Cell-permeable peptide inhibitors of the JNK signal transduction pathway
An inhibitor, JNK technology, applied in the field of inhibitors of protein kinase c-Jun amino-terminal kinase and pharmaceutical compounds with pathophysiological abnormalities, can solve the problem of high cost of inhibitor sequence separation and purification steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0258] Example 1: Identification of JNK Inhibitor Sequences
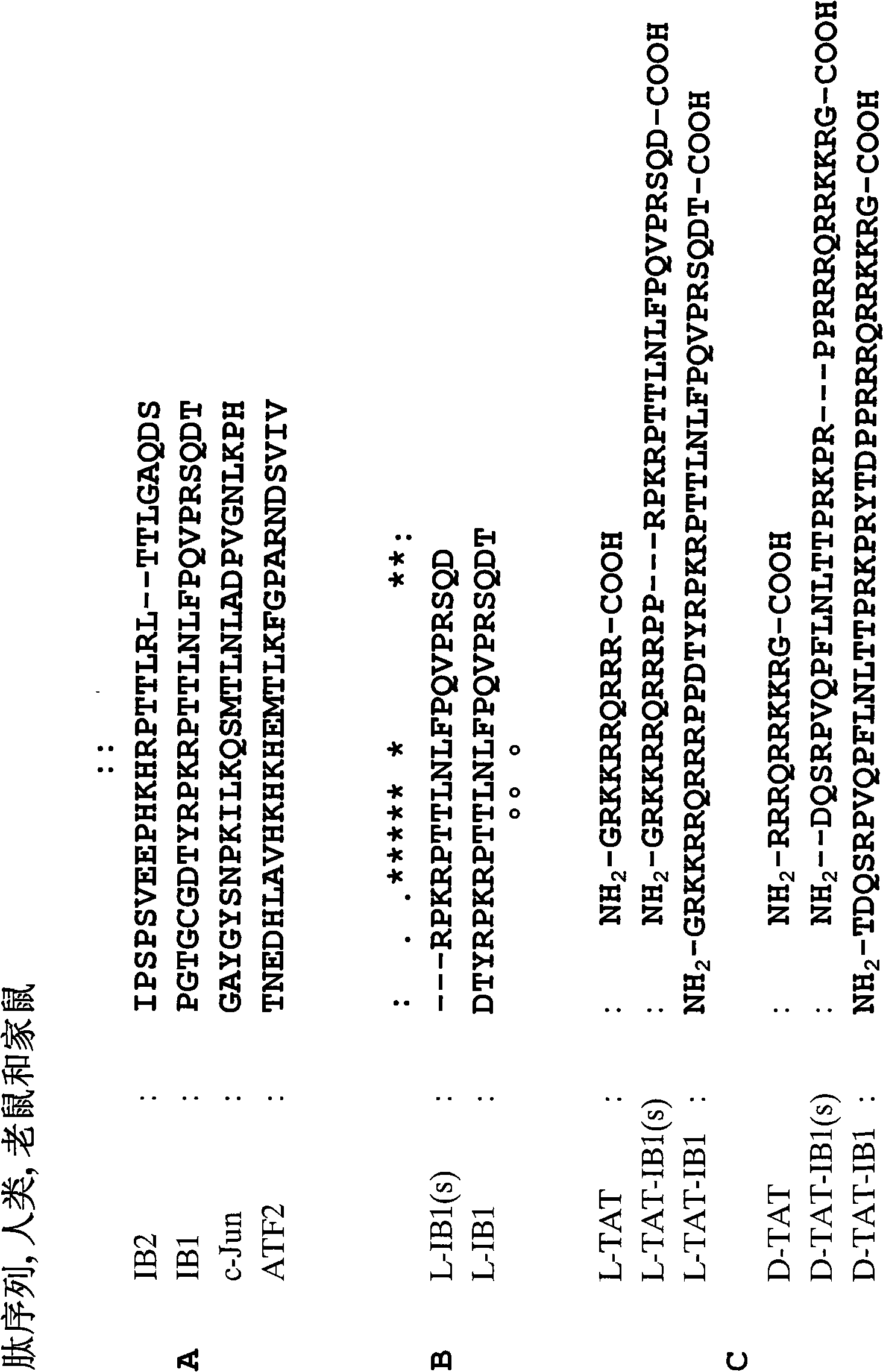
[0259] Amino acid sequences important for effective interaction with JNK were identified by sequence alignment among known JBDs. Sequence comparison between the JBDs of IB1 [SEQ ID NO: 13], IB2 [SEQ ID NO: 14], c-Jun [SEQ ID NO: 15] and ATF2 [SEQ ID NO: 16] defines weak retention The 8 amino acid sequence of ( figure 1 A). Because the JBDs of IB1 and IB2 have approximately 100 folds, they are as efficient as binding c-Jun or ATF2 in JNK (Dickens et al. Science 277:693 (1997), which elaborates on the remaining residues between IB1 and IB2 The importance of bases for conferring maximum binding. A comparison between the JBDs of IB1 and IB2 defined two blocks of 7 amino acids and 3 amino acids that were highly conserved between these two sequences.
[0260] These two blocks are located in the 19 amino acid peptide sequence in L-IB1 [SEQ ID NO: 1] and are shown in the 23 aa peptide sequence derived from IB1 [SEQ ID ...
example 2
[0261] Example 2: Preparation of JNK inhibitor fusion protein
[0262] The JNK inhibitor fusion protein of the present invention according to SEQ ID NO: 9 can be synthesized by covalently linking the C-terminal of SEQ ID NO: 1 to the N-terminal of a 10 amino acid long carrier peptide, wherein the carrier peptide Derived from HIV-TAT4g 57 according to SEQ ID NO: 5 (Vives et al., J Biol. Chem. 272: 16010 (1997)), the linkage is via a linker consisting of two proline residues. This linker allows maximum flexibility and prevents undesired secondary structure changes. These two basic structures were prepared and assigned for L-IB1(s) (SEQ ID NO: 1) and L-TAT [SEQ ID NO: 5], respectively.
[0263] Thus, an all-D retro-inverso peptide according to SEQ ID NO: 11 can be synthesized. These two basic structures were also prepared and assigned from D-IB1 [SEQ ID NO: 2] and D-TAT [SEQ ID NO: 6], respectively.
[0264] D and L fusion peptides of the present invention according to SEQ I...
example 3
[0265] Example 3: Inhibition of cell death by JBD19
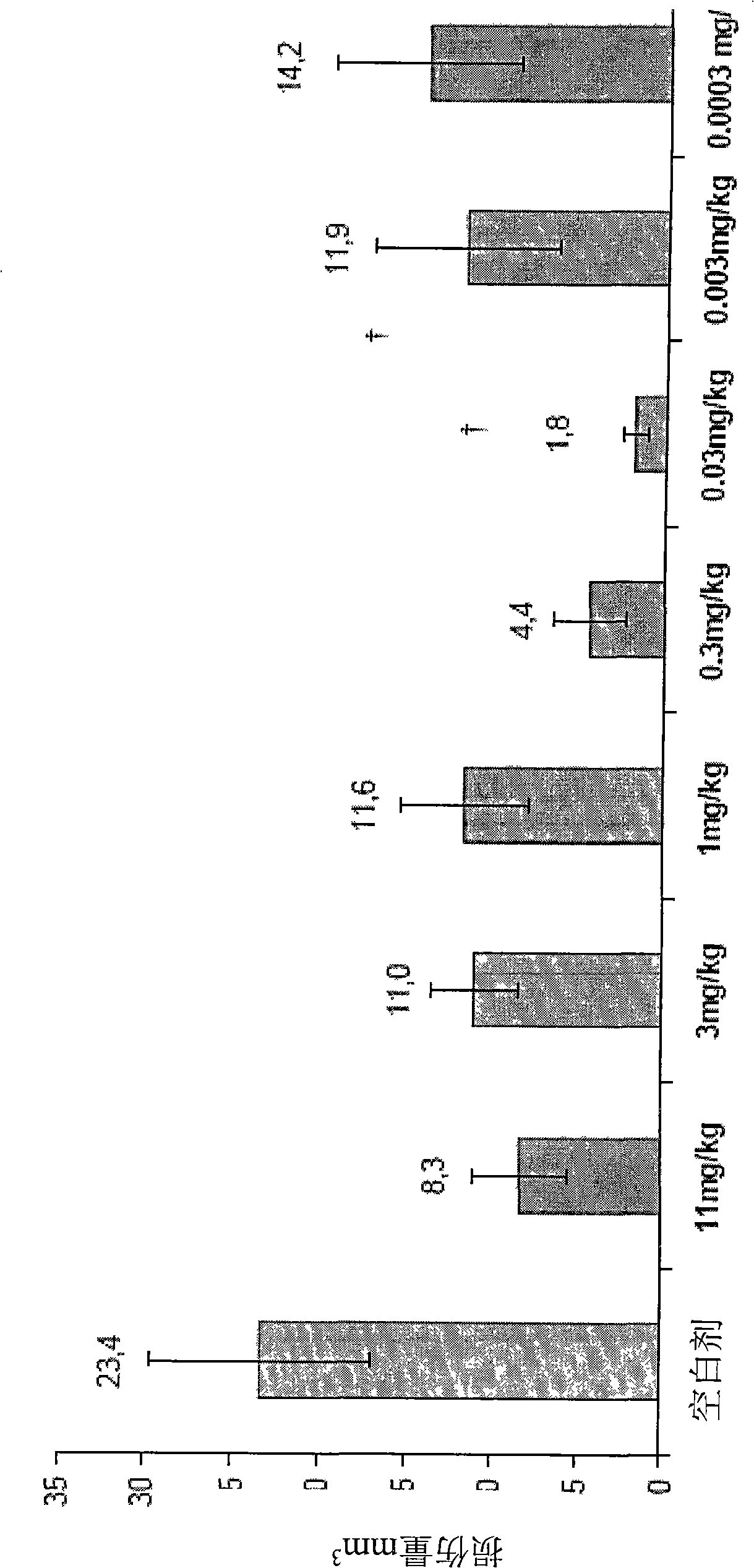
[0266] The role of the 19 aa long JBD on JNK biological activity was studied. The 19aa sequence is linked to the N-terminus of green fluorescent protein (GFP JBD19 construct), and it is estimated that this structure is related to IL1-induced apoptosis of pancreatic cells. Apoptotic patterns were previously shown and masked by transfection with JBD1-280, however, specific inhibitors of ERK1 / 2 or p38 did not confer protection (eg Ammendrup et al., supra).
[0267] Synthesis of an oligonucleotide corresponding to the JBD and having a conserved sequence of 19 amino acids, as well as a sequence that varies in the fully conserved region, and directly inserting the oligonucleotide and sequence into the coding green fluorescent protein (GFP, derived from cloning) EcoRI and SalI positions of pEGFP-N1. Insulin producing TC-3 cells was cultured in RPMI1640 medium, which also had 10% Fetal Calf Serum, 100 μg / mL streptomycin, 100 un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com