Shift register circuit and image display apparatus equipped with the same
A shift register and circuit technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of gate line activation, malfunction, driving ability decline, etc., achieve fast rising and falling speed, prevent malfunction, The effect of preventing the decrease of driving ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
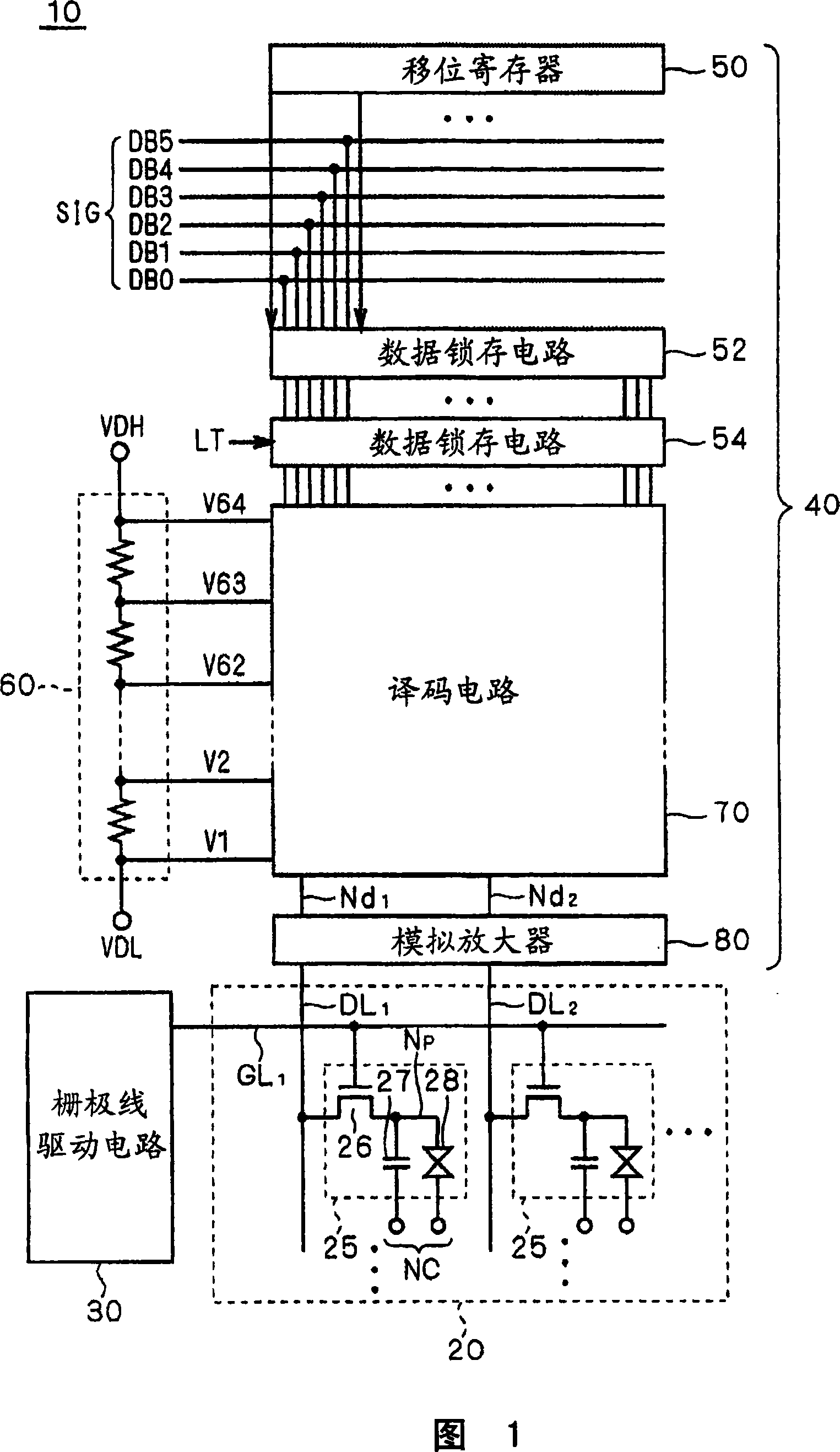
[0066] 1 is a schematic block diagram showing the structure of a display device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and shows the overall structure of a liquid crystal display device 10 as a representative example of the display device.
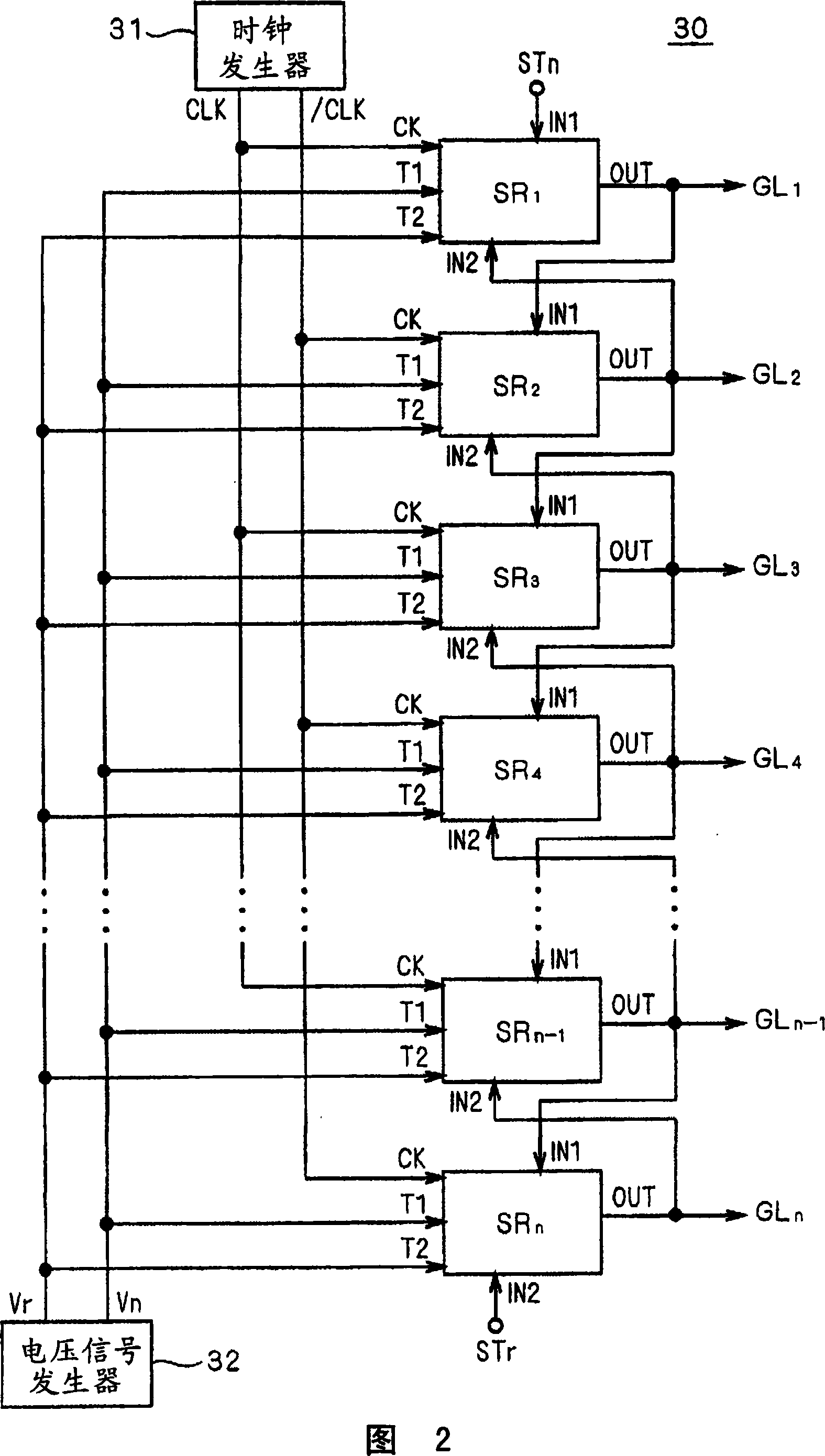
[0067] The liquid crystal display device 10 has a liquid crystal array section 20, a gate line driving circuit (scanning line driving circuit) 30, and a source driver 40. As will be understood from the following description, the bidirectional shift register of the embodiment of the present invention is mounted in the gate line drive circuit 30 and is formed integrally with the liquid crystal array section 20.
[0068] The liquid crystal array section 20 includes a plurality of pixels 25 arranged in a matrix. The gate line GL is arranged for each pixel row (hereinafter also referred to as "pixel line") 1 , GL 2 ...(Generally referred to as "gate line GL"), in addition, data lines DL are arranged for each pixel column (hereinafter a...
Embodiment approach 2
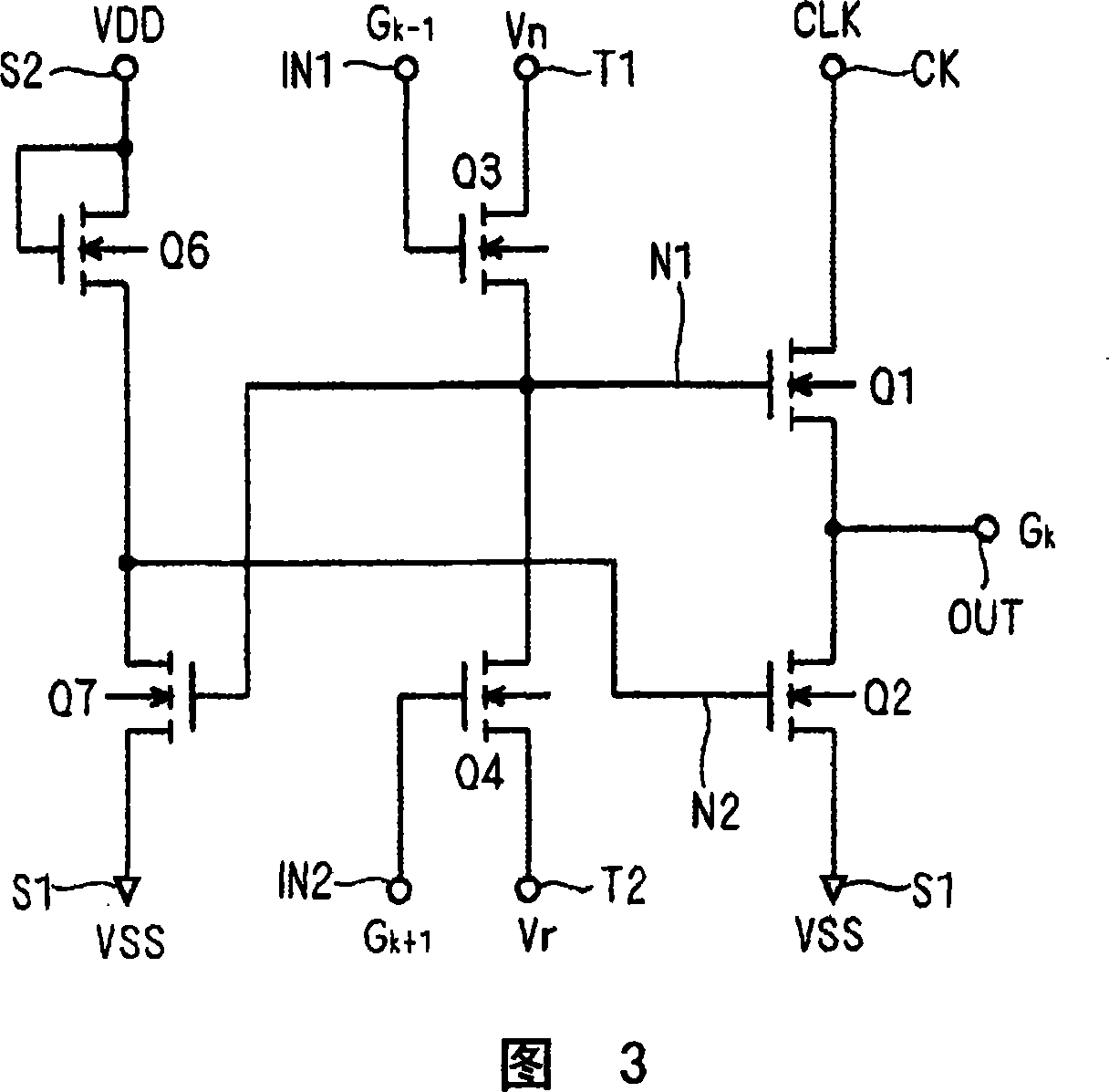
[0157] In the bidirectional shift register SR composed of the a-Si TFT of Embodiment 1 (FIG. 8), since the clock signal / CLK is input to the gate of the transistor Q2, it is possible to suppress the threshold voltage shift of the transistor Q2. The problem of gradual decline in its driving ability (the fourth problem mentioned above) arises. However, the threshold voltage of the transistor Q2 is not completely shifted, and there is a possibility that the threshold voltage gradually shifts when the clock signal / CLK repeatedly changes to the H level, and the above-mentioned problem may eventually occur. In the second embodiment, a unit shift register SR that can further suppress this problem is proposed.
[0158] FIG. 13 is a circuit diagram showing the structure of a unit shift register of the second embodiment. As shown in the figure, the source of the transistor Q2 is connected to the first clock terminal CK1. That is, one main electrode (drain) of the transistor Q2 is connected...
Embodiment approach 3
[0163] As explained using FIG. 10, in the bidirectional unit shift register SR of the first embodiment, the output signal (G k ) When rising, if the voltage between the gate and source of transistor Q5 V GS (Q5) When the threshold voltage Vth (Q5) is exceeded, a current (I(Q5)) flows from the node N1 to the output terminal OUT through the transistor Q5. As described above, normally, this current flows only slightly, and the level of the node N1 that affects the driving ability of the transistor Q1 is not reduced, so it is not a problem. However, the output load capacitance is large and the output When the signal rises slowly, the current I (Q5) flowing through the transistor Q5 may increase, and the driving capability of the transistor Q1 may decrease. In the third embodiment, a bidirectional unit shift register SR is proposed as a countermeasure.
[0164] FIG. 14 is a circuit diagram of a bidirectional unit shift register SR according to the third embodiment. In the unit shift re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com