Tracking by cross correlating central apertures of multiple beams
A tracking error, interrelated technique used in head configuration/mounting, optical recording/reproducing, instrumentation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
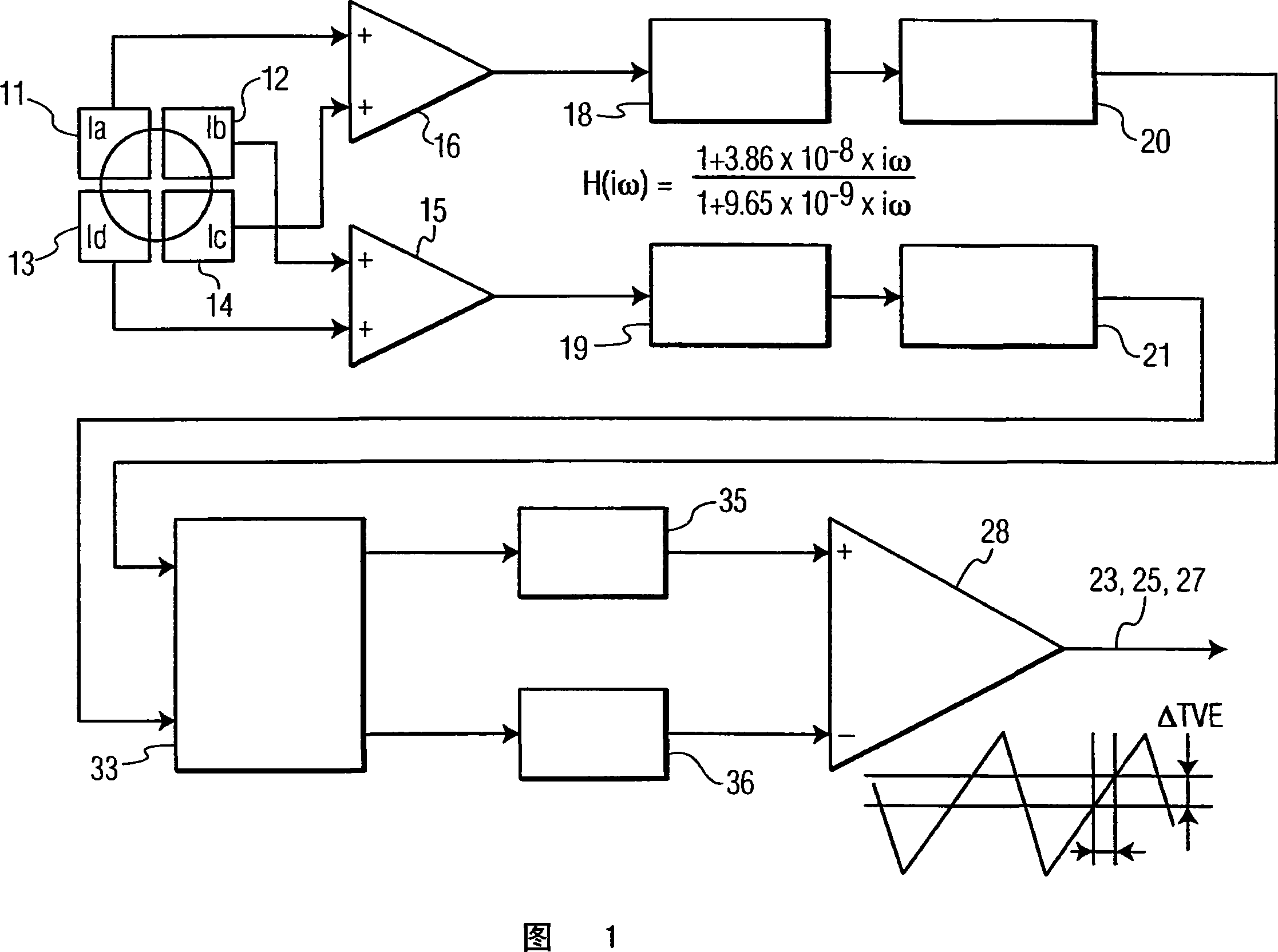
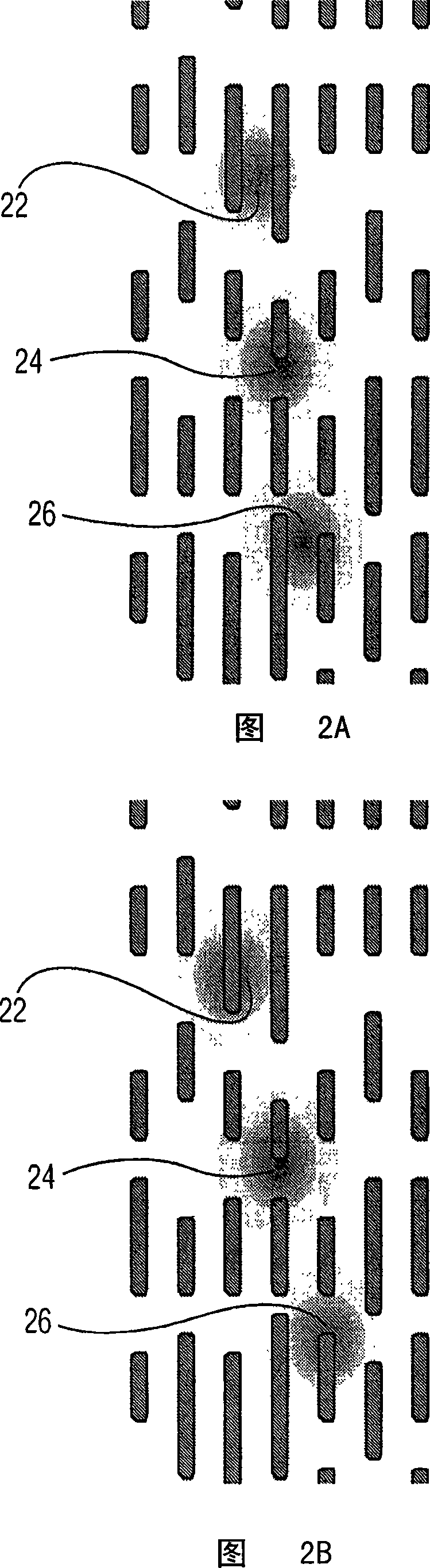
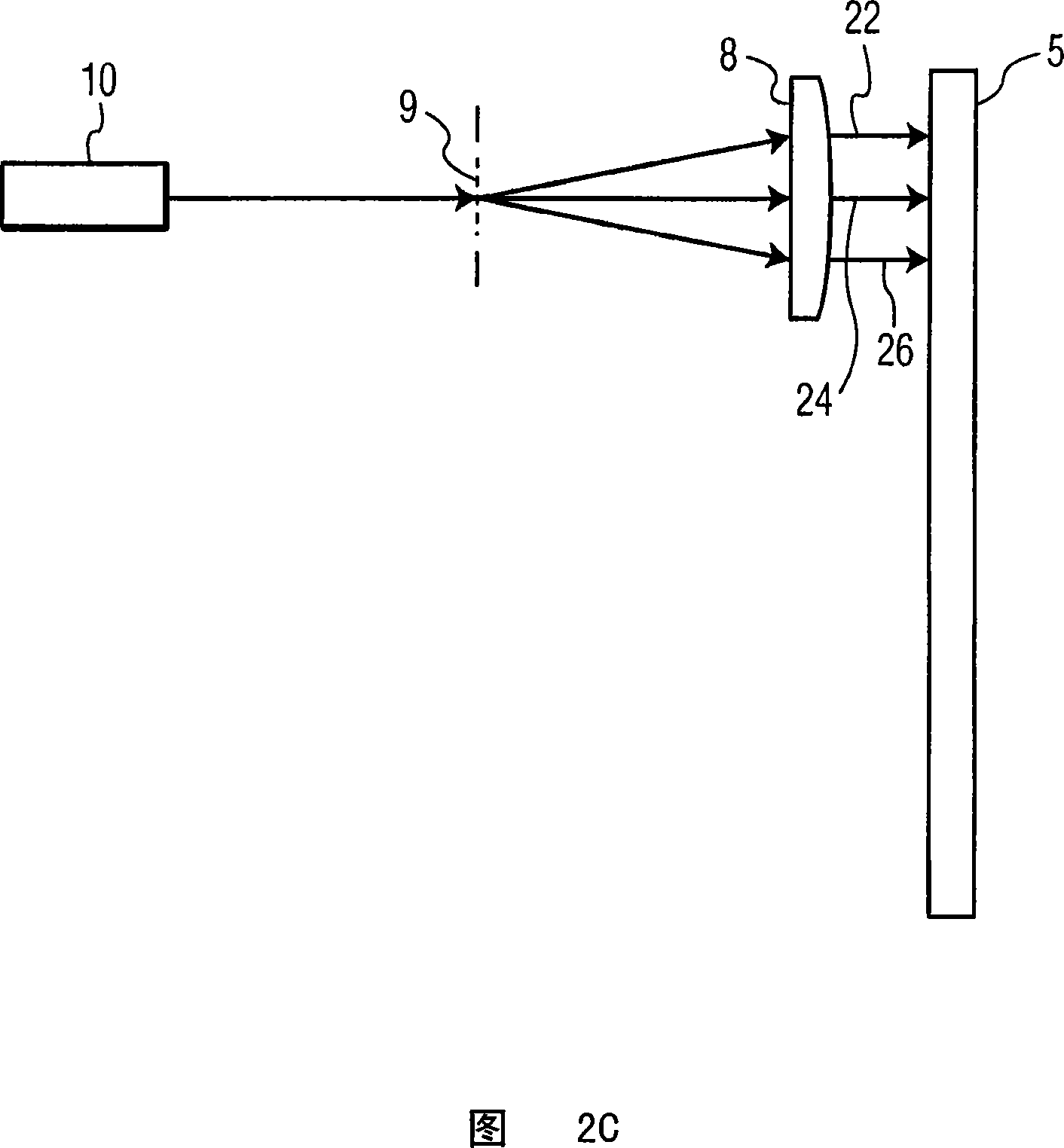
[0020] Referring to FIG. 1 , there is shown a block diagram of differential phase detection (DPD) used in the prior art for detecting light that has been reflected from an optical disc by a single spot. Differential phase detection has been used in the prior art to generate tracking error (TE) signals. Using the DPD shown in FIG. 1 , the TE is generated by difference in phase of the signals received in the diagonal light receiving parts of the four divided photodetectors 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 . The signals received by the photodetectors 11, 12, 13, 14 are fed into amplifiers 15, 16 and arranged so that the tangential diffraction can be determined from the difference between the upper two and the lower two detector quadrants, And radial diffraction can be determined by the difference between the left two and right two detector quadrants. This process using DPD is well known in the art. As shown in FIG. 1, equalizers 18, 19, level comparators 20, 21, phase comparator 33, low pass ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com