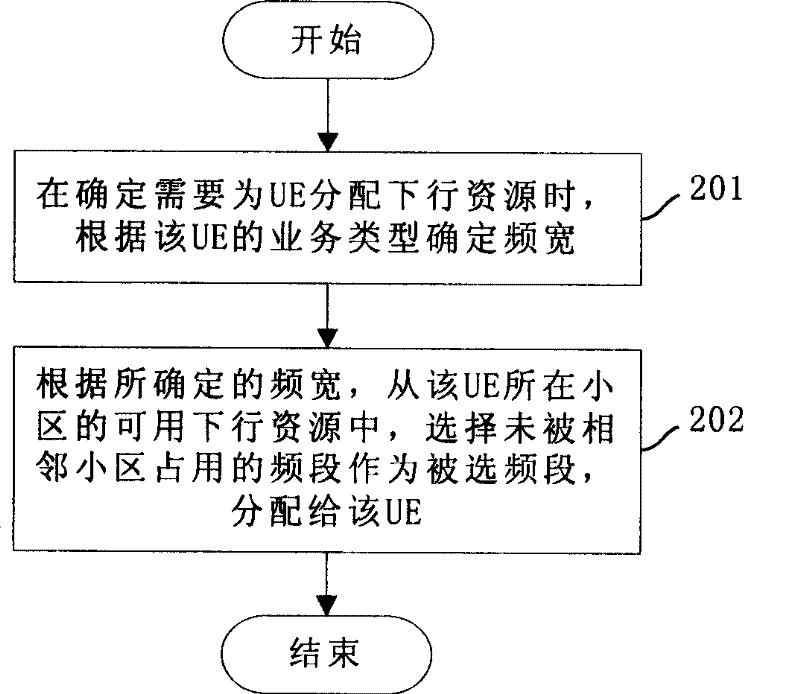
Inter-cell interference restraint method, base station and system for restraining inter-cell interference
A technology of inter-cell interference and base stations, applied in electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as complex execution process, heavy workload, and heavy burden, and achieve the effect of reducing operation complexity, reducing burden, and good operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
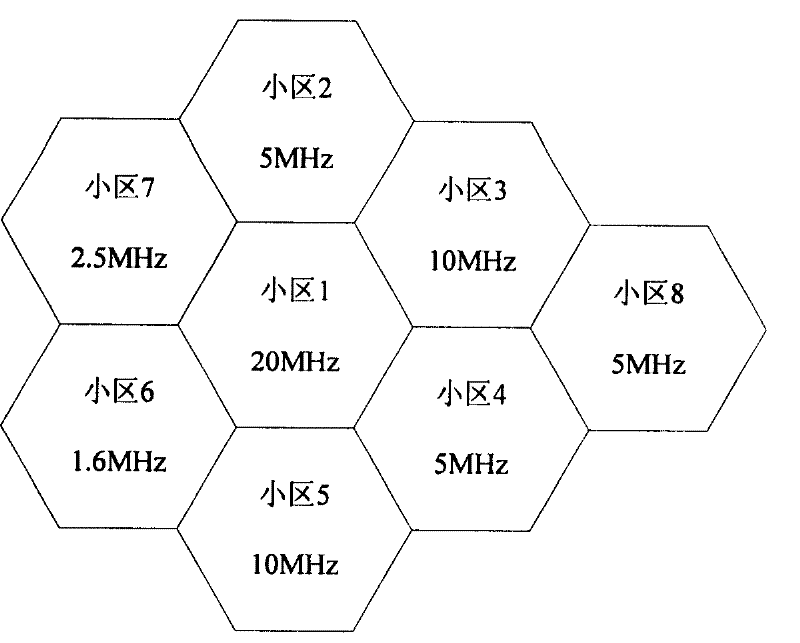
[0051] In this embodiment, the network side assigns priorities to each frequency band for each cell in advance, and the basis for the allocation is that corresponding frequency bands of adjacent cells have different priorities.
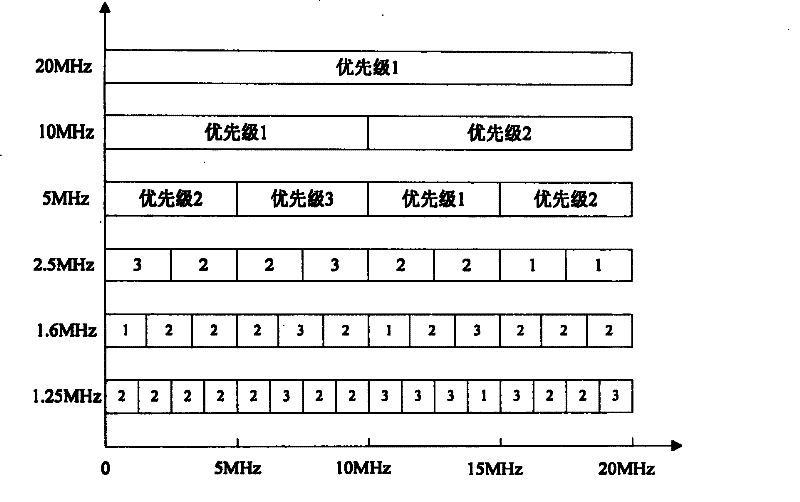
[0052] In the OFDM system, the bandwidth is generally divided into two types: wide bandwidth and narrow bandwidth. Among them, 20MHz, 15MHz, 10MHz, and 5MHz are wide bandwidths; 2.5MHz, 1.6MHz, and 1.25MHz are narrow bandwidths. In this embodiment, when assigning priorities, firstly, the entire frequency range is divided into one or more frequency bands in units of each frequency width, and then priorities are assigned to each frequency band corresponding to each frequency width, and the corresponding frequency bands of adjacent cells Bands have different priorities.
[0053] image 3 A schematic diagram of the priority allocation of the wide bandwidth when the entire frequency range is 0-20 MHz is shown. see image 3 , when the bandwidth required...
Embodiment 2
[0066] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment adds the operation of assigning priorities to RUs in the frequency band according to the UE's occupancy status of RUs, so as to reduce the problems caused by multiple UEs in the same or adjacent cells selecting adjacent RUs. interference, thereby further improving the transmission quality of OFDM signals.
[0067] In an OFDM system, each frequency band is divided into multiple RUs, and each RU includes M subcarriers, where M is greater than or equal to 1. For example, every 375KHz is one RU, and there are 53 RUs in the frequency range of 20MHz. In this embodiment, each RU in each frequency band is assigned a priority in advance. In addition, when the RU is allocated to the UE, the UE accesses the network, and the UE releases the RU, the base station updates the priority of the RU.
[0068] Figure 5 A schematic diagram of RU priority allocation in this embodiment is shown. see Figure 5, Each frequency band within the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com