Process for producing negative electrode material for lithium ion secondary battery
A secondary battery and negative electrode material technology, applied in the direction of secondary batteries, battery electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to achieve the effect of improving grinding ability and suppressing the increase of irreversible capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
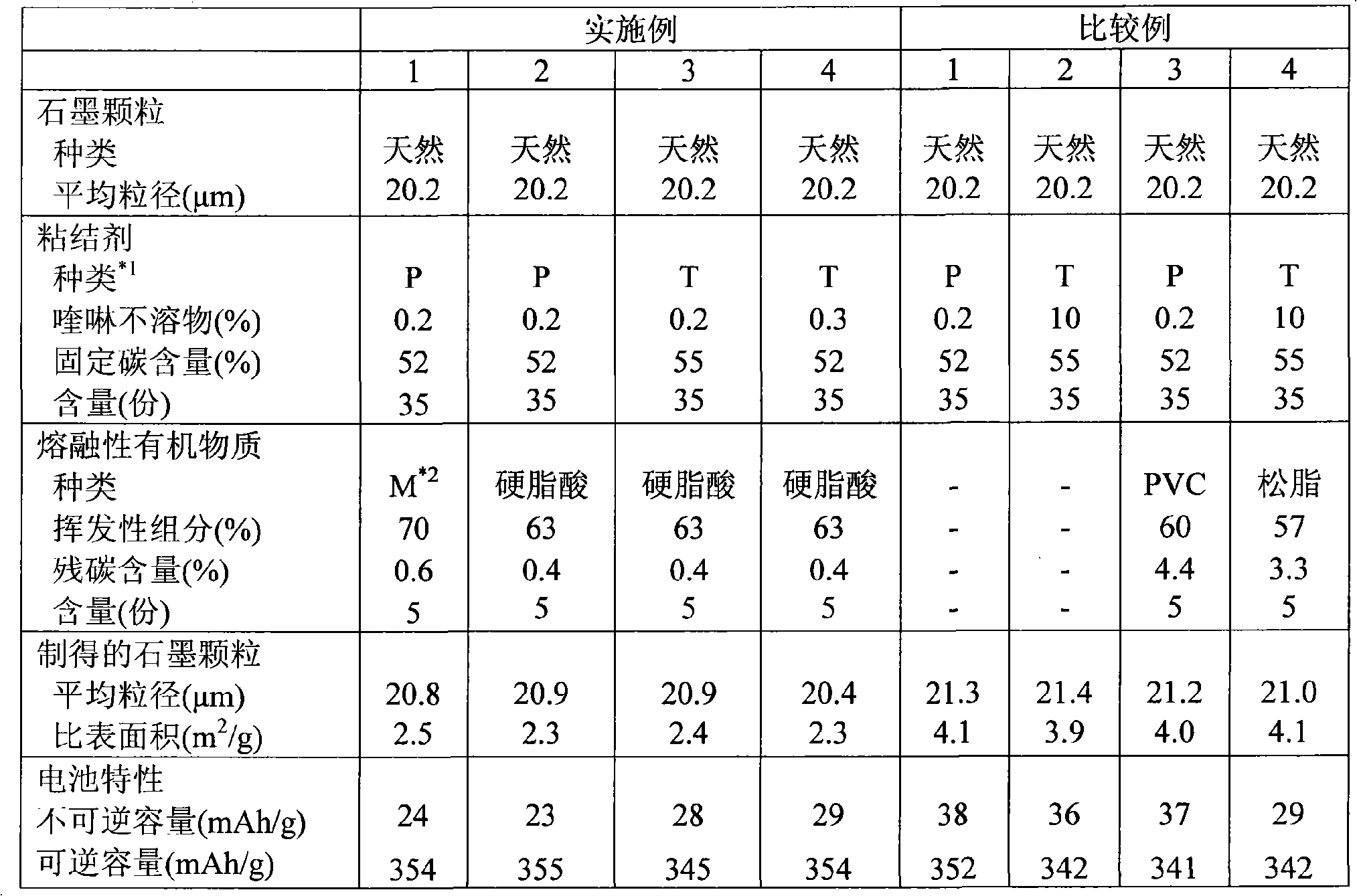
Embodiment 1
[0038] 500 g of natural graphite with an average particle diameter of 20.2 μm and 175 g of coal tar pitch with a quinoline insoluble content of 0.2% and a fixed carbon content of 52% were put into the Werner mixer. The above components were stirred at 130°C for 20 minutes. After adding 25g of molten engine oil as a molten organic substance, the components were melted and kneaded for 10 minutes. The engine oil volatilized 70% under heating at 400°C in air and had a residual carbon content of 0.6% under heating at 800°C in an inert atmosphere.
[0039] After the obtained mixture was cooled, the mixture was placed in a graphite crucible, and the mixture was calcined at 1000° C. in a nitrogen atmosphere to be carbonized. The resulting product was placed in a graphitization furnace and graphitized at 2500°C. The graphitized material was ground using a cyclone sample mill "CSM-F1" (manufactured by Fujiwara Scientific Co., Ltd.), and sieved using a sieve with an aperture of 44 μm to...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The components were melted and kneaded in the same manner as in Example 1, except that stearic acid, which volatilized 63% under heating at 400°C in air and had a carbon residue content of 0.4% under heating at 800°C in an inert atmosphere, was used instead of melting non-toxic motor oil. The mixture was calcined, carbonized and graphitized in the same manner as in Example 1, and sieved to adjust the average particle size to 20.9 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Components are melt-kneaded in the same manner as in Example 1, except that coal tar with quinoline insoluble content of 0.2% and fixed carbon content of 55% is used, and 63% is volatilized under heating at 400° C. in air. Stearic acid with a carbon residue content of 0.4% under heating at 800°C in an inert atmosphere is used instead of molten motor oil. The mixture was calcined, carbonized and graphitized in the same manner as in Example 1, and sieved to adjust the average particle size to 20.9 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com