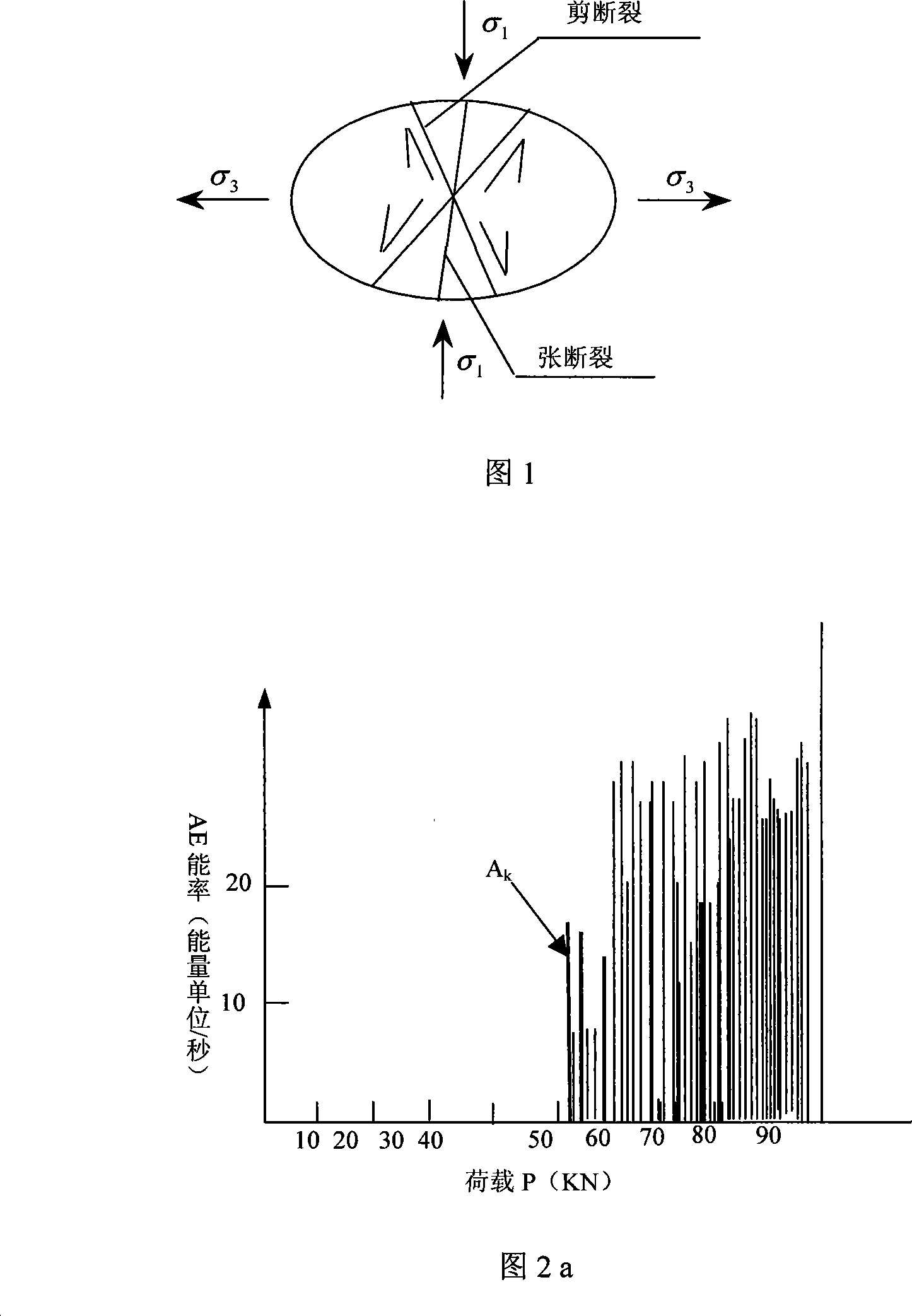
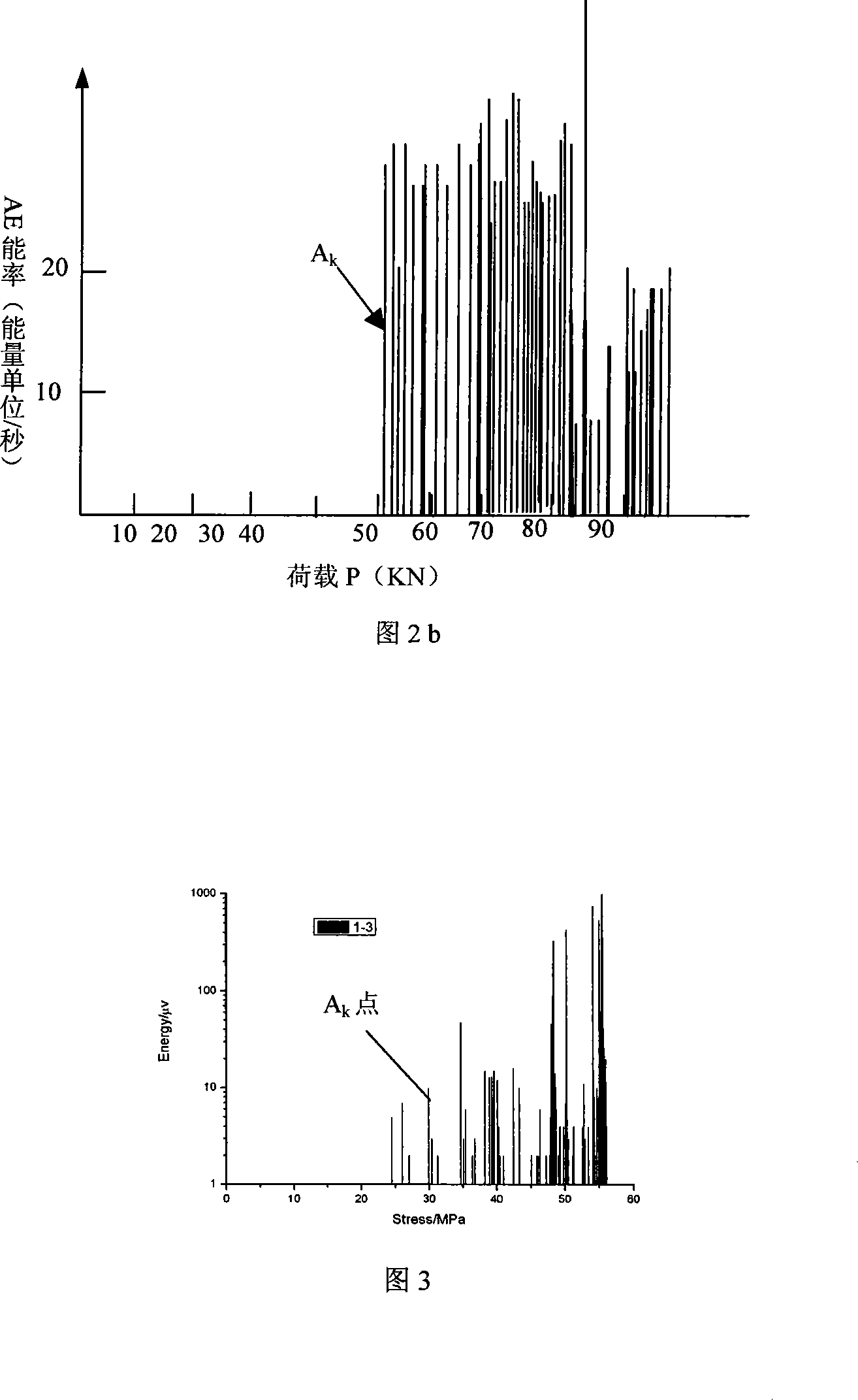
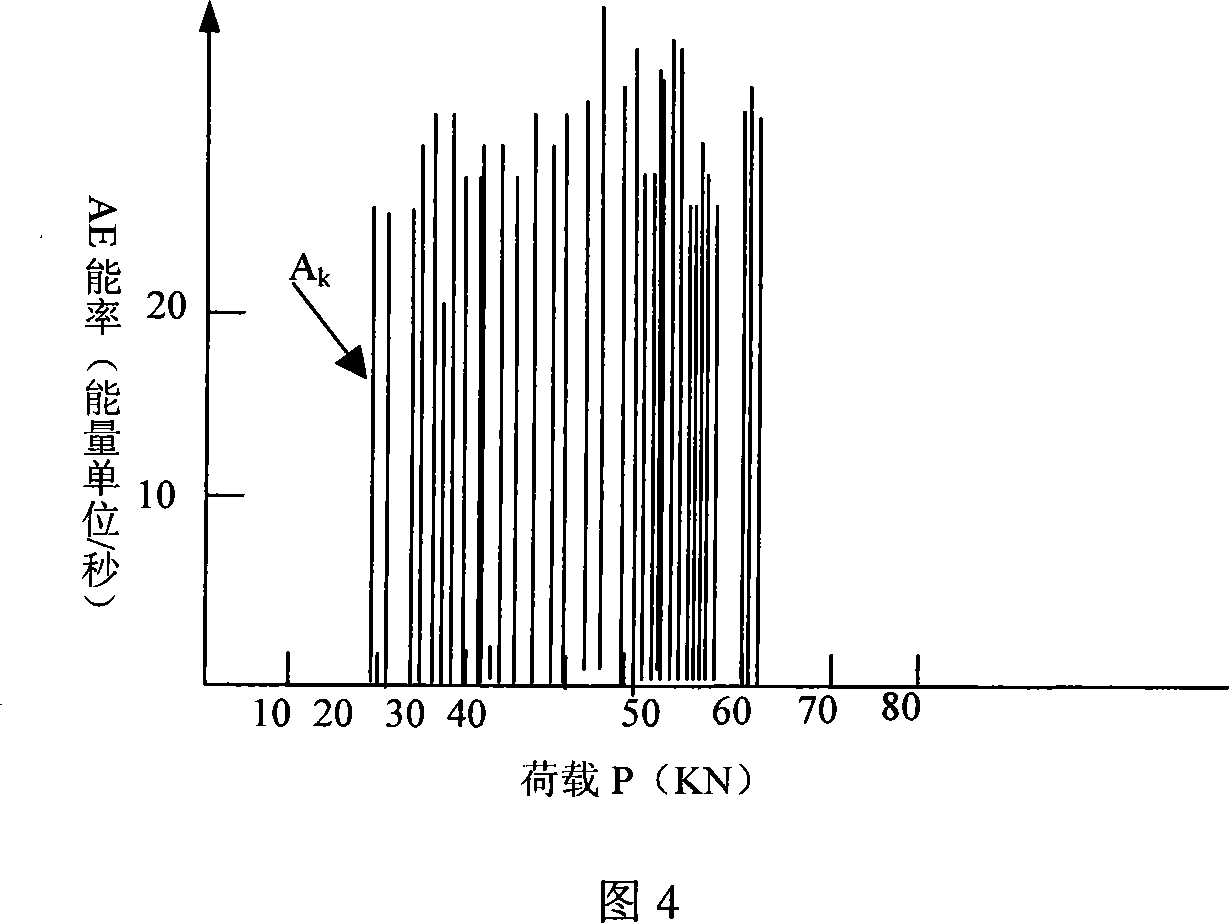
Method for measuring ground stress
A technology of in-situ stress and principal stress, which is applied in the field of geo-stress measurement, can solve the problems of large test workload, far from each other, differences, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient and fast measurement, easy control and operation, and cost reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 Determination of ground stress in a certain mine in Nanjing:
[0029] (1) Determination of the stress direction of a mine in Nanjing:
[0030] Table 1 shows the occurrence of joints and faults in a mine in Nanjing. Due to rock strata, fault F 2 and Joint J 1 The occurrences of the fault F are basically similar. According to geomechanics knowledge, the fault F 2 and Joint J 1 It cannot be an X-conjugate joint, so the fault F can be removed 2 and Joint J 1 . Take the strike line of the rock layer as the rotation axis, and rotate it to the horizontal position in the NW direction. The rotation angle is equal to the inclination angle of the layer of 75°, and the rock layer is restored to the original horizontal position. The yoke joint is J 3 and J 4 , they can be determined as plane X fractures. The acute angle bisector where these two groups of joints intersect is the maximum principal stress σ 1 The orientation of the obtuse angle bisector is the m...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Determination of the in-situ stress of the ore body in the veinlet zone of Dachang Tongkeng Mine
[0047] (1) Determination of in-situ stress direction
[0048] According to the engineering geological analysis results of the veinlet belt in the middle section of -570m, it is known that the strike of the layer is N80°E, inclined to NW, and the dip angle is 25°. After the rock layer is restored to the original horizontal position and turned over, the paired X-conjugate joints J14 and J15 of the same order can be judged (see Table 5). The acute angle bisector where these two groups of joints intersect is the maximum principal stress σ 1 The orientation of the obtuse angle bisector is the minimum principal stress σ 3 The direction shown by the intersection line of the two joints is the intermediate principal stress σ 2 orientation. When the dip angle of the rock formation is 25°, the X conjugate joint J 14 and J 15 Rotate to SE direction, its rotation angle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com