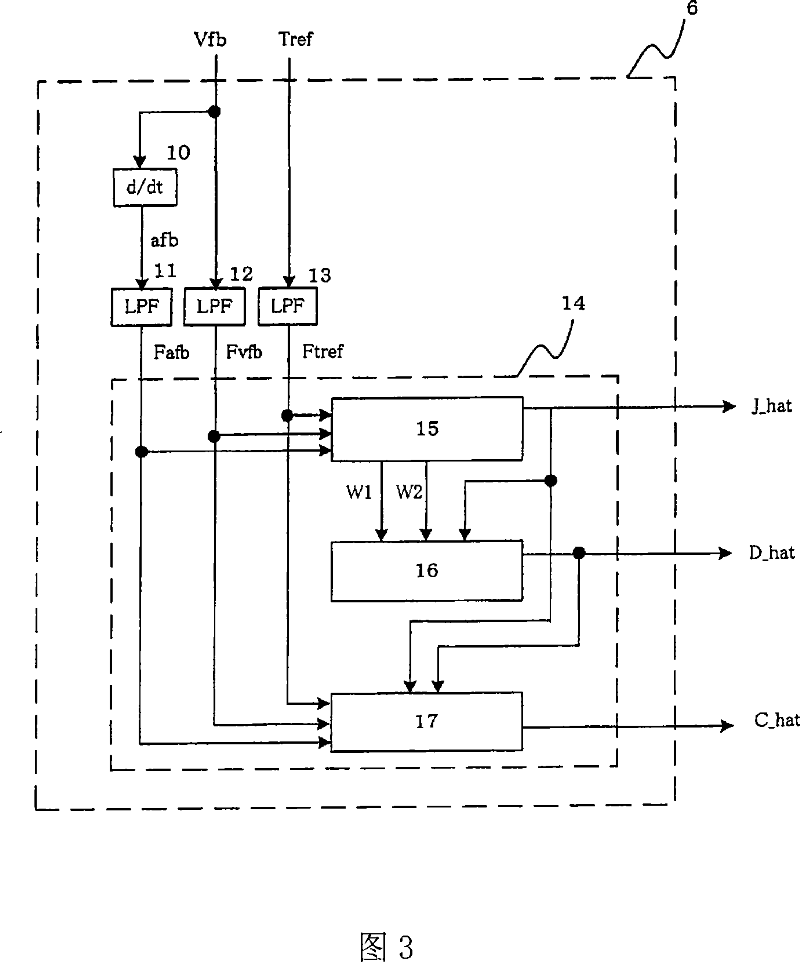
[0164] Fig. 7 is a block diagram showing the internal processing of the recognizer 6, and since it is different from Fig. 3, it will be described below. In the figure, 10 denotes a time differentiator that time-differentiates the speed detection value Vfb to calculate the acceleration detection value afb. Here, in the case of digital control, the time differential calculation may use an approximate differential obtained by dividing the signal difference between this time and the previous time by the control period. 11, 12, and 13 denote a first filter, a second filter, and a third filter, respectively. The filter used here may be a filter whose order of the denominator is three or more hi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com