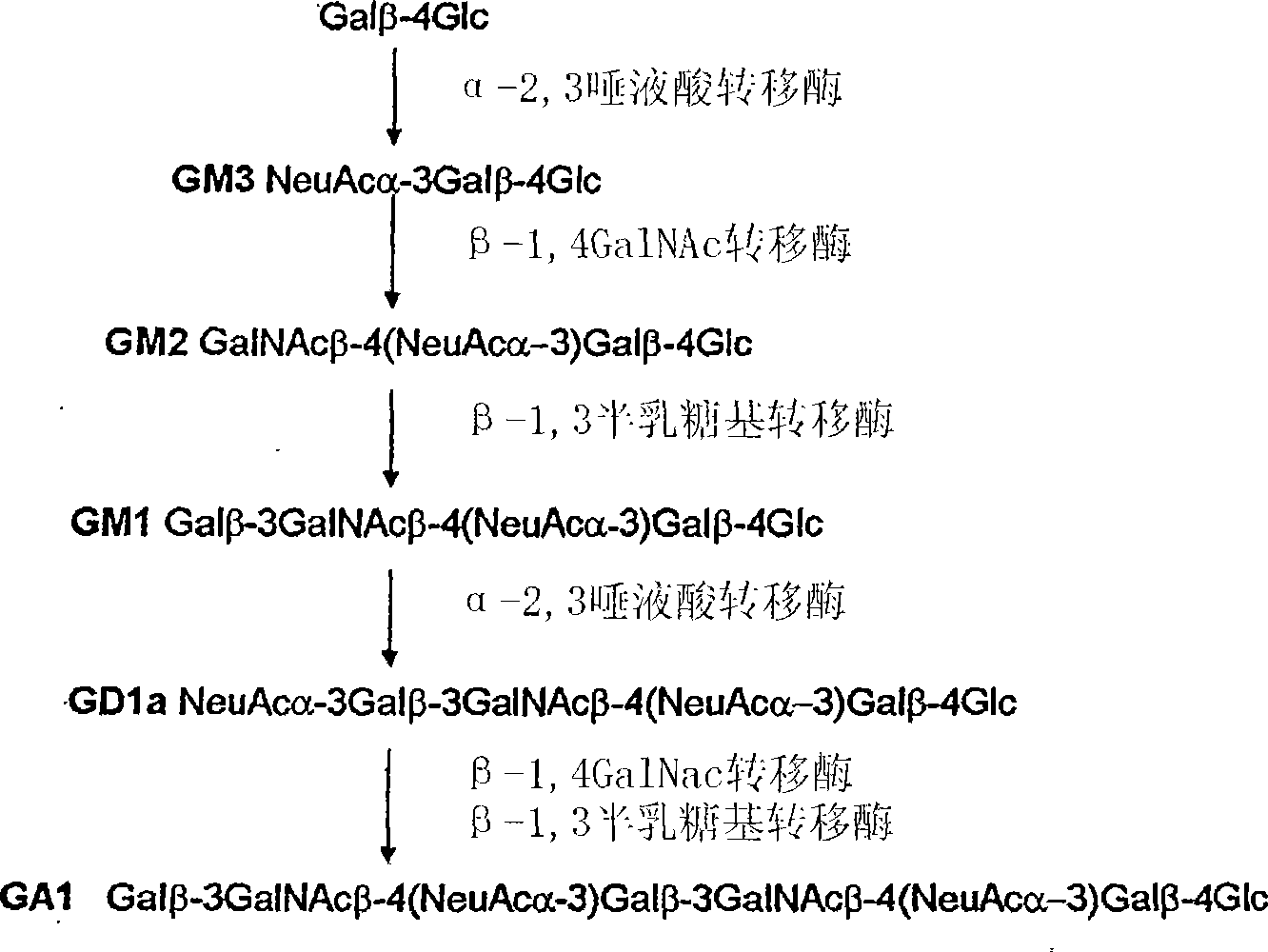Method of producing sialylated oligosaccharides
A technology of oligosaccharides and lactose, applied in the direction of oxidoreductase, transferase, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems that cannot be used in biotechnology processes, high cost of sialic acid, hindering the development of sialooligosaccharides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
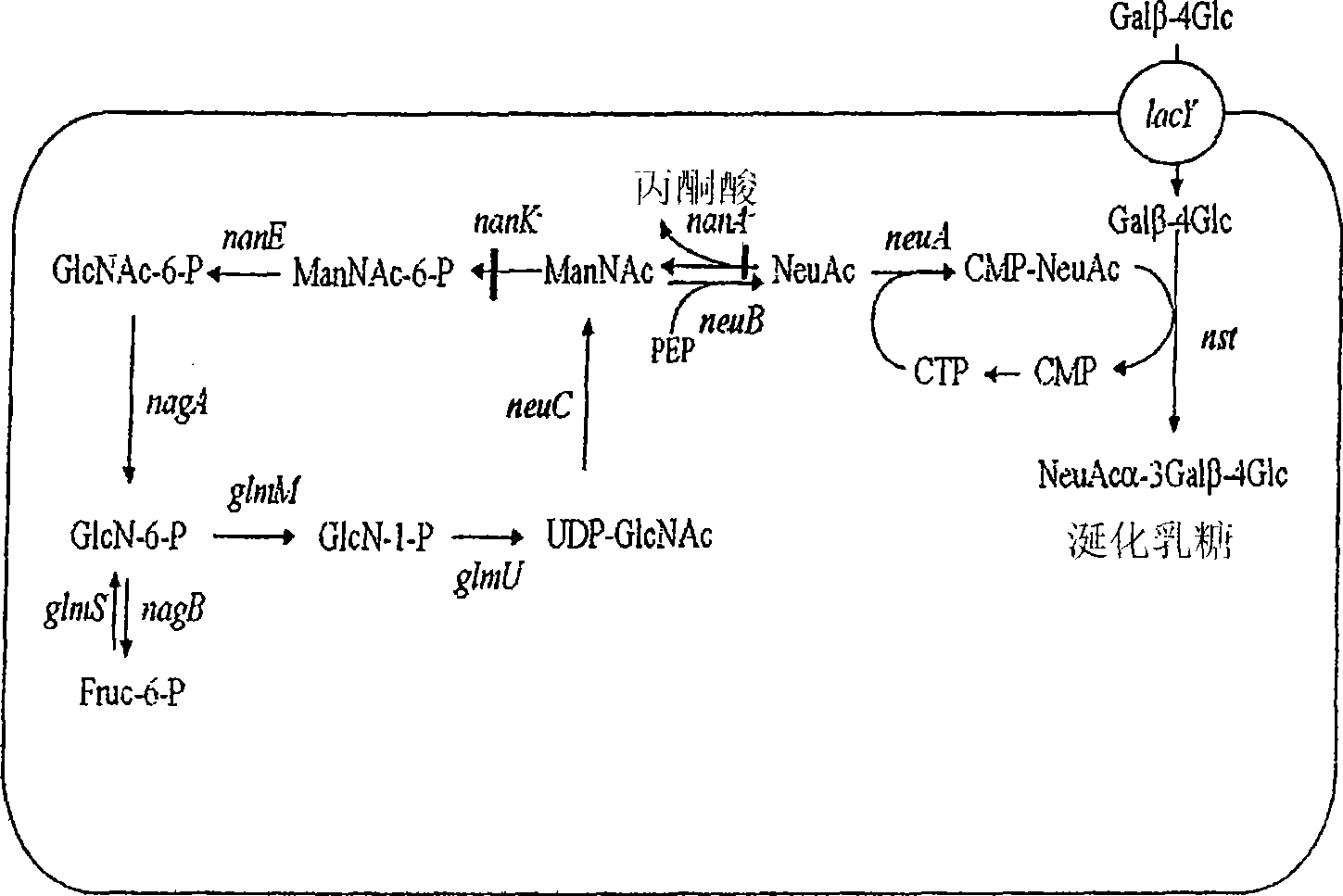
[0102] Production of 3' sialyllactose
[0103] The production of 3' sialyllactose can be achieved by a metabolically engineered strain as defined above expressing an enzyme encoding an α-2,3 sialyltransferase activity, such as α-2,3 sialyltransferase using lactose as an acceptor. Genes for acid transferase or bifunctional alpha-2,3 and alpha-2,8 sialyltransferase. As indicated, this strain lacks sialic acid aldolase, ManNAc kinase, and β-galactosidase activities, and expresses genes encoding CMP-Neu5Ac synthetase, a sialic acid synthase, a GlcNAc-6-phosphate 2 differential A heterologous gene for isomerase. For large-scale production of sialyllactose, this strain can be grown at high cell densities on inexpensive substrates such as glucose or glycerol and fed on lactose, which is internalized by lactose permease and used by recombinant sialyltransferases From such as figure 1 Sialylation of exogenously produced CMP-Neu5Ac in UDP-GlcNAc shown.
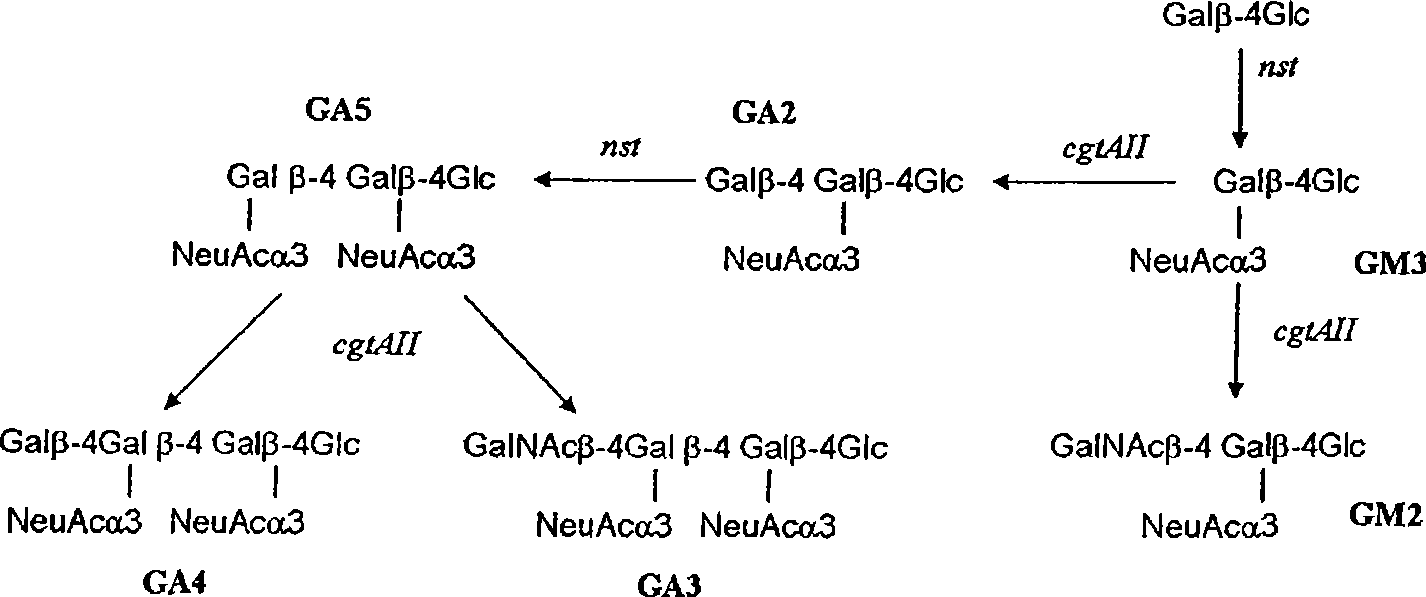
[0104] Production of 6' sial...
Embodiment 1
[0141] Example 1: Construction of nanA, nanKA and nanKETA mutants
[0142] All mutants were constructed from the DC strain (Dumon et al. 2005), a derivative of the DH1 strain carrying the lacZ and lacA mutations. Because all DH1 strain derivatives are recA mutated, they were transformed with the low-copy plasmid pEXT22 carrying a functional recA gene and kanamycin resistance, reverting to transient RecA by a gene inactivation program involving DNA recombination + Phenotype. Once the gene has been disrupted, the plasmid can be restored by growing the cells without kanamycin and selecting for the RecA-phenotype.
[0143] The AZL strain was constructed as a sub-DC strain by inactivating the nanA gene using the suicide plasmid pMAK705 (Hamilton et al. 1989), as previously described (Priem et al., 2002).
[0144] To construct ZLKA from DC strains, the nanKETA gene was disrupted by removing a 3.339 kb fragment in chromosomal DNA using a previously described one-step procedure usin...
Embodiment 2
[0148] Embodiment 2: Cloning of neuBCA gene
[0149] A 2.995 (kb) DNA fragment containing the neuBCA gene sequence was amplified by PCR using Campylobacter jejuni strain ATCC 43438 as a template.
[0150] A KpnI site was added to the left primer: 5'GGTACCTAAGGAGGAAAATAAATGAAAGAAATAAAAATACAA (SEQ ID NO 14)
[0151] Add an XhoI site to the right primer
[0152] 5'CTCGAGTTAAGTCTCTAATCGATTGTTTTTCCAATG (SEQ ID No 15).
[0153] The amplified fragment was first cloned into the pCR4Blunt-TOPO vector (Invitrogen) and then subcloned into the KpnI and XhoI sites of the pBBR1-MCS3 vector to form pBBR3-SS.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com