Method, system and device for media buffer
A multimedia subsystem and media technology, which is applied in the field of network communication, can solve the problems of inability to realize media caching and direct access, and achieve the effects of saving media provision time, optimizing media provision mechanism, and improving multimedia services
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
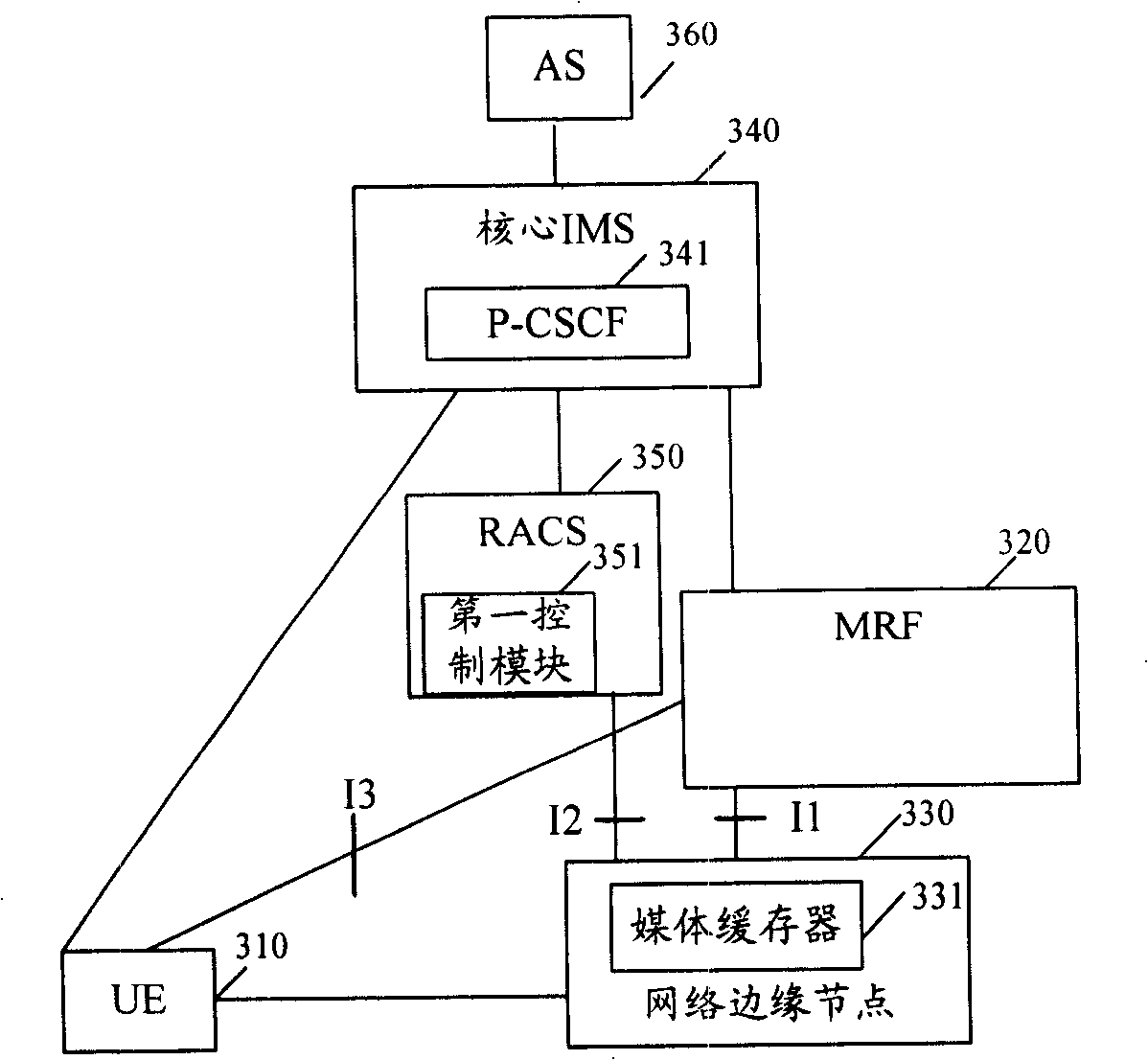
[0060] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the system structure of the first embodiment of the present invention. The system in this embodiment includes a client user equipment (UE, User Equipment) 310 , an MRF 320 that provides media resources, and a network edge node 330 that sets a media cache 331 .
[0061] In this embodiment, a media cache 331 is set in the network edge node 330;
[0062] UE310 sends a service request to MRF320 through the core IMS, and sends a content request to MRF320 according to the service request response carrying the MRF address sent by MRF320 through the core IMS; for example, perform playback control operations such as fast forward, rewind, play, and pause, among which, Interface I3 is an interface between MRF320 and UE310, and this interface can use RTSP or a protocol with similar functions.
[0063] MRF320 obtains the information including the address of the media buffer, and sends a service request response carrying the address of the MRF ...
Embodiment 2
[0156] This embodiment provides a time-shifted TV-on-demand (TsTV) application example that realizes LTV content in a multicast mode. In the LTV stage of the TsTV service, what is buffered in the media buffer is the RTP message in the multicast message, that is, the cached content includes the RTP header. In this embodiment, a media buffer is set on a digital subscriber access multiplexer (DSLAM) of a network edge node, and the MRF is used as a playback control point. The schematic diagram of the system structure of this embodiment and image 3 Similar, the only difference is that the network edge node co-located with the media buffer is a DSLAM, and the network entity UPSF for verification is added, which will not be repeated here.
[0157] Figure 8 It is a schematic flow chart of the second embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the content of the media buffer is provided from the DSLAM to the UE in a multicast manner. Whether the media buffer has conten...
Embodiment 3
[0201] Figure 9 It is a schematic diagram of the system structure of the third embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, it includes a client of a user equipment (UE, User Equipment) 910 , an MRF 920 and a media cache 931 set in a network edge node 930 .
[0202] This embodiment and image 3 In comparison, the main difference is that the MRF 920 provides the access side address of the media buffer 931 to the UE 920 through the core IMS, the media server in the MRF 920 executes the interface I4 between the module 921 and the media buffer 931, and the first The interface I5 between the control module 951 and the media buffer 931 and the interface I6 between the media buffer 931 and the UE 910 have new functional descriptions. The functional characteristics of these three interfaces are described in detail below.
[0203] The interface I4 is the interface between the MRF920 and the media buffer 931, and the media buffer 931 forwards the content request of the U...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com