Separation and purification process of wheat flour starch granule
A technology of wheat flour and starch granules, which is applied in food preparation, food science, application, etc., can solve the problem of lack of particle separation research, and achieve the effects of simple process, short production cycle and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Extraction of wheat flour starch granules
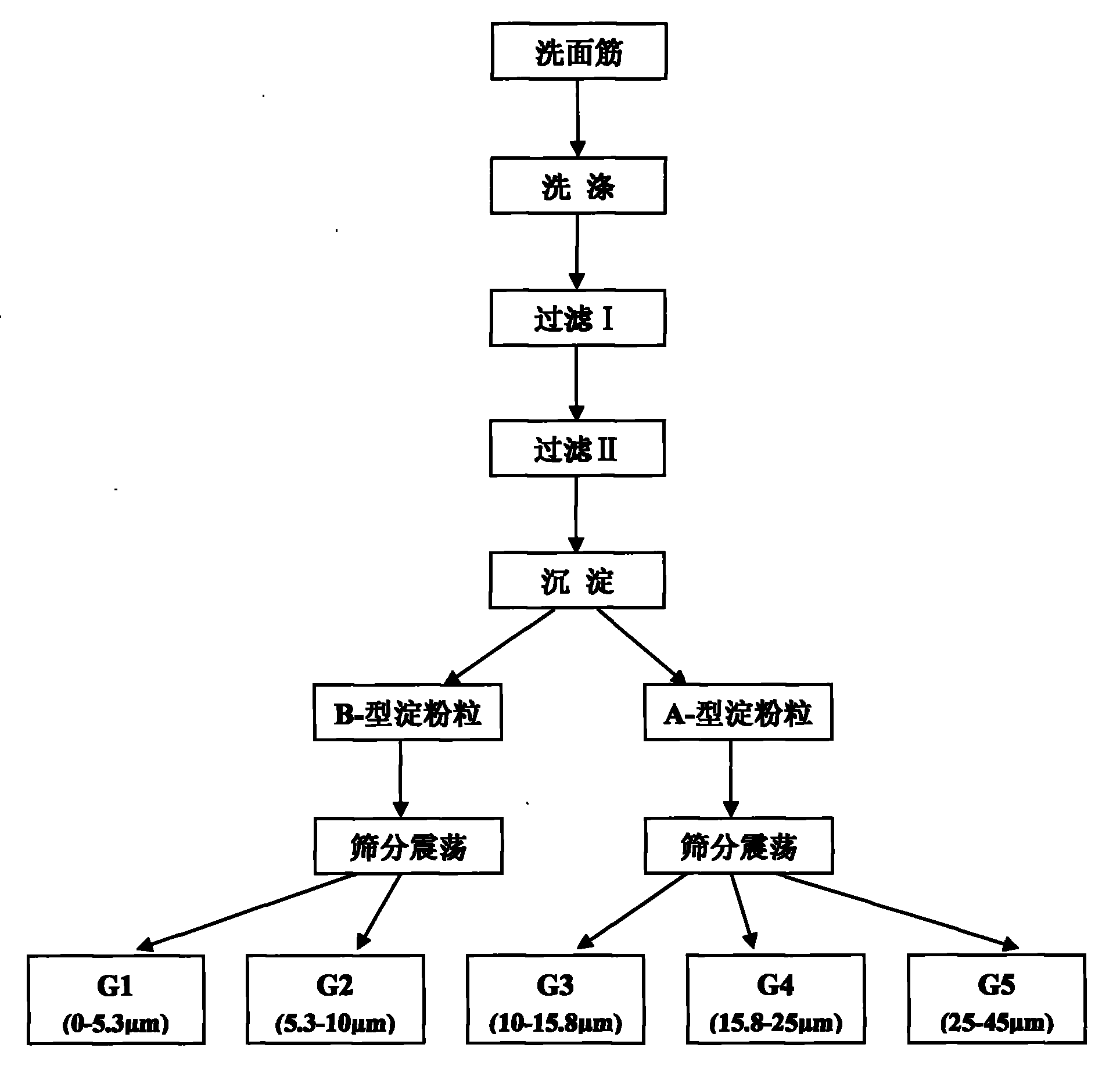
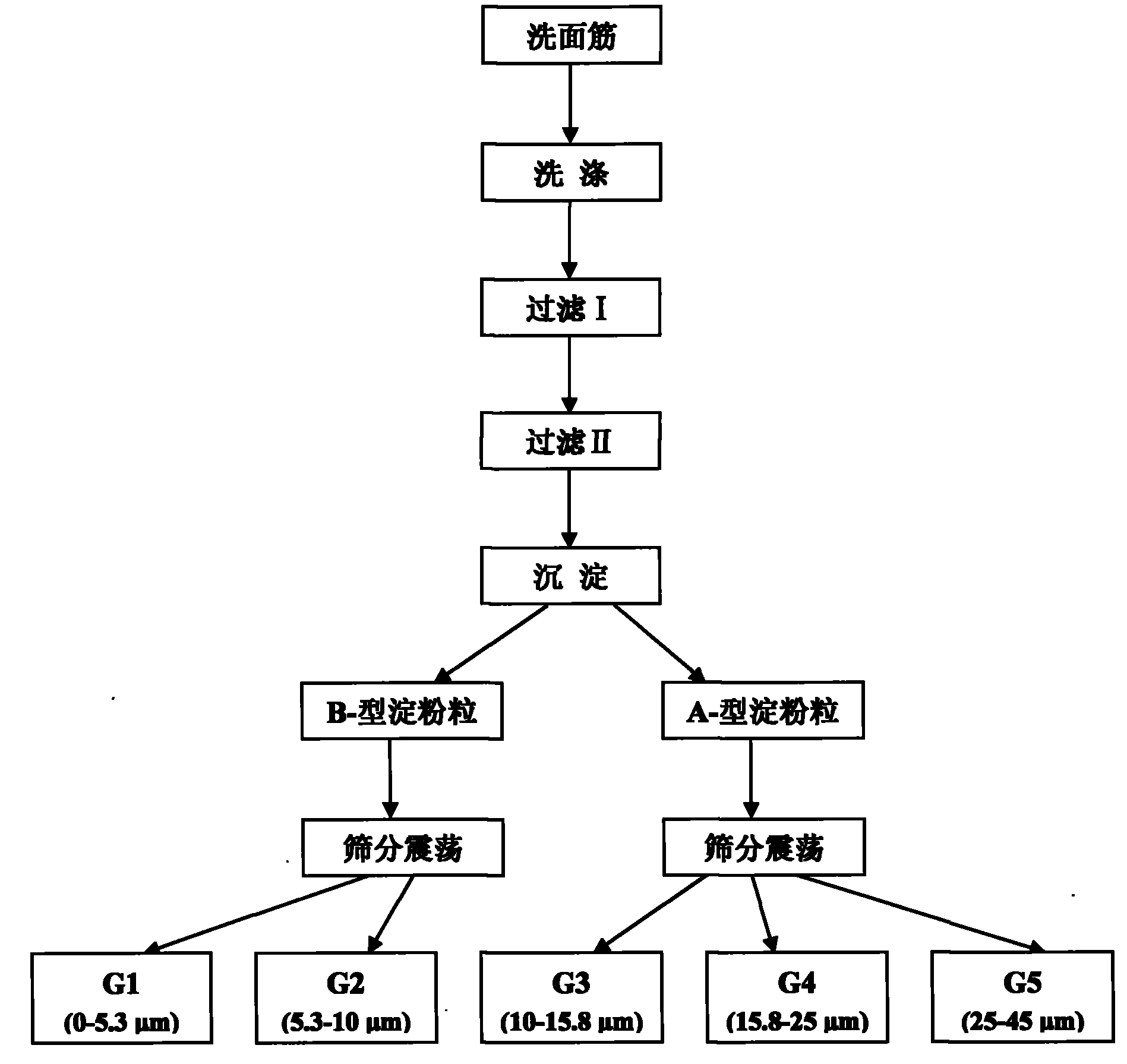
[0035] 1) Protein removal: Refer to the national standard method GB / T 14608-93 to machine wash the flour with a gluten analyzer, and separate the protein in the form of gluten. Centrifuge at 2500×g for 10-20min to discard the supernatant to obtain crude starch;
[0036] 2) Washing: Suspend the crude starch with 10 times the weight of deionized water, centrifuge at 2500×g for 10-20 minutes, discard the upper liquid, and repeat three times to remove residual sodium chloride and water-soluble protein;
[0037] 3) Filtration I: Suspend the crude starch with 10 times the weight of deionized water, pass the suspension through a 45μm screen to remove residual crude fibers and other large particles of impurities, collect and filter the crude starch suspension, centrifuge at 2500×g for 10-20min , Discard the upper liquid;
[0038] 4) Filtration II: Suspend the crude starch with 10 times the weight of absolute ethanol, pass the suspen...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Separation of A-, B-type starch granules
[0041] The wheat flour extracted starch grains of claim 1 were suspended in deionized water at a mass-volume ratio of 1:8 for 1 hour, and 5 / 9 volume of the upper suspension was taken and repeated nine times. The upper suspension was centrifuged at 2500×g for 20 min to obtain the precipitate It is B-type starch granules, and the lower layer is A-type starch granules.
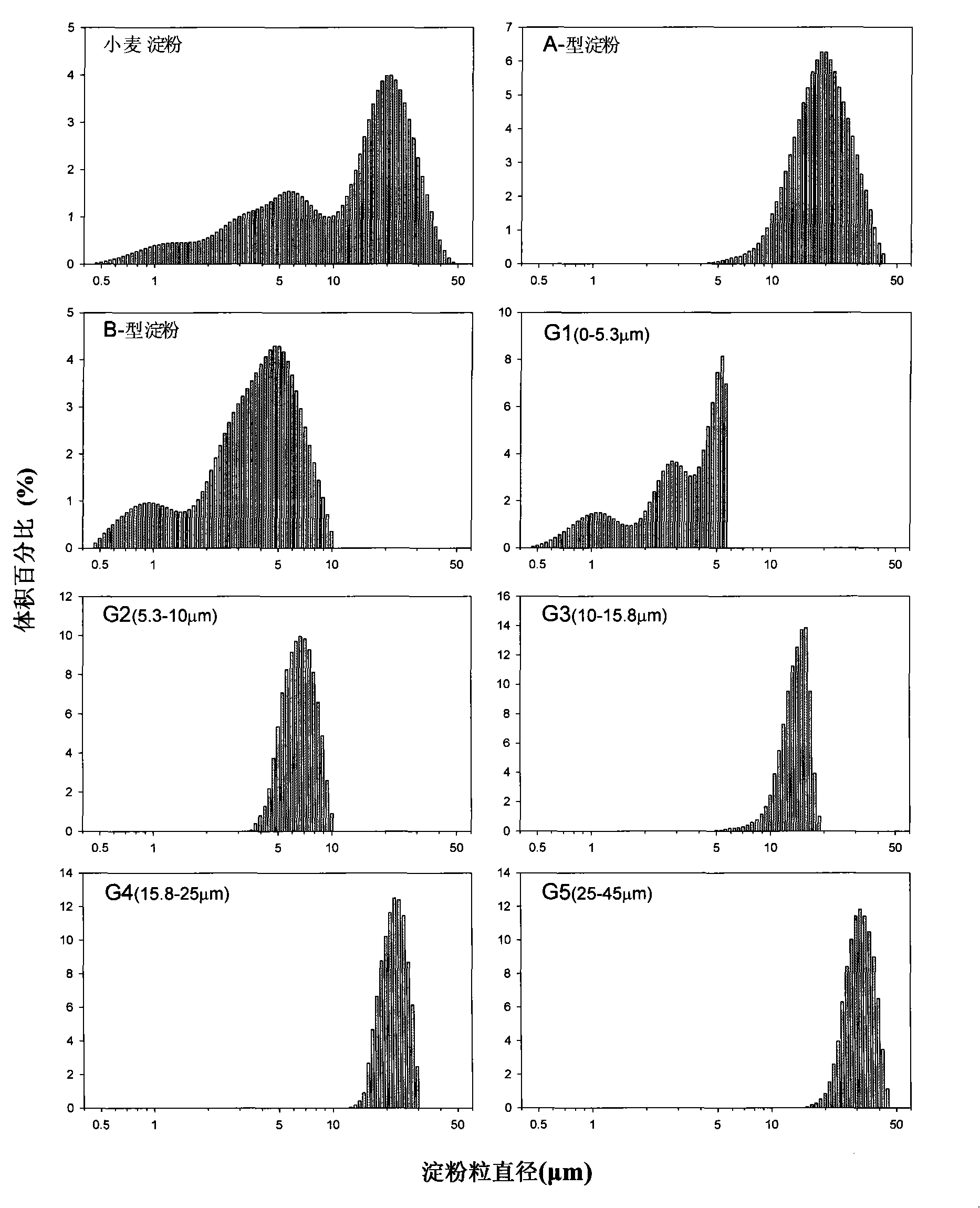
[0042] Experimental analysis shows that: for every 1 kg of wheat flour extracted starch granules of claim 1, 780.11 g of A-type starch granules, 218.78 g of B-type starch granules, A-type starch granules and B-type starch granules can be separated using this technical solution. The yield ratio of starch granules is 3.9:1.1. The process is basically no loss, and the process flow is simple, easy to industrialize, and consumes less energy.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Classification of A-type starch granules
[0044] Under the condition of 0℃, the A-type starch granule suspension was suspended in deionized water at a mass-volume ratio of 1:60, and passed through a 25μm sieve. Using a wet and dry sieving machine to shake at 2800 times / min amplitude for 2 minutes, Sieve starch granules G5, filter the suspension and then pass through a 15.8μm sieve. Use a wet and dry sieving machine to shake at an amplitude of 2800 times / min for 5 minutes to obtain unsieved starch granules G4. The filtered suspension is centrifuged at 2500×g for 20 minutes The resulting starch granules G3.
[0045] Experimental analysis shows that: for every 1 kilogram of A-type starch granules of claim 2, starch granules G3, G4 and G5 can be separated by using this technical solution to be 221.30, 507.61, 266.14 grams, respectively. The process flow is simple, easy to industrialize, and energy-consuming. less.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com