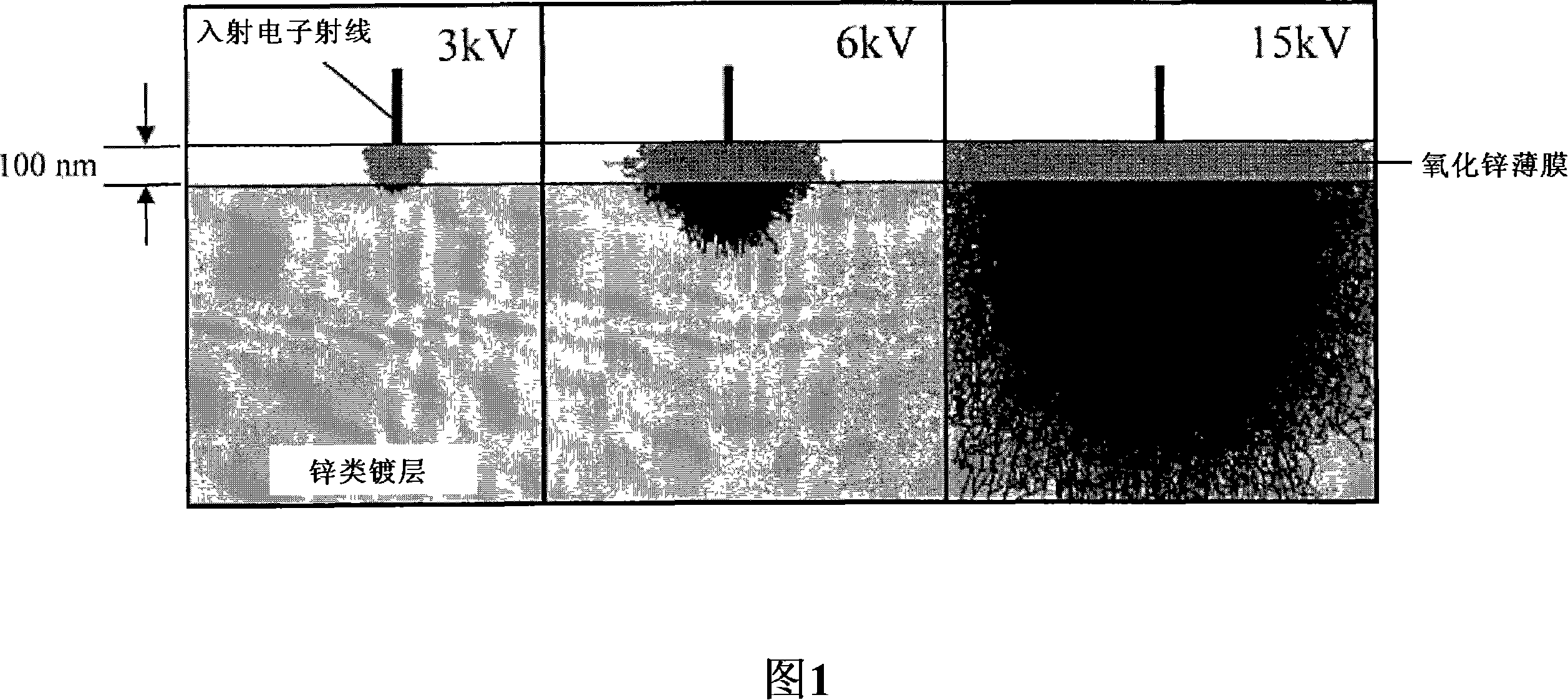
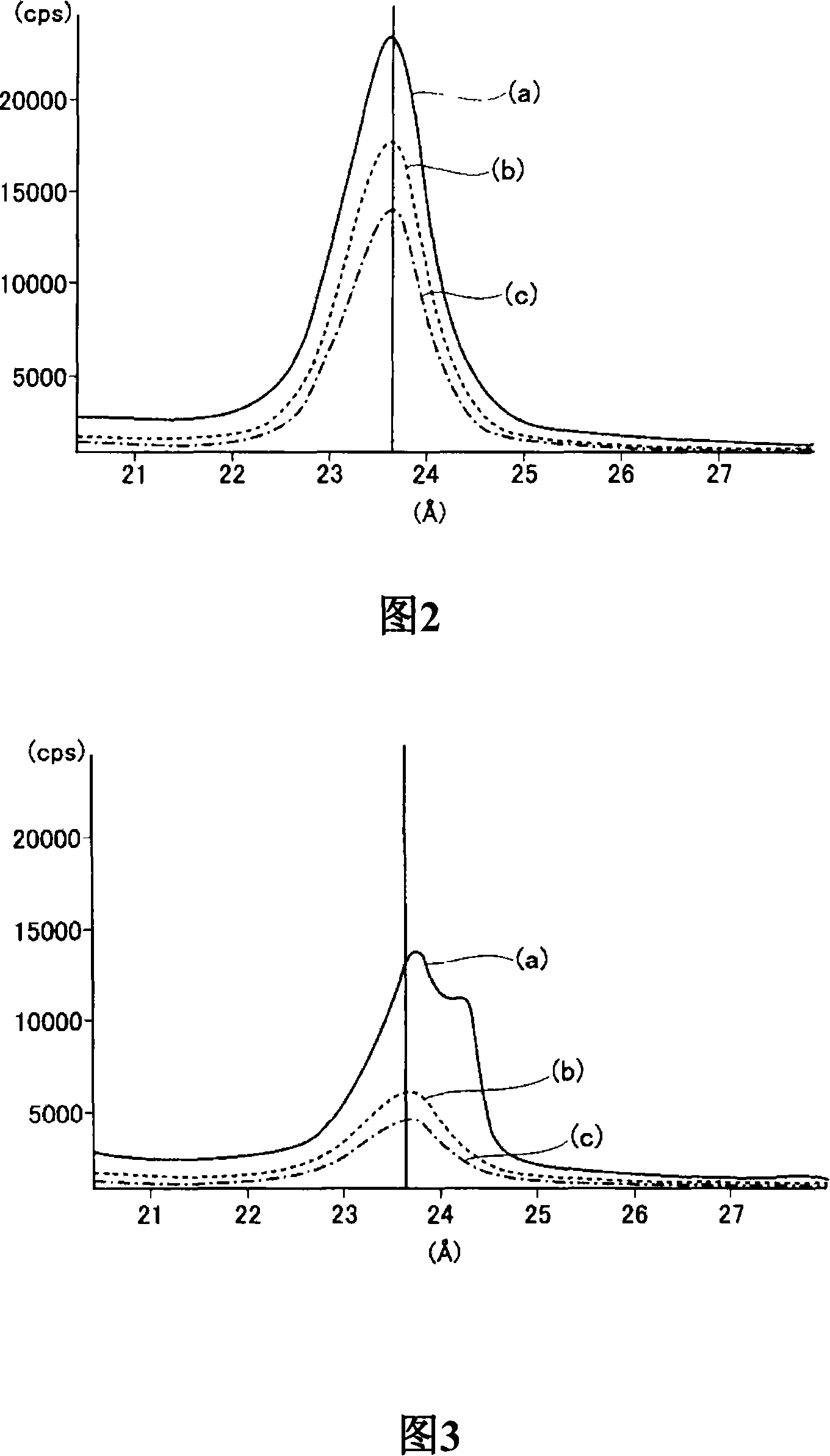
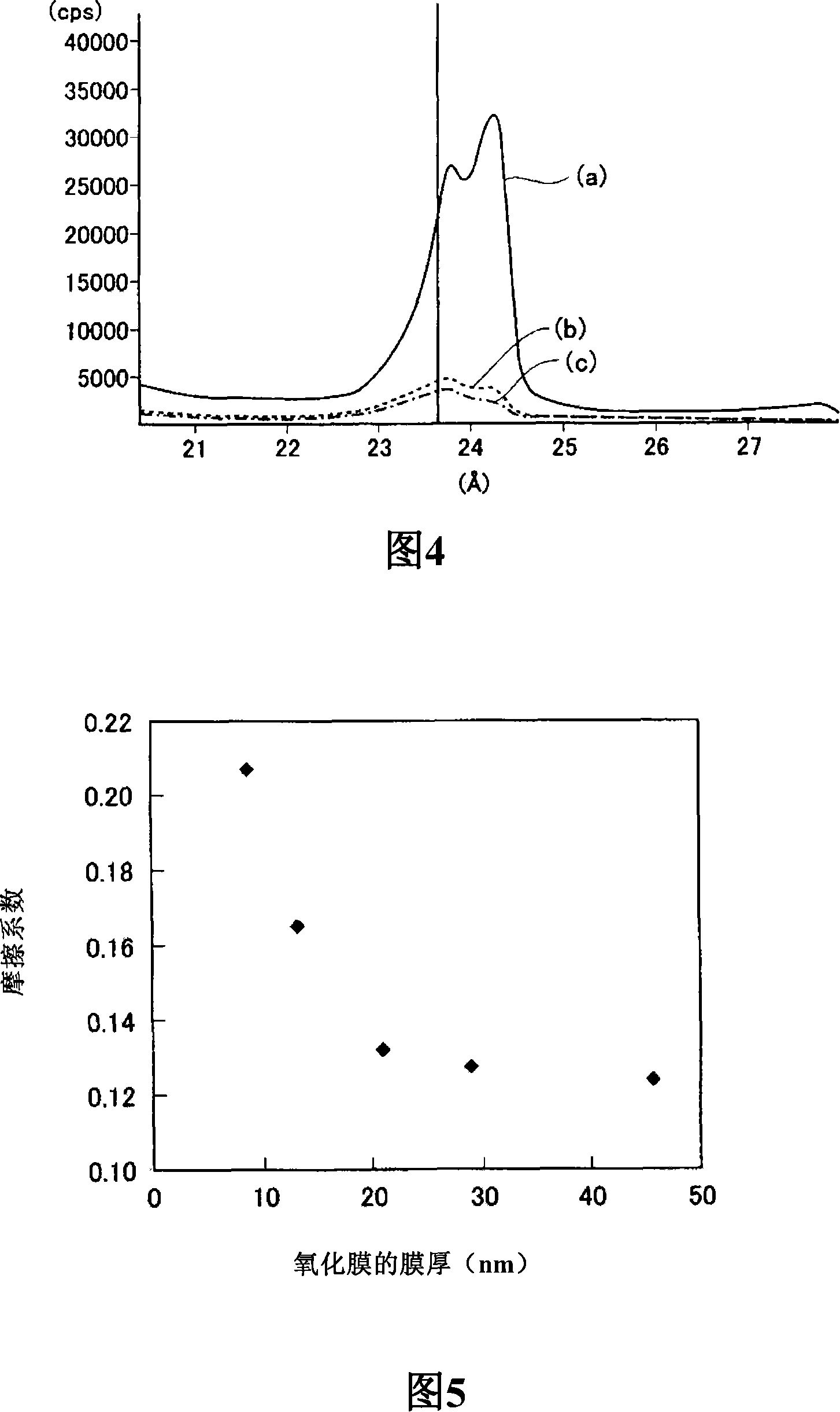
Method for measuring surface layer oxide film thickness of galvanized steel plate
A measurement method and oxide film technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in ensuring the accuracy of film thickness measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] After tempering and rolling an alloyed hot-dip galvanized steel sheet with a thickness of 0.8mm, it was immersed in an acidic sulfuric acid aqueous solution containing 20 g / l of sodium acetate at a pH of 2.0 and a liquid temperature of 50°C for 1 second, and then left to stand. After a predetermined period of time, they were washed and dried to prepare 40 test materials in which zinc-based oxides (including hydroxides) were formed on the surface of the plating layer. The inner and outer surfaces of the test materials were used as oxide films. Determination of thickness. At this time, the leaving time was changed in the range of 2 to 60 seconds to adjust the thickness of the oxide film formed on the flat portion of the test material. After punching the test material to a diameter of 12mm, it was ultrasonically cleaned with toluene for 2 minutes, and then ultrasonically cleaned with ethanol for 1 minute, and then dried with hot air and fixed to the sample holder of EPMA on.
...
Embodiment 2
[0060] After cutting and processing various hot-dip galvanized steel sheets with a thickness in the range of 0.8-1.2mm after tempering and rolling by electric discharge matting rolls into 40mm squares, they are ultrasonically cleaned with toluene for 2 minutes, and then with ethanol Ultrasonic cleaning was carried out for 1 minute, and then it was dried with hot air and used as a test material. The thickness of the oxide film on the surface of these hot-dip galvanized steel sheets is randomly formed in a storage environment or the like, so it does not cover the entire surface uniformly. In this case, the method of measuring the average oxide film thickness by surface analysis is effective.
[0061]EPMA uses the ERA-8600MX produced by Japan Electronics. The acceleration voltage during the measurement was set to 3kY, the beam current was 120nA, the beam diameter was 100μm, and the analytical crystal was LDE1. Under the conditions of 200 points×200 points at a 100μm pitch, the 20mm s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com