Illumination system with optical concentrator and wavelength converting element
A technology of wavelength conversion components and optical concentrators, which is applied in the field of high radiance optical systems and can solve problems such as radiance loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
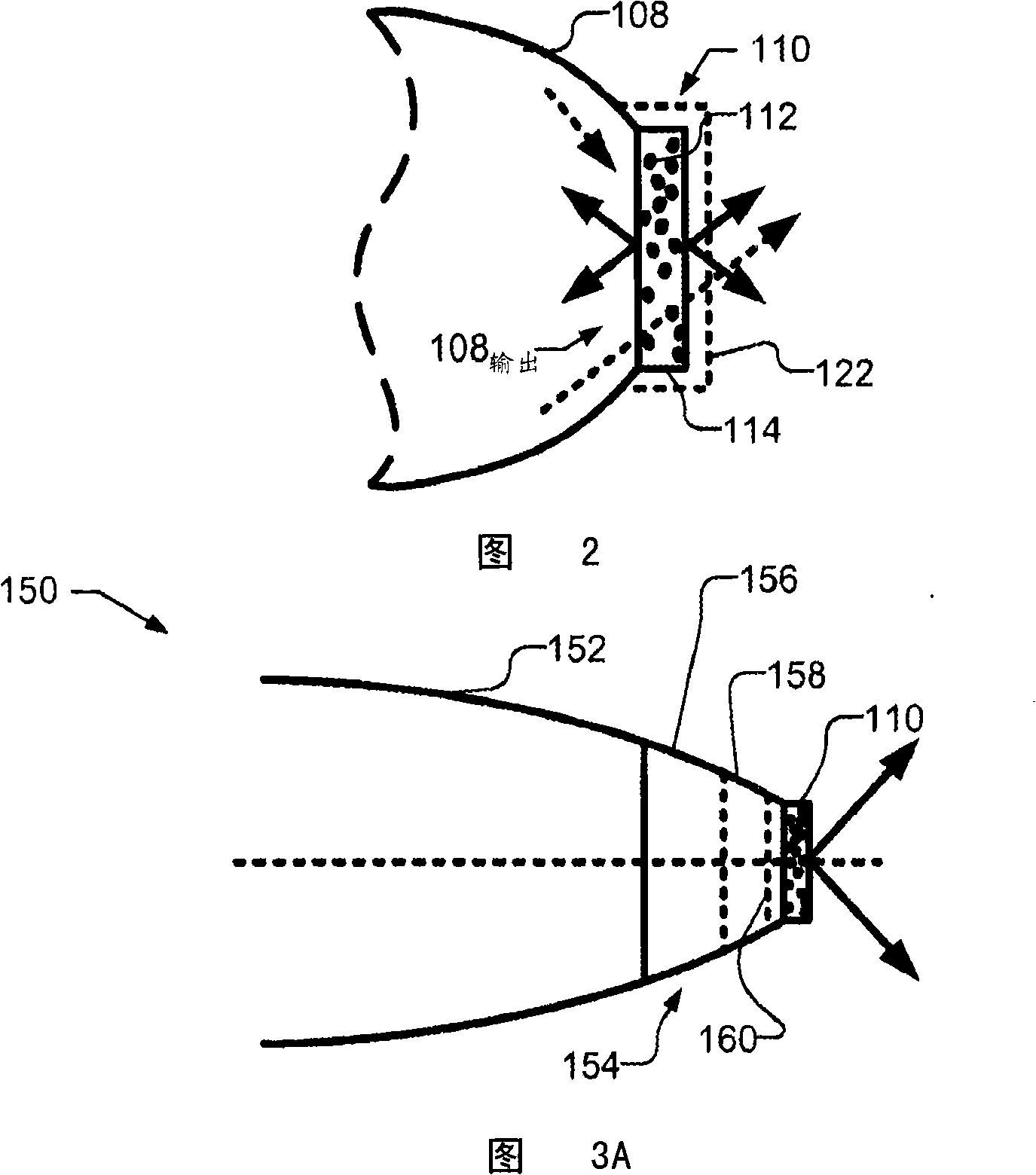
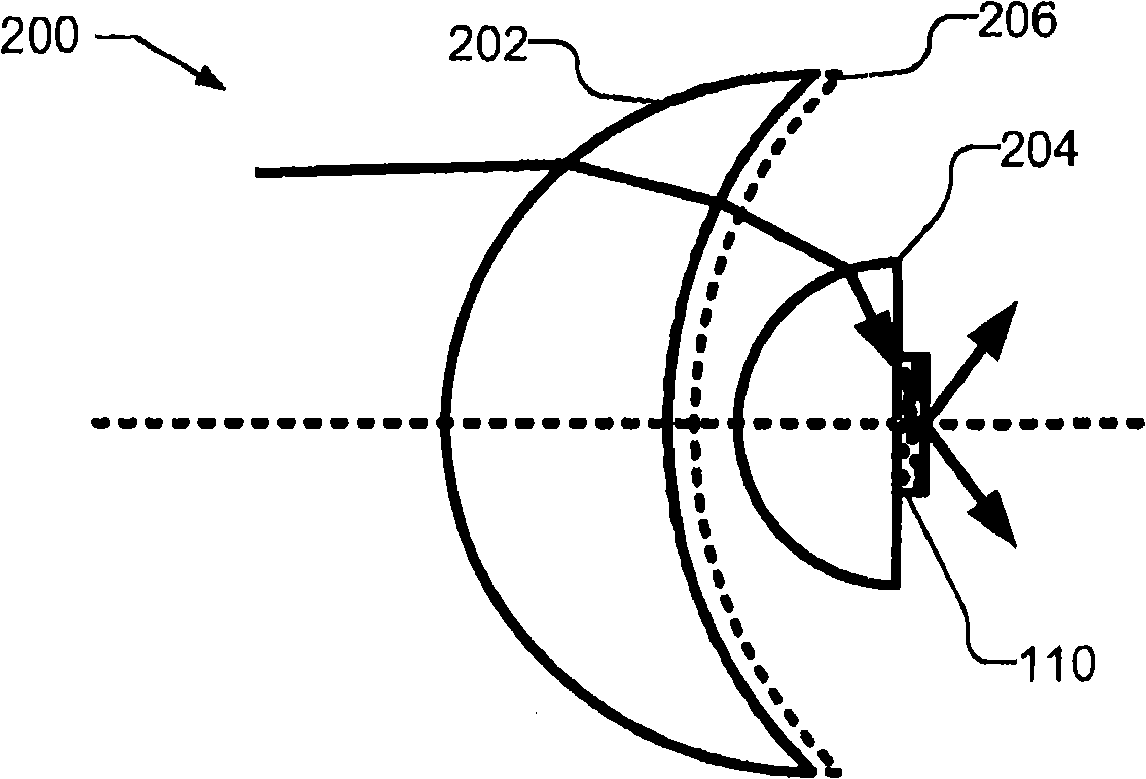
[0011] According to one embodiment of the present invention, the wavelength conversion element (such as a phosphor) is pumped through an optical concentrator with a high refractive index and the generated (converted) light is produced through a low refractive index medium (such as air) to improve Brightness or radiance of an optical system.
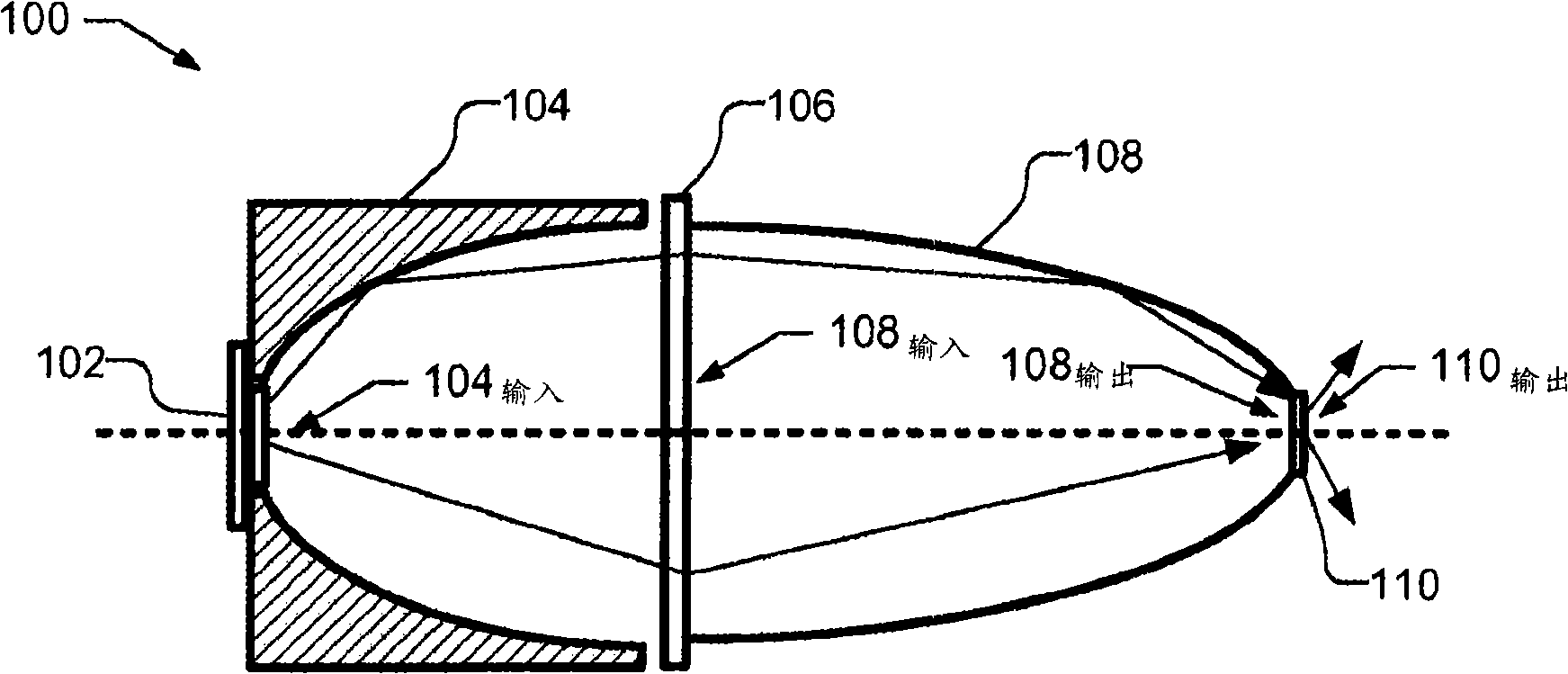
[0012] figure 1 An optical system 100 according to an embodiment of the invention is shown. Optical system 100 includes light emitting device 102, illustrated as a light emitting diode (LED) or an array of LEDs on a substrate, and collection optics 104. Collection optics 104 reduce the cone angle of the emission pattern from light emitting device 102 . For example, collection optics 104 can reduce a ±90° emission cone from light emitting device 102 to an emission pattern of ±30° angle. Collection optics 104 may be, for example, a right-angle converter, a compound parabolic concentrator (CPC), a condenser lens, a Fresnel lens, a lens us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com