Block-wise constructing method for quasi-cyclic LDPC code
A technology of LDPC code and construction method, applied in the direction of error correction/detection using block code, error detection coding applying multi-bit parity bit, data representation error detection/correction, etc., which can solve the problem of poor performance and unfavorable hardware implementation. , high-complexity problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
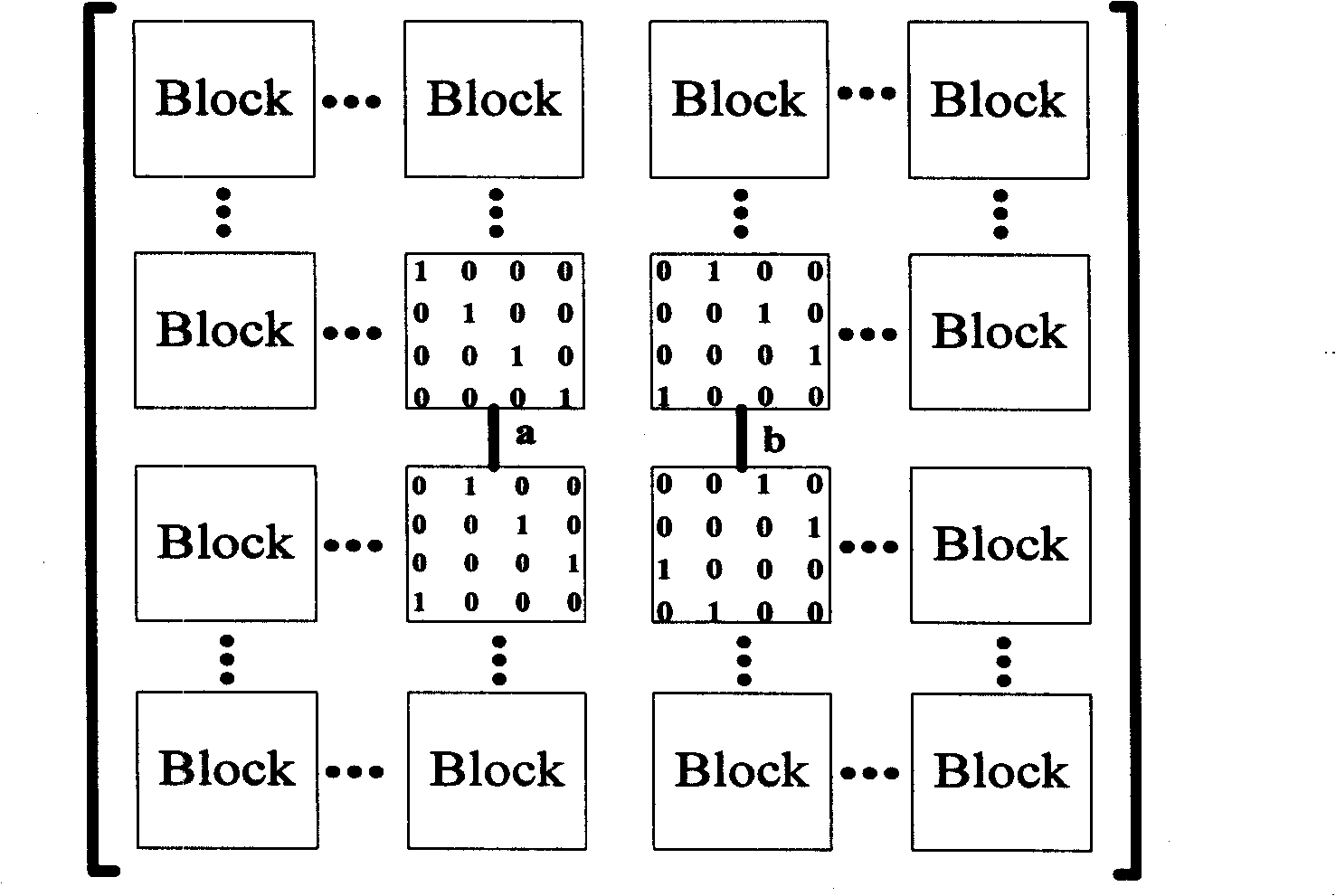
[0027] See figure 1 As shown, to illustrate the necessary and sufficient conditions for the formation of 4 loops in the quasi-cyclic LDPC code based on the cyclic permutation matrix, the solid line represents the difference in the shift order of the two connected cyclic permutation matrices. In the figure, 4 block matrices form 4 rings if and only if a=b mod p.
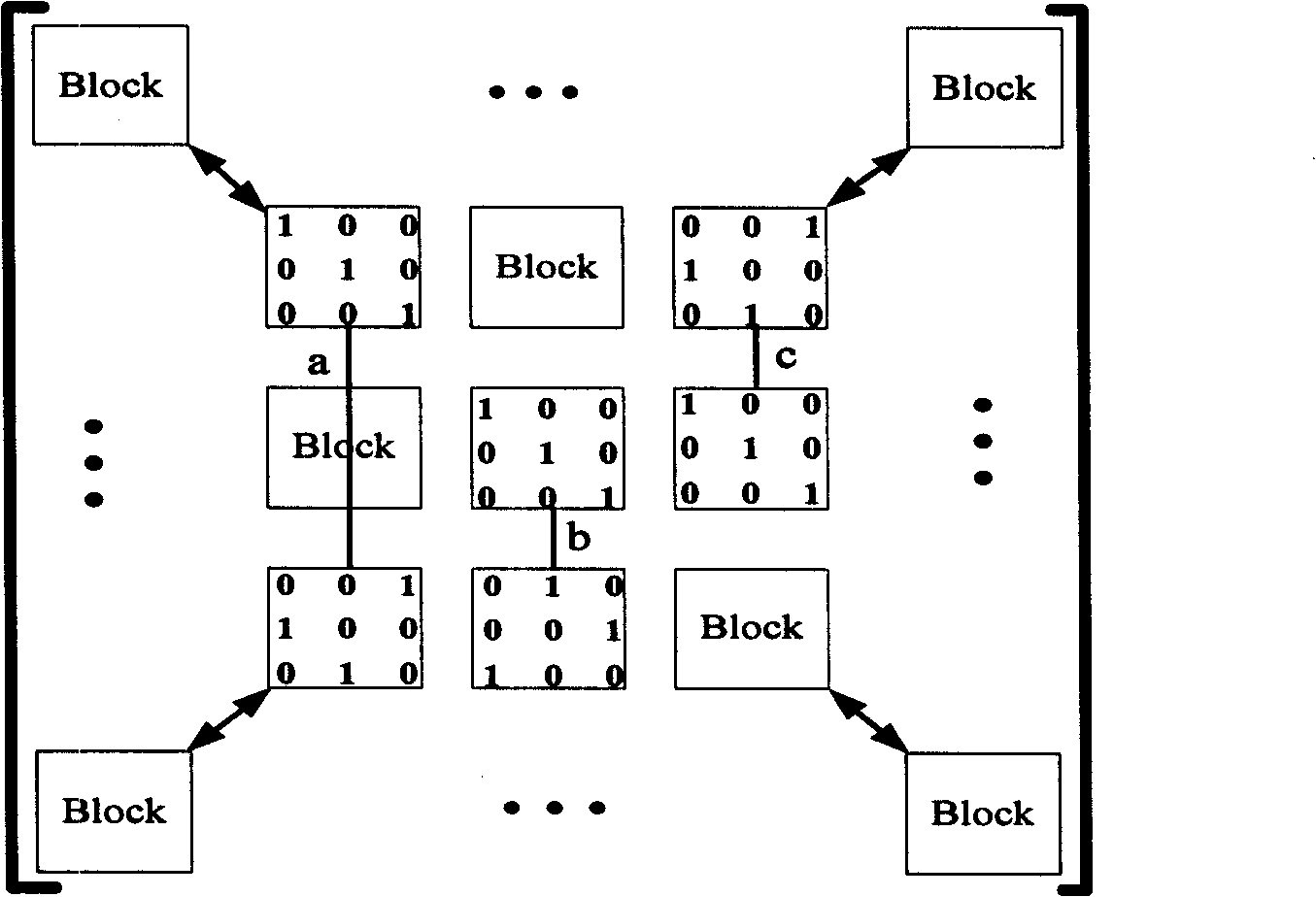
[0028] See figure 2 As shown, to illustrate the necessary and sufficient conditions for the formation of 6 loops in the quasi-cyclic LDPC code based on the cyclic permutation matrix, the solid line represents the difference in the shift order of the two connected cyclic permutation matrices. In the figure, 4 block matrices form 6 rings if and only if a=(b+c)mod p, and intuitively define a as the long side of the 6 rings, and define b and c as the short sides.
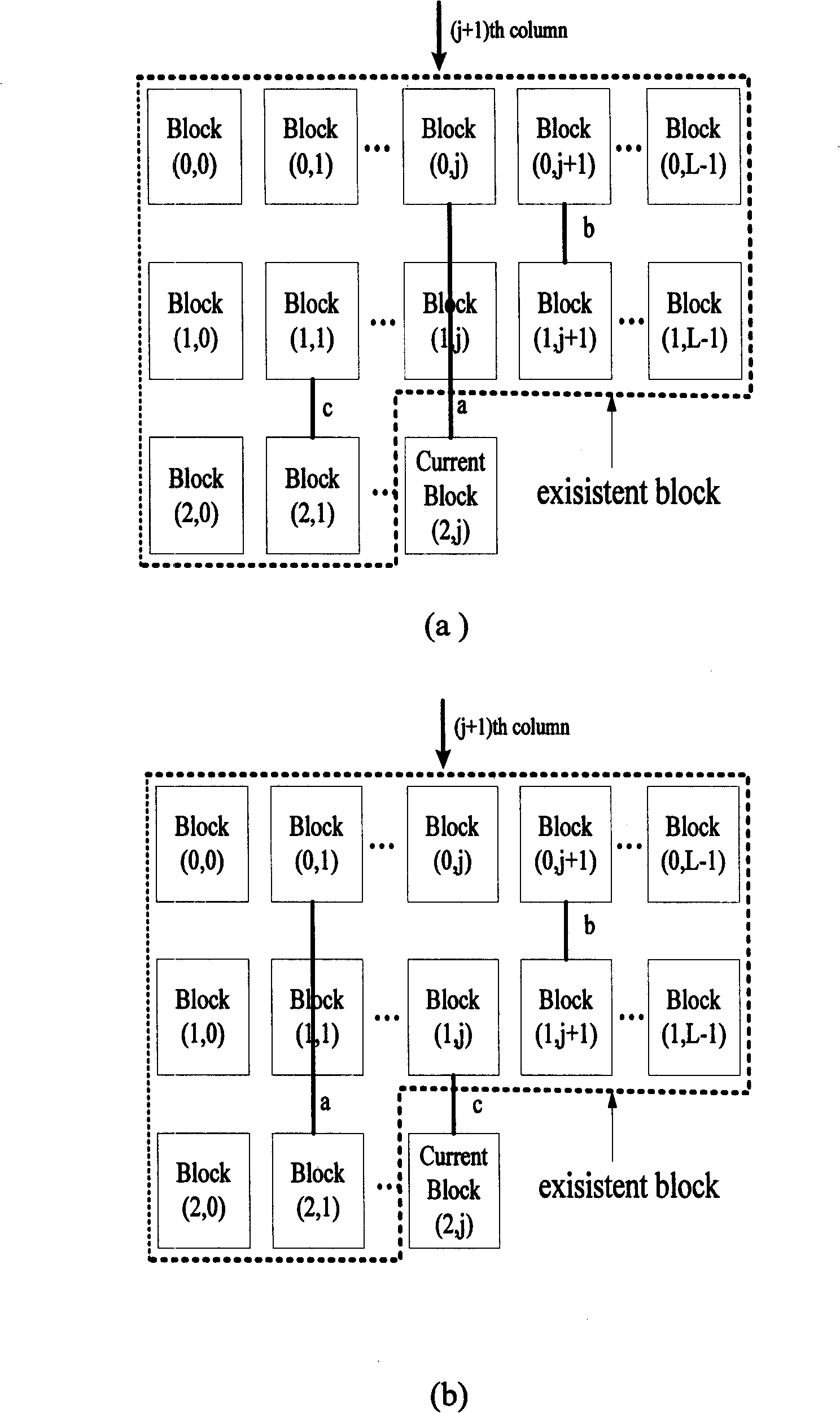
[0029] With the intuitive representation of the above-mentioned 4 rings or 6 rings, we construct the check matrix of the (3, L) quasi-cyclic LDPC code block by b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com