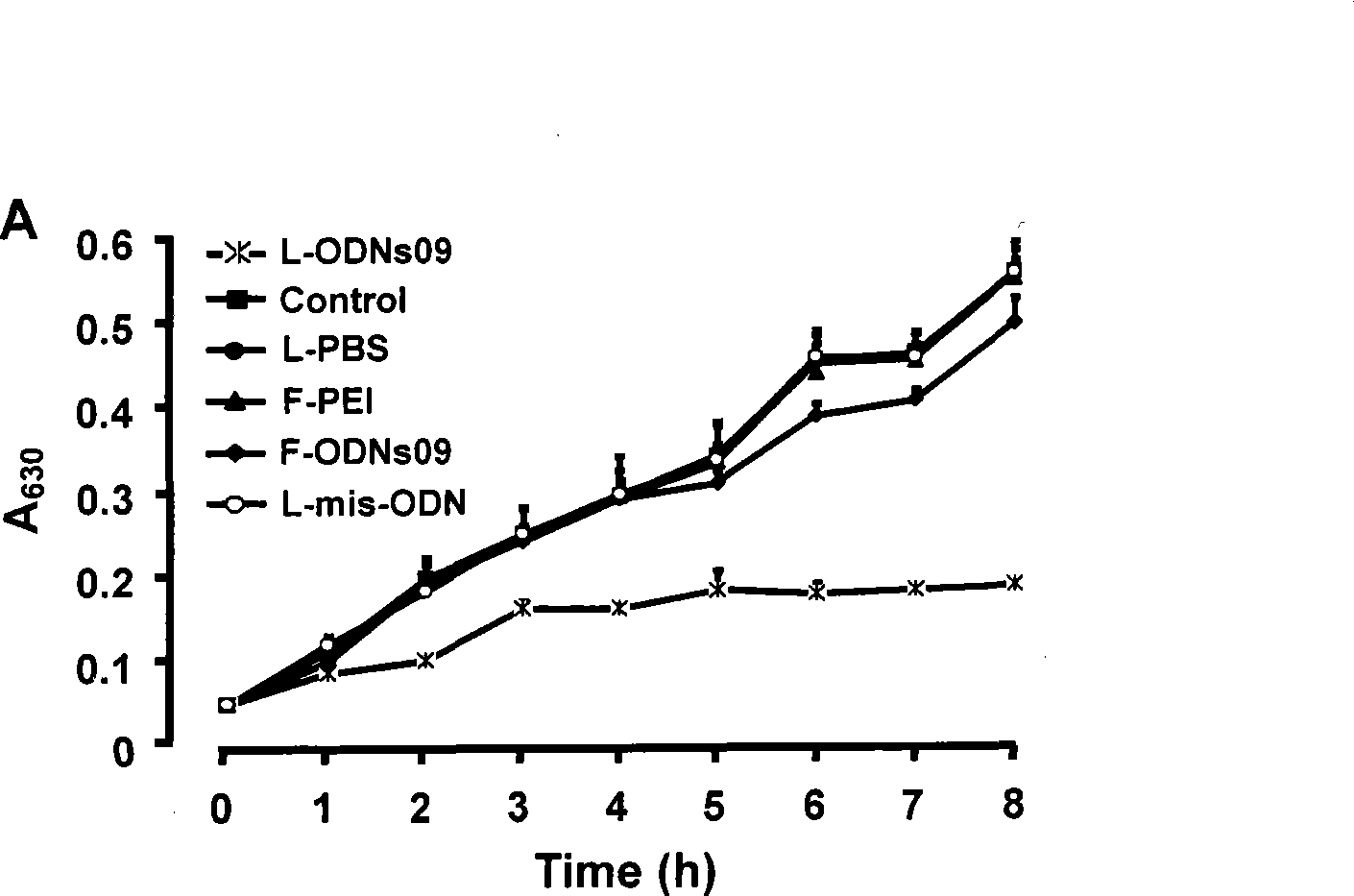
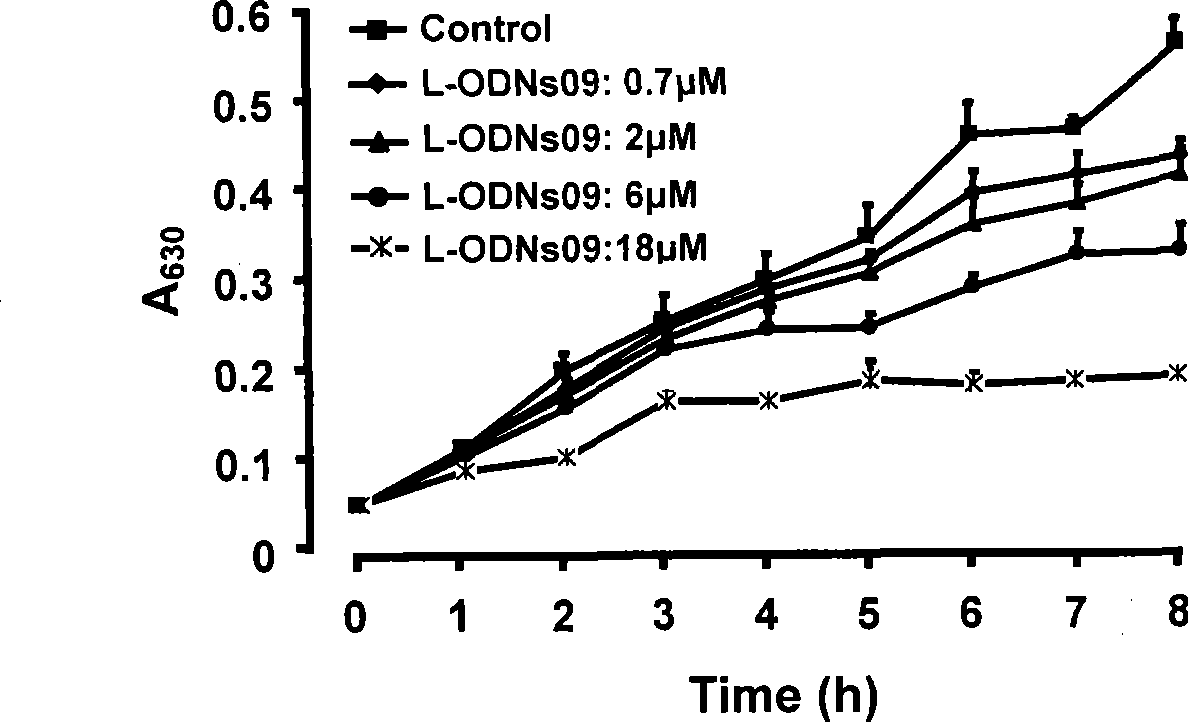
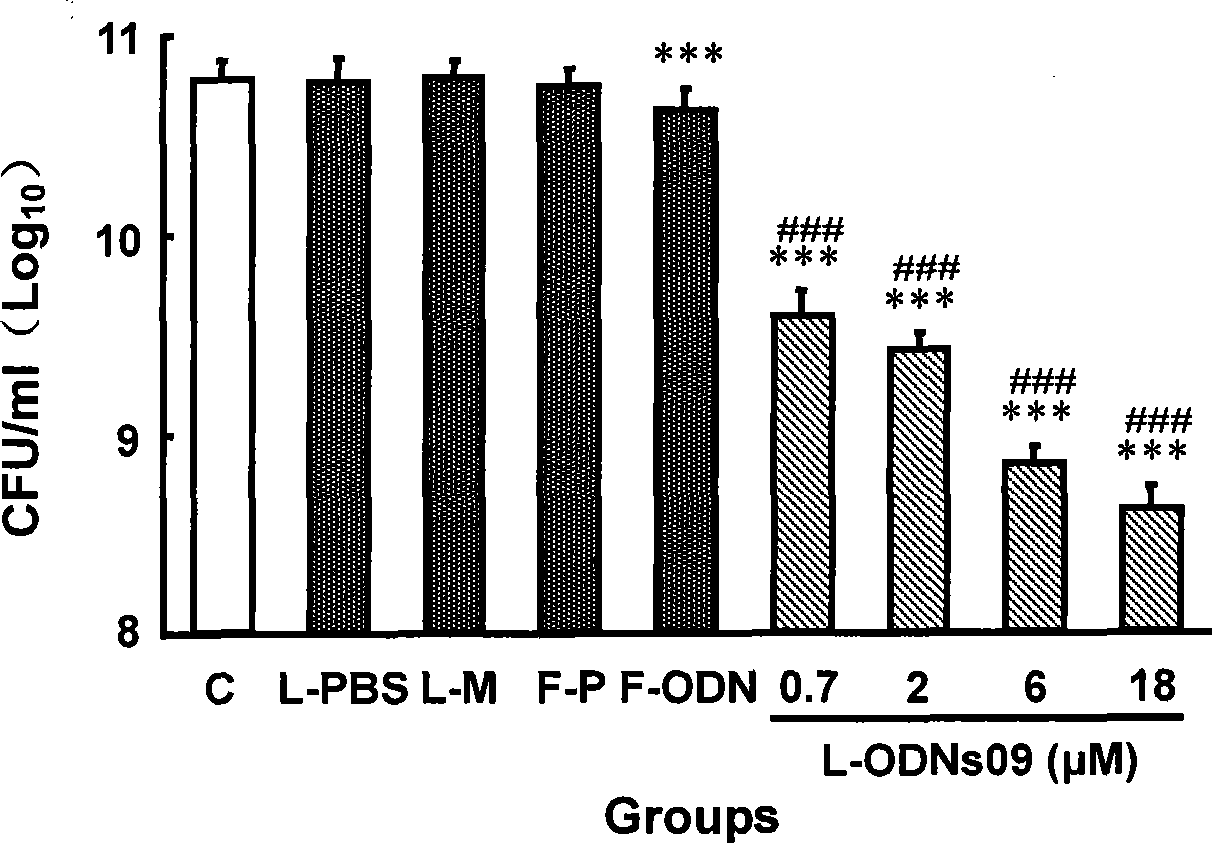
Antisense nucleic acid of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus resistance gene mecA
A methicillin-resistant, drug-resistant gene technology, applied in the field of antisense nucleic acid against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus drug-resistant gene mecA, can solve the problem of no antisense nucleic acid, achieve broad application prospects, and inhibit MRSA The effect of drug resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1 Design of antisense thio-oligodeoxynucleotides (PS-ODNs) against mecA mRNA:
[0025]The genome sequence of the MRSA drug-resistant gene mecA (gene number GI: 2791983) was retrieved from GENBANK. The sequence is 2007 bp in length and encodes PBP2a, which determines the expression of MRSA drug resistance. According to the principle of base complementarity, the mRNA of mecA was obtained from the DNA sequence. We use RNAstructure 4.2 computer software for assisted design, screen out a series of antisense nucleic acid target sites, and design corresponding antisense nucleic acid based on these target sites. RNAstructure can predict the secondary structure of genes according to the principle of minimum free energy. Calculate the energy change when PS-ODN binds to each target, and according to the net energy (Overall ΔG) of PS-ODN binding to the target sequence, the energy required for PS-ODN binding to the linear target sequence (Duplex ΔG or Binding ΔG ), after PS...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Design and synthesis of embodiment 2 PCR primers:
[0029] According to the gene sequence of mecA and 16srRNA of MRSA reported in GeneBank, two pairs of specific amplification primers for mecA and 16srRNA were designed with the software PrimerPremier 5.0. The primers were verified to be highly specific by BLAST software, and were synthesized by Shanghai Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd. The sequences are shown in Table 2.
[0030] Table 2 Design and synthesis of amplification primers
[0031]
Embodiment 3
[0032] The preparation of embodiment 3 anionic liposomes:
[0033] First, we prepared positively charged nanoparticles through electrostatic interaction between PEI and PS-ODN. Stearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (PEG 2000 -DSPE), the film dispersion method prepares anionic liposomes as the drug delivery system for transducing PS-ODN into the MRSA bacterial body.
[0034] In the following examples, the applicant selects PS-ODNs09, which has the best experimental results, as an example. Other thio-oligodeoxynucleotides are also tested according to the following methods.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com