Winding of electrical machine with switch-over mechanism
A switching mechanism and motor winding technology, applied in the shape/style/structure of winding conductors, circuits, electric switches, etc., can solve the problems of complex switching methods, many control switches, and many lead-out wires, and achieve simplified unit structure, contact Reliable, Simple Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
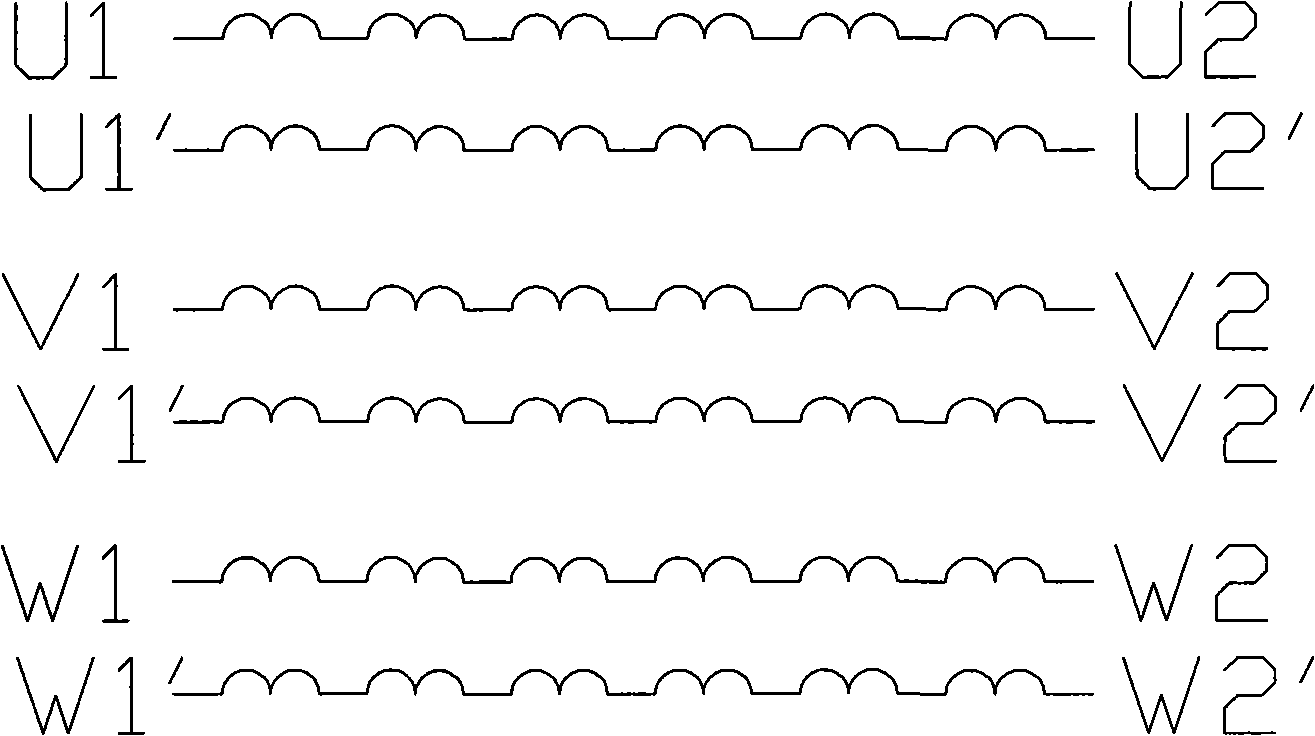
[0021] Embodiment 1 of the motor winding with switching mechanism of the present invention includes an iron core and a winding wound on the iron core and a switching mechanism. Each phase of the three-phase winding has 2 identical sub-windings and is wound in parallel, such as figure 1 As shown, U phase is U 1 -U 2 and U 1 ’-U 2 ’ Two sub-windings are wound in parallel, and the V phase is V 1 -V 2 and V 1 '-V 2 ’ Two sub-windings are wound in parallel, and the W phase is W 1 -W 2 and W 1 ’-W 2 ’ Two sub-windings are wound together.
[0022] u 1 -U 2 , V 1 -V 2 , W 1 -W 2 respectively with U 1 ’-U 2 ’, V 1 '-V 2 ’, W 1 ’-W 2 'After the parallel connection, output according to the conventional delta or star connection. When the same current is passed through the outside, the influence of the armature reaction is ignored. When the torque output of the parallel delta connection is 1, the torque output of the parallel star connection is 1.73.
[0023] u 1 -...
Embodiment 2
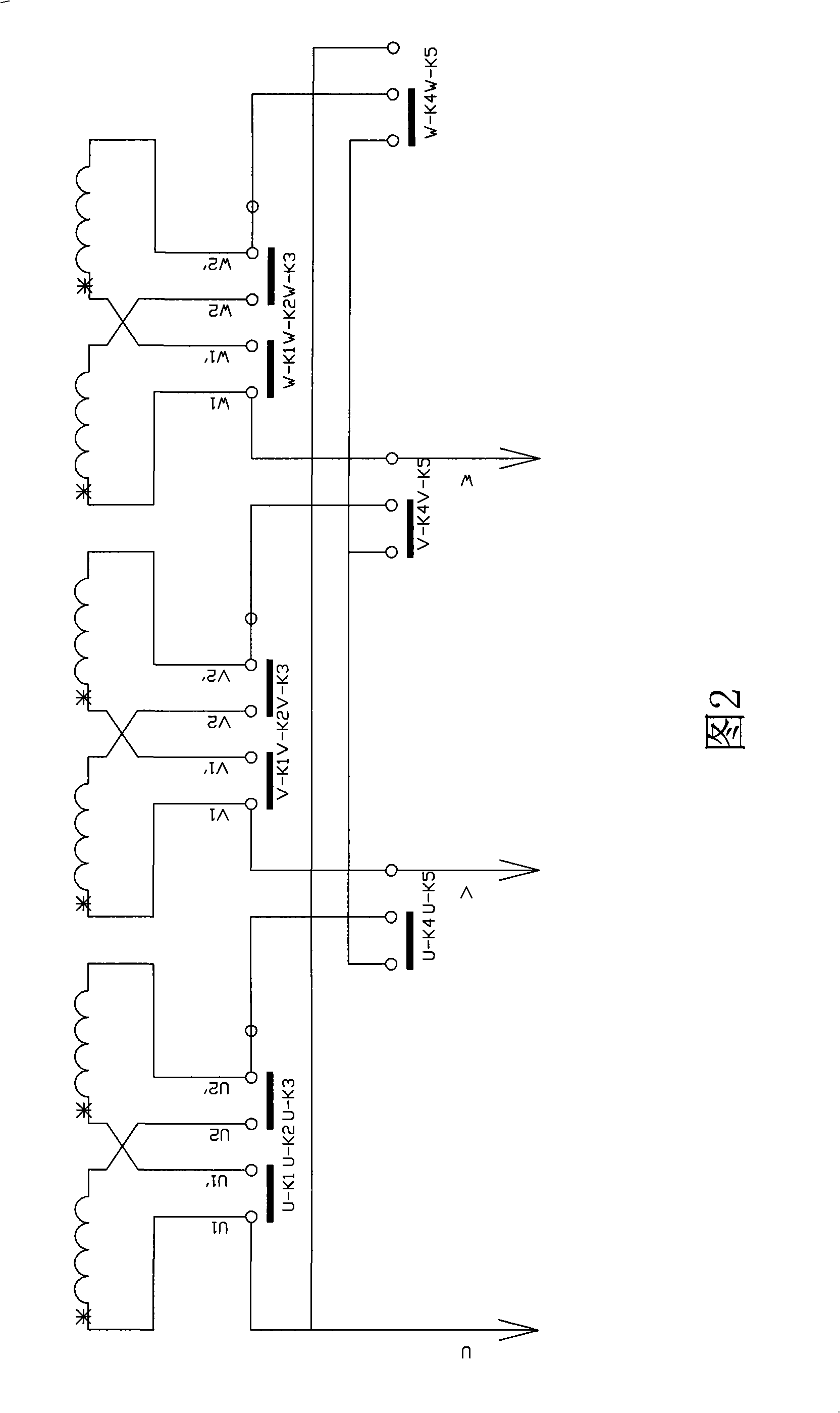
[0044] This example is a simplified structure of Example 1. Same as Example 1, each phase winding has 2 sub-windings, but the three phases are kept in a star connection, and the switching mechanism has only two gears, changing the series-parallel connection of the sub-windings. The different wiring methods of the sub-windings are shown in Figure 6. U in the picture1 , V 1 , W 1 U, V, W are the final leads of the three-phase winding, U 2 ’, V 2 ’, W 2 ’ Connected. Each phase winding has K 1 to K 3 Three touch bridges. UK 1 The sub-winding terminal U corresponding to the U phase 1 , U 1 ’, UK 2 Corresponding endpoint U 1 ’, U 2 , UK 3 Corresponding endpoint U 2 , U 2 ’; VK 1 The terminal point V of the sub-winding corresponding to the V phase 1 , V 1 ’; VK 2 Corresponding terminal V 1 ’, V 2 , VK 3 Corresponding terminal V 2 , V 2 ’; WK 1 Corresponding to the sub-winding terminal W of phase W 1 , V 1 ’, WK 2 Corresponding endpoint W 1 ’, W 2 ;WK 3...
Embodiment 3
[0054] This example is another simplified structure of Example 1. Same as Example 1, each phase winding has 2 sub-windings, but its three phases remain in delta connection. The different wiring methods of sub-windings are as follows: Figure 7 shown. Similar to example 2, in the figure U 1 , V 1 , W 1 U, V, W are the final leads of the three-phase winding, but U 2 ’ with V 1 connected, V 2 ’ with W 1 connected, W 2 ’ with U 1 connect. Same as Example 2, there are two connection methods of series and parallel for sub-windings, and the switching mechanism is the same as Example 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com