B image equalization method and system structure based on two-dimension analysis
A technology of two-dimensional analysis and equalization method, applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of equalization and inability to achieve image brightness, and achieve the effect of simplifying user operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
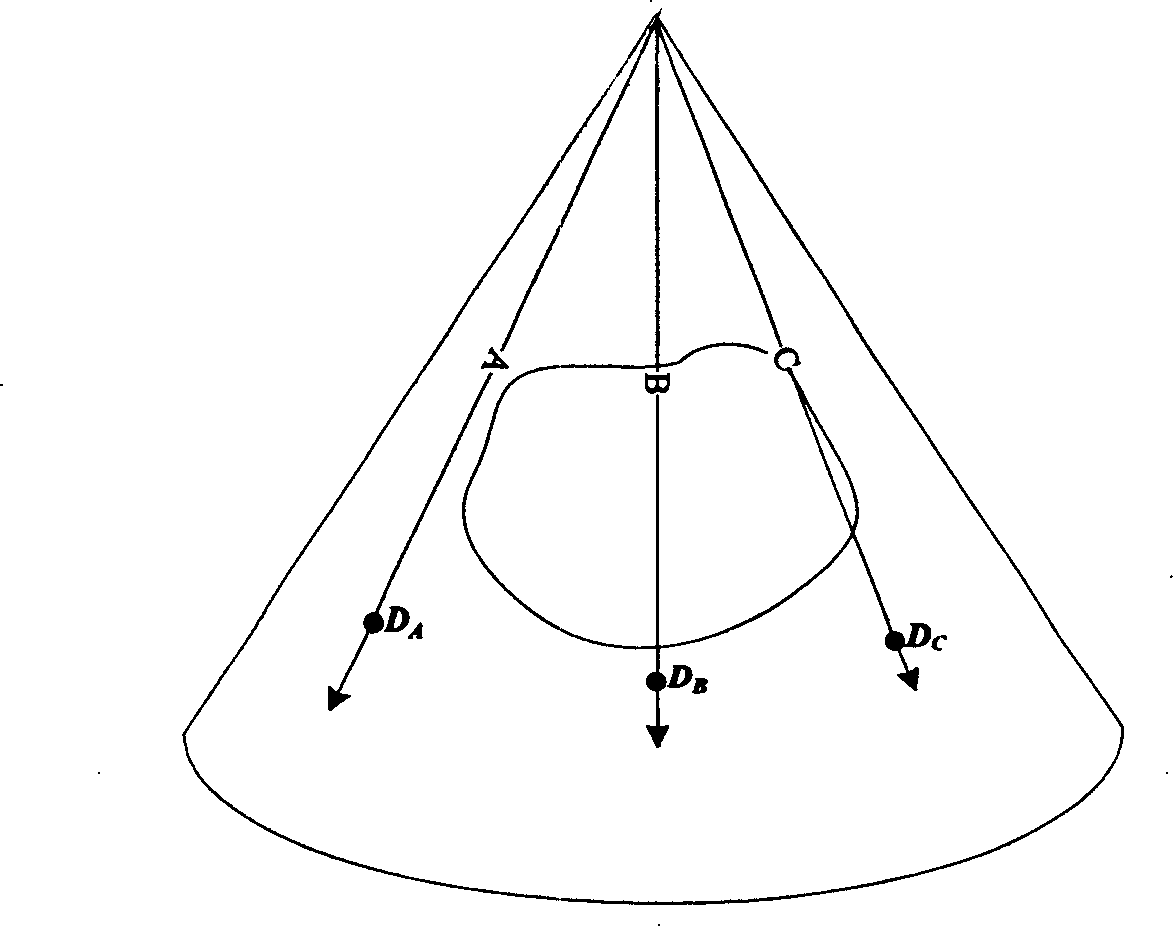
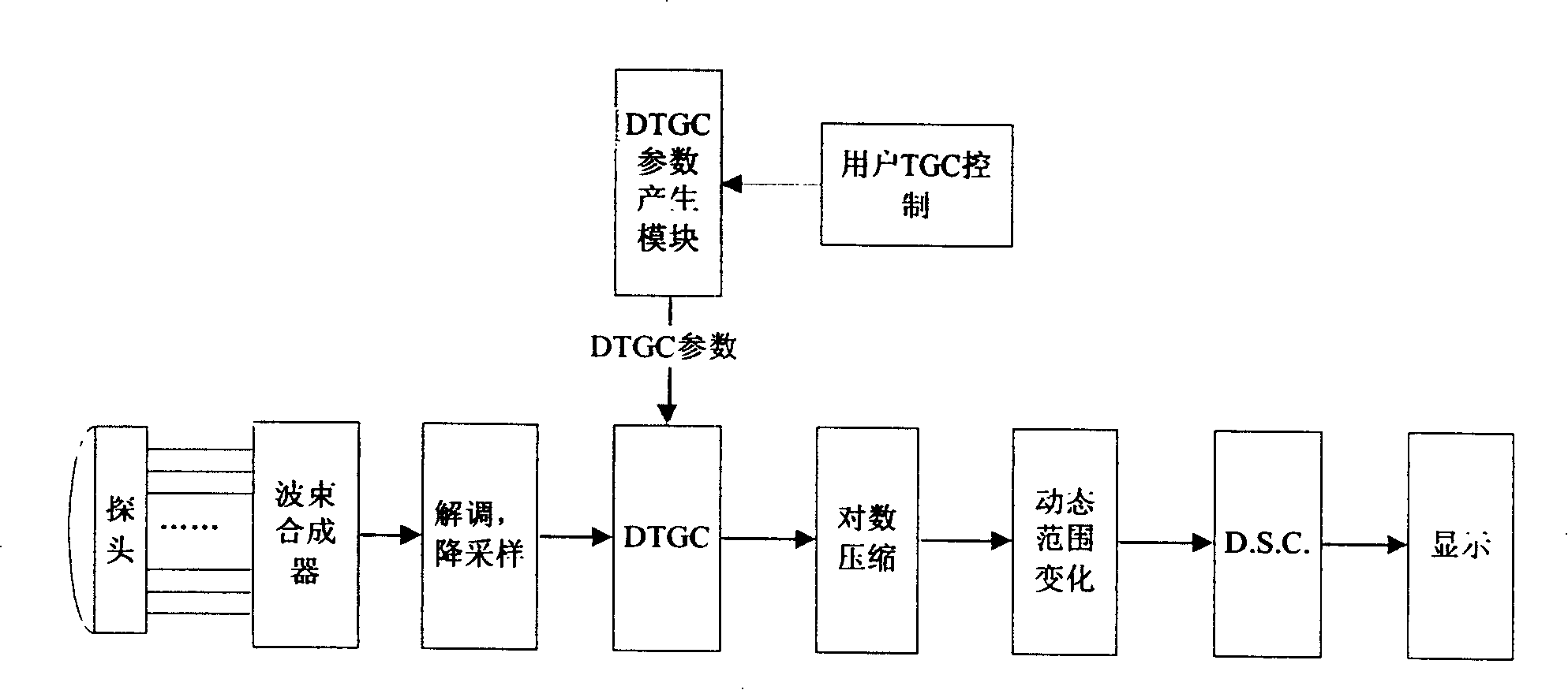
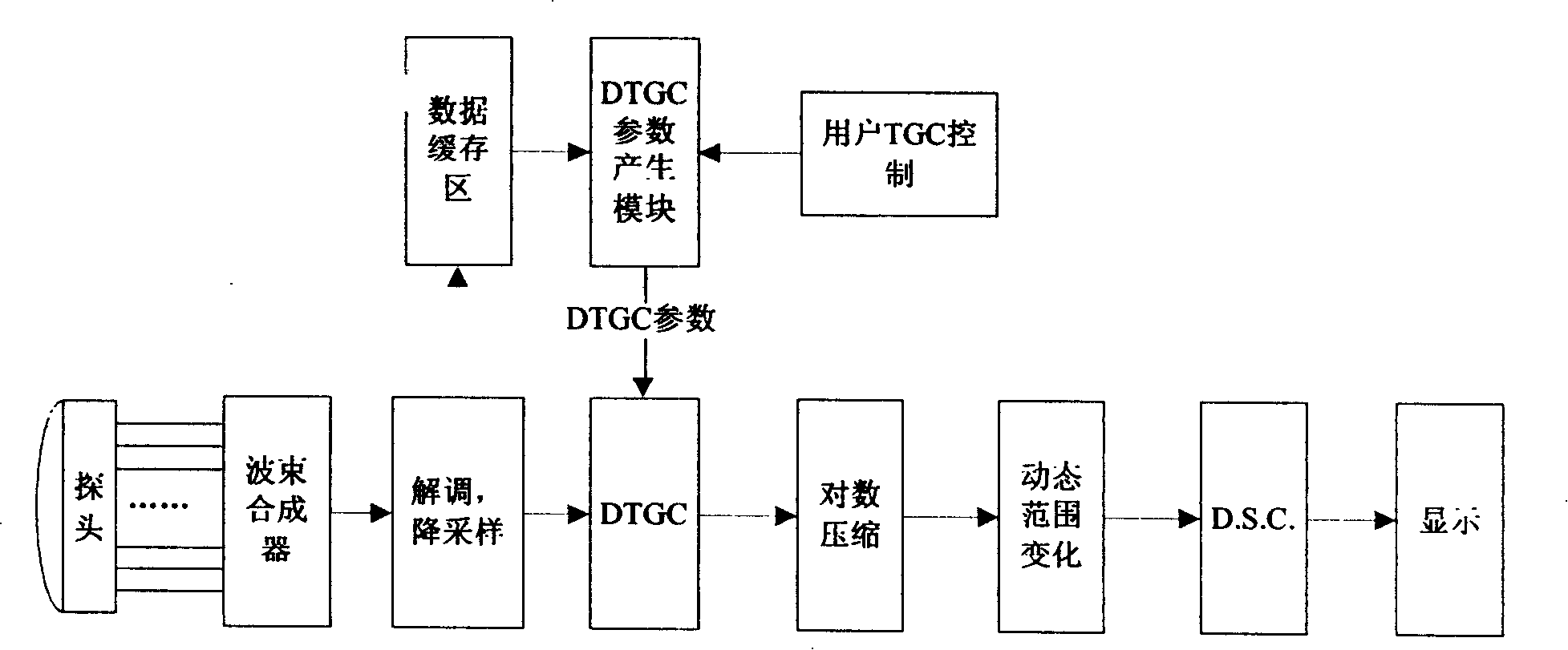
[0018] First, a conventional DTGC calculation method will be described. figure 2 It is a schematic block diagram of a conventional B-type ultrasonic imaging system, and its transmitting part is not drawn because it has little to do with the present invention. The conventional B-type imaging process is usually: the probe emits pulses, and the receiving array elements receive echoes, which are amplified, A / D converted, and added in the beamformer with different delays to obtain radio frequency data. The RF data undergoes envelope detection and down-sampling, DTGC, logarithmic compression, and dynamic range change, and at the same time enters "digital scan conversion" that is D.S.C, and the result of D.S.C is displayed on the screen, that is, B-type image.
[0019] In most systems, DTGC refers to giving different gains to the input data along the depth direction, that is, according to time, in order to make the brightness of the image displayed on the screen more uniform. Gener...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com