Body inside observation device
A technology of observation device and auxiliary device, which is applied in in vivo radio detectors, endoscopes, applications, etc., can solve the problems of prone to allergic reactions, worsening symptoms, and inability to obtain clear images of the intestines.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
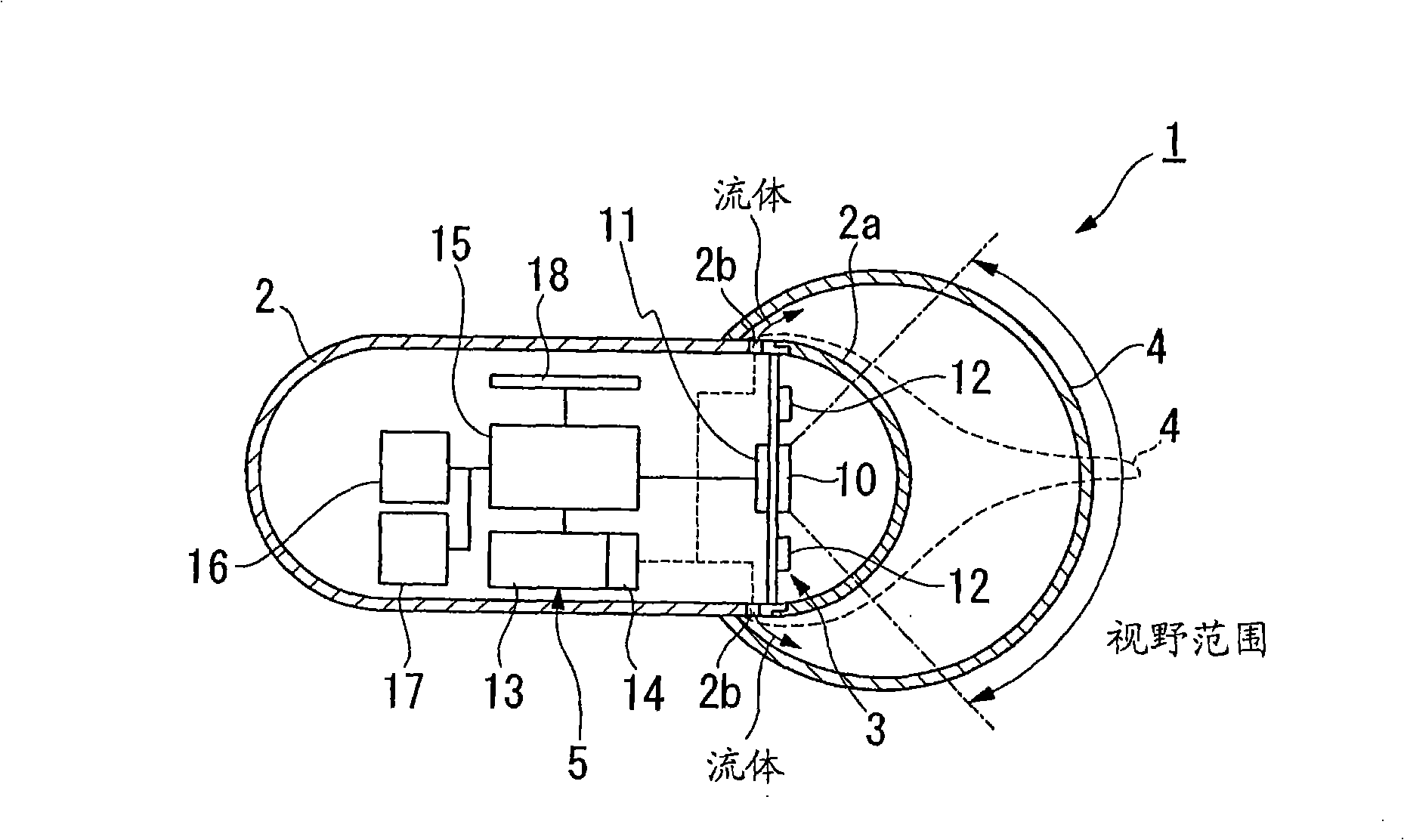
[0116] Refer below figure 1 with 2 A first embodiment of the in-vivo observation device as claimed in the present invention will be described. Such as figure 1 As shown, the in-vivo observation device 1 of this embodiment is provided with a capsule casing 2 for oral intake into the body, an observation system (observation device) 3 installed in the casing 2 for observing the inside of the body, and arranged in the casing 2 so as to cover An optically transparent balloon 4 that is positioned around the periphery of the observation system 3 and can be inflated so as to be in close contact with or attached to body tissue when moving in the body, and by supplying fluid into the balloon 4 to make the balloon 4 Expansion device 5 for expansion.
[0117] In addition, the refractive index n of the transparent material of the balloon 4 a equal to or less than the refractive index n of the fluid supplied to the balloon 4 b (n a ≤n b ).
[0118] The above-mentioned housing 2 is...
no. 2 example
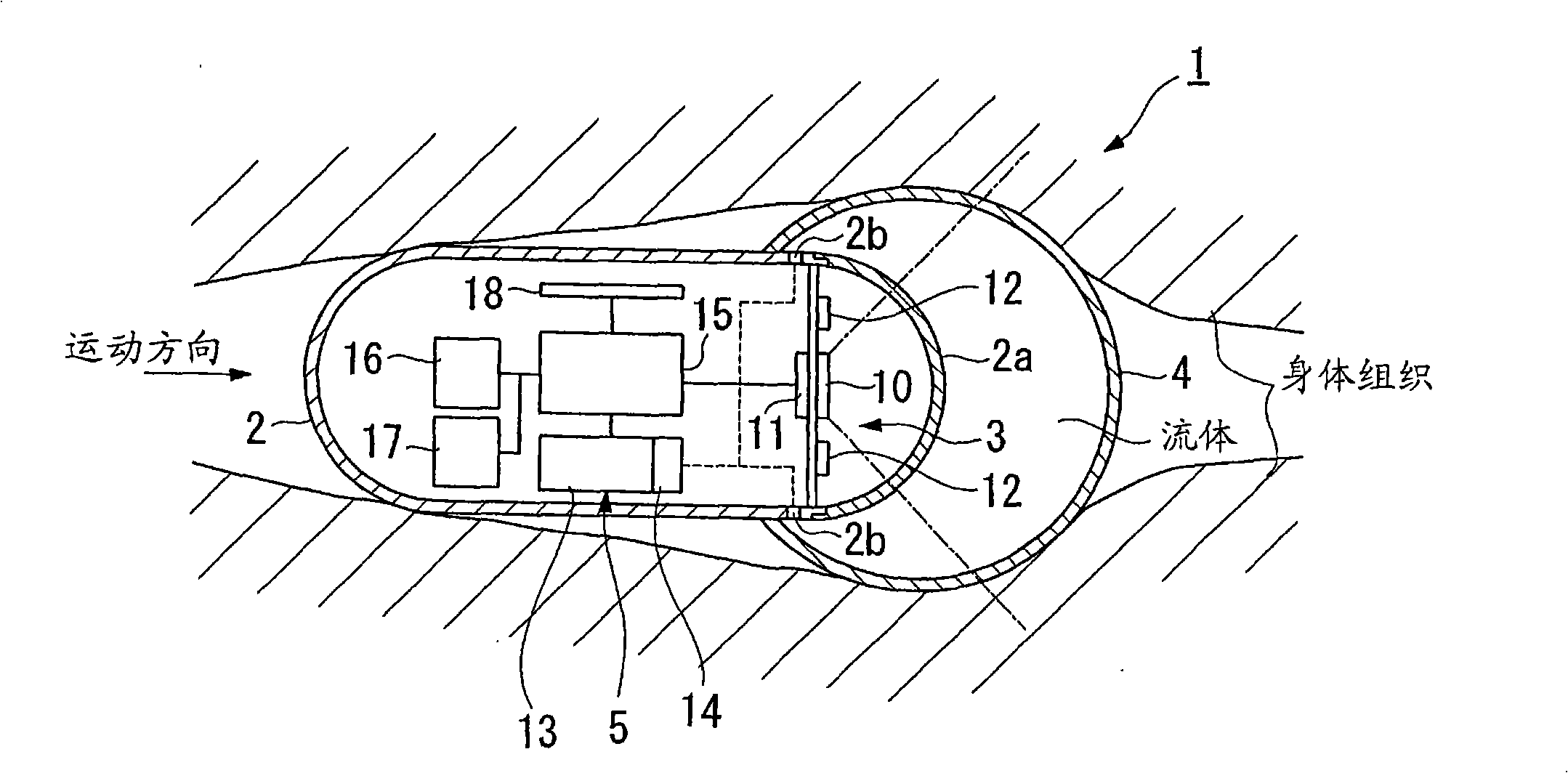
[0133] will then refer to image 3 A second embodiment of the in-vivo observation device as claimed in the present invention will be described.
[0134] In addition, the same constituent features in the second embodiment as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0135] The difference between the first embodiment and the second embodiment is that the fluid A contained in the storage portion 13 is supplied to the balloon 4 through the inflation device 5 when the balloon 4 is inflated in the first embodiment. In contrast, the in-vivo observation device 20 of the second embodiment inflates the balloon 4 using bodily fluids in the body.
[0136] That is, if image 3 As shown, the in-vivo observation device 20 of the current embodiment has an acquisition part 22 for acquiring body fluid in the body, and an expansion vessel (an expansion part) for inflating the balloon 4 according to the water content of the...
no. 3 example
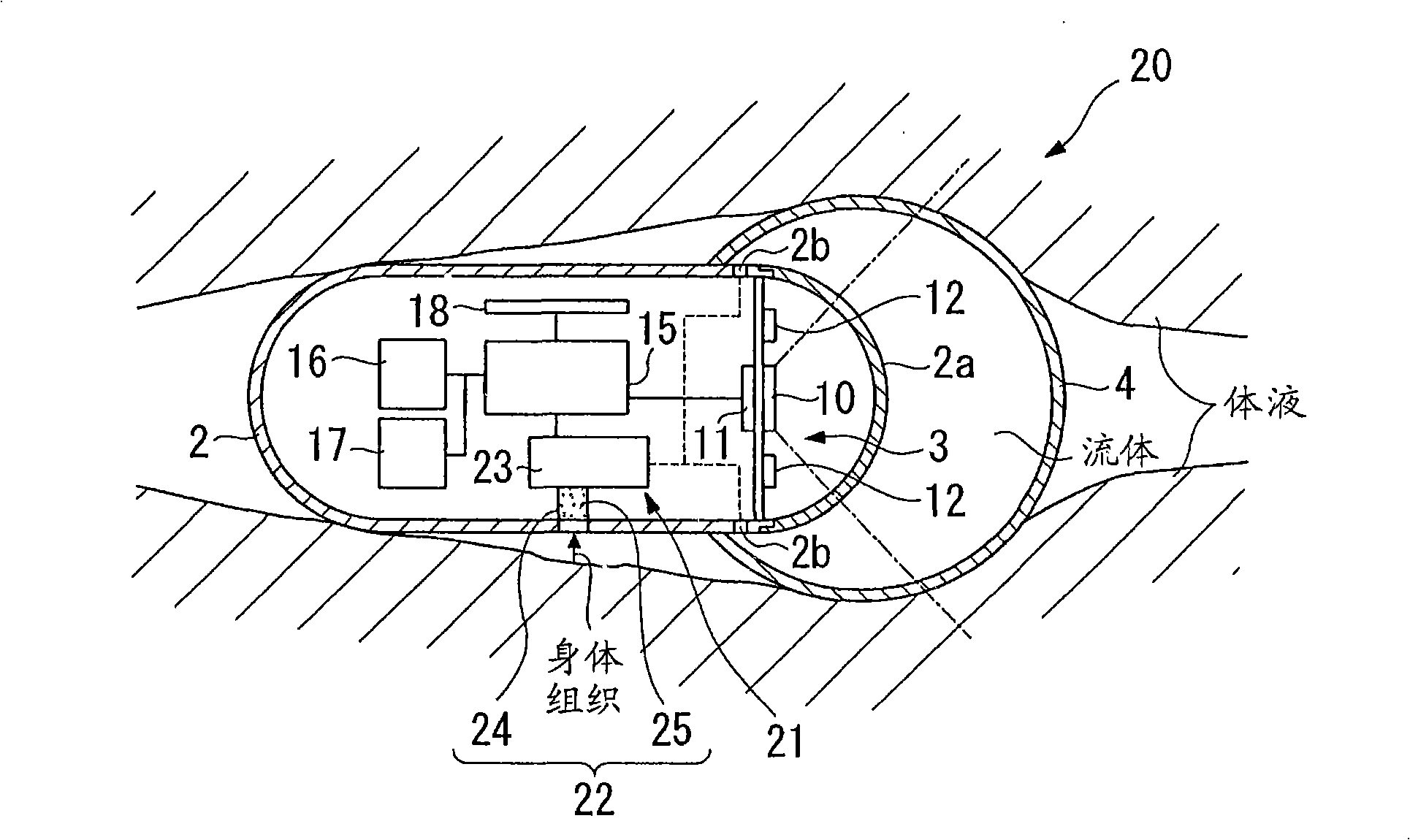
[0143] will then refer to Figure 4 A third embodiment of the in-vivo observation device as claimed in the present invention will be described.
[0144] In addition, the same reference numerals are used to denote those constituent features in the third embodiment that are the same as those in the first embodiment, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0145] The difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that, unlike in the first embodiment, the fluid A contained in the storage portion 13 is supplied to the balloon 4 through the inflation device 5 when the balloon 4 is inflated. In contrast, the in-vivo observation device 30 of the third embodiment inflates the balloon 4 using air (fluid) in the body.
[0146] That is, if Figure 4 As shown, the in-vivo observation device 30 of the current embodiment is provided with a pipeline 31 for connecting the outside and inside of the balloon 4 in the housing 2, and the expansion device 32 is provided with a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com