Instant patch for dermal drug delivery
A drug and skin technology, applied in the field of skin drug delivery system, can solve the problem of high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
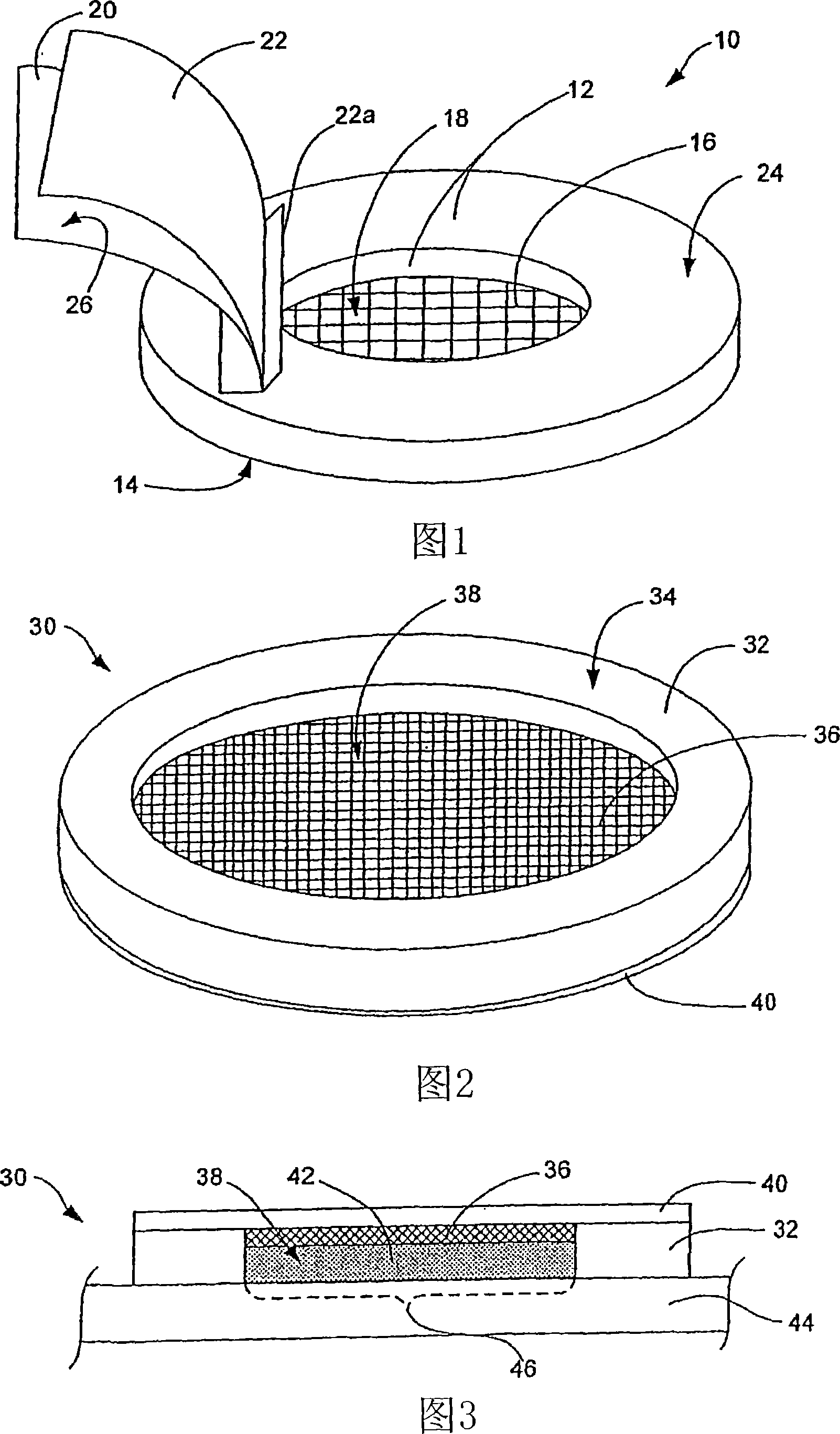
[0051] A cavity patch (top loading) was prepared with a structure similar to that in Figure 1 . The drug-containing composition (solution) contains the active drug and 15% polyvinyl alcohol in water. The cavity patch contains an absorbent mesh material that is made with about 5 mg / cm 2 A thin layer of absorbent gauze impregnated with sodium borate and attached to the underside of the ring patch wall (made of soft flexible foam strips) such that the mesh covers, but does not close the lower end of the cavity in the ring. The impermeable cover layer is made of an impermeable tape, such as 3M's 1525 Adhesive Tape, with a release liner covering the adhesive side.
[0052] To use the system, the user first applies the cavity patch to the skin so that the adhesive layer securely seals the bottom of the patch to the skin. Eight hundred milliliters of the drug-containing composition is dispensed on the mesh and spreads over the area of skin defined by the cavity. The user then pu...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The drug-containing composition (solution) and materials in the cavity patch were the same as those in Example 1, but the structure of the cavity patch was the bottom loading type as shown in FIG. 2 . A quantity of the drug-containing composition is dispensed into the open cavity of the cavity patch prior to attachment of the patch to the skin. After the drug-containing solution is dispensed into the open cavity, the user attaches the cavity patch to the skin using the adhesive layer coated on the bottom of the cavity patch wall. This seals the patch to the skin and seals the drug-containing composition in the open cavity. The drug-containing composition gelled to a soft solid and left no residue when the cavity patch and gel were removed at the end of the planned administration period.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Research four kinds have the structure as shown in Fig. 2 and contain 0.5, 1, 2 and 4mg / cm 2 Cavity patches of borate to determine the optimal amount of borate (a gelling initiator) required to gel a 15% polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) (a gelling agent) solution. The open cavity was 3 mm deep, 14 mm in diameter, and the adsorptive material was a thin layer of nonwoven membrane impregnated with borate. The nonwoven material was attached to the underside of an impermeable cover layer (3M1523 polyethylene film) such that the nonwoven film covered the entire open cavity area. Specifically, containing 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 mg / cm 2 Each of the borate cavity patches was dosed with approximately 0.5 mL of 15% PVA in water to fill each cm of the open cavity 2 Approximately has 50 mg PVA. The ratios of borate to PVA per unit area of the patch were approximately 1:100, 2:100, 4:100 and 8:100, respectively. Each patch was then attached to the upper arm of a study volunteer. After 3 hours,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com